Understanding the Components of a Motorcycle Engine Diagram
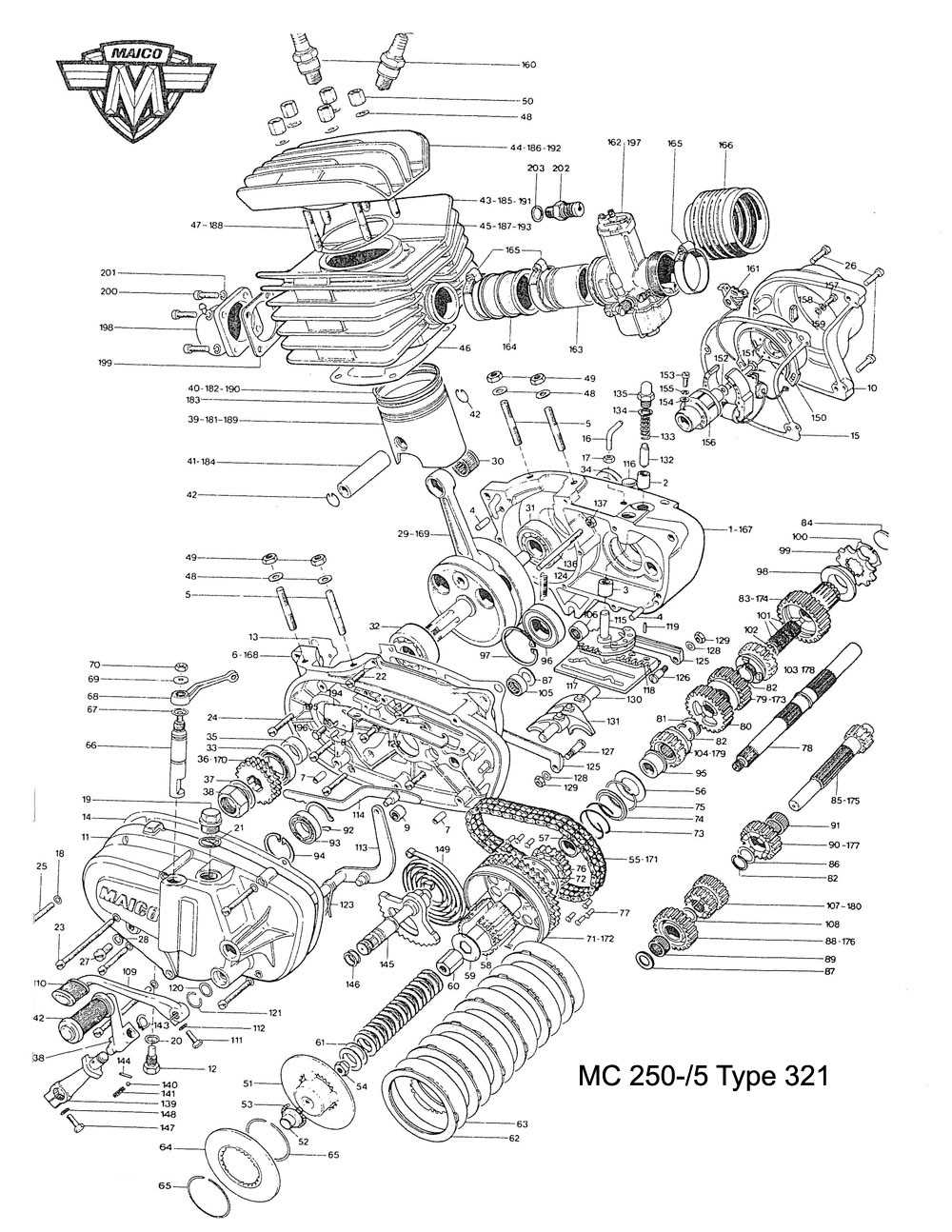
Exploring the intricate components that contribute to the functionality of two-wheeled vehicles unveils a fascinating world of mechanics. Each element plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth operation and optimal performance, showcasing the marvels of engineering innovation. From the initial ignition to the seamless transition of power, every aspect is vital for achieving the desired speed and efficiency.
