Ps2 Controller Parts Layout Guide
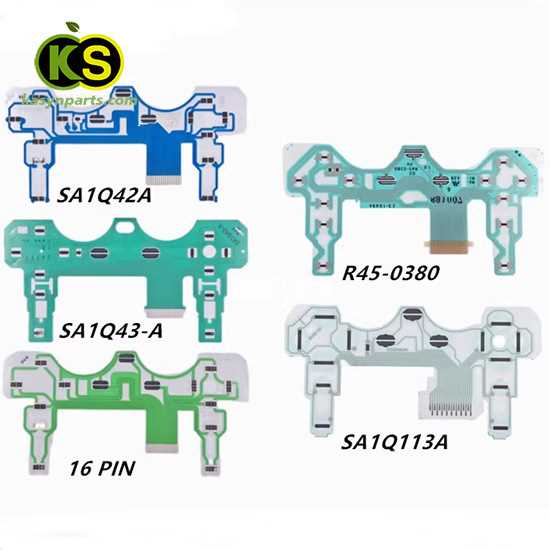

Every gaming enthusiast knows how essential it is to have a device that responds accurately and swiftly to commands. The design of these handheld devices has been refined over the years, blending comfort with precision. Exploring the internal layout of such devices allows us to appreciate the complexity and ingenuity behind each component that contributes to an immersive gaming experience.
From tactile buttons to joysticks that offer smooth movement, every feature serves a unique purpose. The careful arrangement of these elements ensures that players can engage in their favorite activities seamlessly. Delving into the internal structure offers valuable insights into how each section contributes to overall functionality and user satisfaction.
For those who are curious about the specific elements involved, understanding how the individual components are connected can provide a deeper appreciation of the craftsmanship involved. This detailed examination highlights the intricate design and innovative engineering behind a widely recognized accessory used by gamers around the world.
PS2 Controller Parts Overview
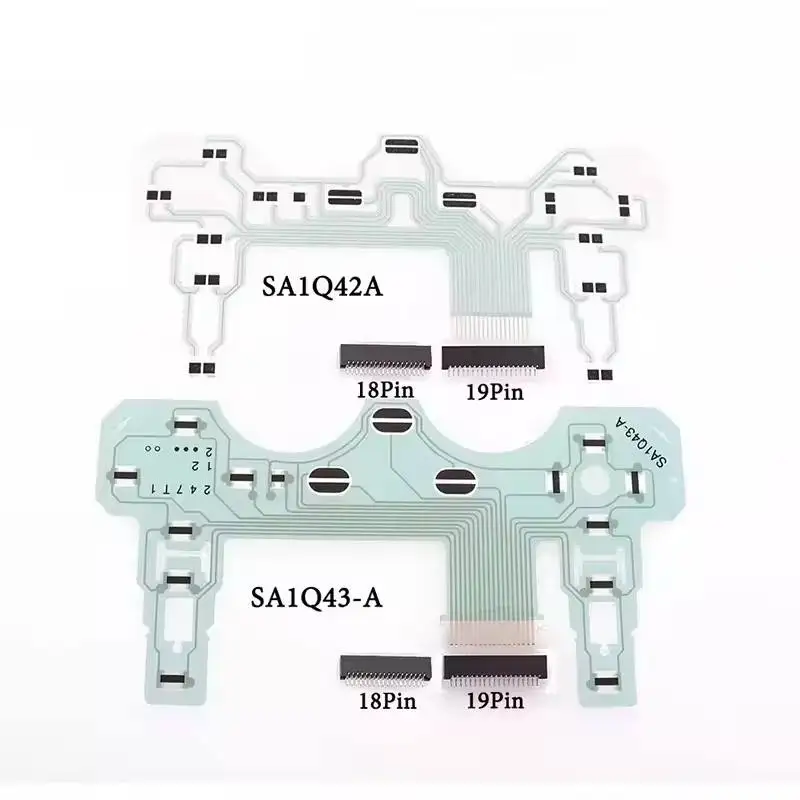

Understanding the structure of this gaming accessory involves recognizing the essential components that make it work seamlessly. Each part plays a vital role in delivering responsive and accurate commands, creating an immersive gaming experience. The buttons, triggers, and internal mechanisms all interact to provide smooth control and feedback.
