Understanding the Singer 99 Parts Diagram for Repair and Maintenance
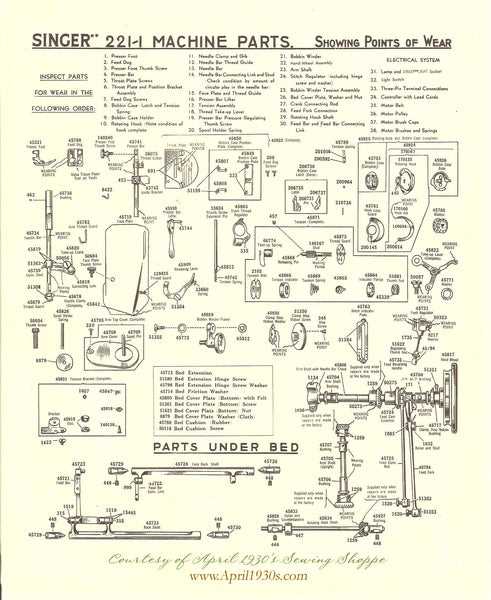
When diving into the world of mechanical devices, it’s essential to become familiar with the internal setup and layout of the equipment. These machines may appear complex at first, but each element plays a critical role in their smooth operation. By grasping how these parts interconnect, one can gain deeper insight into both the functionality and maintenance needs of the machine.
Examining the overall framework allows for a clear understanding of how various mechanisms collaborate to create seamless motion. Every component has a specific task, contributing to the overall precision and efficiency of the device. Knowing the layout and specific roles of each element not only helps in troubleshooting but also enhances the user’s confidence in performing minor repairs or adjustments.
In this guide, we will explore the key segments of this renowned model, breaking down its structure to ensure a comprehensive understanding of how it operates. Whether you’re a seasoned expert or just starting out, gaining this knowledge will support your efforts in keeping the machine in optimal working condition.
Overview of Singer 99 Sewing Machine Components

The sewing machine model offers a wide variety of interconnected mechanisms that work in harmony to provide efficient stitching results. Each element has its own unique role in ensuring the overall performance, making it essential to understand how these various elements function together to achieve seamless operation.
Main Mechanisms
The core components of the device include systems responsible for fabric movement, needle control, and thread tension. These mechanisms are designed to ensure precision and consistency in sewing, enabling smooth and even stitches across different fabric types. Proper coordination of these parts allows the machine to function with high accuracy.
Additional Features
Beyond the fundamental mechanisms, there are additional features that enhance usability and adaptability. These include the adjustment levers, controls for stitch length, and accessories that provide flexibility for various types of projects. Understanding how to properly adjust these features can greatly improve both the ease of use and the quality of the sewing experience.
Main Mechanism and Functionality
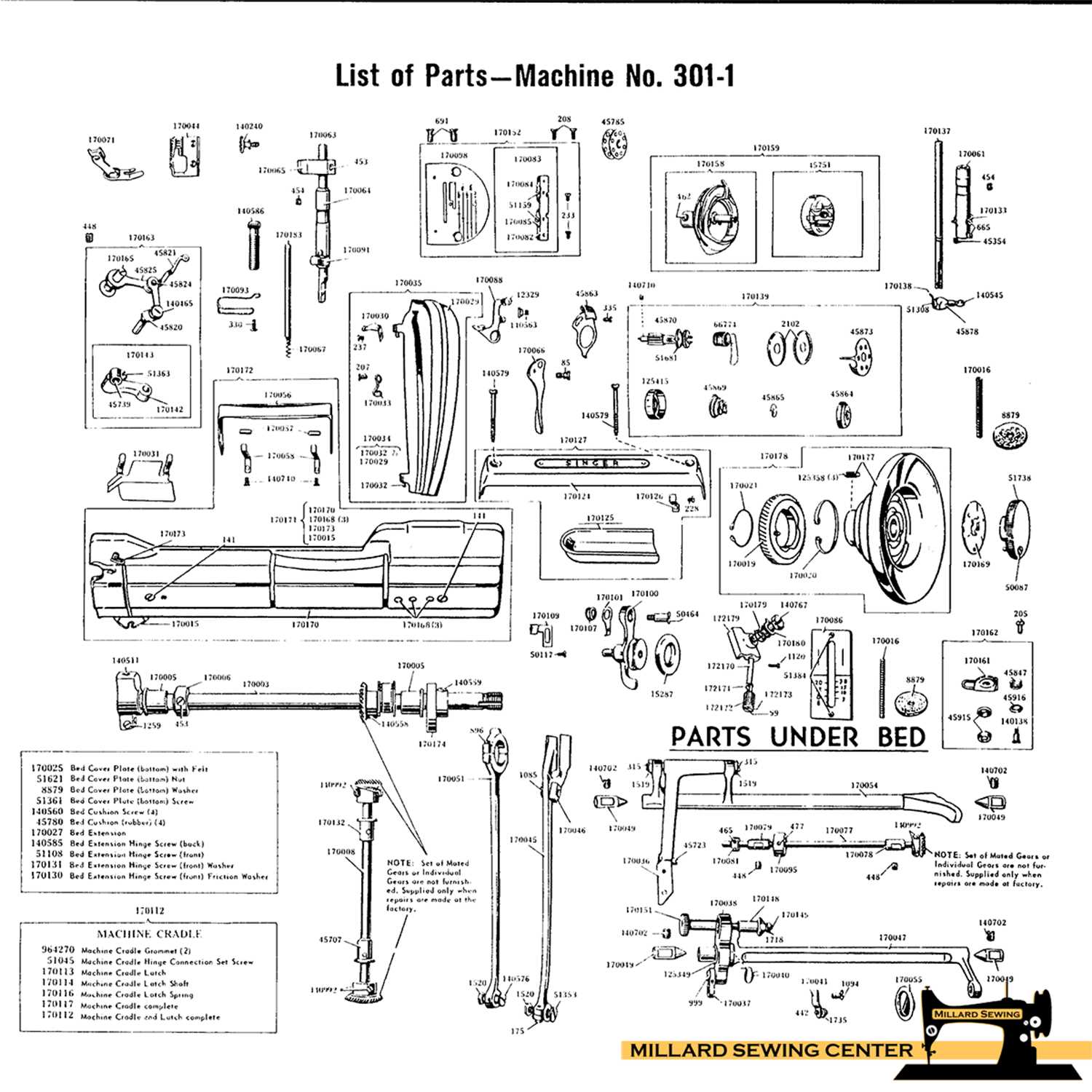
