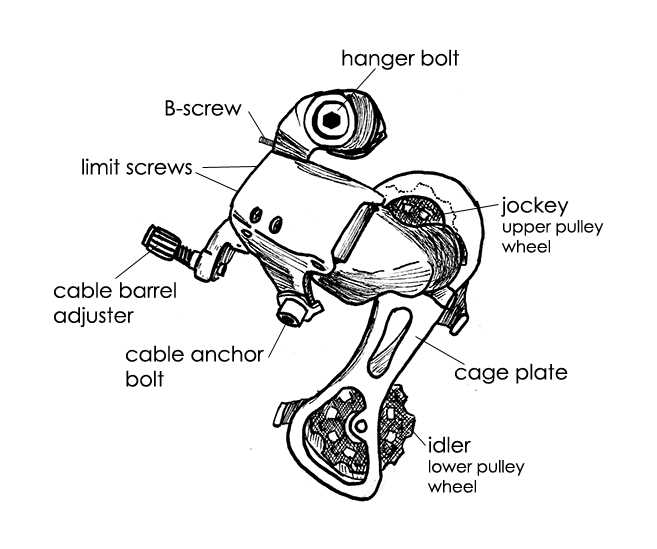
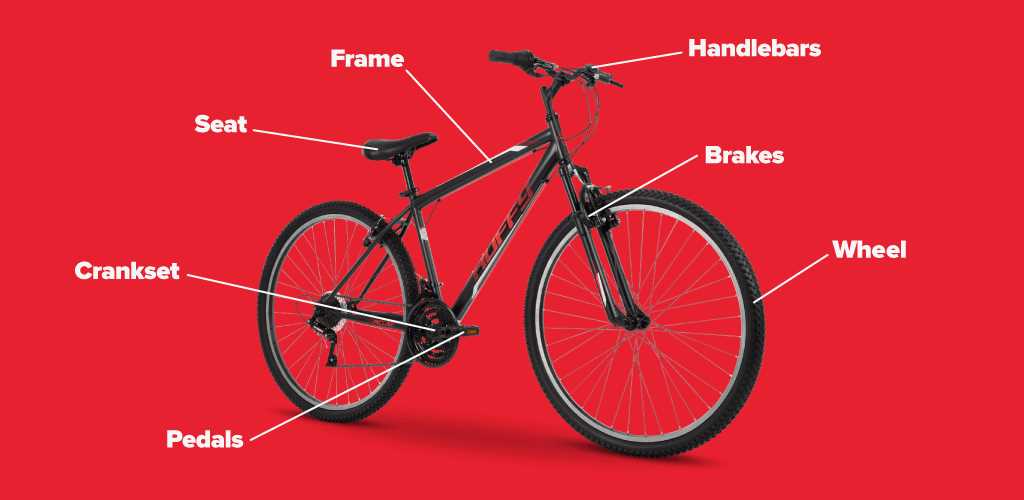
Bike Derailleur Parts Diagram
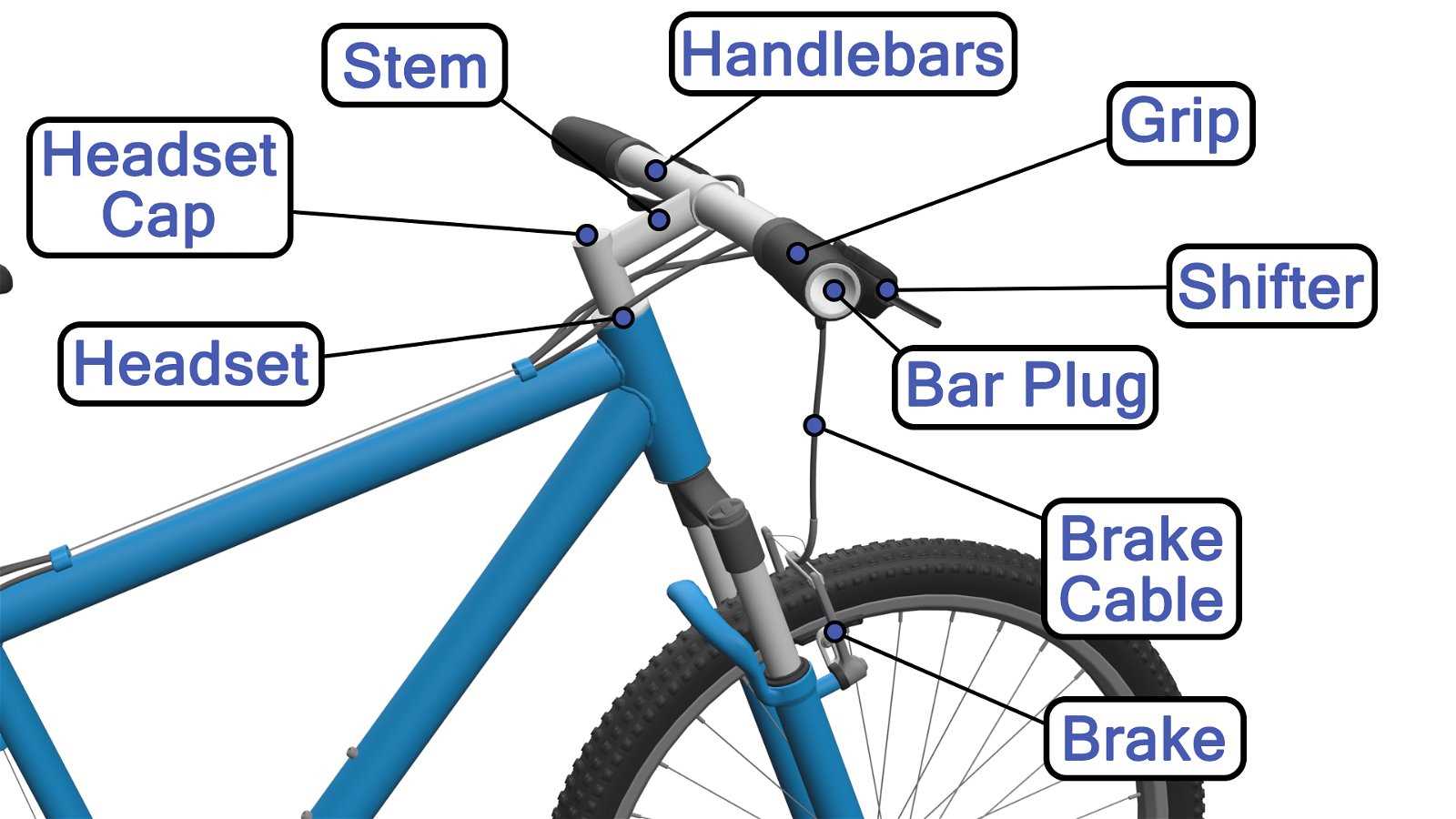
The functionality of modern two-wheeled transport relies heavily on the precision and interaction of its gear-changing mechanisms. These intricate systems allow for smooth transitions between different levels of resistance, helping to maintain efficiency across varying terrains. A clear understanding of these mechanisms is essential for anyone looking to enhance performance or ensure proper maintenance.
Each segment within these systems plays a distinct role in facilitating gear shifts. From small connectors to larger, more prominent elements, every piece works in harmony to deliver the desired outcome. Exploring the layout and purpose of these elements can offer valuable insights into how they contribute to overall functionality.
By examining the structure and operation of these components, we gain a deeper appreciation for the technology behind gear transitions. Understanding the relationship between individual pieces helps to ensure proper care and timely adjustments, ultimately extending the lifespan of the system.
