Understanding Components for Honda Foreman 450

Understanding the intricate layouts of various components in utility vehicles can be crucial for effective maintenance and upgrades. This guide delves into the detailed structures of mechanical elements, ensuring enthusiasts and professionals alike have a clear reference when tackling issues or making improvements.
The focus is on identifying connections, configurations, and the overall setup of the essential mechanisms that keep these vehicles running smoothly. By gaining insight into these technical aspects, you’ll be better equipped to handle troubleshooting and repairs with precision and confidence.
Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a newcomer, grasping the layout of these elements will aid in optimizing performance and extending the lifespan of your off-road machine. Detailed schematics act as a map, guiding you through each step of the process, from diagnostics to implementation.
Exploring the Key Components Overview

Understanding the fundamental elements of this model is essential for maintenance and enhancement. Each component serves a crucial role in ensuring optimal functionality, providing reliability and performance on varied terrains. This section outlines the most critical aspects, focusing on their placement, purpose, and interactions within the larger framework.
Primary Structure Elements
The core framework of the vehicle provides support to all other components. This includes the chassis, control mechanisms, and other integral parts that ensure stability and control during operation. Knowing the layout and function of these elements can aid in troubleshooting and upgrading efforts.
Engine and Power Transmission Components
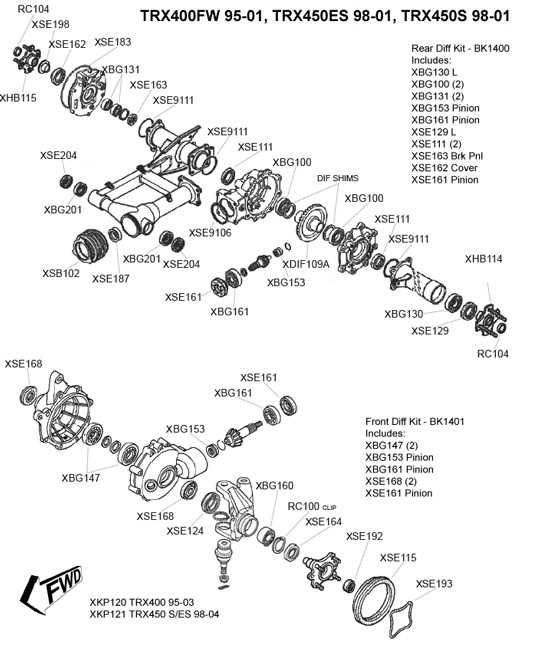
The engine and transmission systems are vital for delivering consistent power and managing speed. This section details the various components responsible for energy conversion and transfer, highlighting their role in providing efficiency and adaptability to different conditions.
| Component | Function | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Drive System | Transfers power from the engine to the wheels | Connected to the engine’s output shaft |
| Control Assembly | Manages the steering and handling | Located at the front, linked to the handlebars |
| Suspension Units | Absorbs shocks and maintains stability | Mounted above the wheels |
Engine Assembly Details and Layout
The organization and configuration of the engine’s core elements play a vital role in its overall functionality and performance. Understanding the structure helps in identifying specific components, ensuring proper maintenance, and making precise adjustments when needed.
- Cylinder Configuration: The layout of the cylinders is designed for optimal efficiency, influencing the power output and smooth operation of the machine.
- Crankshaft Alignment: This component’s position is crucial for transferring motion from the engine to the other mechanical systems, directly impacting movement and force distribution.
- Cooling System Integration: Efficient cooling pathways are integrated into the assembly to prevent overheating, allowing the engine to perform consistently under various conditions.
- Ignition Components Arrangement: The placement of ignition elements within the assembly ensures reliable startup and steady power delivery during operation.
- Lubrication Flow: Proper alignment of the lubrication channels is essential for reducing friction between moving parts, thereby enhancing longevity and reducing wear.
This structured layout not only boosts engine efficiency but also simplifies the process of diagnosing issues, making repairs, and implementing upgrades. Understanding these details supports optimal performance and extends the lifespan of the machine’s core systems.
