Understanding the Parts Diagram of Powerwinch 912

In the realm of mechanical assistance, effective equipment relies on a well-structured array of components that work harmoniously to achieve reliable functionality. Each element within such a system plays a vital role in ensuring smooth operation and user satisfaction. A thorough understanding of these elements is essential for proper maintenance and effective troubleshooting.
By examining the intricate layout of a winching assembly, one can gain insights into how each component interacts and contributes to the overall performance. Familiarity with this configuration not only aids in optimizing functionality but also helps users make informed decisions when it comes to repairs or enhancements.
Whether you are a seasoned professional or a novice enthusiast, recognizing the significance of each part can enhance your knowledge and confidence in working with these systems. Understanding the intricacies of your equipment leads to improved safety, efficiency, and longevity in your operations.
Overview of Powerwinch 912 Components
This section provides a comprehensive understanding of the various elements that constitute the winching system, highlighting their functionality and importance. Each component plays a critical role in ensuring efficient operation, reliability, and overall performance.
The assembly includes a robust motor, which serves as the driving force, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy. Coupled with the motor is a durable gear mechanism that enhances torque and allows for smooth operation under load. Additionally, the unit features a sturdy frame designed to withstand harsh conditions, ensuring longevity and resilience.
Another vital element is the control system, which provides user-friendly operation and enhances safety by allowing precise control over the winching process. Moreover, various accessories such as cables, hooks, and pulleys are integral to the system, facilitating effective attachment and load management. Understanding these components is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting, ensuring optimal performance in various applications.
Understanding Winch Functionality
Winches are essential devices designed to facilitate the movement and lifting of heavy loads. Their operation relies on a combination of mechanical and electrical components that work together to provide the necessary torque and pulling force. A clear understanding of these mechanisms is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring safety during use.
Core Components of a Winch
- Drum: The central cylinder where the cable or rope is wound.
- Motor: The power source that drives the winch, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy.
- Gearbox: A set of gears that adjusts the motor’s output to provide higher torque.
- Cable or Rope: The flexible component that connects the load to the winch.
- Control System: The interface that allows the operator to manage the winch’s functions.
How Winches Operate
- The operator activates the control system to engage the motor.
- The motor drives the gearbox, increasing the torque output.
- The drum rotates, winding or unwinding the cable as needed.
- The load is lifted or moved, depending on the application.
Understanding these functionalities enhances the user’s ability to effectively operate and maintain winches, ensuring they perform efficiently and safely in various applications.
Detailed Parts Breakdown
This section delves into the intricate components of the winch system, providing a comprehensive examination of each element’s role and functionality. Understanding these individual components is crucial for both maintenance and efficient operation, ensuring the equipment performs optimally in various scenarios.
Key Components Overview
The winch consists of several essential elements, including the motor, gear assembly, and spool. Each part plays a vital role in the overall mechanism. The motor serves as the driving force, converting electrical energy into mechanical motion. Meanwhile, the gear assembly facilitates torque multiplication, enabling the winch to handle heavy loads effortlessly.
Additional Features
Further examination reveals auxiliary features such as the control switch and the braking system. The control switch allows for user-friendly operation, enabling precise movements. In contrast, the braking system ensures safety by preventing accidental release of tension, providing users with confidence during operation.
Exploring Electrical System Layout
Understanding the arrangement of the electrical components is crucial for effective operation and maintenance. This section delves into the structure and connections that form the backbone of the system, providing insights into how each element contributes to the overall functionality.
The electrical layout encompasses various key elements, including:
- Wiring Harness: Connects different components and ensures smooth power distribution.
- Control Unit: Manages the system’s operations and integrates user inputs.
- Power Sources: Supplies energy required for operation, including batteries and alternators.
- Switches and Relays: Control the flow of electricity to various components based on user commands.
- Sensors: Monitor conditions and provide feedback to the control unit for adjustments.
A well-organized electrical arrangement not only enhances efficiency but also simplifies troubleshooting. Proper documentation of the layout aids in identifying potential issues and performing necessary repairs. Below is a typical order of examining the system:
- Review the wiring schematic to understand the connections.
- Inspect the power sources for proper voltage levels.
- Test switches and relays to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Evaluate sensors for accurate readings and responsiveness.
