Tow Motor Component Layout Explained
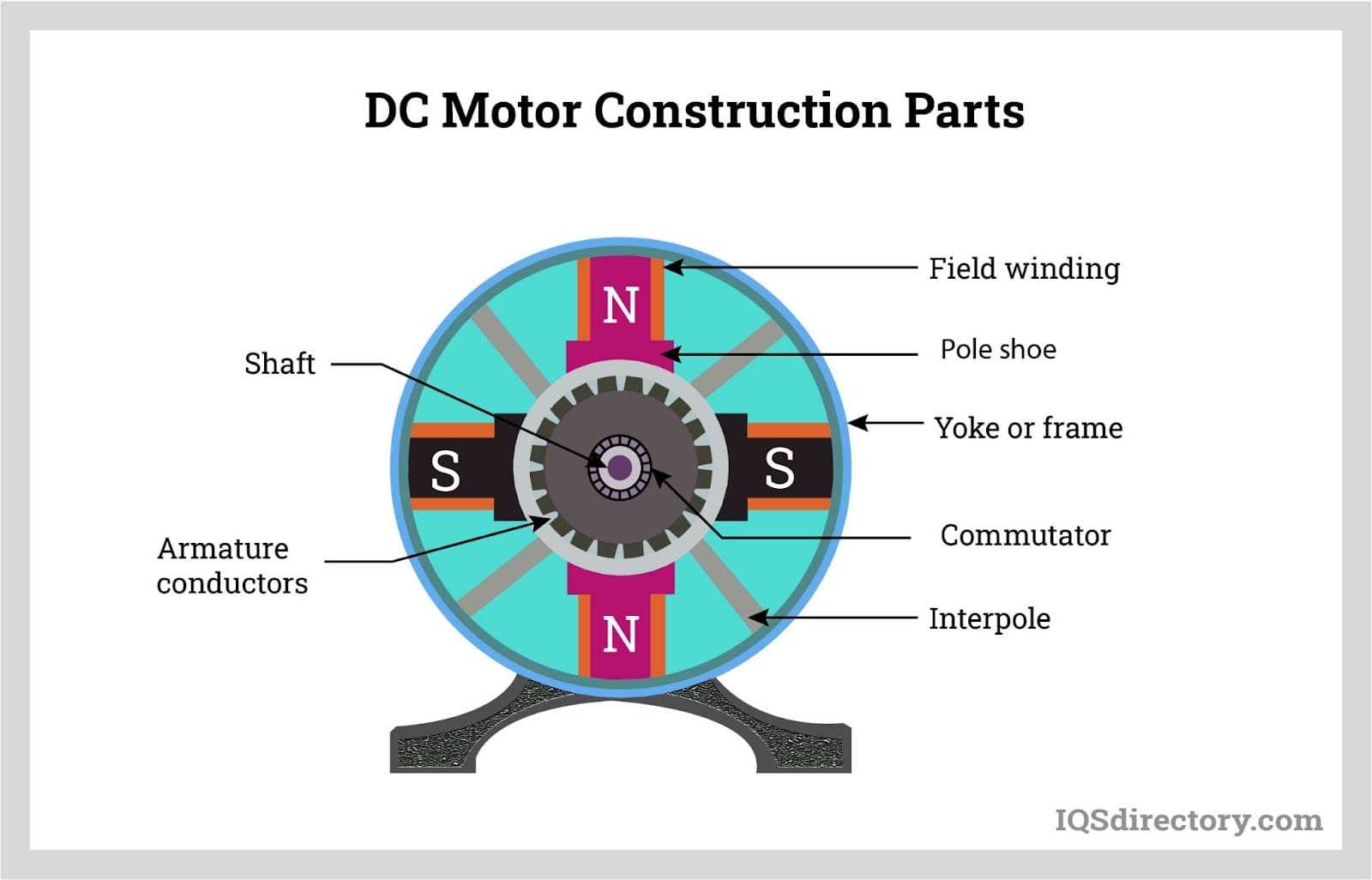
When it comes to analyzing the inner workings of mechanical equipment, recognizing how each element interacts is essential for smooth operation. A clear view of the arrangement and connections among these elements provides a deeper insight into their functionality and aids in efficient maintenance and repairs.