Bike Derailleur Parts Diagram
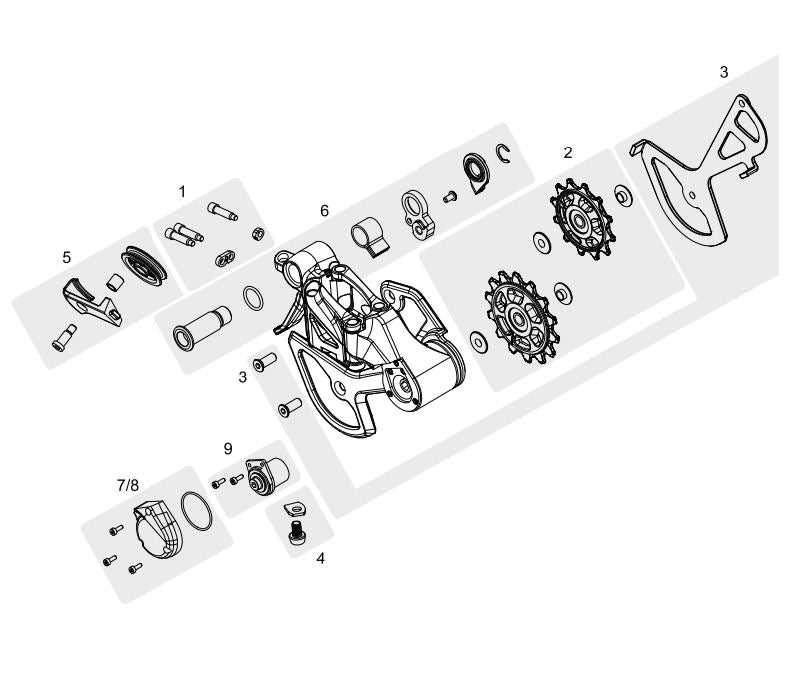
The mechanism responsible for changing gears in a two-wheeled vehicle consists of multiple components that work together to ensure smooth transitions between different speed settings. Understanding how these elements interact can help maintain proper functionality and prevent breakdowns during use.
- Frame-mounted connector that holds the gear-shifting device in place
- Movable arm that guides the chain across sprockets
- Spring-loaded tensioner to keep the chain tight and responsive
- Cable attachment point to adjust shifting precision
- Small rollers to manage chain movement and alignment
