2003 Toyota Sequoia Parts Diagram Overview
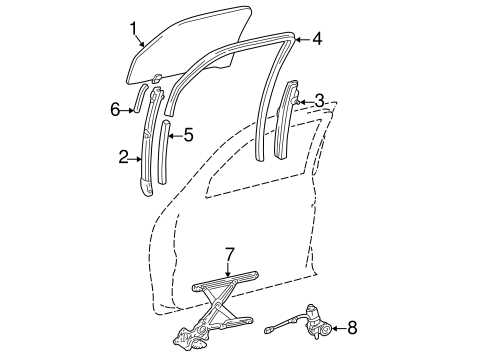
When it comes to maintaining and repairing a trusted vehicle, having a clear and precise overview of its essential elements is crucial. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional, a visual guide that illustrates the various systems and configurations within an SUV can make all the difference. This type of resource helps you quickly identify what’s needed for maintenance, saving time and ensuring accuracy.
For those seeking clarity on the inner workings of an SUV, a comprehensive outline of its mechanical and electrical features provides valuable insights. From the arrangement of the engine components to the layout of the interior fittings, such diagrams help users better understand how different sections function together. By navigating through these layouts, users can develop a deeper understanding of their vehicle’s overall structure and address issues with confidence.
Exploring the specifics of a trusted model also unveils the intricate relationships between its numerous elements. This information can be especially useful for troubleshooting, as it allows individuals to pinpoint precise areas that require attention. With a detailed overview, any vehicle owner can become more familiar with each segment, ultimately enhancing their repair and maintenance capabilities.
2003 Toyota Sequoia Parts Overview
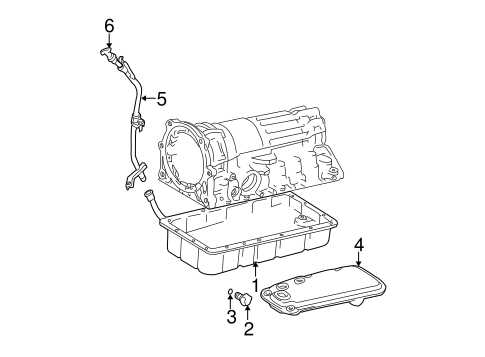
Understanding the individual components that contribute to the vehicle’s overall performance is essential for anyone looking to maintain or repair their vehicle. This section provides insights into the key elements of the vehicle’s structure, from its engine system to the interior features, each designed to work in harmony to ensure a reliable and comfortable driving experience.
Engine and Transmission Components
The engine and transmission are at the heart of this vehicle, delivering the power and efficiency needed for both city driving and off-road adventures. Key elements include the V8 engine, known for its robust output, and a 5-speed automatic transmission that provides smooth gear shifts. Together, these systems ensure responsive acceleration and controlled handling under various driving conditions.
Interior and Exterior Features
Inside the cabin, comfort and convenience take center stage. The interior includes a spacious seating arrangement, advanced climate control options, and integrated technology that caters to both drivers and passengers. On the exterior, a durable frame and high-performance suspension system enhance stability and durability, making it suitable for a wide range of terrains and driving conditions.
Engine Components Layout Explained
The engine’s intricate arrangement consists of numerous interconnected parts, each contributing to overall functionality. Understanding this layout provides insight into how these pieces work together, supporting the vehicle’s efficient operation. By familiarizing yourself with the main sections and their roles, you gain a clearer view of the engine’s complex yet coordinated structure.
Main Components Overview
The cylinder block serves as the foundation, housing essential parts like pistons and connecting rods. Nearby, the cylinder head contains valves, allowing air and fuel to enter while controlling exhaust flow. These areas work in tandem, driving the engine’s core functions and enabling the conversion of fuel into motion.
Additional Functional Areas

Other crucial sections include the intake system, which brings in air needed for combustion, and the exhaust system, responsible for expelling gases. The cooling system surrounds the engine block, regulating temperature through components like the radiator and thermostat. Together, these elements ensure that the engine operates at optimal conditions, sustaining reliable performance over time.
