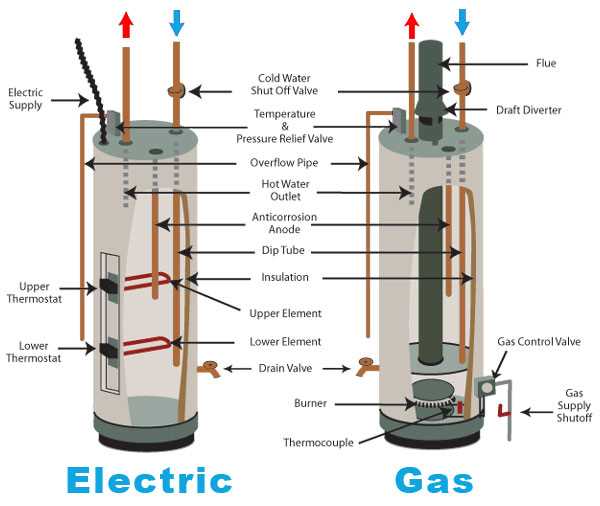
Electric Hot Water Heater Parts Diagram Overview
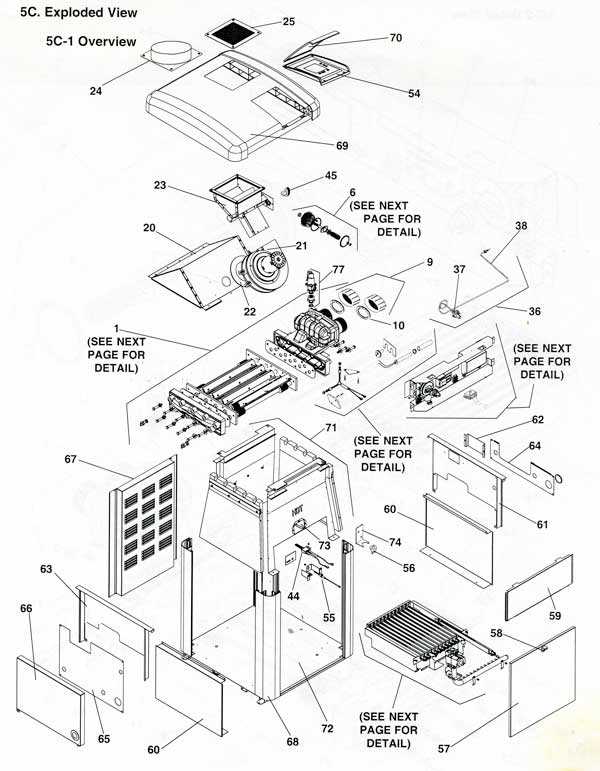
In many homes, the heating system is an essential part of daily comfort. It is crucial to have a clear understanding of how the various elements within the system work together to provide warmth. This guide explores the internal mechanisms, focusing on the key elements that ensure efficient operation.
While the external appearance may seem straightforward, the system is made up of numerous interconnected components. Each piece plays a specific role in regulating and maintaining the temperature of the liquid it processes. By examining these elements closely, you can gain a deeper appreciation of how the entire setup functions.
Whether you are troubleshooting an issue or simply looking to enhance your knowledge, understanding the structure of these systems can be incredibly valuable. We will look into the critical sections that make everything run smoothly and efficiently, ensuring that your unit operates at its best.
Electric Hot Water Heater Parts Overview
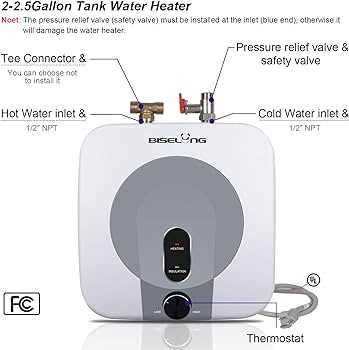
Understanding the components of a system that provides heated fluid is essential for maintaining its efficient operation. These units are made up of various key elements that work together to ensure the smooth functioning of the appliance.