The central system of this classic device operates through a combination of interconnected elements that work in harmony to achieve seamless performance. These components are designed to coordinate various movements, ensuring smooth and reliable operation, which is essential for efficient use.
The driving mechanism is responsible for powering the internal movements, transferring energy to key elements that handle motion. Its precision ensures consistent output, while its simplicity allows for easy adjustments when needed.
Another important aspect of the system involves the control of speed and motion, ensuring that the device operates according to the user’s preferences. This flexibility allows for a variety of tasks to be performed, all while maintaining high accuracy.
Key Elements of the Needle System
The needle system is an essential component that plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth operation. Understanding its structure and functions allows for better performance and precision during use. Each part of this system works in harmony, contributing to the overall efficiency and accuracy.
Below is a table outlining the key elements of the needle mechanism and their roles:
| Element | Description | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Needle Eye | The small opening through which the thread passes. It is designed to guide the thread accurately into the fabric. | ||||||||||||||
| Shank | The upper part that connects the needle to the machine, providing stability during use. | ||||||||||||||
| Groove | A long channel along the needle, helping to protect the thread from excessive tension as it moves through the fabric. | ||||||||||||||
| Point |
| Foot Type | Function | Fabric Suitability |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Foot | General use, provides even pressure | Cotton, lightweight fabrics |
| Zipper Foot | Used for stitching along zippers | All types of fabrics |
| Walking Foot | Feeds fabric from both top and bottom for better control | Multiple layers, quilts |
| Roller Foot | Helps in sewing on sticky or thick fabrics | Leather, vinyl, thick fabrics |
Thread Tension Mechanism Details
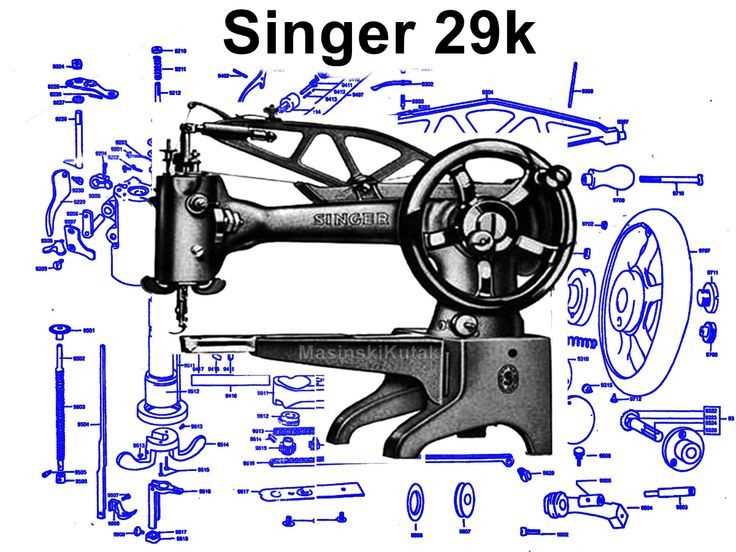
The control of thread tension plays a crucial role in achieving balanced and precise stitching. This system ensures that the upper and lower threads are pulled with equal force, preventing issues like puckering or loose stitches. It is a vital component that regulates the tightness of the thread as it passes through the needle and the fabric.