Brake System and Key Parts
The braking mechanism is a critical component of any vehicle, designed to ensure safe and controlled stops under various driving conditions. This section provides an overview of the essential elements that work together to decelerate and halt the vehicle effectively. By understanding these components, you can maintain the system more effectively and recognize potential issues early.
Brake Pads and Rotors: These parts work in unison to create friction, which is essential for slowing down the vehicle. The brake pads press against the rotors when the brake pedal is applied, generating the force needed to reduce speed. Over time, both pads and rotors can wear down and require replacement.
Brake Calipers: The calipers are responsible for holding the brake pads and pressing them against the rotors. Typically equipped with pistons, these components are activated by hydraulic pressure, transferring the force from the pedal to the braking surface. Properly functioning calipers are essential for balanced and effective braking.
Brake Lines and Hoses: These tubes carry the hydraulic fluid that powers the braking system. When the pedal is pressed, fluid travels through the lines to the calipers, applying pressure to the pads. Regular inspection of these lines helps prevent leaks that can lead to decreased braking performance.
Master Cylinder: As the heart of the braking system, the master cylinder generates hydraulic pressure when the brake pedal is pressed. It acts as a reservoir for brake fluid and is crucial for transferring force to the brake lines. A malfunctioning master cylinder can significantly affect overall braking power.
Anti-lock Braking System (ABS): This safety feature prevents wheel lock-up during sudden braking, allowing for better steering
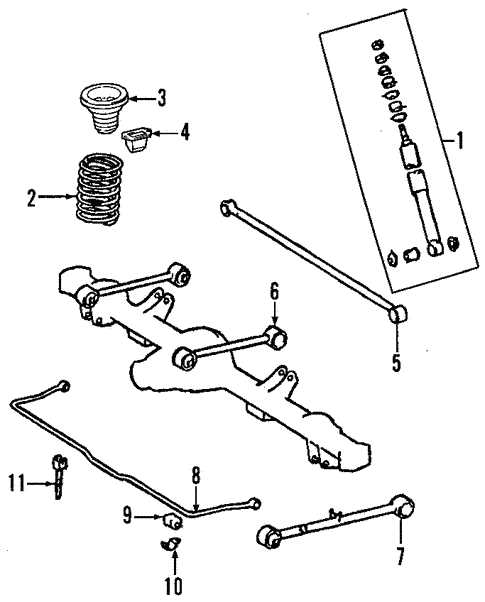
Suspension Parts Guide for Smooth Rides
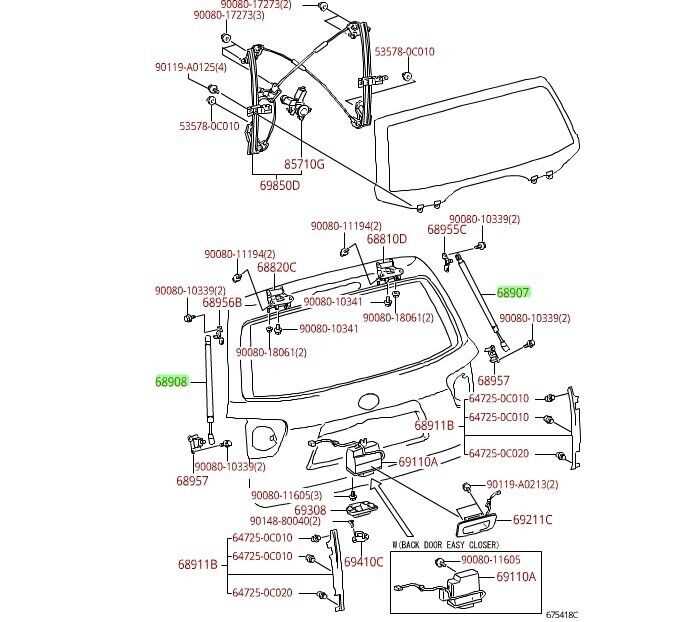
A vehicle’s suspension system is essential for ensuring a comfortable, balanced driving experience. This system connects the wheels to the mainframe, absorbing road impacts and providing better stability and control. The components within this setup work in harmony to reduce vibrations and maintain tire contact with the ground, promoting a safe and pleasant journey.