In this section, we will delve into the specifics of the structural setup and how individual elements interconnect within the system. By exploring these details, you will gain a more comprehensive understanding of how each piece plays its role in ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Emphasizing the significance of proper alignment and organization, we aim to make the intricate network of components easier to grasp. Whether you’re troubleshooting issues or simply enhancing your knowledge, this guide will serve as a valuable resource in navigating the layout of these essential mechanical systems.
Understanding the fundamental elements of this equipment is crucial for efficient operation and maintenance. Each component plays a significant role in the overall functionality, ensuring that the machinery performs reliably under various conditions. This section provides a comprehensive breakdown of these key elements, highlighting their purpose and importance without diving into overly technical specifics.
Engine Structure and Main Features

The construction of an internal system is crucial for delivering optimal performance and efficiency. Understanding the primary elements and their functions helps to ensure reliability and longevity in mechanical operations.
Key Components of the System
- Cylinder Block: This is the foundation, housing essential elements that contribute to power generation and overall stability.
- Pistons and Crankshaft: These parts work in unison to convert energy into mechanical movement, driving the entire mechanism forward.
- Cooling Mechanism: It regulates temperature, preventing overheating and maintaining operational balance under various conditions.
Main Features and Performance Enhancements
- Fuel Efficiency: The design includes features that optimize energy use, reducing fuel consumption without sacrificing power.
- Durability and Strength: Reinforced components are designed to withstand intense stress, ensuring long-lasting performance.
- Low Maintenance Requirements: Simplified engineering reduces the need for frequent upkeep, making it a cost-effective solution for extended use.
Chassis Design and Frame Analysis
The structural foundation of a vehicle’s framework plays a crucial role in maintaining stability, durability, and overall functionality. Understanding how the underlying frame supports and distributes mechanical loads is essential for ensuring optimal performance and resilience in various conditions.
Structural Integrity and Material Selection
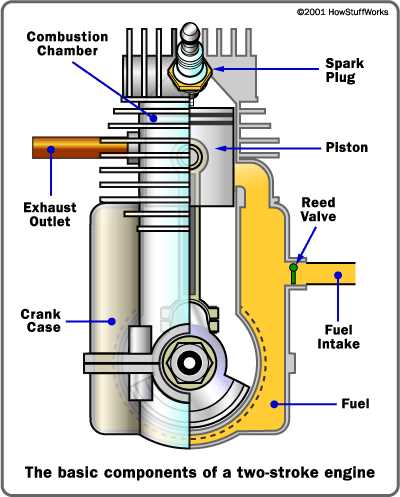
Achieving a balance between strength and weight is key to effective design. Structural integrity relies heavily on choosing the right materials that can withstand stress without compromising the frame’s flexibility. Engineers often analyze different alloy compositions to find a suitable blend that enhances durability while minimizing excess mass.
Load Distribution and Stress Points
Analyzing how forces interact with the frame highlights critical areas known as stress points. These zones require special attention to ensure they can handle concentrated loads without deformation. Proper distribution of force throughout the chassis helps in reducing wear and extending the lifespan of the vehicle’s structure.
Brake System Components Explained
The braking mechanism plays a crucial role in ensuring safety by providing the necessary control to slow down or halt a machine effectively. Understanding the essential elements of this setup is key to grasping how the overall mechanism functions seamlessly during operation.
Core Elements of the Braking Mechanism
At the heart of the system lies the master cylinder, which initiates the process when the operator engages the controls. This component generates the hydraulic pressure needed to activate other parts, enabling smooth and controlled deceleration.
Additional Supporting Components
To enhance the effectiveness of the system, various elements like brake pads and rotors come into play. These parts work together to create the friction required for reducing speed. Proper maintenance of these elements ensures longevity and reliable performance under diverse conditions.
Transmission and Gear Mechanism Overview
The transmission and gear mechanism play a crucial role in ensuring smooth and efficient movement within various machines. This system is designed to manage the transfer of power, directing energy where it’s needed to control speed and torque. By precisely adjusting gear ratios, it adapts to different conditions, enhancing the performance and reliability of the equipment.