Button Layout is one of the primary elements, offering directional input and action commands. These tactile features ensure precise gameplay and allow users to execute moves easily. Each input is connected to internal mechanisms that convert physical action into in-game performance.
The grip and handling features are also crucial. They ensure the device remains comfortable to hold for extended periods. Materials used in the design help maintain durability and comfort, preventing strain during long gaming sessions.
Lastly, the internal electronics and connectivity systems ensure that signals are transmitted without delay. This seamless interaction between the player and the system enables a fluid and enjoyable experience.
Internal Structure of a PS2 Controller
The inner workings of this gamepad consist of various interconnected components that enable precise input recognition. These elements work together to translate user actions into digital signals, ensuring responsive and accurate gameplay. Understanding the internal layout reveals the intricate design that allows for smooth operation during gaming sessions.
Main Components and Functions
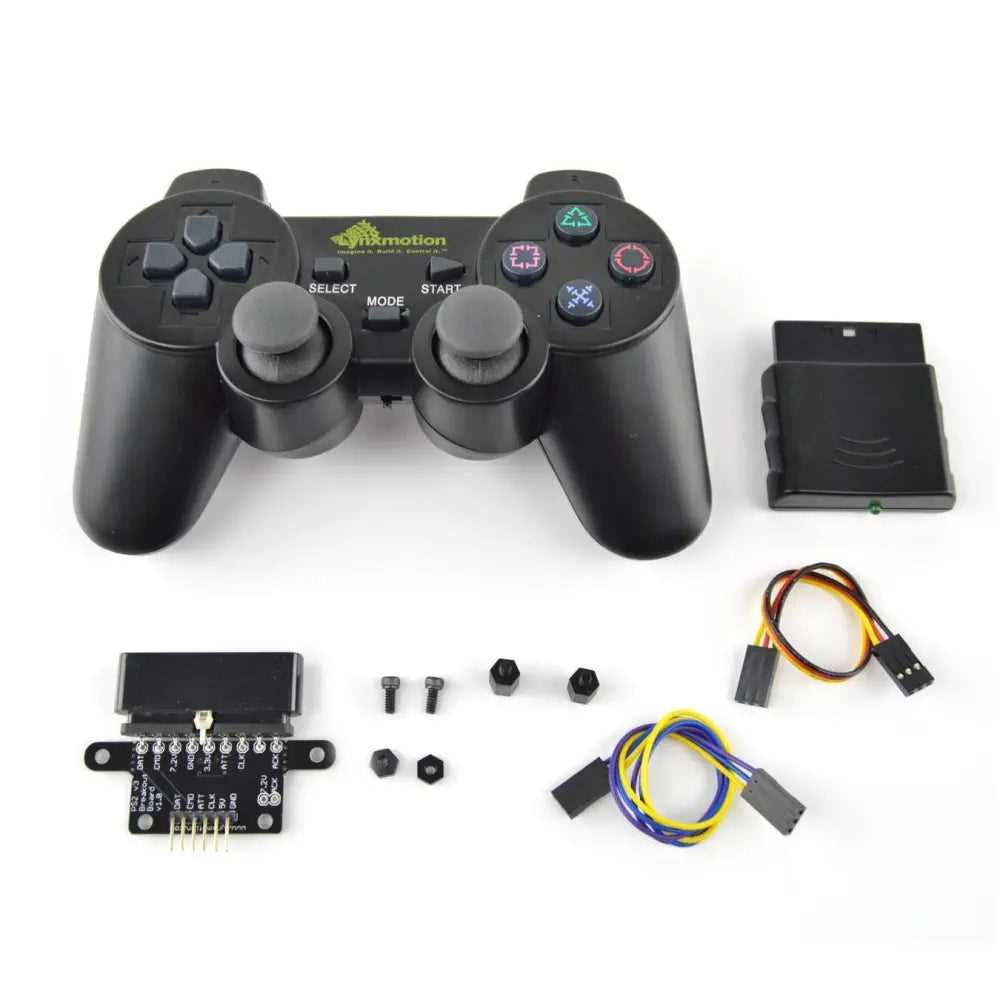

Inside, a circuit board acts as the central hub, linking various elements such as buttons, joysticks, and a directional pad. Each button press or movement triggers an electrical response, which is processed and transmitted to the console. The ergonomically designed layout ensures efficient communication between user inputs and the system.