Each part contributes to the overall performance, ensuring efficient power transmission and a smooth ride. Proper maintenance and periodic checks of these elements will extend their longevity and enhance riding experience.
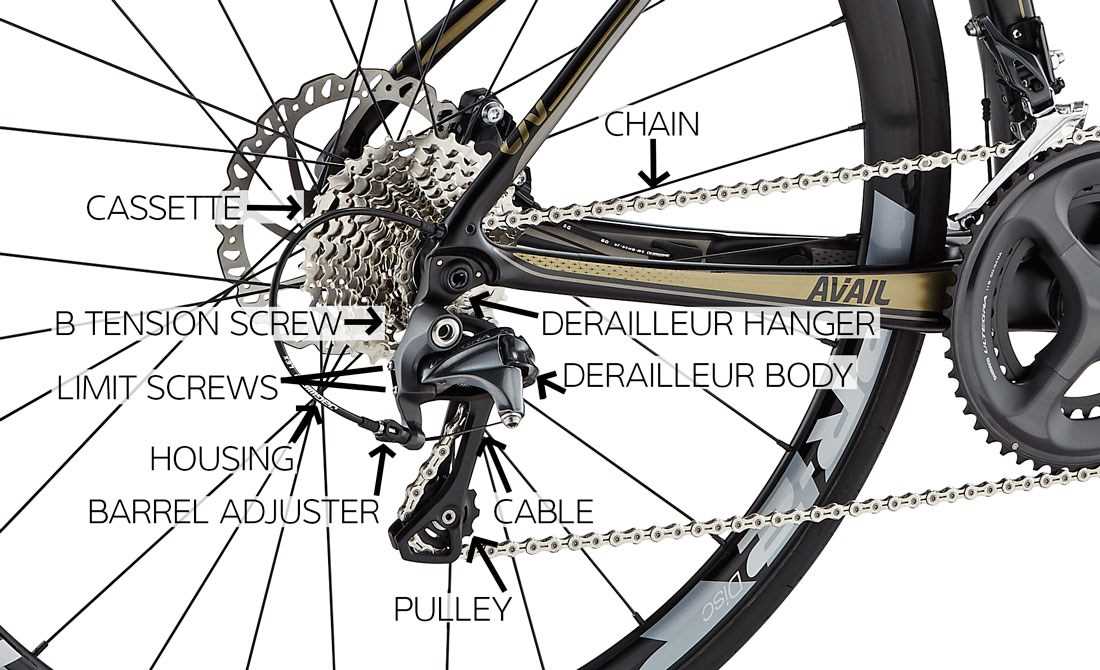
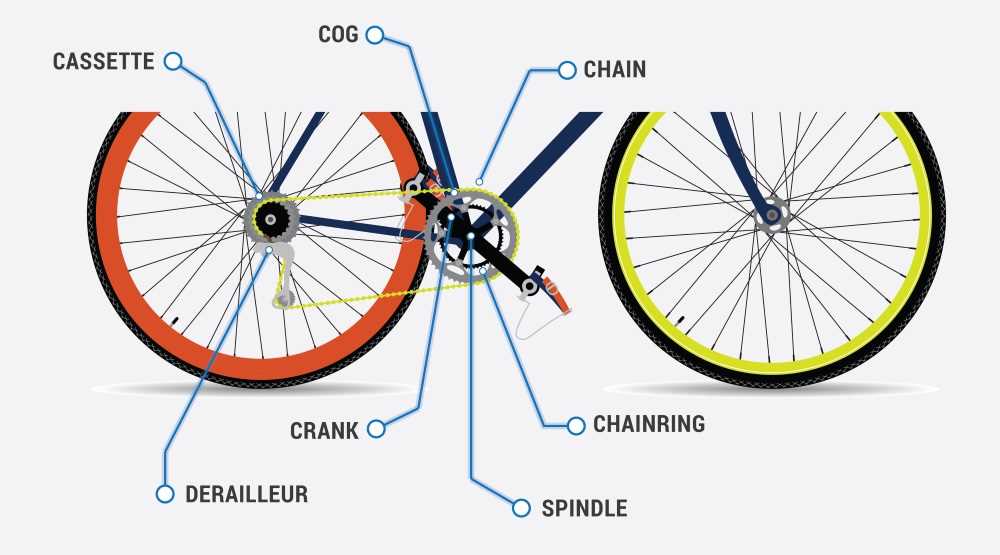
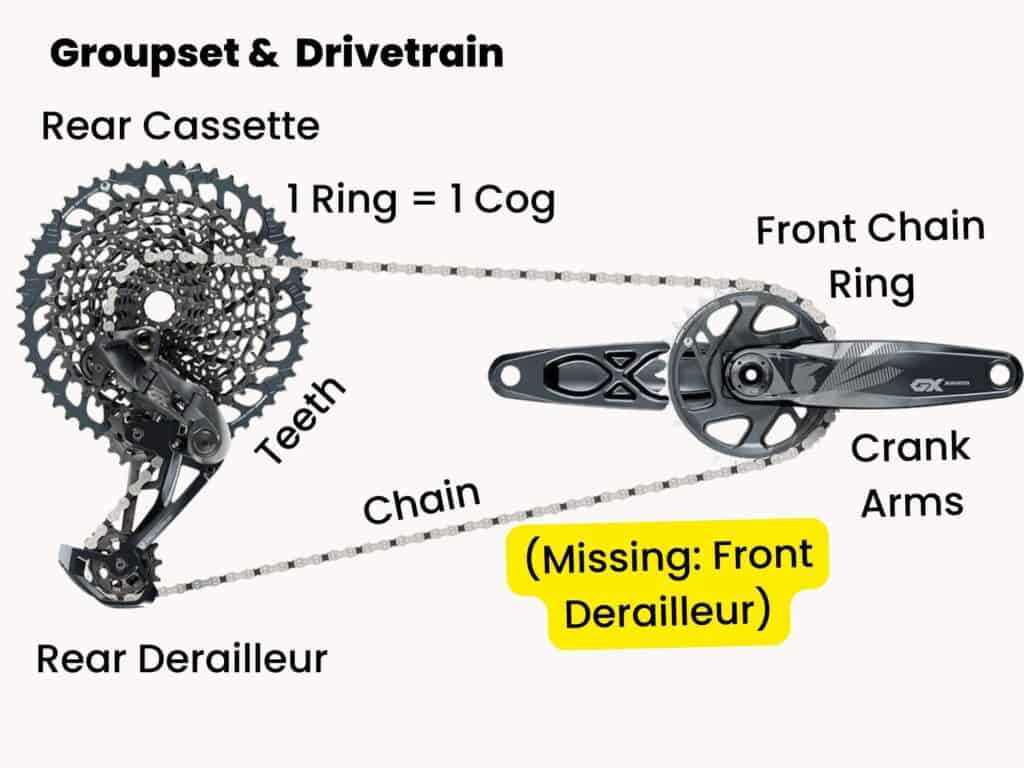
Main Components of a Bike Derailleur
The mechanism that manages gear shifting consists of several crucial elements working together to ensure smooth transitions between different speed levels. Each part has a specific role that contributes to the overall efficiency and performance of the system. Understanding these elements can help in maintaining and adjusting the shifting system properly.
