Understanding Car Door Parts with Detailed Diagrams
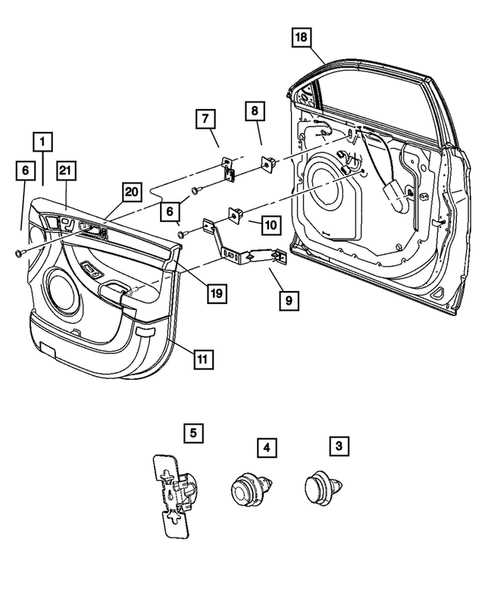
Exploring the various elements that facilitate access to automobiles reveals a fascinating interplay of design and functionality. Each component serves a unique purpose, contributing to the overall security and usability of the vehicle.
By examining these elements closely, one can appreciate the engineering behind their arrangement and operation. The intricate connections and roles of each segment not only enhance performance but also elevate user experience.
For those eager to delve deeper into this subject, identifying each crucial segment allows for a greater understanding of how they collectively achieve the ultimate goal of providing safe and efficient entry to the vehicle.
Understanding Car Door Mechanisms
Delving into the inner workings of entry barriers reveals a complex interplay of components designed for functionality and safety. Each element plays a crucial role in the overall efficiency of the structure, ensuring smooth operation and user comfort.
Key Components

- Handle: Initiates the opening process.
- Latch: Secures the closure, providing safety.
- Locking mechanism: Prevents unauthorized access.
- Hinge: Allows pivoting for seamless movement.
- Window regulator: Facilitates glass elevation and lowering.
Functionality Overview
- The handle is engaged to release the latch.
- The latch disengages, allowing the structure to open.
- The hinge supports the weight during movement.
- The locking mechanism secures the entry when closed.
- The window regulator ensures visibility and ventilation.
Key Components of Door Systems
Understanding the essential elements that make up the opening mechanism of vehicles is crucial for anyone interested in automotive engineering. These components work together to ensure functionality, safety, and convenience for users.
Locking Mechanism: This element is vital for securing the entryway, providing safety and peace of mind. It may include electronic or traditional systems that engage and disengage based on user interaction.
Handle Assembly: The handle serves as the primary interface for users to access the interior. It is designed for ease of use and can come in various forms, including pull, push, or twist designs.
Hinges: These joints enable the opening and closing motion. High-quality hinges allow for smooth operation while ensuring the structure remains stable over time.
Weather Seals: Essential for protection against environmental elements, these seals prevent water and air from entering the interior. They play a critical role in maintaining comfort and cleanliness.
Window Mechanism: This component facilitates the operation of the glass panel, allowing it to be raised or lowered seamlessly. Various technologies, such as manual or power-assisted systems, are used to achieve this function.
Control Systems: Modern vehicles often incorporate advanced control units that manage locking, unlocking, and window operations. These systems enhance user experience through features like keyless entry and automated window adjustments.
Each of these elements contributes to the overall functionality and reliability of the entry system, making them essential for both performance and user satisfaction.
Types of Car Door Designs
This section explores various configurations and structures of vehicle entrances, highlighting their distinctive characteristics and functionalities. Understanding these variations can enhance appreciation for automotive design and innovation.
Common Configurations
- Traditional Hinged: Opens outward from a fixed point, widely used for practicality.
- Sliding: Moves parallel to the vehicle’s body, ideal for tight spaces.
- Suicide: Hinges are positioned at the rear, allowing for unique aesthetics and accessibility.
- Scissor: Lifts vertically, often seen in sports models for dramatic effect.
Innovative Features
- Keyless Entry: Enhances convenience and security.
- Electric Operation: Provides ease of use, especially for larger models.
- Enhanced Insulation: Improves soundproofing and temperature control.
Functionality of Door Locks Explained
The mechanisms that secure entryways play a crucial role in safety and accessibility. Understanding how these devices operate can enhance awareness of their importance in everyday life.
