BMX Bike Parts Diagram Explained

The construction of a specialized two-wheeled stunt machine involves numerous interconnected components, each contributing to its overall performance and control. These elements come together to provide stability, maneuverability, and durability for performing tricks and handling various terrains.
The core frame ensures structural integrity, while other segments focus on comfort and precision. Balancing flexibility
Parts of a BMX Bike Diagram
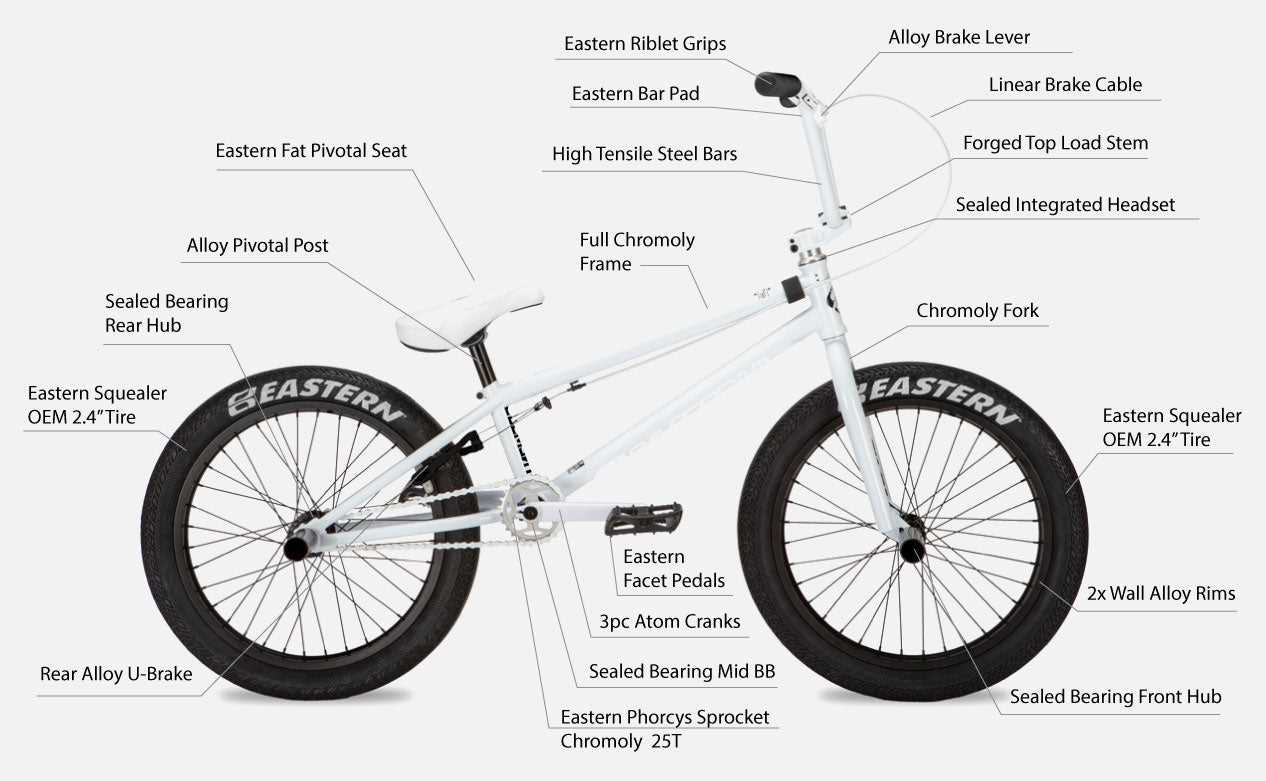
A freestyle ride is made up of several key elements, each working together to ensure smooth performance and control. Understanding the structure helps riders maintain their equipment and achieve the best riding experience, whether on the streets or tracks.
- Frame: The foundation that holds everything together, designed to handle impacts and provide stability.
- Handlebars: Essential for steering and balance, offering grip and control during tricks and maneuvers.
- Brake Levers: Attached to the handlebars, these levers initiate the braking process by pulling the cables.
- Cable Housing: Protective sleeves that guide and shield the inner cables, reducing friction and wear.
- Brake Calipers: Devices mounted near the wheels that clamp onto the rims when activated, s
Pedals, Cranks, and Bottom Bracket

The connection between a rider and their machine is crucial for performance and control. This section explores key components that facilitate motion and power transfer, enabling smooth maneuverability and responsiveness.
Each element plays a vital role in achieving optimal efficiency and strength during various maneuvers. Understanding these components allows riders to appreciate their significance in enhancing overall experience.
Component Description Pedals These are the platforms where the rider’s feet make contact, crucial for propulsion and stability. Cranks Connected to the pedals, these levers transmit the rider’s force to the drivetrain, affecting speed and control. Bottom Bracket This assembly houses the spindle and bearings, allowing the cranks to rotate smoothly while providing structural integrity. Seatpost, Saddle, and Clamping Mechanism
The connection between the seating area and the frame is crucial for stability and comfort during rides. This section discusses the components that facilitate this connection, emphasizing their significance in ensuring an optimal riding experience.
Functionality and Comfort
The seating system plays a vital role in providing support and comfort to the rider. It is designed to accommodate various riding styles and preferences, allowing adjustments for individual comfort. This adaptability is essential for enhancing the overall riding experience.