Shock Absorbers are designed to dampen the effects of uneven road surfaces, making the ride less jarring. They play a crucial role in managing the vehicle’s movement by controlling the bounce and sway caused by speed bumps, potholes, and other obstacles.
Struts support the vehicle’s weight while also acting as shock absorbers. These parts help to stabilize the frame and provide a firm foundation, reducing body roll during sharp turns and sudden stops. Struts are integral to the overall balance of the suspension system, enhancing control on various terrains.
Springs are responsible for absorbing the energy generated by the vehicle’s motion and road irregularities. They work closely with the shock absorbers and struts to ensure that the wheels maintain consistent ground contact, contributing to a smoother and more controlled ride.
Control Arms link the wheels to the vehicle’s structure, allowing for controlled up-and-down motion while minimizing horizontal movement. By maintaining the correct wheel alignment, control arms prevent excessive tire wear and improve steering responsiveness.
Stabilizer Bars, also known as sway bars, connect the suspension on either side of the vehicle to reduce body lean during turns. These bars improve handling and stability, especially on winding roads, by balancing the weight distribution and minimizing the effects of centrifugal force.
Regular maintenance and inspection of these key suspension elements can help prolong their lifespan and ensure a more comfortable, safe driving experience. Investing in quality components and timely replacements will keep the system performing at its best, allowing for smooth and controlled rides across various road conditions.
Understanding the Fuel System Structure
The fuel delivery framework is essential for ensuring that an engine receives the proper amount of fuel for efficient operation. This system involves a series of interconnected components working together to store, filter, and transport fuel to the engine. Let’s explore the primary parts of this system and their unique functions, which collectively contribute to a vehicle’s overall performance.
Key Components in the Fuel Flow Process
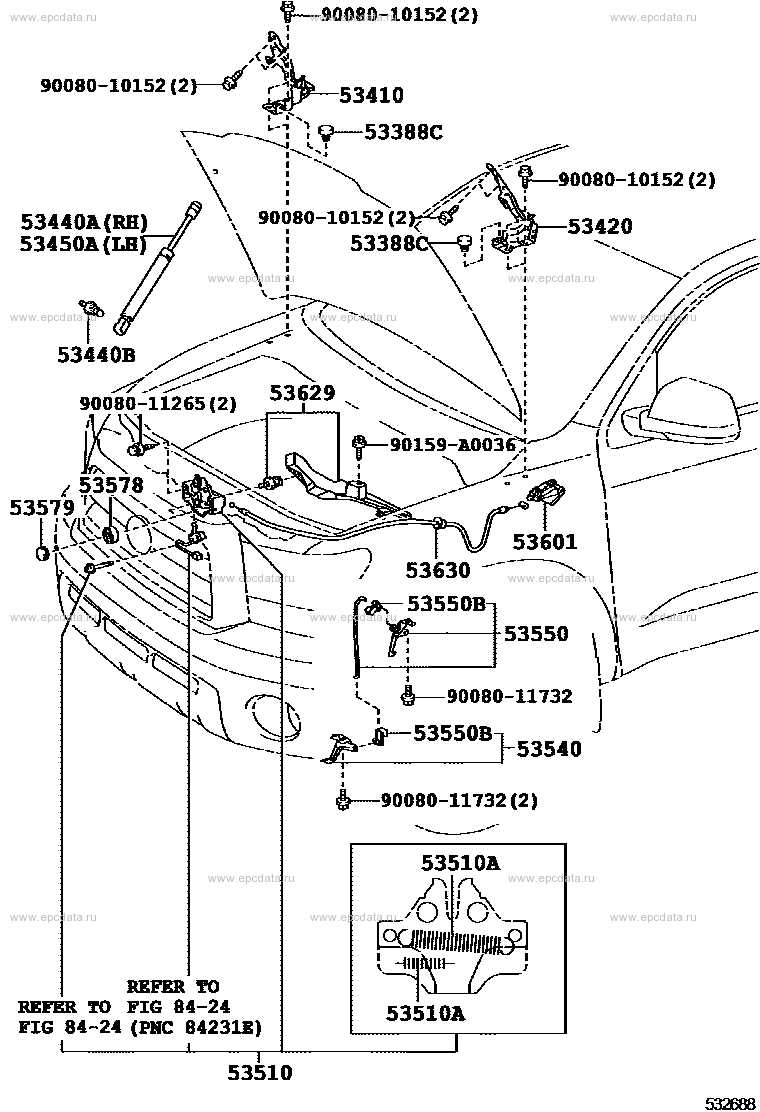
The fuel system comprises various components, each with a specific role in transferring fuel from the storage area to the engine. These include the fuel tank, fuel pump, and fuel injectors, among others. Each of these parts ensures that fuel moves smoothly through the system and reaches the engine in the required amounts, promoting effective combustion.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Fuel Tank | Serves as the main storage unit for fuel, holding it until needed for combustion. |
| Fuel Pump | Draws fuel from the tank and delivers it through the lines to the engine at the required pressure. |
| Fuel Filter | Removes contaminants and debris from the fuel to prevent clogging and protect the engine components. |