Additional Mechanical Elements
Alongside the electronics, mechanical parts like springs and rubber membranes provide tactile feedback, enhancing the overall gaming experience. These elements ensure that each action feels responsive and intuitive, contributing to the smooth interaction that gamers expect from this device.
Key Components of Button Mechanism

The button mechanism plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth and responsive input during use. It involves various interconnected elements that work together to translate physical pressure into electronic signals. Understanding these elements helps in grasping how each press delivers a specific action efficiently and accurately.
Contact pads are essential, as they establish the connection between the button and the underlying circuit, triggering the desired function. Elastic materials are often incorporated to provide a tactile response, ensuring the button returns to its original position after being pressed.
Another significant element is the spring system, which helps manage the resistance felt when pressing. This ensures durability and long-term usability. Together, these parts contribute to the reliable operation of the device’s interface, making it both responsive and durable.
Analog Stick Design and Functionality

The analog stick is a crucial input mechanism that allows for precise movement and control in various directions. It operates by detecting subtle shifts in its position, translating them into smooth and responsive actions. This design ensures that users can easily maneuver within virtual environments, offering a high degree of accuracy compared to other directional inputs.
Functionality is achieved through a combination of mechanical and electronic components, which work together to register even the smallest movements. By providing feedback based on the pressure and direction applied, the stick enhances the interactive experience, making it ideal for dynamic and fluid motion control. Its ergonomic design also ensures comfort during extended use, further improving the overall efficiency of the device.
How the D-Pad Operates Internally
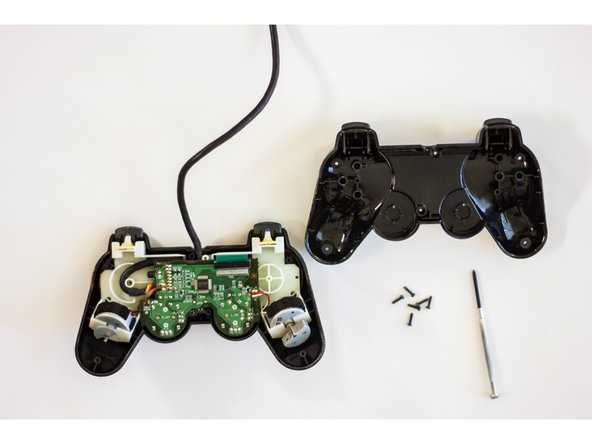

The directional pad, commonly known as the D-Pad, relies on a straightforward yet effective mechanism to register user input. This system allows for precise control, responding instantly to the player’s movements. The internal structure ensures a balance between durability and sensitivity, making it ideal for extended use in various gaming scenarios.
Internally, the D-Pad functions through the interaction of several key components:
- Contact Pads: When a directional button is pressed, these pads make contact with the circuit, sending an electrical signal.
- Conductive Material: Beneath each button lies a conductive layer that helps complete the circuit, ensuring accurate registration of the movement.
- Rubber Dome: A soft dome beneath the D-Pad provides tactile feedback while maintaining flexibility for repeated presses.
- Support Structure: A sturdy frame holds the entire mechanism in place, ensuring the D-Pad stays aligned during usage.
Each of these elements works in unison, allowing the D-Pad to function smoothly and accurately during gameplay.