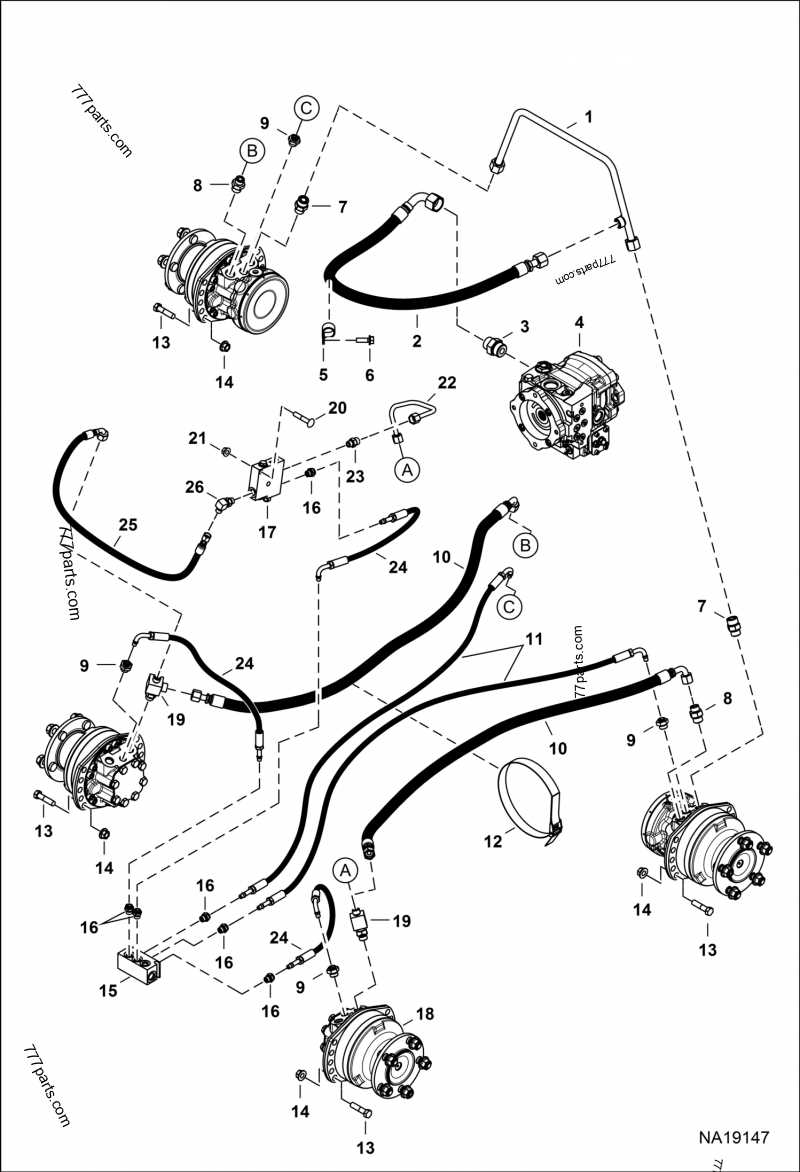
Transmission System Structure Analysis
The transmission system is a crucial component in ensuring efficient power delivery and control. This section focuses on the detailed breakdown of its inner workings, highlighting the mechanisms that enable smooth transitions between various speed levels and torque outputs.
Key Components and Their Roles: Each element within the transmission assembly plays a specific role in facilitating the motion and speed regulation. Understanding how these components interconnect is essential for maintaining optimal performance and durability.
Synchronization and Gear Shifts: Synchronizers and gear sets are pivotal in managing transitions between gears. These parts are meticulously engineered to reduce friction and wear, enabling precise shifts while minimizing mechanical strain.
The integration of multiple gears and shafts allows for variable power distribution, adapting to different driving conditions. The design intricacies of these elements ensure that the system operates seamlessly, balancing efficiency with reliability.
Electrical Wiring and Connections Guide
This section provides a detailed overview of the wiring and connections involved in setting up and maintaining an electrical system. The aim is to ensure a clear understanding of how each component interacts within the setup, enhancing both efficiency and safety.
Main Circuit Connections
The primary circuits play a crucial role in distributing power throughout the system. Proper alignment and secure attachment of these connections are essential to avoid electrical issues and ensure optimal performance.
- Power Distribution: Focus on the correct placement of wires to manage the flow of electricity evenly across the system.
- Grounding: Proper grounding is vital to prevent electrical faults and reduce risks of short circuits.
- Insulation: Use appropriate insulating materials to protect the wiring from environmental damage and wear.
Secondary Wiring Layout
Secondary connections support additional functionalities within the electrical setup. These connections must be organized efficiently to facilitate smooth operation and easy troubleshooting.
- Auxiliary Connections: Ensure that secondary wires are routed neatly to avoid tangling and interference with other components.
- Connection Labels: Clearly label each wire to simplify future maintenance and identify specific lines quickly.
- Connection Points: Regularly inspect these areas for signs of corrosion or loose fittings to maintain
Brake Mechanism and Hardware Description
The braking system is a crucial component designed to ensure the safe and efficient operation of the vehicle. Understanding the layout of its mechanical elements can help identify potential issues and maintain optimal performance. This section provides a detailed look into the components that make up the entire stopping mechanism, highlighting their roles and interactions.