| Fuel Injectors | Precisely spray fuel into the engine’s intake manifold or directly into the combustion chamber for efficient combustion. |
Fuel Regulation and Efficiency
The regulation of fuel pressure is another vital aspect of the fuel system. It is managed by a pressure regulator, which maintains consistent fuel pressure within the lines, adjusting as needed to meet the engine’s demands. This consistency not only improves fuel efficiency but also ensures smoother performance and reduced emissions.
Exhaust Components for Emission Control
Effective management of exhaust emissions is crucial for maintaining environmental standards and ensuring vehicle efficiency. Various components work together within the exhaust system to minimize harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere. Understanding these elements is essential for anyone looking to enhance performance or ensure compliance with regulations.
Key Elements of the Exhaust System

- Catalytic Converter: This device plays a vital role in converting harmful gases into less toxic emissions. It facilitates chemical reactions that reduce pollutants such as carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides.
- Oxygen Sensors: These sensors monitor the levels of oxygen in the exhaust gases, allowing the engine control unit to adjust the air-fuel mixture for optimal combustion.
- Exhaust Manifold: This component collects exhaust gases from multiple cylinders and directs them into the exhaust system. Its design is crucial for ensuring efficient gas flow.
- Muffler: The muffler minimizes noise produced by the engine’s exhaust system while also helping to maintain optimal back pressure.
- Exhaust Pipes: These pipes transport gases away from the engine to the tailpipe, facilitating efficient flow and minimizing resistance.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Routine inspection and maintenance of exhaust components are essential for ensuring their proper functioning. Neglecting these elements can lead to increased emissions, reduced fuel efficiency, and potential engine damage. Key maintenance practices include:
- Regularly checking for leaks or damage.
- Replacing worn-out oxygen sensors.
- Cleaning or replacing the catalytic converter when necessary.
- Ensuring proper mounting of exhaust components to prevent vibrations and noise.
By prioritizing the upkeep of exhaust components, vehicle owners can contribute to a cleaner environment while enhancing overall performance.
Cooling System Diagram and Parts

The cooling mechanism in a vehicle is essential for maintaining optimal operating temperatures. It ensures that the engine runs efficiently while preventing overheating. This system comprises several components that work together to regulate the temperature and facilitate heat exchange, ultimately safeguarding the engine and enhancing performance.