Exploring the Circuit Board Layout
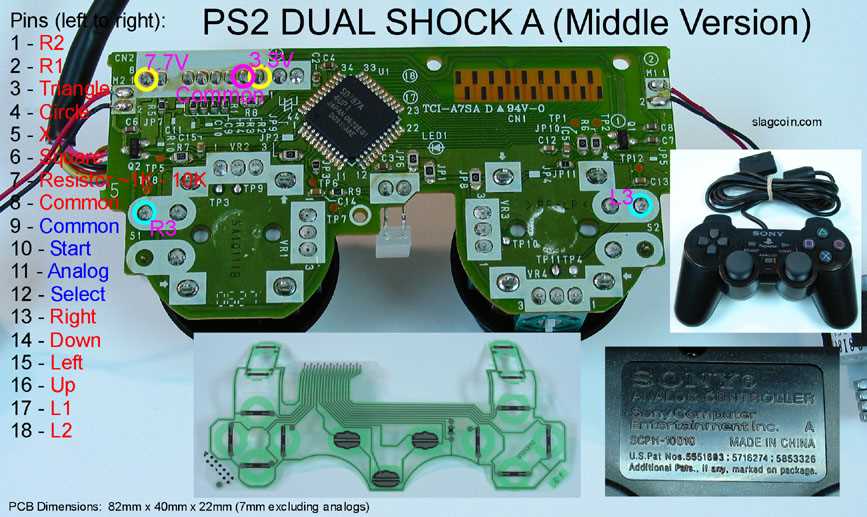
The internal arrangement of electronic components is crucial for the functionality of any device. Understanding this configuration can enhance troubleshooting and repair processes. This section delves into the intricate layout of the main circuitry, highlighting key elements that contribute to performance and usability.
At the heart of this layout, you will find various sections dedicated to specific functions. Each component plays a vital role, working in concert to ensure seamless operation. Below is a table summarizing the primary sections of the circuit board:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Microcontroller | The central unit that processes input and manages commands. |
| Input Connectors | Ports that facilitate communication with external devices. |
| Power Supply Circuit | Distributes power to various components. |
| Signal Processing Unit | Handles data transmission and reception. |
| Feedback System | Provides tactile responses to user interactions. |
Recognizing the layout and functionality of these elements can greatly assist in any maintenance or upgrades. A thorough understanding of the circuit design ensures effective modifications and repairs, ultimately prolonging the lifespan of the device.
PS2 Controller Wiring and Connections
Understanding the internal structure and linking methods of gaming devices is essential for troubleshooting and repairs. This section explores the essential wiring and connection techniques that make these gadgets function seamlessly.
The wiring system consists of several key components that interact with each other. Here are the main elements involved:
- Wires: Conductive paths that transfer signals between different parts.
- Connectors: Interfaces that allow for secure and reliable connections.
- PCB (Printed Circuit Board): The foundation where all components are mounted.
- Microcontroller: The brain that processes input and sends signals to the system.
Each of these components plays a critical role in ensuring the device operates correctly. Properly organized wiring can prevent malfunctions and enhance overall performance. Here’s a brief overview of how the connections typically work:
- The microcontroller receives input from the buttons.
- Signals are transmitted through the wires to the PCB.
- Connectors link the PCB to the main system.
- The system processes the input and responds accordingly.
Understanding these connections can significantly aid in diagnosing issues and performing effective repairs, ensuring the longevity of your gaming experience.
Trigger Button and Shoulder Parts Explained
The mechanism of the trigger and shoulder components plays a vital role in the overall functionality and user experience of gaming devices. These elements are designed to provide precise control and responsiveness during gameplay, enhancing the interaction between the user and the device.
Trigger Buttons are typically located on the rear section, allowing players to perform actions with ease. Their design often includes a spring mechanism that enables quick feedback, which is essential for fast-paced gaming. The sensitivity of these buttons can significantly impact performance, making it crucial for users to be familiar with their responsiveness.
Shoulder Components, located on the upper side, are essential for additional controls. They facilitate actions that may require more than just thumb engagement, such as aiming or special moves. The integration of these parts ensures a seamless transition between various actions, providing an ergonomic advantage during extended gaming sessions.
PS2 Controller Vibration Motor Breakdown
The vibration mechanism within gaming devices plays a crucial role in enhancing the overall experience by providing tactile feedback during gameplay. This component adds an extra layer of immersion, allowing users to feel the action as it unfolds. Understanding the structure and functionality of this motor is essential for anyone interested in the mechanics behind these devices.