Within this exploration, one can observe how interconnected elements collaborate harmoniously to deliver an exhilarating experience. The synergy between various mechanisms is essential, as they interact to transform fuel into motion. Recognizing these relationships enhances our appreciation for the technical sophistication inherent in these machines.
As we delve deeper into the specific functions and roles of each component, we will uncover the complexity and precision required for flawless operation. Understanding these intricacies not only fosters a greater respect for the craftsmanship involved but also equips enthusiasts and operators with the knowledge necessary for maintenance and troubleshooting.
Understanding Motorcycle Engine Components
Gaining insight into the critical elements that drive a two-wheeled vehicle is essential for any enthusiast or mechanic. Each component plays a significant role in ensuring the overall performance and reliability of the machine. Familiarity with these elements not only enhances maintenance practices but also deepens the appreciation for engineering excellence.
Key Elements and Their Functions
At the heart of the operation lies the assembly responsible for converting fuel into motion. This includes a series of intricate mechanisms, such as the assembly that compresses the mixture, enabling combustion to occur. Additionally, the system that regulates the flow of gases is vital for optimal efficiency and power output.
Maintenance and Upgrades
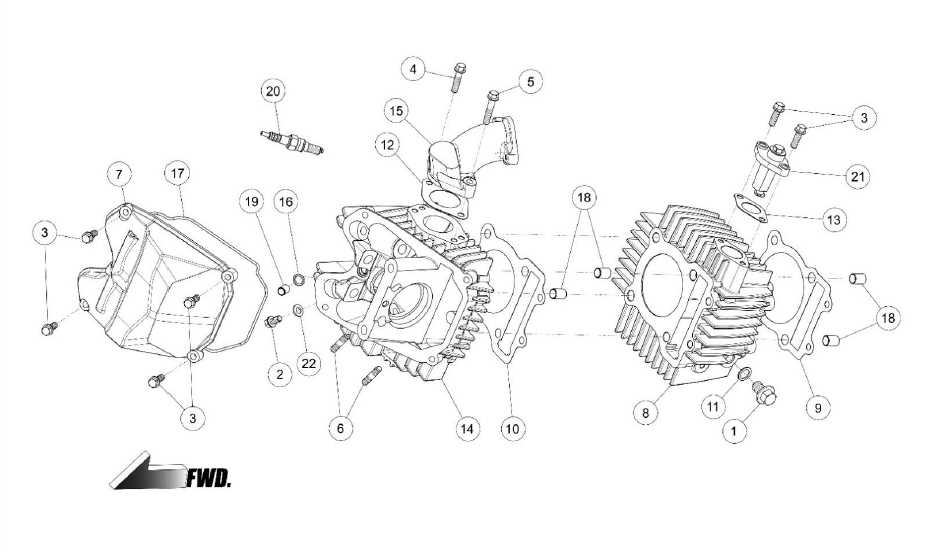
Understanding these integral systems allows for informed decisions when it comes to upkeep and enhancements. Regular inspections and timely replacements can prevent significant issues and enhance performance. Moreover, knowing which components can be upgraded opens the door to improved speed and handling, leading to a more exhilarating riding experience.
Key Elements of Engine Diagrams
Understanding the essential components illustrated in technical representations is crucial for anyone exploring mechanical systems. These visual guides serve as blueprints, highlighting the intricate relationships and functions of various elements.
First and foremost, the core units are typically emphasized, showcasing their roles in the overall assembly. This allows viewers to grasp how each section contributes to the system’s performance.
Moreover, annotations and labels provide clarity, ensuring that each component is easily identifiable. This detailed information enhances the learning experience and aids in troubleshooting.
Finally, the arrangement and flow of elements are critical for comprehending operational dynamics, helping users visualize how energy is transformed and transferred throughout the structure.
Types of Motorcycle Engines Explained
Understanding the different power sources used in two-wheeled vehicles is essential for enthusiasts and aspiring riders alike. Each type has its unique characteristics, benefits, and applications, catering to various riding styles and preferences.
- Single-Cylinder: Known for their simplicity and lightweight design, these units are often found in smaller bikes and offer good torque at lower RPMs.