Below is a table outlining the primary components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Thermostat | Regulates the temperature by controlling when the heating element is activated. |
| Heating Element | Responsible for converting electrical energy into heat to warm the liquid inside the tank. |
| Dip Tube | Directs incoming cold fluid to the bottom of the container for proper circulation and heating. |
| Pressure Relief Valve | Ensures safety by releasing excess pressure to prevent over-pressurization. |
| Anode Rod | A protective rod that prevents corrosion inside the tank by attracting harmful elements in the fluid. |
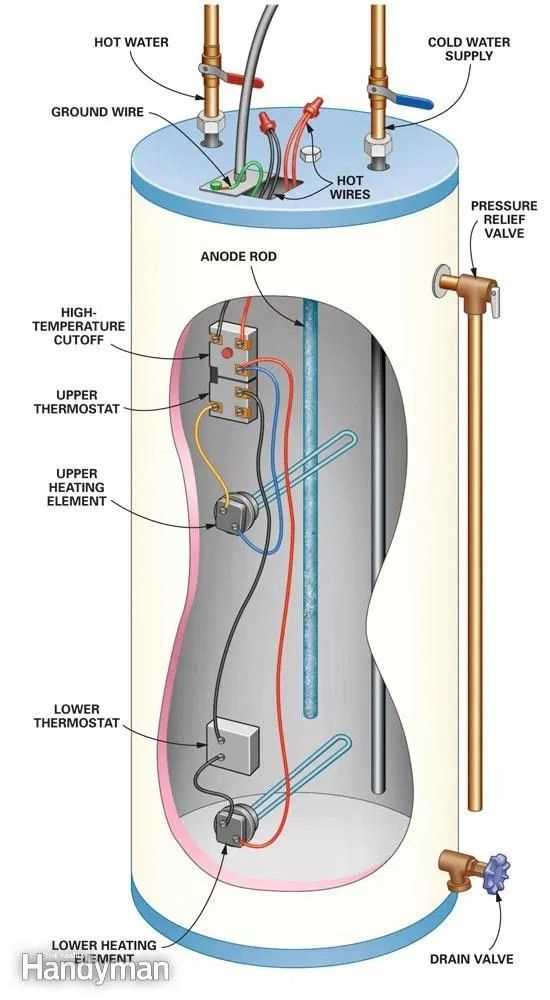
Main Components of an Electric Water Heater
This section provides an overview of the essential elements that contribute to the functionality of a system designed to provide heated fluid. Understanding these components is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key Elements
The following are fundamental components typically found in these systems:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Thermostat | Controls the temperature by regulating the heating element. |
| Heating Element | Responsible for generating heat to warm the fluid. |
| Tank | Holds the heated fluid until it is needed for use. |
| Insulation | Minimizes heat loss from the tank, improving efficiency. |
| Pressure Relief Valve | Ensures safety by releasing excess pressure in the tank. |
Understanding the Functionality
Each element plays a pivotal role in the overall operation of the system, working in harmony to ensure efficient performance. Regular inspection and maintenance of these components can enhance longevity and reliability.
Heating Elements and Their Function
Heating elements are crucial components that facilitate the generation of warmth in various systems. Their primary role is to convert electrical energy into thermal energy, ensuring efficient heating. These elements are designed to withstand high temperatures and deliver consistent performance, making them essential in many applications.
Types of Heating Elements
There are several types of heating elements, each serving specific functions based on the requirements of the system. The most common types include:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Resistive | Utilizes resistance to generate heat as electric current passes through it. |
| Infrared | Emits infrared radiation to transfer heat directly to objects without heating the air in between. |
| Induction | Uses electromagnetic fields to produce heat within conductive materials, resulting in rapid heating. |
Functionality and Efficiency
The efficiency of these elements is vital for optimal operation. They are designed to minimize energy loss and maximize heat output. Proper insulation and placement enhance their effectiveness, allowing for uniform heating and reduced operational costs. Regular maintenance ensures that these components function correctly and maintain their performance over time.
Thermostat Role in Temperature Control
The thermostat serves as a crucial component in maintaining the desired warmth within a thermal appliance. By monitoring and adjusting the temperature, it ensures optimal performance and user comfort. This device not only regulates the heat but also plays a significant part in energy efficiency and safety.
How the Thermostat Functions
- Detects current temperature levels.
- Compares them with the preset settings.
- Activates or deactivates the heating mechanism accordingly.
Importance of Proper Calibration
Accurate calibration of the thermostat is essential for effective temperature management. If the settings are incorrect, it can lead to:
- Inconsistent temperatures.
- Increased energy consumption.
- Potential damage to the appliance.