Brake Pads and Shoes: The friction materials in the setup, commonly known as brake pads and shoes, are essential for converting kinetic energy into heat. They create the necessary resistance when engaged, slowing down or stopping the movement. Proper inspection of these elements is vital to avoid wear-related malfunctions.
Rotors and Drums: These elements work in unison with the friction materials to provide a surface for the pressure to be applied. The condition of the rotors or drums directly influences the efficiency of the entire system. Even minor imperfections on their surfaces can lead to reduced braking performance.
Additional Hardware: Supporting parts such as springs, clips, and adjusters play a significant role in the stability and function of the system. These small yet critical pieces ensure that all components remain correctly aligned and operate smoothly under various conditions. Regular checks of these elements can prevent unexpected failures and extend the longevity of the system.
Suspension Components and Their Placement
The suspension system of an all-terrain vehicle plays a crucial role in providing stability and comfort during rides. Understanding the various elements that make up this system and their correct positioning is essential for optimal performance and handling. Each component contributes to the overall dynamics of the vehicle, ensuring a smooth ride over uneven terrains.
Main Components
Key components of the suspension system include shock absorbers, springs, and wishbones. Shock absorbers are designed to dampen the impact of bumps and jolts, while springs support the weight of the vehicle and allow for controlled movement. The placement of these elements is critical; shock absorbers are typically mounted vertically, whereas springs are located near the wheel assembly to maintain the proper ride height.
Proper alignment of the suspension components is vital for maintaining steering accuracy and tire wear. Adjustments may be necessary to ensure that the geometry of the suspension is correct, allowing for optimal handling characteristics. Regular maintenance and inspection of these components can prevent premature wear and improve the overall longevity of the system.
Fuel System Components Breakdown
The fuel system is a critical part of any vehicle, responsible for delivering the proper amount of fuel to the engine for optimal performance. Understanding the various elements within this system is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. Each component plays a specific role, ensuring that fuel is efficiently transported, filtered, and injected into the engine.
Key Components

- Fuel Tank: Stores the fuel before it is sent to the engine.
- Fuel Pump: Transfers fuel from the tank to the engine, ensuring adequate pressure.
- Fuel Filter: Cleans the fuel of impurities before it reaches the engine.
- Fuel Injectors: Atomizes the fuel, allowing for proper combustion within the engine.
- Fuel Lines: Tubes that transport fuel between the tank, pump, filter, and injectors.
Maintenance Tips
- Regularly check and replace the fuel filter to maintain clean fuel flow.
- Inspect fuel lines for any signs of wear or leaks.
- Ensure the fuel pump is functioning correctly to avoid starting issues.
- Keep the fuel tank filled to prevent sediment from clogging the system.
By paying attention to these elements and their maintenance, vehicle owners can enhance the longevity and efficiency of the fuel system, ultimately leading to better overall performance.