- Guide Arm: This is the component responsible for positioning the chain accurately onto the desired gear.
- Tensioner: Helps maintain the correct amount of slack in the chain as gears are changed.
- Shift Cable: Connects to the lever, transferring the input required to move between different gears.
- Spring Mechanism: Assists in returning the chain guide to its original position after a shift has occurred.
- Mounting Bracket:
Understanding the Function of the Cage
The cage plays a crucial role in the smooth operation of the shifting mechanism, guiding the movement of the chain across different gears. This component ensures that the chain transitions efficiently, providing stability and reducing the risk of misalignment. By controlling the chain’s position, the cage contributes to a seamless riding experience, especially when shifting under load.
- Maintains proper chain alignment between gears
- Prevents chain slippage or derailment
- Improves overall performance during transitions
Without a well-functioning cage, shifting would become unreliable, leading to increased wear and potential issues during gear changes. It is essential to keep this component in good condition to ensure efficient performance and safety.
Role of the Pulleys in Shifting
The small wheels within the shifting mechanism play a crucial role in guiding the movement of the chain between different gears. Their precise operation ensures smooth and accurate changes in gear ratios, allowing for a seamless transition during motion. These components are essential for maintaining proper tension and alignment.
Guiding the Chain
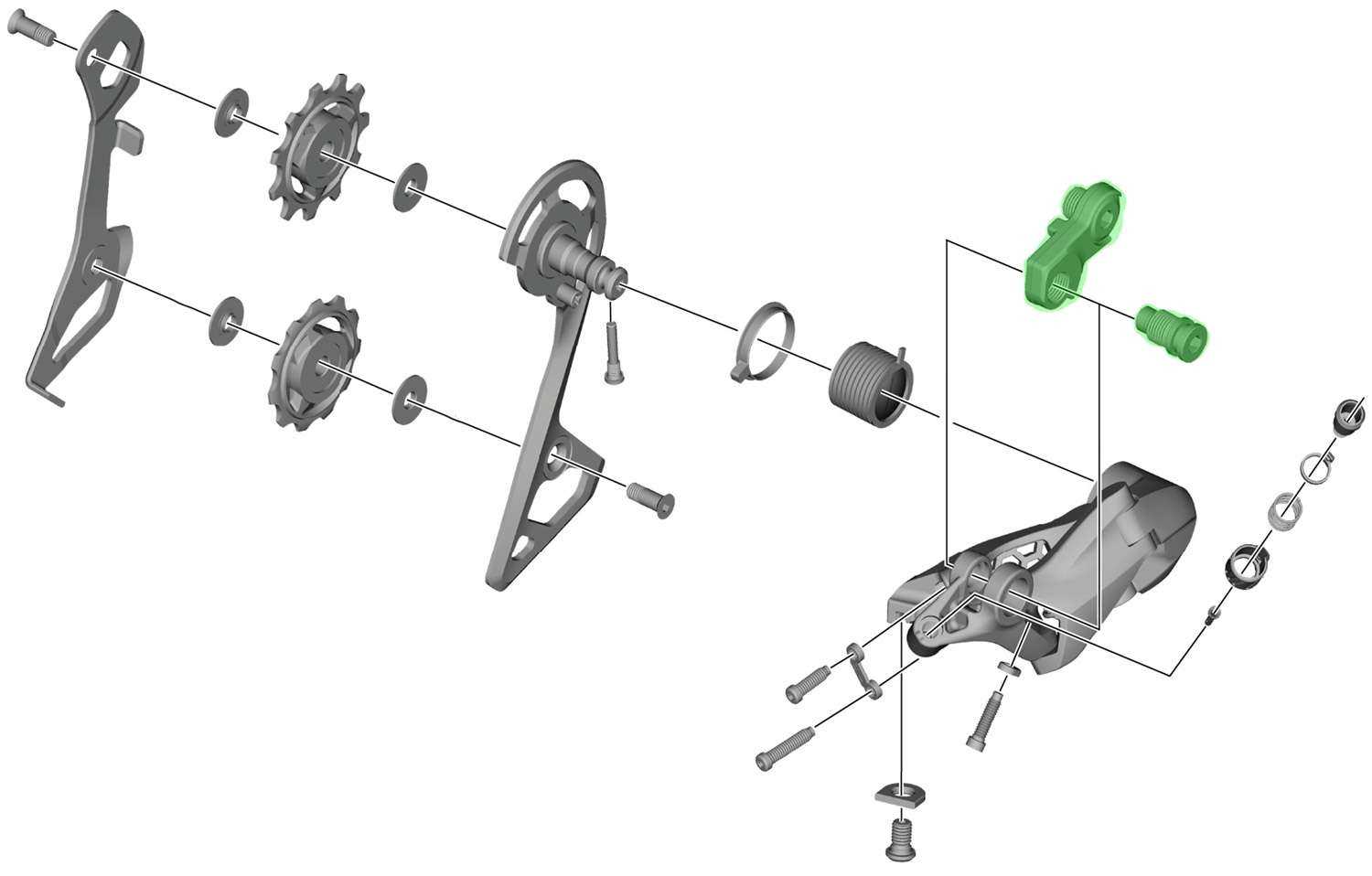
The upper pulley, often referred to as the guide, directs the chain as it moves from one gear to another. It maintains close contact with the chain, ensuring its path remains aligned with the chosen gear, minimizing friction and misalignment.