How Lock Mechanisms Work
At their core, these devices utilize a series of components that interact to provide security. Here are the primary functions:
- Engagement: The lock engages with the frame, preventing unauthorized access.
- Key Compatibility: Different designs require specific keys or codes for operation.
- Durability: Materials are chosen to withstand wear and potential tampering.
Types of Lock Mechanisms
Several varieties exist, each serving unique purposes:
- Deadbolts: Offer enhanced security by requiring a key for locking and unlocking.
- Knob Locks: Commonly found on residential entryways, easy to use but less secure.
- Smart Locks: Utilize technology for keyless entry, often controlled via smartphone apps.
Understanding these mechanisms can lead to better choices for security solutions. Exploring different types helps in determining the ultimate fit for specific needs.
Role of Hinges in Door Operation
The functionality of any entryway relies significantly on the elements that allow it to pivot smoothly. These components are essential for facilitating access while ensuring stability and ease of movement. Understanding their mechanics reveals their vital contribution to everyday usage.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Support | Provides a stable axis for movement. |
| Alignment | Ensures proper positioning for seamless operation. |
| Load Distribution | Balances weight to prevent wear and tear. |
| Durability | Constructed to withstand repeated use over time. |
Window Mechanisms in Car Doors
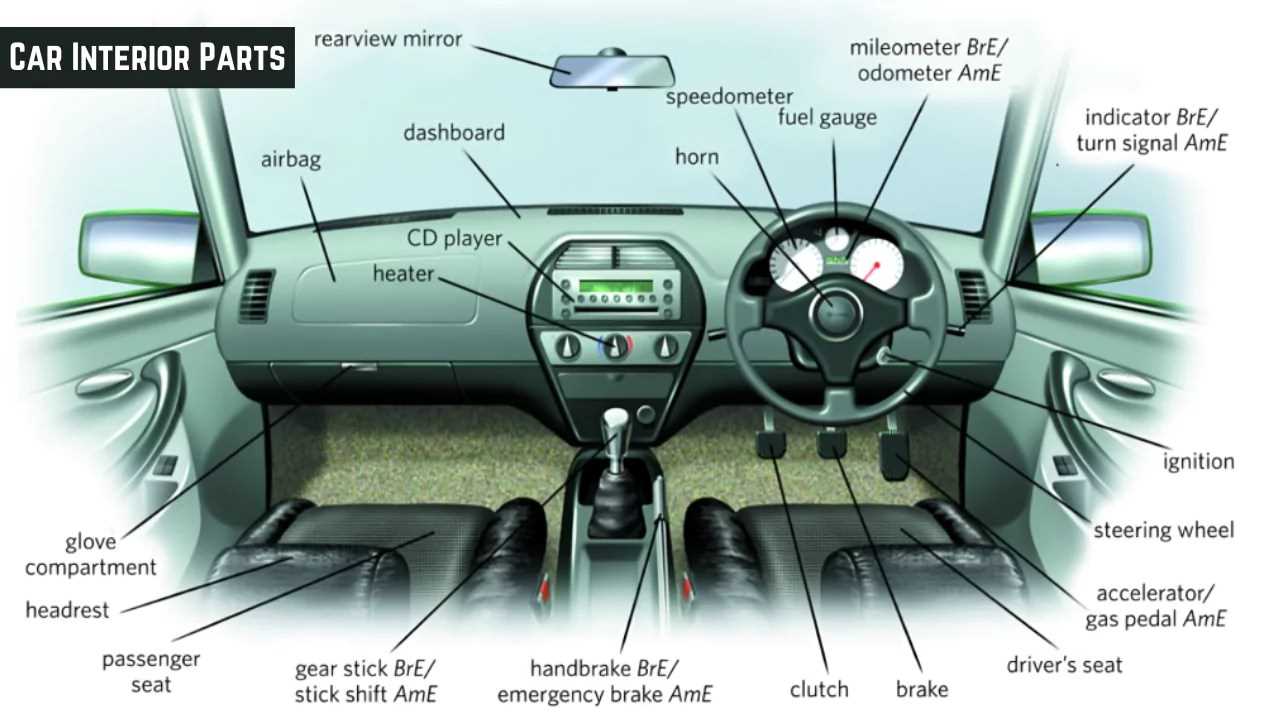
Within the realm of automotive design, the systems that enable the movement of transparent panels play a crucial role in enhancing convenience and comfort. These mechanisms are essential for the seamless operation of openings, allowing occupants to easily access fresh air and light.