Core Components and Their Functions
At the heart of this setup are several key elements that work in unison. Gears of varying sizes mesh together to modify the power output, while the transmission manages the transition between different gear states. The seamless integration of these components ensures optimal efficiency during operation.
Impact on Performance and Efficiency

Understanding how the transmission and gear mechanism influences overall functionality is essential. When properly aligned, this system minimizes energy loss and enhances responsiveness, making it possible to handle various tasks with precision. It allows the machinery to adapt quickly to changing demands, ensuring maximum productivity and control.
Hydraulic Pump and Control System

The hydraulic pump and its accompanying control mechanisms play a crucial role in converting mechanical energy into fluid power. This assembly directs and regulates the fluid flow, ensuring precise operation across various components. Understanding its structure and functionality is essential for maintaining efficiency and reliability.
Main Components
- Pump Unit: Responsible for generating the necessary force to move the hydraulic fluid throughout the system.
- Control Valves: Manage the direction, pressure, and rate of the fluid flow, allowing smooth and controlled movements.
- Reservoir: Stores the fluid and provides a cooling effect to prevent overheating during continuous operations.
System Functionality
The interaction between the pump and the control elements defines the system’s performance. Proper synchronization of these parts ensures that the fluid reaches the intended destinations with the correct pressure levels.
- Fluid is drawn from the reservoir into the pump.
- The pump pressurizes the fluid, sending it through control valves.
- The valves distribute the fluid to the target actuators, facilitating precise mechanical actions.
Detailed Look at Electrical Wiring
Understanding the electrical layout is essential for diagnosing and maintaining the overall system. This section provides an in-depth examination of how the different connections interact to ensure functionality and reliability. By studying the arrangement of these components, one can gain insight into troubleshooting and potential upgrades.
- Wiring Connections: A comprehensive overview of how individual lines connect to create a complete circuit, highlighting the key elements and their interactions.
- Color-Coding System: A guide to the color-coding conventions used to identify various connections, making it easier to trace lines and detect issues.
- Common Issues: An analysis of frequent wiring problems, including loose connections and damaged insulation, with suggestions for preventive measures.
- Inspect the connections: Regularly checking the status of each link can help identify potential issues before they lead to larger problems.
- Replace faulty components: Identifying and replacing damaged sections ensures the system remains efficient and safe to operate.
- Follow safety protocols: Always adhere to recommended safety practices to avoid risks during maintenance or inspection.
Steering Assembly and Maneuverability
The steering mechanism plays a vital role in ensuring efficient navigation and control of industrial vehicles. Its design and functionality directly influence how effectively the equipment can be operated in various environments.
A well-constructed steering assembly provides the following advantages:
- Enhanced precision in directional changes
- Improved stability during operation
- Reduced operator fatigue through ergonomic design
Key components contributing to maneuverability include:
- Steering Wheel: The primary interface for the operator, enabling direct control over the vehicle’s path.
- Steering Linkage: Connects the steering wheel to the wheels, translating the operator’s input into movement.
- Pivot Points: Critical for smooth turning and responsiveness, allowing the vehicle to navigate tight spaces.
In summary, the effectiveness of the steering assembly is crucial for achieving optimal performance and safety in industrial applications. Proper maintenance and understanding of this system enhance overall maneuverability.
Lift Mechanism and Fork Functionality
The lift system plays a crucial role in ensuring that heavy loads can be elevated and transported efficiently. Understanding its design and operation is essential for optimal use and maintenance.
Overview of the Lift Mechanism

This system is primarily responsible for raising and lowering the load-carrying arms. Key components include:
- Hydraulic Cylinder: Converts fluid pressure into mechanical force.
- Pulleys and Cables: Assist in controlling the movement of the arms.
- Control Valves: Regulate fluid flow, allowing for precise positioning.
Functionality of the Forks

The forks are the interface between the vehicle and the load. Their functionality depends on several factors:
- Design: Forks are typically tapered for easy insertion under loads.
- Material: Constructed from high-strength steel to withstand heavy weights.
- Adjustability: Many forks can be adjusted to accommodate various load sizes.