By familiarizing oneself with the electrical configuration, operators can ensure optimal performance and longevity of the system.
Gear Mechanisms and Specifications
In the realm of mechanical systems, gear mechanisms play a vital role in transmitting power and motion. These intricate arrangements enable efficient movement by altering speed, torque, and direction. Understanding the specifications and types of gear systems is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring durability.
Types of Gear Mechanisms: Various types of gears are employed, each serving distinct purposes. For instance, spur gears are commonly used for parallel shaft applications, while bevel gears are ideal for changing the axis of rotation. Worm gears offer significant speed reduction and high torque, making them suitable for applications requiring low-speed operations.
Specifications to Consider: When evaluating gear mechanisms, several specifications must be taken into account. Gear ratio, which defines the relationship between the input and output speeds, is paramount for achieving desired performance levels. Additionally, factors such as load capacity, material selection, and manufacturing precision significantly influence the reliability and lifespan of the gear assembly.
By comprehensively understanding the various gear types and their specifications, users can make informed decisions to enhance the efficiency and functionality of mechanical systems.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Ensuring the prolonged functionality of any mechanical equipment requires diligent care and regular upkeep. Implementing a structured maintenance routine not only enhances performance but also prevents unexpected breakdowns, ultimately extending the service life of the device.
Regular Inspection
Conducting frequent assessments is crucial in identifying potential issues before they escalate. Check all components for wear and tear, paying close attention to signs of rust or corrosion that may compromise performance.
Lubrication and Cleaning
Proper lubrication of moving parts minimizes friction and reduces wear. Additionally, regular cleaning removes debris and contaminants, ensuring smooth operation and preventing damage. Utilize appropriate cleaning agents and lubricants to maintain the integrity of materials.
| Task | Frequency | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Inspection | Monthly | Check for any signs of wear, rust, or malfunction. |
| Lubrication | Every 3 months | Apply lubricant to all moving parts to ensure smooth operation. |
| Cleaning | Every month | Remove dirt and debris from all surfaces to prevent buildup. |
Common Replacement Parts List
When maintaining equipment, it’s essential to have a thorough understanding of the components that may need replacement over time. Familiarity with frequently used items can help ensure smooth operation and longevity of the machinery. Below is a list of typical components that users might consider replacing as part of their maintenance routine.
Frequently Replaced Components
- Motor Assembly
- Control Switch
- Gearbox
- Drum
- Clutch
- Electrical Wiring
Additional Replacement Items
- Bearings
- Seals
- Fasteners
- Mounting Brackets
- Remote Control Units
By keeping these components on hand or knowing where to source them, operators can minimize downtime and maintain efficient functionality of their equipment.
Identifying Wear and Tear Signs

Recognizing the signs of deterioration is crucial for maintaining the longevity and functionality of any mechanical system. Over time, components can exhibit various indicators of wear that, if left unaddressed, may lead to decreased performance or even failure. Regular inspection is essential to ensure optimal operation and prevent unexpected issues.
One common sign of wear is the presence of frayed or damaged cables. This can affect the overall efficiency and safety of the device. Additionally, rust or corrosion on metal surfaces indicates exposure to moisture and environmental factors, potentially compromising structural integrity. Signs of excessive heat, such as discoloration or melting, can suggest overuse or improper functioning of the motor.
Another key aspect to monitor is the alignment and movement of parts. Misalignment can lead to increased friction and rapid wear, while unusual noises during operation may signal underlying problems. Regular maintenance and keen observation of these factors will contribute to a more reliable and effective operation.