- Parallel Twin: Featuring two cylinders aligned next to each other, these configurations provide a balance of power and efficiency, making them popular in a variety of models.
- V-Twin: With cylinders arranged in a V shape, this type delivers strong low-end torque and a distinctive sound, commonly associated with cruisers and touring models.
- Inline Three: Offering a unique combination of smoothness and power, these setups are less common but are celebrated for their distinctive performance characteristics.
- Inline Four: Popular in sport and touring machines, this configuration provides high RPM capabilities and smooth acceleration, making it a favorite among speed enthusiasts.
- Boxer: With horizontally opposed cylinders, this type is known for its low center of gravity, contributing to improved stability and handling.
Choosing the right type significantly impacts the riding experience, influencing factors like performance, handling, and maintenance. Understanding these variations allows riders to select a vehicle that aligns with their preferences and riding style.
Essential Parts for Engine Functionality
The performance of any vehicle relies on a series of critical components that work in harmony to ensure smooth operation. Understanding these essential elements is key to appreciating how power is generated and transmitted effectively.
Fuel Delivery System: This system plays a vital role in supplying the necessary energy source to the combustion chamber. It consists of various elements that ensure optimal mixing and flow for maximum efficiency.
Combustion Chamber: Here, the magic happens as fuel ignites, creating the force needed for movement. The design and integrity of this area significantly influence overall performance and power output.
Cooling Mechanism: To maintain optimal functioning, a reliable cooling system prevents overheating, allowing the machine to operate smoothly even under heavy loads.
Lubrication System: Essential for minimizing friction, this setup ensures that moving parts remain in good condition, thereby extending the lifespan and efficiency of the entire assembly.
Ignition System: This component is crucial for initiating the combustion process. A reliable ignition ensures that the energy is released at the right moment for effective performance.
How to Read Engine Schematics
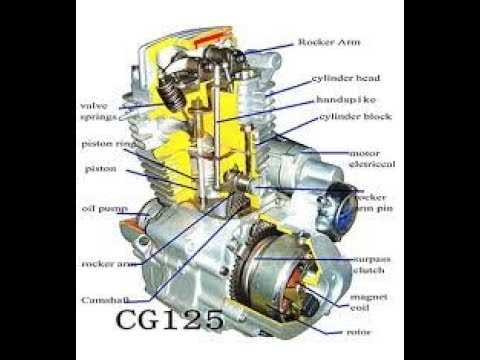
Understanding technical illustrations is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. These visual representations convey complex relationships and functionalities in a simplified manner, allowing individuals to grasp the overall structure and operation of various components.
To effectively interpret these illustrations, consider the following steps:
- Familiarize Yourself with Symbols:
- Each symbol typically represents a specific component or function.
- Refer to a key or legend if available to understand the meaning of each symbol.
- Identify Connections:
- Look for lines that indicate connections between elements, which may represent physical links or electrical pathways.
- Note the direction of flow, whether it’s fuel, air, or electrical current.
- Examine Labels:
- Components often have labels that provide additional information, such as part numbers or specifications.
- Take note of any annotations that may clarify the purpose or function of a particular section.
- Understand Flow and Function:
- Determine the sequence of operations by following the flow from the start to the end of the schematic.
- Recognize how different components interact to achieve the overall functionality.
By mastering these techniques, you’ll enhance your ability to analyze and work with technical illustrations effectively, leading to improved problem-solving skills and maintenance practices.