Proper maintenance of both the lift mechanism and forks ensures safety and efficiency in handling tasks.
Battery Maintenance and Safety Tips
Proper upkeep of the energy source is crucial for ensuring longevity and optimal performance. Regular attention can help prevent unexpected failures and enhance the overall efficiency of the equipment. Here are essential recommendations for maintaining and safely handling the energy supply.
- Regular Inspection: Routinely check for corrosion, loose connections, or any signs of damage.
- Cleanliness: Keep the battery and its terminals clean to prevent buildup that can hinder performance.
- Secure Connections: Ensure all cables are tightly secured to prevent any electrical issues during operation.
In addition to regular inspections, it’s important to follow safety guidelines:
- Use Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear gloves and goggles when handling the energy source.
- Avoid Sparks: Keep metal objects away from terminals to prevent accidental short circuits.
- Proper Disposal: Follow local regulations for disposing of old or damaged batteries to protect the environment.
By adhering to these maintenance practices and safety precautions, users can ensure their energy source remains in peak condition, contributing to the reliable operation of the machinery.
Cooling System Parts and Efficiency
The effectiveness of an engine’s cooling mechanism plays a vital role in maintaining optimal performance. This system not only prevents overheating but also contributes to overall operational reliability. Understanding the components involved and their efficiency can greatly enhance performance and longevity.
Key Components
The primary components of a cooling mechanism include various elements designed to manage and dissipate heat effectively. Each part works in harmony to ensure the engine remains within safe temperature limits, thereby enhancing performance and fuel efficiency.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Radiator | Dissipates heat from the coolant. |
| Thermostat | Regulates coolant flow based on temperature. |
| Water Pump | Circulates coolant throughout the engine. |
| Coolant Reservoir | Holds excess coolant and allows for expansion. |
Enhancing Efficiency
To maximize the effectiveness of the cooling mechanism, regular maintenance is essential. This includes checking fluid levels, inspecting components for wear and tear, and ensuring there are no leaks. Proper maintenance not only enhances the system’s efficiency but also prolongs the lifespan of the engine.
Analyzing Wheels and Tire Configurations
The assessment of wheel and tire setups plays a crucial role in enhancing the overall performance and stability of various vehicles. Understanding the relationship between these components can lead to improved handling, traction, and durability, which are essential for effective operation in diverse environments.
Different configurations may yield varying results based on factors such as load capacity, surface type, and intended use. It is vital to evaluate how these elements interact to optimize functionality and safety.
| Configuration Type | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Single Wheel | A standard setup with one wheel per side, common in lighter applications. | Enhanced maneuverability and reduced weight. |
| Dual Wheel | Utilizes two wheels on each side for increased stability and load distribution. | Improved weight handling and traction on soft surfaces. |
| Triple Wheel | A specialized arrangement featuring three wheels on each side, designed for heavy-duty applications. | Maximum load capacity and stability in challenging conditions. |
Common Replacement Parts and Upgrades
When maintaining or enhancing a lifting vehicle, understanding essential components and available enhancements is crucial. Regularly assessing these elements can lead to improved efficiency and longevity of the equipment.
Here are some frequently replaced components and potential upgrades:
- Batteries: Upgrading to a higher-capacity battery can significantly extend operational time and reduce downtime.
- Tires: Choosing the right tires for specific surfaces can enhance stability and traction, improving overall safety and performance.
- Brakes: Regularly replacing brake pads and adjusting the braking system ensures effective stopping power, crucial for safety.
- Hydraulic Fluids: Using high-quality hydraulic fluids can enhance lifting performance and protect the hydraulic system.
- Lift Chains: Upgrading to heavy-duty chains can improve lifting capabilities and reduce the risk of failure.
In addition to replacements, consider implementing the following enhancements:
- LED Lighting: Installing LED lights can improve visibility in low-light conditions, enhancing safety during operation.
- Ergonomic Controls: Upgrading to more ergonomic control systems can reduce operator fatigue and improve handling.
- Advanced Safety Features: Adding features like anti-collision sensors can significantly enhance operational safety.
By focusing on these crucial elements, operators can ensure their equipment remains reliable and efficient for various tasks.