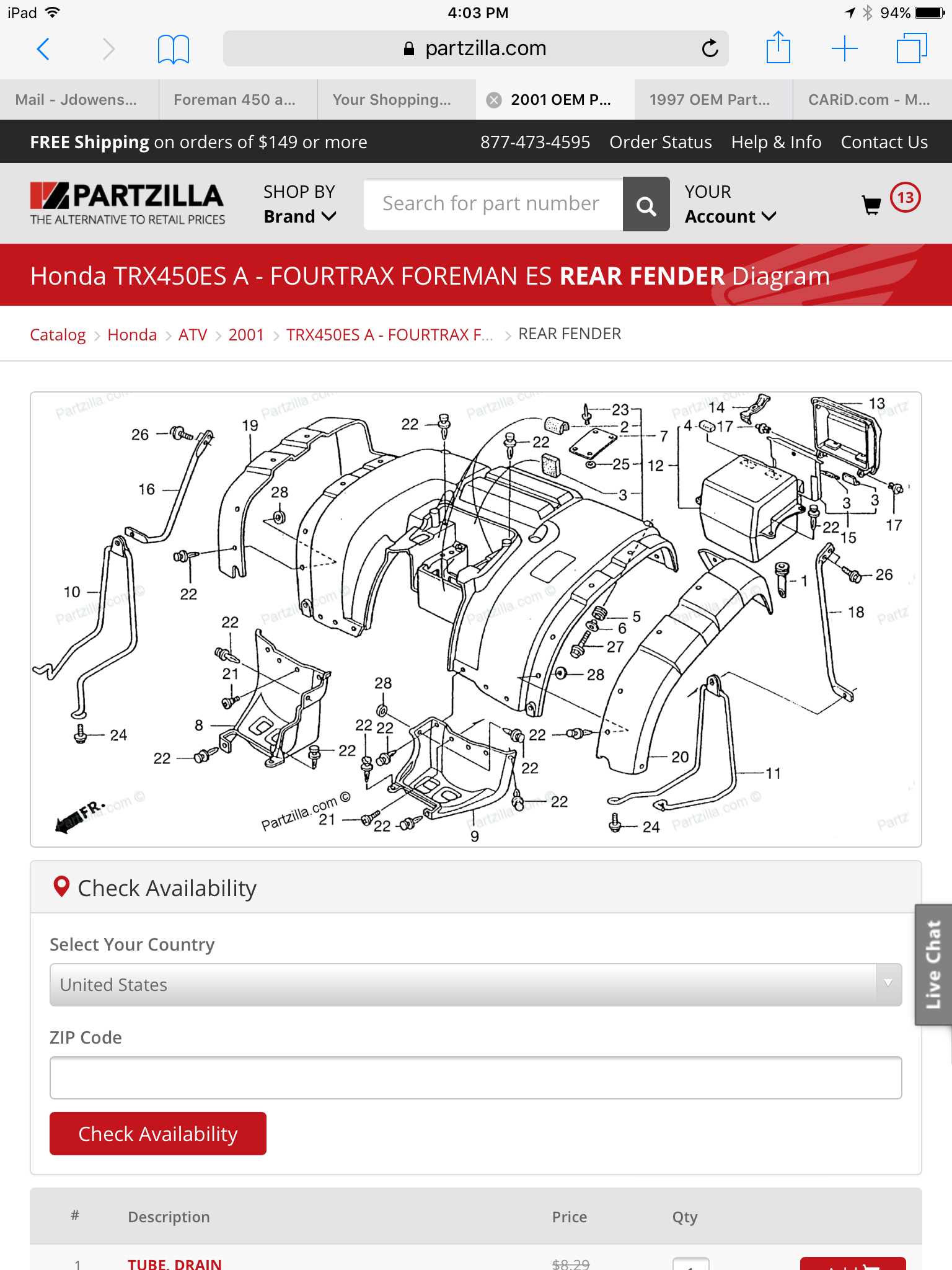
Body Frame and Structural Elements
The framework of an all-terrain vehicle is a crucial component that provides stability, support, and durability. This section explores the various structural elements that contribute to the overall integrity and performance of the vehicle. Understanding these components is essential for maintaining and optimizing functionality during operation.
Key Components of the Frame

The primary structure consists of several interconnected parts designed to withstand stress and provide a solid foundation. Each element serves a specific purpose, ensuring the vehicle can handle rough terrains and heavy loads.
Component Description Main Frame The central structure that supports all other parts, providing rigidity and strength. Subframe A secondary structure that supports additional components, such as the engine and suspension. Cross Members Reinforcements that connect the main frame and subframe, enhancing structural stability. Mounting Points Designated locations for securing various assemblies, ensuring proper alignment and function. Importance of Structural Integrity
Maintaining the strength of these structural elements is vital for safety and performance. Regular inspections and appropriate repairs are necessary to prevent deterioration and ensure reliable operation in challenging environments.
Handlebar Controls and Related Elements

The controls situated on the handlebars play a vital role in the operation and maneuverability of an all-terrain vehicle. These components are designed to ensure that the rider can easily access essential functions, enhancing both safety and convenience during rides.
Primary Functions of Handlebar Controls
Typically, the primary controls include throttle, brakes, and various switches that manage lighting and additional accessories. Each of these elements is strategically placed to allow the rider to maintain control without needing to shift their grip significantly. This ergonomic design facilitates quick adjustments while navigating challenging terrains.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tips
Regular inspection of handlebar controls is essential to ensure optimal performance. Check for any signs of wear or damage, particularly in the cables and connectors. If any control feels unresponsive or sticky, it’s advisable to clean and lubricate the moving parts. Addressing these issues promptly can prevent more serious malfunctions and enhance the overall riding experience.
Tire and Wheel Assembly Information
This section provides essential insights into the components that constitute the wheel and tire setup of all-terrain vehicles. Understanding these elements is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, safety, and longevity of the vehicle.
Components Overview
The assembly includes various parts such as the rim, tire, valve stem, and lug nuts. Each component plays a significant role in maintaining the stability and traction of the vehicle. Regular inspection of these elements is recommended to prevent potential failures during operation.
Maintenance Tips
Proper care for the tire and wheel assembly is vital. Inflation levels should be checked regularly, as improper pressure can lead to uneven wear and reduced performance. Additionally, it is important to inspect for damage or signs of wear on the tires and rims to ensure a safe driving experience.