Assembly and Disassembly Procedures
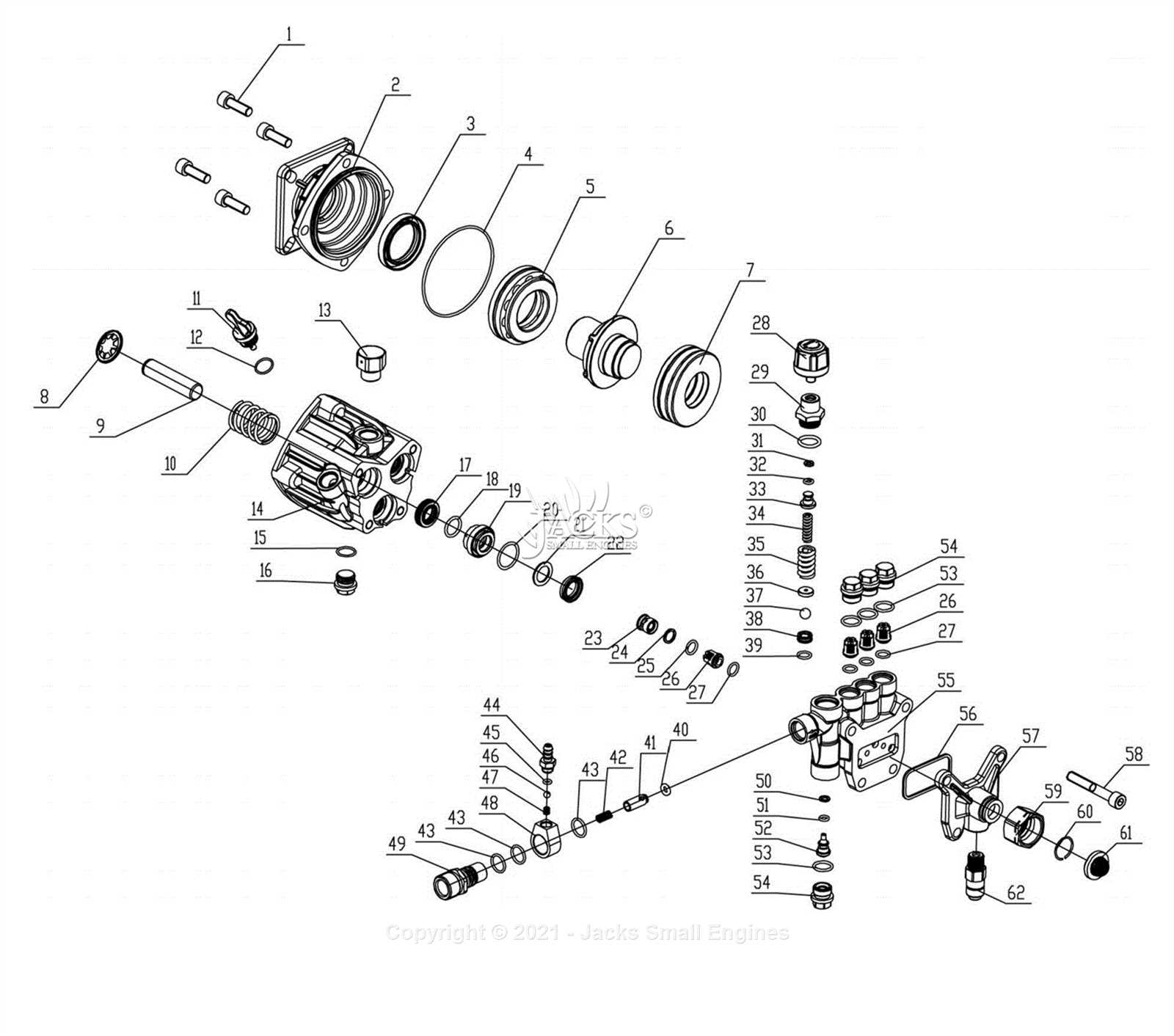
Understanding the correct methods for putting together and taking apart equipment is crucial for maintenance and repair. Proper techniques ensure that all components fit together seamlessly and function effectively. In this section, we will outline the essential steps to follow during these processes, emphasizing the importance of precision and care.
Preparation is key to a successful assembly or disassembly task. Start by gathering all necessary tools and components, ensuring that everything is within reach. This minimizes delays and distractions during the procedure. Familiarize yourself with the structure and functionality of each part to ensure an efficient workflow.
When disassembling, begin with careful inspection of the unit. Identify any screws, bolts, or fasteners that may require removal. Use appropriate tools to avoid damaging components. As you take parts apart, organize them systematically to facilitate reassembly. It can be helpful to take notes or photographs at each stage, capturing the arrangement of parts.
For assembly, follow the reverse order of disassembly, ensuring that each component is positioned correctly. Alignment is crucial; improper placement can lead to operational issues. Apply torque to fasteners according to specifications to prevent loosening or over-tightening. Always double-check connections and fittings before completing the process to ensure everything is secure.
By adhering to these guidelines, the tasks of assembling and disassembling machinery can be completed efficiently and effectively, promoting longevity and performance.