Importance of Each Engine Part
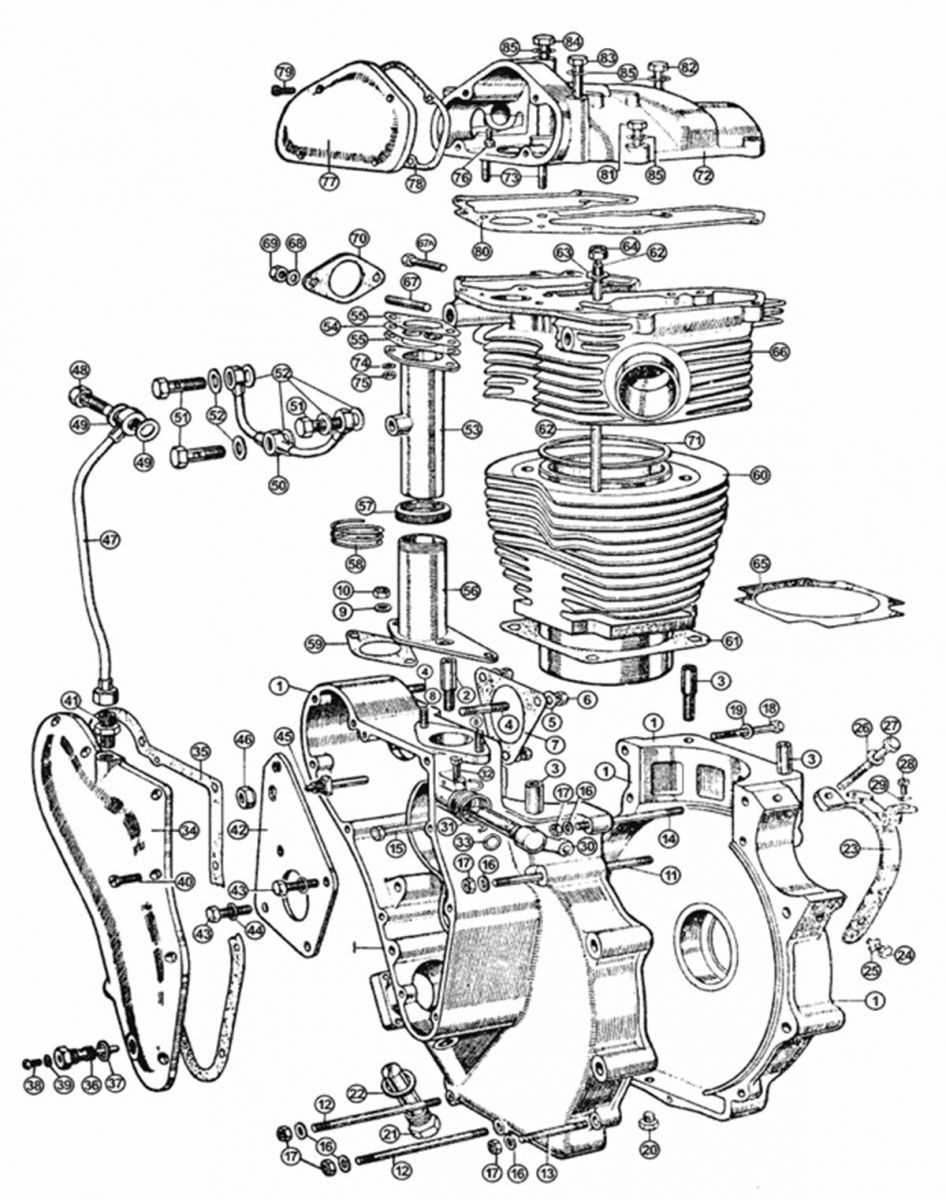
Understanding the significance of various components within a propulsion system is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Each element plays a unique role, contributing to the overall functionality and efficiency of the mechanism. Recognizing how these individual elements interact allows for better maintenance and enhancement.
Key Functions
Every component serves a specific function, whether it’s generating power, controlling flow, or ensuring smooth operation. These roles are interdependent, creating a harmonious system that drives performance.
Impact on Performance
Neglecting the importance of any single element can lead to inefficiencies or failures. Regular assessment and understanding of each unit’s role help in maintaining peak operational standards and extending the lifespan of the entire system.
Common Issues in Engine Components
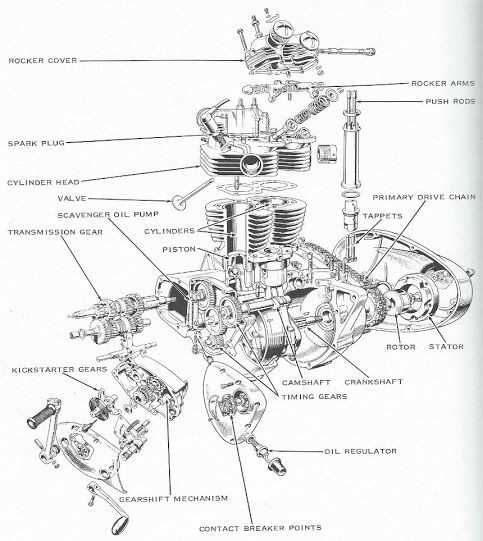
Understanding the frequent challenges that arise in various mechanical systems is essential for maintaining optimal performance. Issues often stem from wear and tear, environmental factors, or improper maintenance, leading to reduced efficiency and potential breakdowns.