Components of the Vibration Motor

The vibration motor consists of several key elements that work together to create the desired feedback. These parts include:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Motor | The primary element that generates movement. |
| Weights | Attached to the motor to create vibrations when spun. |
| Housing | Enclosure that protects the internal components. |
| Wiring | Connects the motor to the device’s circuitry. |
Functionality and Operation
The operation of the vibration mechanism is straightforward yet effective. When activated, the motor spins the attached weights, creating an off-balance motion that results in vibrations. This action is controlled by the device’s software, allowing for different levels of intensity and frequency, which can enhance the player’s experience based on the gameplay scenario.
The Role of the Ribbon Cable
The ribbon cable serves a crucial function in the functionality of various electronic devices, acting as a vital link between different components. Its design enables efficient data transmission and power supply, making it an indispensable element in ensuring seamless operation. Understanding its significance can help in troubleshooting and maintenance processes.
Structure and Functionality
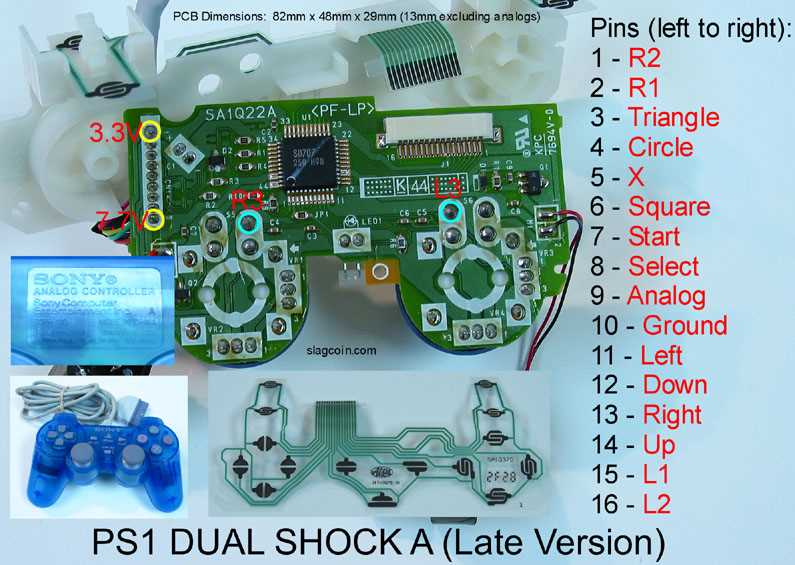
This flexible connector consists of multiple conductors arranged in a flat configuration, allowing for compact and organized connections. Its structure facilitates ease of installation and replacement, minimizing the risk of damage to adjacent components during servicing. The versatility of this cable type makes it suitable for a wide range of applications, from gaming systems to computing devices.
Common Issues and Solutions
Like any electronic part, ribbon cables can encounter problems such as wear and tear, which may lead to connection failures. Regular inspections can help identify issues before they escalate. If a cable becomes frayed or damaged, replacing it promptly can restore proper functionality and prevent further complications.
| Issue | Symptoms | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Fraying | Intermittent connection | Replace the ribbon cable |
| Loose connections | Device not responding | Reconnect securely |
| Worn connectors | Poor signal quality | Inspect and replace if necessary |
Connector Port Details and Specifications

This section outlines the essential features and requirements of the interface used for connecting various devices. Understanding these specifications is crucial for ensuring compatibility and optimal functionality between components.
The connector port serves as the critical interface, facilitating communication and power transfer between the device and external systems. Below are the key specifications relevant to this connection:
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Multi-pin connector |
| Pin Configuration | Typically includes 9 pins for various functions |
| Data Transfer Rate | Up to 12 Mbps |
| Voltage | 5V DC |
| Material | Durable plastic housing with metal contacts |
It is essential to adhere to these specifications to maintain performance and reliability when interfacing devices. Proper understanding aids in troubleshooting and enhances the overall user experience.