Regular maintenance and checks can help ensure that the thermostat operates correctly, providing both comfort and efficiency.
Pressure Relief Valve Importance
The pressure relief valve serves a critical function in maintaining the safety and efficiency of heating systems. Its primary role is to regulate pressure levels, preventing potential hazards that can arise from excessive build-up. Understanding its significance is essential for both users and maintenance personnel.
This component plays a vital role in ensuring that the system operates within safe parameters. Here are some key reasons highlighting its importance:
- Safety: By releasing excess pressure, the valve minimizes the risk of explosions or leaks, protecting both equipment and individuals.
- Longevity: Maintaining appropriate pressure levels can extend the lifespan of the entire system, reducing the need for costly repairs.
- Efficiency: A properly functioning valve contributes to optimal performance, ensuring the system operates effectively and efficiently.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many regions require compliance with safety standards, making this component a legal necessity.
Regular inspection and maintenance of the pressure relief valve are essential. Failure to ensure its proper functioning can lead to serious issues, including system failure or catastrophic accidents. Therefore, it is crucial to prioritize its upkeep in any heating arrangement.
Anode Rod and Its Purpose
The anode rod plays a critical role in maintaining the longevity of various heating systems. It acts as a sacrificial component, designed to protect the interior surfaces from corrosive elements that can lead to deterioration over time. By attracting these damaging substances, the rod effectively extends the lifespan of the entire system.
How the Anode Rod Works
This essential component is typically composed of magnesium, aluminum, or zinc, materials known for their electrochemical properties. When installed, the anode rod creates a process that inhibits corrosion by sacrificing itself. As it corrodes, it helps prevent the inner linings from succumbing to rust and other harmful effects.
Maintenance and Replacement
How the Dip Tube Works
The dip tube is a crucial component that plays a significant role in the efficiency and functionality of a water storage unit. Its primary purpose is to ensure the proper distribution of fluid within the tank, enhancing overall performance. By facilitating the movement of liquid from the top to the bottom, it helps maintain optimal temperature levels and ensures a steady supply of heated fluid when needed.
Functionality and Mechanism
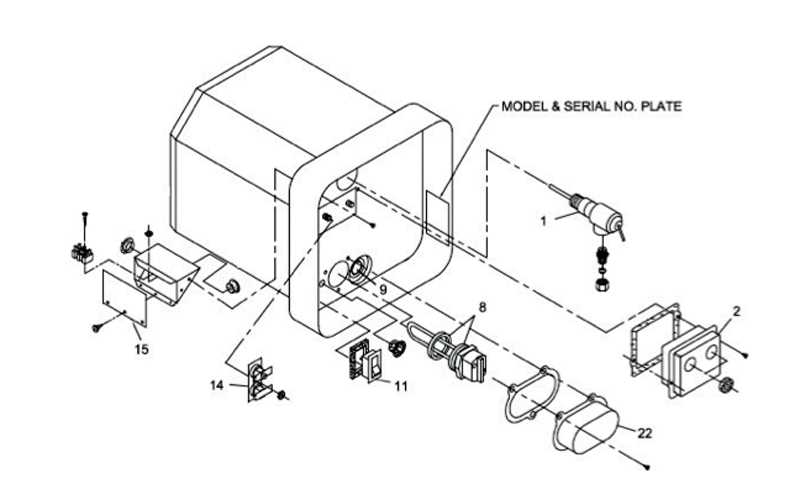
The dip tube is designed to transport incoming fluid from the supply line to the bottom of the storage unit. This process allows the heated liquid to rise naturally to the surface, where it can be drawn out for use. The tube is typically made from durable materials to withstand varying pressures and temperatures, ensuring longevity and reliability in operation.
Importance in System Efficiency
Without an effective dip tube, the heating process would be compromised, leading to inefficient heating and inconsistent temperatures. By promoting a seamless flow, this component plays an essential role in energy conservation, ultimately reducing operational costs. Regular maintenance of the dip tube is vital to prevent clogs or damage, which can impede performance and affect the overall system.