Overheating is a prevalent concern, typically caused by insufficient cooling or lubrication. This can result in severe damage, necessitating timely intervention.
Another common problem is excessive vibration, which may indicate imbalances or misalignments. This can lead to accelerated wear of neighboring components, impacting overall functionality.
Leaks are also a significant issue, often arising from degraded seals or gaskets. These can compromise the system’s integrity and require prompt attention to avoid further complications.
Lastly, contamination from dirt or debris can hinder performance, making regular inspections and maintenance crucial for longevity and reliability.
Maintenance Tips for Engine Longevity
Proper care and attention are essential for ensuring the durability and efficiency of any mechanical system. By following a few key practices, one can significantly extend the life of critical components and maintain optimal performance over time.
Regular inspections are vital. Check for any signs of wear, leaks, or unusual noises that might indicate underlying issues. Addressing small problems early can prevent more significant damage down the line.
Fluid levels should be monitored consistently. Ensuring that lubricants and coolants are at appropriate levels helps reduce friction and overheating, which are common causes of premature wear. Use high-quality products recommended by the manufacturer to achieve the best results.
Periodic cleaning is also crucial. Accumulation of dirt and debris can impede functionality and lead to corrosion. A clean system operates more efficiently and lasts longer, so make it a habit to remove any buildup regularly.
Lastly, adhering to a proper usage schedule will help in maintaining efficiency. Avoiding excessive strain during operation and allowing for adequate cool-down periods can greatly benefit the overall health of the machinery.
Differences Between Two-Stroke and Four-Stroke
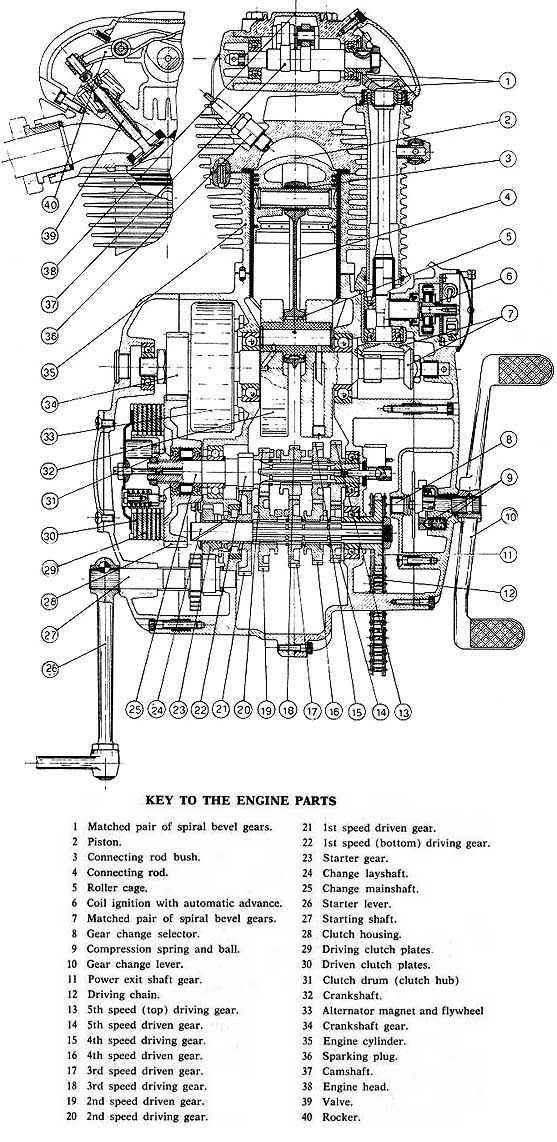
The distinction between two-stroke and four-stroke mechanisms revolves around their operational cycles and efficiency. Each type possesses unique characteristics that cater to various applications, influencing performance, emissions, and maintenance requirements.