Typically, two main types of systems are prevalent: manual and electric. Manual systems rely on mechanical handles and cables, while electric variants utilize motors and switches for effortless control. Each type comes with its own set of advantages, influencing user experience and vehicle functionality.
Components such as regulators, guides, and tracks are integral to these systems, ensuring smooth operation and durability over time. Regular maintenance is vital for longevity, preventing issues like misalignment or failure in movement.
Understanding these mechanisms not only aids in effective troubleshooting but also enhances appreciation for the intricate engineering behind everyday functions in modern vehicles.
Importance of Weatherstripping Materials
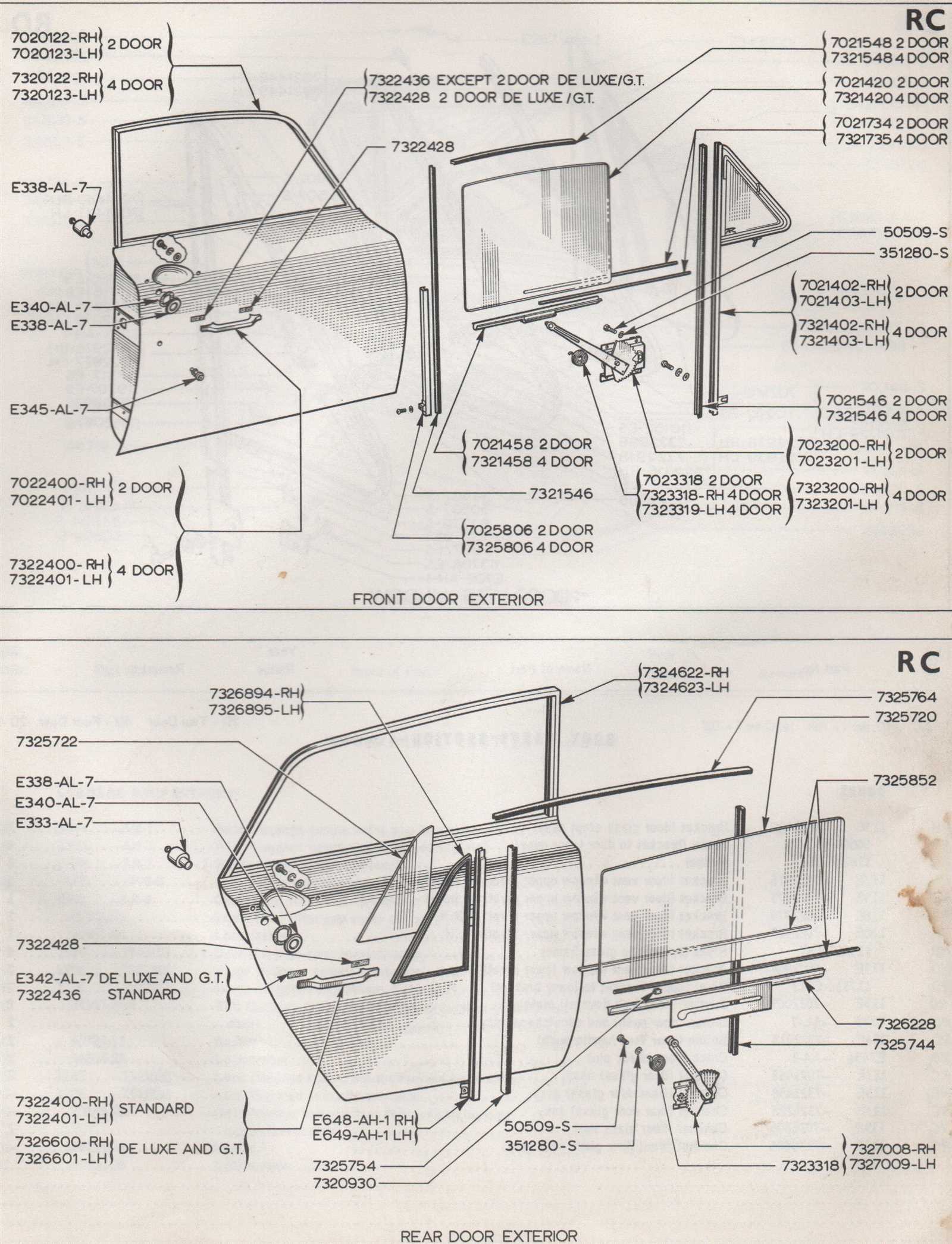
Effective sealing solutions play a crucial role in enhancing the longevity and functionality of vehicles. These materials not only prevent external elements from infiltrating the interior but also contribute significantly to energy efficiency and comfort.