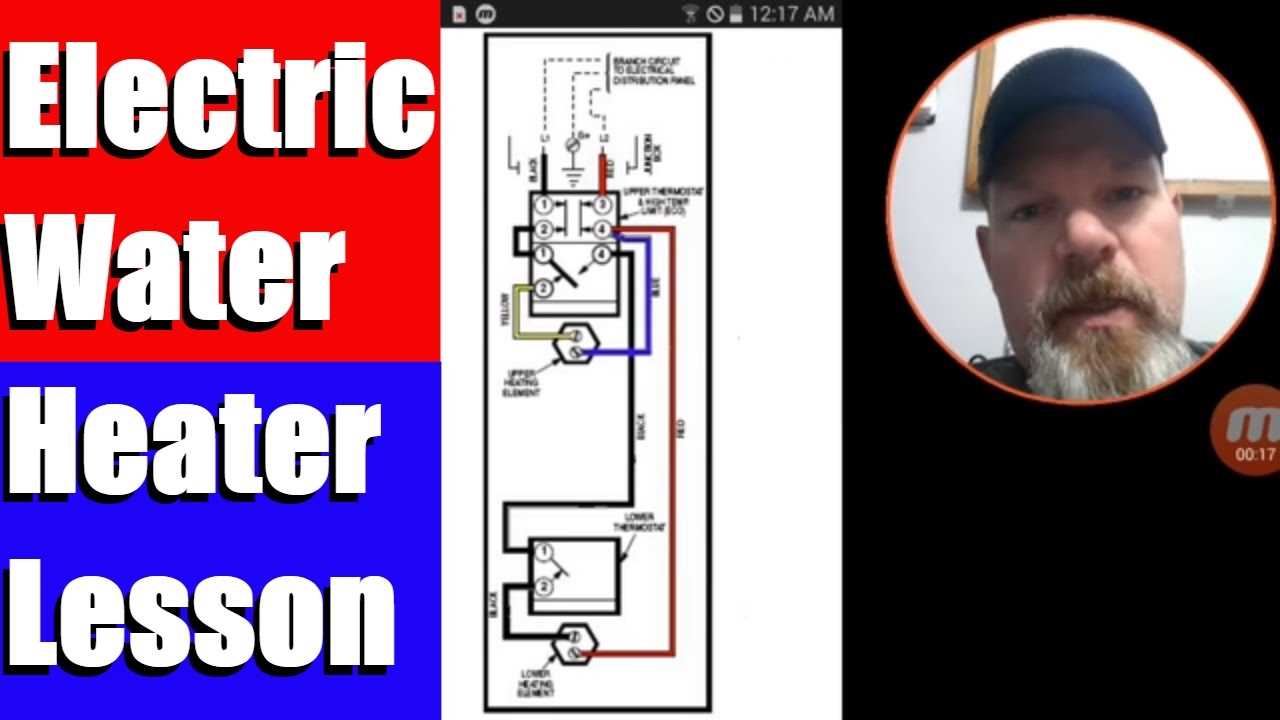
Wiring Diagram for Electric Heaters
Understanding the connections involved in various heating appliances is crucial for effective installation and troubleshooting. A comprehensive overview of the electrical connections provides valuable insights into the functioning of these devices, ensuring safe and efficient operation. This section presents a structured approach to wiring setups, highlighting key components and their interrelationships.
Key Components
The wiring configuration includes essential elements that facilitate the flow of electricity throughout the system. Below is a brief summary of these components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Power Supply | Source of electrical energy to the system. |
| Thermostat | Device for regulating temperature settings. |
| Heating Element | Converts electrical energy into heat. |
| Circuit Breaker | Provides protection by interrupting the flow of current in case of overload. |
Connection Overview
Proper connections between the components ensure optimal performance and safety. Each element plays a pivotal role in the overall functionality. A well-organized configuration not only aids in performance but also simplifies maintenance and troubleshooting tasks.