Aftermarket vs. OEM Parts Comparison
When it comes to selecting components for mechanical systems, consumers often face a crucial decision: whether to opt for original manufacturer products or explore alternatives available in the market. Each choice presents its own set of advantages and drawbacks, influencing performance, cost, and reliability.
Advantages of OEM Components
Original manufacturer components are designed to meet the specifications set forth by the equipment creator. This ensures compatibility and performance consistency. Key benefits include:
- Guaranteed fit and function
- High quality and reliability
- Potentially longer lifespan
- Warranty protection from the manufacturer
Benefits of Aftermarket Options
Aftermarket options often provide an economical alternative, catering to budget-conscious consumers. They may also offer enhanced performance features. Benefits of aftermarket products include:
- Lower price points
- A wider variety of choices and brands
- Potential for improved performance or customization
- Accessibility in various markets
Ultimately, the decision between original and alternative components should be guided by individual needs, budget considerations, and specific application requirements.
Wiring and Connection Diagrams
This section explores the intricacies of electrical setups and connectivity options essential for efficient operation. Understanding the arrangement of connections is crucial for maintaining optimal functionality and ensuring safe usage. This guide aims to provide clear insights into the wiring layouts, emphasizing their importance in the overall system performance.
Proper wiring is fundamental to achieving reliable operations. Below is a basic overview of typical connection types, highlighting their respective roles in the overall configuration:
| Connection Type | Description | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| Power Input | Connects the main power source to the unit. | Primary energy supply for operation. |
| Control Switch | Allows user to activate or deactivate the system. | Used for operational control. |
| Motor Connection | Links the motor to the power supply and control switch. | Enables movement and functionality. |
| Ground Connection | Provides a safety path for electrical faults. | Essential for safe operation. |
Understanding these connections and their configurations is key to ensuring proper functionality and safety during operation. Proper attention to detail in wiring can prevent common issues and enhance the longevity of the system.
Upgrading Components for Better Performance
Enhancing the efficiency and reliability of your equipment often involves selecting superior elements. Upgrading key components can lead to noticeable improvements in functionality, longevity, and overall user experience. This process not only maximizes the potential of the device but also ensures it operates smoothly under demanding conditions.
Key Components to Consider for Upgrades
- Motor: A high-performance motor can significantly increase power output and reduce energy consumption.
- Control System: Advanced control systems allow for more precise operation, improving response times and overall performance.
- Gearbox: A more efficient gearbox can enhance torque transfer and reduce wear and tear on the system.
- Wiring: Upgrading to higher quality wiring can improve conductivity and minimize voltage drop, leading to better overall performance.
- Battery: A robust battery with higher capacity can extend operational time and improve reliability.
Benefits of Upgrading
- Increased Efficiency: Higher quality components often perform better, leading to reduced energy consumption.
- Enhanced Durability: Upgraded parts can withstand more wear and tear, prolonging the lifespan of the equipment.
- Improved Functionality: Enhanced features can offer better control and versatility in operation.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Investing in quality components may reduce the frequency of repairs and replacements, saving money in the long run.
Resources for Parts Sourcing
Finding reliable sources for component acquisition is essential for maintaining equipment efficiency. A variety of options are available to ensure access to necessary supplies, from authorized distributors to online marketplaces. Knowing where to look can significantly enhance the repair and replacement process, ensuring that all required items are readily available.
Online Retailers: Numerous e-commerce platforms specialize in selling mechanical components. Websites like Amazon and eBay often feature a wide range of items, including hard-to-find components. Customer reviews and ratings can guide buyers in making informed choices.
Manufacturer’s Websites: Visiting the official websites of manufacturers can provide valuable information regarding compatible items. These platforms often offer direct purchasing options and detailed specifications, ensuring that customers obtain the right products for their needs.
Local Distributors: Establishing relationships with nearby suppliers can be advantageous. Local distributors frequently stock essential components and can offer personalized assistance, helping customers quickly identify the necessary items.
Forums and Community Groups: Engaging with online communities and forums dedicated to specific machinery can lead to useful insights. Members often share their experiences and recommendations for sourcing components, as well as tips on where to find the best deals.
By exploring these resources, individuals can streamline the process of locating necessary items, enhancing their overall efficiency and satisfaction.