Key Components of the Cooling Mechanism

Several critical elements contribute to the efficiency of the cooling system. The radiator plays a vital role by dissipating heat from the coolant. As the engine generates heat, the coolant absorbs it and flows to the radiator, where air passing through cools it down. The water pump circulates the coolant throughout the system, ensuring consistent temperature regulation.
Additional Elements to Consider
In addition to the radiator and water pump, the thermostat is crucial in controlling the coolant flow based on the engine’s temperature. It opens and closes as needed to maintain optimal heat levels. Other significant components include the hoses, which transport coolant between various parts, and the expansion tank, which accommodates changes in coolant volume due to temperature fluctuations.
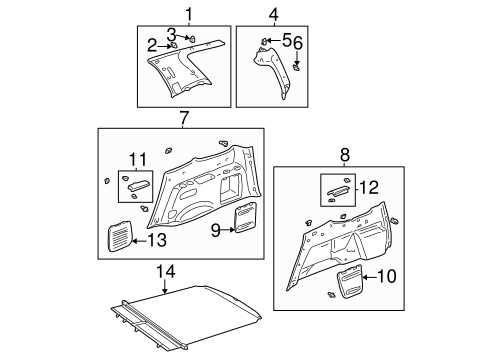
Interior Components and Their Functions
The interior of a vehicle is meticulously designed to enhance comfort, functionality, and safety for its occupants. Each component plays a pivotal role in creating a harmonious driving experience, offering both convenience and accessibility. Understanding these elements and their specific roles can significantly enhance the appreciation of automotive engineering.
Dashboard: The dashboard serves as the primary interface for the driver, housing essential controls and displays. It provides critical information such as speed, fuel level, and engine status, ensuring that the driver is always informed.
Seats: Ergonomically designed seats offer comfort and support during travel. Various adjustments allow passengers to find their ideal position, contributing to an overall enjoyable journey.
Center Console: This central feature often contains storage compartments, cup holders, and controls for entertainment and climate systems. Its layout promotes ease of access, allowing drivers to manage functions without distraction.
Door Panels: These panels not only provide a finished look but also house controls for windows and locks, enhancing the convenience for all passengers. They also contribute to the vehicle’s insulation against noise and temperature.
Headliner: The headliner, which covers the interior roof, plays a significant role in noise reduction and contributes to the overall aesthetic of the cabin. It can also house lighting elements, enhancing visibility and ambiance.
Floor Mats: While often overlooked, these components protect the vehicle’s flooring from dirt and wear. They also contribute to the overall cleanliness and comfort of the interior space.
In summary, each element within the cabin is meticulously crafted to provide functionality and enhance the overall experience of traveling. By understanding their roles, occupants can better appreciate the thoughtful engineering that goes into creating a comfortable and safe environment.
Lighting and Electrical System Layout
This section provides an overview of the configuration and organization of the illumination and electrical components within the vehicle. Understanding the arrangement of these systems is crucial for effective maintenance, troubleshooting, and upgrades. The layout facilitates easy access to essential elements, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Key Components
The electrical framework consists of various vital elements that work together to ensure the vehicle’s lighting and electronic systems function seamlessly. Below is a summary of the primary components involved:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Headlights | Provide illumination for night driving and adverse weather conditions. |
| Taillights | Signal the presence of the vehicle to others from behind. |
| Turn Signal Lights | Indicate the direction of intended turns or lane changes. |
| Fuses | Protect electrical circuits from overloads and shorts. |
| Wiring Harness | Connect various electrical components, ensuring reliable communication. |
System Overview
The electrical system operates through a network of wires and connectors that distribute power from the battery to all lighting fixtures and electronic devices. A comprehensive understanding of this layout allows for efficient troubleshooting and enhances the ability to modify or upgrade lighting systems as needed.
Transmission and Drivetrain Parts Overview
This section provides a comprehensive look at the components involved in the transmission and drivetrain system of a vehicle. These elements are crucial for the effective transfer of power from the engine to the wheels, ensuring smooth operation and optimal performance on the road.