Adjusting the tension involves modifying the spring-loaded mechanism, which controls the amount of pressure applied to the thread spool. A tighter setting pulls the thread more tightly, while a looser setting allows for more slack. This delicate balance ensures that the threads intertwine smoothly during the sewing process, producing a clean and consistent stitch pattern.
Fine-tuning the tension is essential for different types of fabrics and threads. Each material may require specific adjustments to maintain optimal results, ensuring that the sewing machine operates effectively without causing thread breakage or fabric damage. By understanding the inner workings of this mechanism, users can achieve the best performance tailored to their projects.
Motor Assembly and Power System
The drive unit and electrical mechanism play a crucial role in the overall functionality of the machine. These components are responsible for converting electrical energy into mechanical movement, ensuring that the device operates smoothly and efficiently. In this section, we will explore the structure and operation of the motor and its power system.
Motor Unit Components
- Motor housing: The outer casing that protects the internal elements of the motor.
- Armature: The rotating part of the motor that works in conjunction with the field magnets.
- Commutator: A key element that helps maintain the electrical connection during rotation.
- Brushes: Conductive elements that maintain contact with the commutator, transferring current to the armature.
Power Transmission
The motor’s power is transmitted through a series of gears and belts, which help to regulate the speed and torque. These components ensure that the machine operates at the desired efficiency and power output.
- Drive belt: Connects the motor to the driven parts of the system.
- Gears: Adjust the speed and force applied to the machine’s mechanical parts.
Maintenance Tips for Machine Longevity
Proper upkeep is essential for ensuring that your equipment remains functional and efficient over time. Regular maintenance prevents wear and tear, extending the lifespan of key components and enhancing overall performance. Here are some useful tips to keep your device running smoothly for years to come.
- Cleanliness: Keep the machine free from dust and debris. Regularly clean the internal and external parts to avoid the build-up of materials that may cause friction or block moving parts.
- Lubrication: Apply the appropriate lubricants to moving parts. This reduces friction, prevents rust, and ensures smooth operation.
- Inspect for Damage: Frequently check for any signs of wear, cracks, or other damages in key components. Early detection helps prevent more serious issues from arising.
- Check Thread Tension: Adjust thread tension according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. Proper tension ensures smooth stitching and prevents unnecessary strain on the machine.
- Regular Servicing: Schedule routine professional servicing to ensure your equipment is in optimal condition. A technician can address areas you might miss during regular use.
Following these simple yet effective practices will help maintain your machine in top condition, preventing unnecessary breakdowns and ensuring it performs well for an extended period.
Understanding the Stitch Length Control
The mechanism responsible for adjusting the length of stitches plays a crucial role in determining the overall appearance and functionality of a sewn piece. By altering this setting, the user can influence the distance between each stitch, ensuring that the stitch pattern fits the specific requirements of a project. This component allows for both fine and coarse adjustments, depending on the nature of the fabric and the type of stitch being used.
How It Works
The stitch length control operates by regulating the movement of the needle and feed dogs, which work together to determine how much fabric is advanced with each stitch. A longer stitch is ideal for basting or decorative seams, while a shorter stitch is preferred for heavier fabrics or seams that need extra durability. Adjusting this control ensures precision in both simple and complex sewing tasks.
Impact on Sewing Projects

The ability to change stitch length is essential for tailoring the machine’s performance to different tasks. Whether you’re working with delicate fabrics or thicker materials, having control over the stitch length enhances the quality and strength of the final product. This feature contributes significantly to achieving professional-looking results in both hand-sewing and machine-based applications.
Identifying Parts for Easy Replacement

When it comes to maintaining and repairing machinery, understanding its components and knowing where to find them is essential for smooth operation. Being able to quickly identify the key elements helps ensure that you can replace faulty parts with minimal effort. The first step in this process involves recognizing the components that are most prone to wear and tear.
Key Components to Watch
Paying attention to the critical components that are frequently exposed to strain can save you time and effort. These elements often require replacement after extended use, and identifying them early on allows for quicker fixes. Take note of parts that may wear out over time and require periodic attention.
Replacement Process
Once the necessary components have been identified, finding the correct replacements is the next crucial step. Ensure that replacements match the specifications of the original elements to avoid compatibility issues. It’s advisable to keep a few spare items on hand to reduce downtime when repairs are needed.