Mechanism Overview
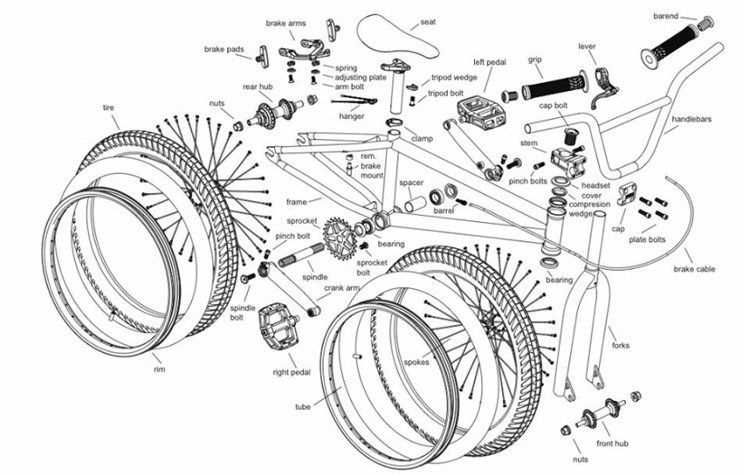
The mechanism that secures the seating arrangement consists of several elements working in harmony. Each component contributes to the functionality and stability of the system. Understanding these elements helps riders appreciate their significance and ensure proper maintenance.
Component Description Post The vertical tube that connects the seat to the frame. Saddle The surface on which the rider sits, designed for comfort. Clamp The mechanism that secures the post at the desired height. Tire Types and Tread Patterns
The selection of rubber surfaces plays a crucial role in optimizing performance and handling on various terrains. Different varieties of tires are designed to cater to specific riding styles and conditions, influencing grip, speed, and durability.
Among the available options, slick tires are characterized by a smooth surface, ideal for achieving higher speeds on flat surfaces. In contrast, knobby tires feature protruding patterns, providing enhanced traction on rough and uneven ground.
Tread patterns also significantly impact the overall experience. Open-tread designs allow for better mud clearance, making them suitable for wet or loose surfaces, while tight patterns enhance stability and control during high-speed maneuvers. Understanding these differences helps riders select the most suitable rubber for their unique needs.
Chain and Sprocket Configuration
The connection between the moving elements is crucial for efficient power transfer. This system plays a significant role in the overall performance and responsiveness of the entire apparatus. Proper alignment and integration of the components are essential to ensure a smooth ride and minimize wear over time.
Typically, the mechanism consists of two main elements: a circular device with teeth that engages the chain, and a flexible loop made of interlinked segments. These components work together to convert the rotational force generated by the rider into forward motion. The choice of sizes and the arrangement of these elements can greatly influence acceleration and top speed.
Maintaining the integrity of the connection is vital. Regular inspections for wear and proper tension help ensure optimal functionality. Adjustments may be necessary to keep everything in alignment, enhancing both durability and performance. Understanding how these components interact allows for better customization and tuning for individual preferences.
Fork Construction and Offset
The design and geometry of a front suspension element significantly influence the overall performance and handling characteristics of the two-wheeled vehicle. Understanding the construction and offset of this crucial component helps riders make informed choices tailored to their riding style and terrain.
Construction materials play a vital role in the weight, strength, and durability of the suspension element. Commonly used materials include:
- Steel: Offers robustness and longevity but tends to be heavier.
- Aluminum: Lighter than steel, providing a good balance between strength and weight.
- Carbon Fiber: Extremely lightweight and strong, often preferred for high-performance applications.
Another critical aspect is the offset, which refers to the distance between the steering axis and the front axle. The offset affects how the vehicle turns and handles in various conditions:
- Positive Offset: Enhances stability during high-speed maneuvers and promotes straight-line tracking.
- Negative Offset: Allows for quicker steering response, beneficial for technical riding and tight turns.
In conclusion, grasping the intricacies of the construction and offset of the front suspension element empowers riders to enhance their overall experience, tailoring their setup to meet specific preferences and demands.
Pegs, Axles,
The components responsible for stability and performance during tricks and maneuvers are essential in any two-wheeled apparatus designed for action sports. These elements allow for various stunts and provide a platform for balance and control, significantly enhancing the overall riding experience.
Pegs
Pegs serve as extensions that attach to the frame, providing additional points for the rider to execute tricks. They can be used for grinding on rails or ledges, making them a popular choice among enthusiasts of aerial displays. Available in various materials and sizes, pegs can be tailored to suit individual preferences and riding styles.
Axles
Axles play a critical role in the structure by connecting wheels to the frame, ensuring smooth rotation and stability. These rods are designed to withstand significant stress and are crucial for maintaining the integrity of the entire system. The choice of axle can impact weight distribution and overall performance, allowing riders to optimize their setup.
Component Function Materials Pegs Facilitate grinding and tricks Steel, Aluminum, Plastic Axles Connect wheels and provide stability Chromoly, Steel
Frame Structure and Geometry
The core framework plays a crucial role in determining how a two-wheeled design handles different surfaces and maneuvers. Its shape and proportions influence stability, control, and responsiveness, making it essential for riders seeking both precision and comfort.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Top Tube Length | Affects the overall reach and comfort, balancing agility and control. |