Maintaining Tension
The lower pulley, or tensioner, helps maintain the necessary tension on the chain. By adjusting to the shifting movement, it prevents the chain from becoming too loose or too tight, which is essential for ensuring a consistent, efficient performance.
Importance of the B-Screw in Adjustment
In fine-tuning the performance of your bicycle’s shifting mechanism, one critical component plays a pivotal role: the B-screw. This tiny yet significant adjustment feature enables precise control over the rear derailleur’s position relative to the cassette. Its primary function revolves around optimizing the derailleur’s distance from the cassette’s cogs, influencing both shifting smoothness and chain tension during gear changes.
The B-screw, often found on the rear derailleur assembly, allows cyclists to achieve: The B-screw, typically located near the derailleur’s upper pivot, facilitates: – Enhanced gear shifting precision. – Improved accuracy in gear transitions. – Better chain stability on different gear combinations. – Optimal chain stability across various gear combinations. – Reduction of chain chatter and potential derailments. – Minimization of chain noise and derailment risks. Understanding how to adjust the B-screw correctly is essential for maintaining efficient gear shifting performance over time. By controlling the derailleur’s angle relative to the cassette, cyclists can achieve smooth, reliable gear changes tailored to different riding conditions and terrains.
How the Jockey Wheels Operate
Jockey wheels play a crucial role in the movement and efficiency of a bicycle’s drivetrain system. Positioned within the derailleur mechanism, these small components facilitate the smooth transition of the chain across various gears. Their function involves guiding the chain as it shifts, ensuring minimal friction and optimal engagement with the cassette or freewheel.
By maintaining tension and alignment, jockey wheels help stabilize the chain during gear changes, preventing slippage and ensuring consistent performance. Their design incorporates bearings or bushings to reduce friction, allowing for efficient power transfer from the pedals to the rear wheel. This operational principle underscores their importance in enhancing overall cycling experience, particularly in terms of gear shifting precision and reliability.
Exploring the Hanger’s Purpose
The role of the hanger in the mechanism of a bicycle’s gear shifting system is pivotal, yet often overlooked in its subtlety. Positioned strategically, it serves as a crucial link between the frame and the derailleur, facilitating precise movement and alignment. Its design intricacies allow for adjustments that optimize gear shifting performance, contributing significantly to the overall functionality and smooth operation of the bicycle.
- Facilitates precise alignment between the frame and the derailleur
- Enhances gear shifting performance through strategic positioning
- Allows for adjustments to optimize functionality
- Ensures smooth operation of the gear shifting system
Differences Between the Inner and Outer Plates
The structure of the two plates plays a crucial role in the overall performance. These components are designed with distinct purposes, ensuring smooth interaction during operation. The differences in their design are not random; each has a specific function that complements the other, improving efficiency.
Shape and Functionality
Inner plates tend to be narrower and are shaped to fit tightly, providing stability and reducing friction. Their streamlined form allows for easier movement, especially when transitioning. Outer plates, on the other hand, are generally wider and designed to guide movement, ensuring alignment. Their role is more focused on control rather than reducing friction.