At the heart of this system lies the transmission, which is responsible for managing the gear ratios, allowing for the efficient conversion of engine power. Complementing the transmission is the driveshaft, a vital component that transmits torque to the wheels. Additionally, the differential plays a key role in allowing the wheels to rotate at different speeds, particularly during turns.
Other essential elements include the clutch, which facilitates smooth engagement and disengagement of gears, and the transfer case, found in all-wheel and four-wheel-drive configurations, distributing power to both the front and rear axles. Understanding these components is crucial for maintaining the vehicle’s functionality and performance.
In summary, the transmission and drivetrain encompass a range of interconnected components that work together to deliver power effectively and ensure a smooth driving experience.
Steering Mechanism and Key Parts
The steering assembly plays a crucial role in providing maneuverability and control over a vehicle’s direction. This intricate system consists of various components that work together to facilitate smooth navigation. Understanding the key elements of this mechanism can enhance maintenance and troubleshooting efforts.
Essential Components
Several vital components contribute to the efficient functioning of the steering mechanism. Each part serves a unique purpose, ensuring that drivers can steer with precision and ease.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Steering Wheel | The primary interface for the driver, allowing for input to the steering system. |
| Steering Column | A shaft that connects the steering wheel to the gearbox, transmitting the driver’s input. |
| Steering Gearbox | Converts the rotational movement from the steering wheel into lateral motion for the wheels. |
| Linkage System | Consists of rods and joints that connect the gearbox to the wheels, facilitating movement. |
| Power Steering Pump | Provides hydraulic assistance, reducing the effort required to turn the steering wheel. |
Functionality and Maintenance
Regular inspection and maintenance of these key components are essential for ensuring optimal performance and safety. Identifying wear and tear early can prevent more extensive issues and enhance the overall driving experience.
Body Panels and Exterior Parts

The exterior framework of a vehicle plays a crucial role in both aesthetics and functionality. This section delves into the various components that comprise the outer shell, highlighting their significance in maintaining structural integrity and enhancing visual appeal.
Fenders are essential elements that protect the wheels while contributing to the overall design. They are often subject to damage from road debris and minor collisions, making their quality and condition vital for safety.
Hoods not only provide access to the engine compartment but also significantly influence the vehicle’s look. Their design can vary greatly, impacting aerodynamics and cooling efficiency.
Doors serve as critical entry points while also ensuring passenger safety. Their construction involves a careful balance of strength and weight, with materials chosen for durability and insulation properties.
Bumpers are engineered to absorb impacts, thereby protecting vital components during collisions. These elements come in various styles and finishes, reflecting the vehicle’s character while providing necessary functionality.
Grilles are often overlooked yet play a vital role in engine cooling. They can also serve as distinctive design features that enhance the vehicle’s identity, combining form with function.
Understanding the importance of each element within the vehicle’s exterior is essential for proper maintenance and restoration. Regular inspections can help identify wear or damage, ensuring that the vehicle remains in optimal condition.
Accessories and Optional Add-ons
Enhancements and additional features can significantly improve the functionality and comfort of your vehicle. Various accessories and optional upgrades are available, allowing owners to customize their experience to better suit their needs and preferences. These enhancements range from practical tools to luxury items, contributing to both convenience and style.
Popular Accessories
- Floor Mats: Protect the interior from dirt and wear with durable mats designed to fit perfectly.
- Roof Racks: Increase cargo capacity for adventures or road trips.
- Towing Packages: Enhance the ability to haul trailers or other equipment.
- Upgraded Audio Systems: Enjoy superior sound quality with advanced audio options.
Optional Add-ons for Comfort
- Heated Seats: Provide warmth during colder months for a cozy ride.
- Navigation Systems: Ensure effortless travel with integrated GPS and real-time traffic updates.
- Sunshades: Reduce glare and heat inside the cabin, improving overall comfort.
Investing in these enhancements not only adds convenience but also elevates the overall driving experience, making each journey more enjoyable.