Operational Cycle
Two-stroke designs complete a power cycle in two movements of the piston, resulting in a power stroke with every revolution. In contrast, four-stroke configurations require four movements for a complete cycle, generating power every other revolution, which often leads to smoother operation.
Efficiency and Emissions

Two-stroke systems typically offer higher power output for their size but can lead to greater fuel consumption and emissions due to incomplete combustion. Four-stroke alternatives, while generally more fuel-efficient and cleaner, may sacrifice some power density for enhanced environmental compliance and quieter operation.
Role of Cooling Systems in Engines
Efficient temperature management is crucial for the longevity and performance of any mechanical system. Without proper regulation, excessive heat can lead to various malfunctions and reduced efficiency. Thus, a well-designed cooling mechanism plays an essential role in maintaining optimal operational conditions.
These systems primarily function to dissipate heat generated during operation, ensuring that components remain within safe temperature limits. By using various methods, including liquids or air, they effectively prevent overheating and protect sensitive parts from damage. The reliability of these systems directly impacts overall performance, making them vital for smooth operation.
Moreover, maintaining an ideal thermal environment not only enhances efficiency but also contributes to better fuel consumption and lower emissions. This ultimately leads to improved sustainability and a reduction in environmental impact. Therefore, understanding the intricacies of cooling mechanisms is key for anyone involved in mechanical systems.
Fuel Delivery Systems Overview
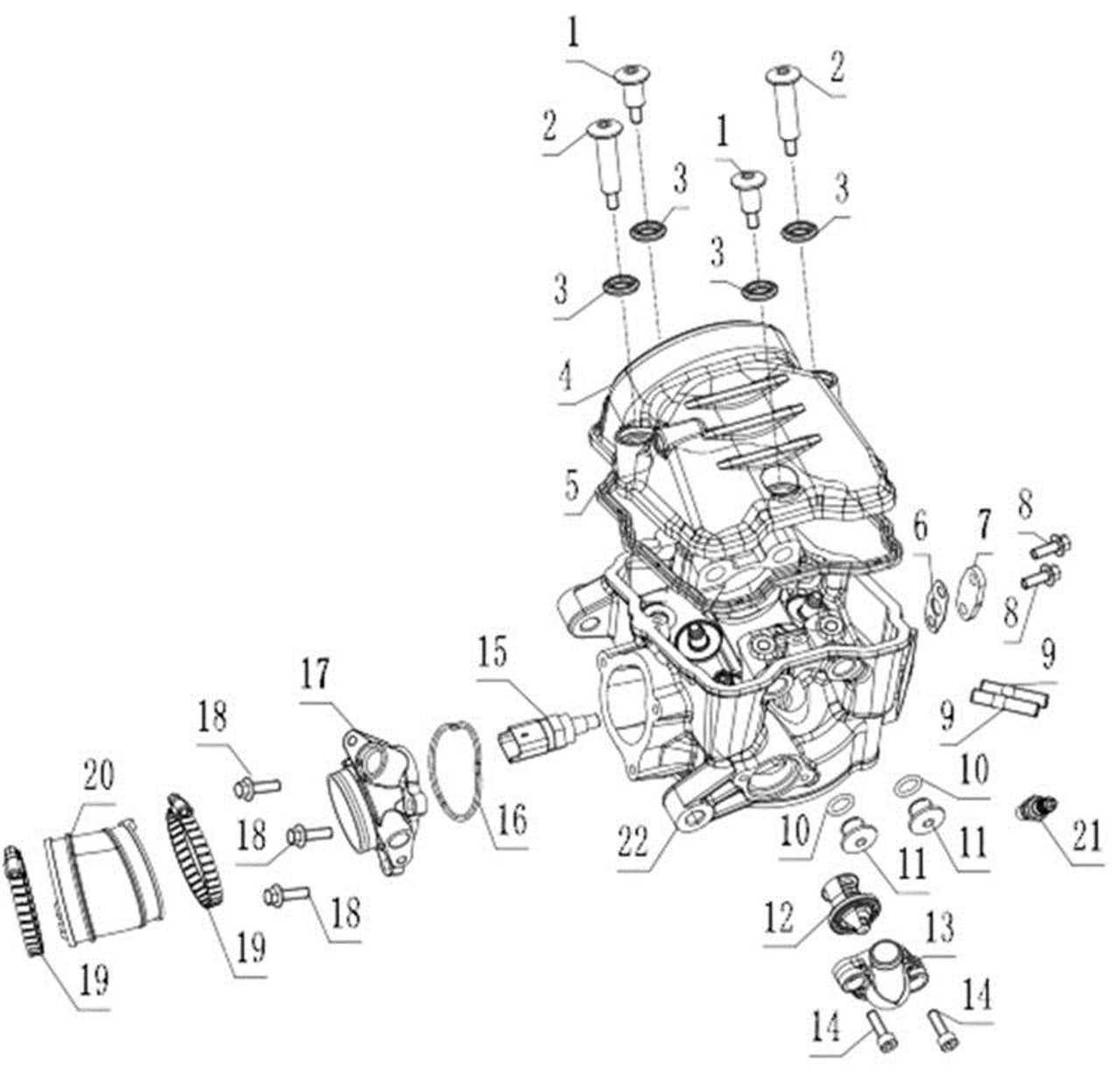
The efficient transfer of combustible substances is crucial for optimal performance and longevity of two-wheeled vehicles. This section delves into the various mechanisms responsible for ensuring that the appropriate mixture reaches the combustion chamber, thus facilitating smooth operation and enhancing power output.