Durability and Wear
The materials used in each plate also differ in terms of durability. Outer plates are built to withstand more
Impact of the Limit Screws on Performance
Limit screws play a crucial role in controlling the range of movement for certain components, ensuring that they operate within a specific boundary. Proper adjustment of these screws directly affects the smoothness and accuracy of mechanical shifts, preventing overextension or insufficient movement. When correctly tuned, they help achieve optimal precision and reduce wear over time.
Fine-Tuning for Accuracy
Adjusting the limit screws allows for precise control over mechanical transitions. Misaligned screws can lead to issues such as incomplete movement or excessive strain on the system. To optimize performance, each screw must be set according to the desired range of motion.
- Prevent overreaching by adjusting the outer screw
- Ensure full alignment by fine-tuning the inner screw
- Check for smooth operation after each adjustment
Common Performance Issues

Poorly adjusted screws can cause a variety of performance i
The Importance of Cable Tension
Proper tension in the control mechanism is crucial for optimal performance and responsiveness. Ensuring that this tension is correctly adjusted can significantly affect the overall functionality of the shifting system. When the tension is accurate, gear changes are smoother and more reliable, which enhances the overall riding experience.
Key Benefits of Correct Tension
- Smooth Shifting: Adequate tension allows for seamless transitions between gears, reducing the chances of misalignment.
- Improved Control: With the right amount of tension, the rider can easily manage gear changes, allowing for better handling and stability.
- Increased Longevity: Maintaining appropriate tension can minimize wear on the components, leading to a longer lifespan of the system.
Adjusting Cable Tension
Regularly checking and adjusting the tension is essential for maintaining performance. Here are some tips for proper adjustment:
- Identify the tension adjustment mechanism.
- Check the current tension by shifting through the gears.
- Make small adjustments as needed, testing the system after each change.
- Ensure that the cable moves freely and is not frayed or damaged.
Materials Used in Derailleur Manufacturing
The choice of materials in the construction of shifting mechanisms plays a crucial role in their performance and durability. Manufacturers strive to find a balance between weight, strength, and resistance to wear, which directly impacts the efficiency and longevity of these components.
Aluminum is a popular choice due to its lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion. It provides a good strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for various components.
Carbon fiber is another advanced material used in high-end applications. Its remarkable stiffness and lightness contribute to enhanced performance, although it comes at a higher cost.
Steel is commonly employed for critical parts that require durability and strength. Its ability to withstand significant stress makes it a reliable option, despite being heavier than alternatives.
Lastly, plastic composites are frequently utilized for specific elements. These materials can be molded into intricate shapes and provide a good balance between weight and strength, making them suitable for various applications.
Common Issues with Bike Derailleurs

Many cyclists encounter various challenges with their shifting mechanisms. Understanding these issues can enhance performance and prolong the lifespan of the equipment. Below are some frequent problems faced by riders, along with potential solutions.
Misalignment of Components

One of the most common problems arises from misalignment. This can lead to improper shifting and can cause excessive wear on the chain and gears. Here are signs of misalignment:
- Difficulty in shifting between gears
- Chain skipping or jumping
- Unusual noise during shifting
Regular inspection and adjustments can help maintain proper alignment.
Worn or Damaged Parts
Another significant issue is the wear and tear of components over time. As parts age, they may lose their effectiveness, affecting overall performance. Common indicators include:
- Slipping gears
- Inability to stay in a selected gear
- Visible damage to the chain or sprockets
Regular maintenance and timely replacement of worn components can prevent further complications.
Maintenance Tips for Long-Lasting Performance
Proper upkeep is essential for ensuring the longevity and efficient functioning of your cycling equipment. Regular attention to certain components can prevent wear and enhance overall performance, allowing for a smoother and more enjoyable riding experience.
To achieve optimal results, consider incorporating the following maintenance practices into your routine:
Task Frequency Tips Cleaning Weekly Use a gentle brush and degreaser to remove dirt and grime. Lubrication Every 2-4 weeks Apply a suitable lubricant to moving parts to minimize friction. Adjustment As needed Check alignment and tension regularly to ensure smooth operation. Inspection Monthly Look for signs of wear and replace any damaged components promptly. Storage Off-season Keep equipment in a dry place to prevent rust and degradation. By adhering to these guidelines, you can maintain the functionality of your cycling equipment, ensuring a reliable and enjoyable ride for years to