Protection Against the Elements
Weatherstripping serves as a barrier against moisture, dust, and noise, ensuring a more pleasant driving experience. By minimizing the ingress of rain and wind, these materials help maintain the integrity of the vehicle’s interior.
Enhancing Energy Efficiency
Utilizing high-quality weatherstripping can lead to improved thermal insulation. This ultimately reduces the workload on climate control systems, promoting fuel efficiency and saving on energy costs. Investing in superior sealing solutions is essential for optimal performance and sustainability.
How Door Handles Work Internally
The mechanism behind the opening and closing of access points relies on a series of interconnected components. Understanding this system reveals the intricacies that allow for smooth operation and security features.
Key Components
- Lever: The primary element that initiates the action.
- Latch: Engages or disengages to allow entry or exit.
- Linkage: Connects the lever to the latch mechanism.
Operating Mechanism
- When the lever is pressed or turned, it exerts force.
- This force is transmitted through the linkage.
- The latch then moves, allowing the mechanism to either secure or release the entry point.
Common Issues with Door Parts
When it comes to entryway mechanisms, several common challenges can arise, impacting their functionality and reliability. Understanding these frequent problems can aid in timely identification and resolution, ensuring smooth operation and enhanced safety.
Wear and Tear: Over time, components may experience natural degradation due to regular use. This can lead to difficulties in opening or closing smoothly.
Misalignment: External factors such as temperature changes or physical impact can cause misalignment. This issue may result in gaps, which can compromise insulation and security.
Locking Mechanism Failures: The locking system is critical for safety. Issues such as rust, dirt accumulation, or internal malfunctions can prevent proper engagement, posing a security risk.
Electrical Failures: For models equipped with electronic features, electrical malfunctions can occur. Faulty wiring or dead batteries may hinder functionalities such as remote locking or automatic opening.
Noise and Rattling: Unwanted sounds during operation often indicate loose components or insufficient lubrication. Addressing these can enhance the overall experience and prevent further damage.
By being aware of these prevalent concerns, individuals can better maintain their mechanisms, ensuring longevity and optimal performance.
Upgrading Door Hardware for Performance
Enhancing the components that secure and operate the entryways of vehicles can significantly improve overall functionality and efficiency. By investing in high-quality materials and innovative designs, enthusiasts can achieve a smoother experience, greater reliability, and even aesthetic appeal. This section delves into various enhancements that can elevate performance to new heights.
Material Selection
Choosing superior materials is crucial for boosting durability and responsiveness. Components crafted from high-strength alloys or carbon composites can withstand greater stress, ensuring longevity. Upgrading to corrosion-resistant finishes also safeguards against wear and tear, particularly in challenging environments.
Technological Innovations
Incorporating advanced technologies can transform traditional mechanisms into cutting-edge solutions. Options such as electronic locking systems provide enhanced security and convenience, while smart actuators facilitate quicker and more precise operation. Adopting these innovations can greatly enhance user experience and performance.
Visual Guide to Door Assembly
This section provides an informative overview of the various components involved in the assembly of a vehicle entryway. Understanding these elements is essential for effective maintenance, repairs, and upgrades. Each component plays a crucial role in the overall functionality, safety, and aesthetic appeal of the structure.
Key Elements of the Assembly
In any entryway assembly, certain elements are indispensable. Each of these components interacts with one another, ensuring smooth operation and reliability. Below is a summary of the essential components typically found in such an assembly:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Frame | The main structure providing support and shape. |
| Seal | Gasket or rubber lining that prevents water and air from entering. |
| Handle | Mechanism for opening and closing the entryway. |
| Locking Mechanism | System that secures the entryway in a closed position. |
| Window | Transparent panel allowing visibility and light into the interior. |
Importance of Each Component
Each element contributes uniquely to the overall efficiency of the assembly. The frame ensures structural integrity, while seals play a vital role in environmental protection. Handles and locking systems enhance accessibility and security, respectively, and windows add both functionality and aesthetic value. A comprehensive understanding of these components fosters better care and prolongs the lifespan of the assembly.