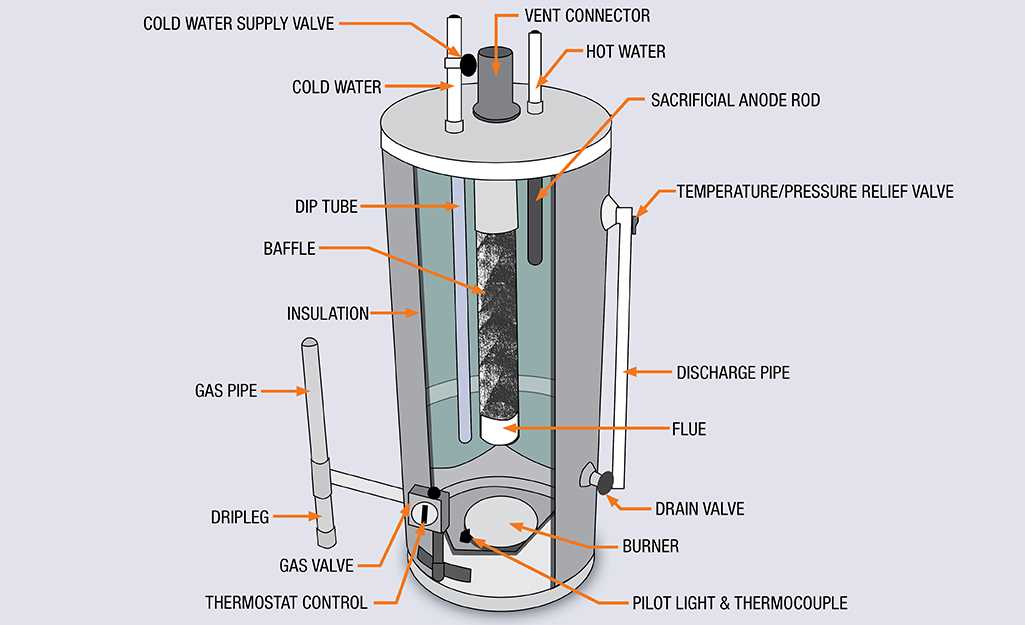
Tank Structure and Insulation
The design and composition of a storage vessel play a crucial role in its efficiency and effectiveness. A well-constructed unit ensures optimal heat retention, reducing energy consumption while maintaining desired temperatures. The arrangement of materials and the incorporation of insulating elements are key factors that contribute to the overall performance of the system.
Components of the Storage Vessel
The main elements of the container include the shell, lining, and insulating layer. Each component serves a specific purpose, contributing to the durability and energy efficiency of the unit.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Shell | Formed from robust materials, providing structural integrity and resistance to corrosion. |
| Lining | Offers a protective barrier, ensuring that the inner surfaces remain clean and free from contaminants. |
| Insulation | Applied around the outer surface to minimize heat loss, enhancing energy efficiency. |
Importance of Insulation
Proper insulating materials significantly reduce heat dissipation, ensuring that stored substances remain at the desired temperature for longer periods. Effective insulation not only improves energy efficiency but also contributes to safety by minimizing the risk of burns or accidental exposure to high temperatures.
Common Issues with Heater Parts
Heating systems can encounter a variety of challenges that may affect their performance and efficiency. Understanding these common malfunctions is crucial for maintaining optimal functionality. Users often report problems related to specific components, which can lead to diminished heating output or complete system failure.
One frequent issue arises from the malfunctioning of the thermostat, which is responsible for regulating temperature. If this component fails, it can result in inconsistent heating, leading to discomfort. Additionally, sediment build-up in the storage tank can significantly impede efficiency, requiring periodic flushing to prevent blockage and maintain heat transfer.
Another common concern involves the failure of heating elements. These elements may become corroded or burned out over time, leading to insufficient heating. Regular inspection can help identify such issues before they escalate. Finally, leaks in the system can not only waste energy but also cause damage to surrounding areas. Addressing these concerns promptly can prolong the lifespan of the entire heating unit.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
To ensure the extended lifespan of your appliance, regular upkeep is essential. Implementing simple yet effective practices can greatly enhance its efficiency and reliability over time. By prioritizing maintenance, you can prevent potential issues and promote optimal performance.
Regular Inspection: Periodically check the unit for any signs of wear or damage. Look for leaks, corrosion, or unusual noises that may indicate a problem. Early detection can save you from more significant repairs down the line.
Temperature Settings: Adjusting the temperature to an appropriate level can prevent excessive strain on the system. Keeping the settings between 120°F and 140°F is generally recommended for efficiency.
Flushing the Tank: Sediment buildup can affect performance. Schedule a routine flush to remove any accumulated debris. This process will help maintain efficiency and prolong the life of the equipment.
Check Anode Rod: The anode rod plays a vital role in preventing corrosion. Inspect it annually and replace it as needed to ensure continued protection against rust.
Professional Maintenance: Consider scheduling regular professional servicing. Experts can conduct thorough inspections and perform necessary repairs, ensuring the appliance operates at peak efficiency.