Key Components

- Fuel Tank: The primary reservoir that stores the combustible liquid.
- Fuel Pump: A device that moves the fuel from the tank to the delivery system.
- Fuel Filter: A component designed to remove impurities from the fuel before it enters the system.
- Carburetor or Fuel Injector: Mechanisms that mix fuel with air to create the optimal mixture for combustion.
- Fuel Lines: Hoses or tubes that transport fuel from one component to another.
Types of Fuel Delivery Systems

- Carbureted Systems: Utilize a carburetor to blend air and fuel in the appropriate ratio.
- Fuel Injection Systems: Employ injectors to directly deliver fuel into the combustion chamber, offering precise control and efficiency.
Understanding these systems allows for better maintenance and tuning, contributing to improved performance and reliability in various riding conditions.
Advanced Technologies in Modern Engines
Innovative advancements in propulsion systems have significantly transformed the performance and efficiency of contemporary vehicles. These developments incorporate cutting-edge materials, intelligent control mechanisms, and enhanced designs that ultimately optimize power delivery while minimizing environmental impact.
Materials and Manufacturing Techniques
Modern propulsion units benefit from lightweight, high-strength composites and alloys, which contribute to improved durability and reduced weight. Advanced manufacturing processes, such as 3D printing, allow for intricate designs that enhance airflow and cooling, leading to superior thermal management and efficiency.
Intelligent Control Systems
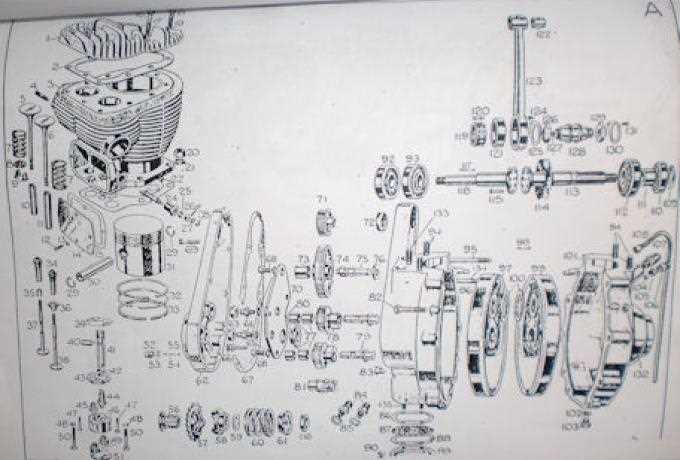
Integrating smart technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, enables real-time adjustments to performance parameters. These systems analyze data from various sensors, ensuring optimal operation under diverse conditions, thus enhancing both responsiveness and fuel economy.