Honda WB30XT Parts Breakdown and Component Overview
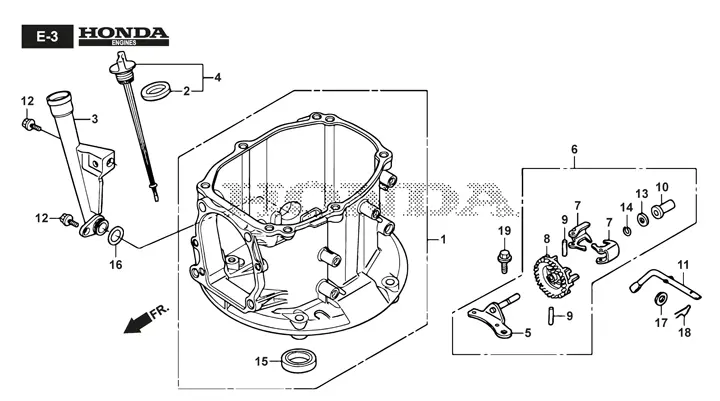
Understanding how various mechanisms interconnect is essential for maintaining and optimizing the performance of industrial and domestic equipment. A clear representation of these connections ensures that individual elements function smoothly within the system, allowing for effective troubleshooting and routine maintenance.
Each system relies on well-integrated assemblies, where every element plays a role in ensuring proper functionality. Examining how these components are structured provides insight into the engineering principles behind them, helping users and technicians alike maintain operational efficiency.
In this overview, we will explore the internal framework of a popular water-moving machine. Focusing on critical elements, this section aims to assist those seeking clarity on the equipment’s construction and the way different parts fit together. This understanding can support both repairs and performance enhancements.
Overview of the WB30XT Model Components
This section provides an in-depth look at the key elements that make up the functionality of the pump system. Each component works in unison to ensure efficient performance, durability, and reliability across various tasks.
Pumping Mechanism: At the core is the primary mechanism responsible for fluid movement, designed to handle large volumes effectively while maintaining consistent output under different operating conditions.
Engine System: The power source ensures that the flow remains steady, even under demanding loads. Its construction focuses on minimizing energy loss and ensuring smooth operation over extended periods.
Frame and Housing: The structure provides support and stability, protecting internal parts from potential impacts. It also facilitates easy transportation and placement on uneven surfaces.
Valves and Seals: These elements play a crucial role in regulating pressure and preventing leakage. High-quality materials enhance durability and ensure long-term efficiency.
Connections and Fittings: The unit features multiple connectors for seamless integration with hoses and accessories, ensuring compatibility with a variety of applications.
Main Functions of Engine Elements
An engine is made up of numerous interconnected components, each contributing to the overall operation and efficiency of the system. These elements work in harmony to generate power, regulate movement, and maintain stability during operation.
The combustion chamber serves as the core where fuel and air mix to produce energy through controlled explosions. The crankshaft transforms this energy into rotational force, enabling mechanical movement. Cylinders house pistons that move up and down, transferring force through the connecting rods.
The cooling system ensures that the engine maintains optimal temperature, preventing overheating. Meanwhile, the lubrication system reduces friction between moving parts, enhancing performance and extending the lifespan of internal elements. Valves control the intake and exhaust processes, regulating the flow of gases with precision.
In essence, every element of the engine has a specific purpose, and their seamless interaction ensures consistent power output and operational reliability.
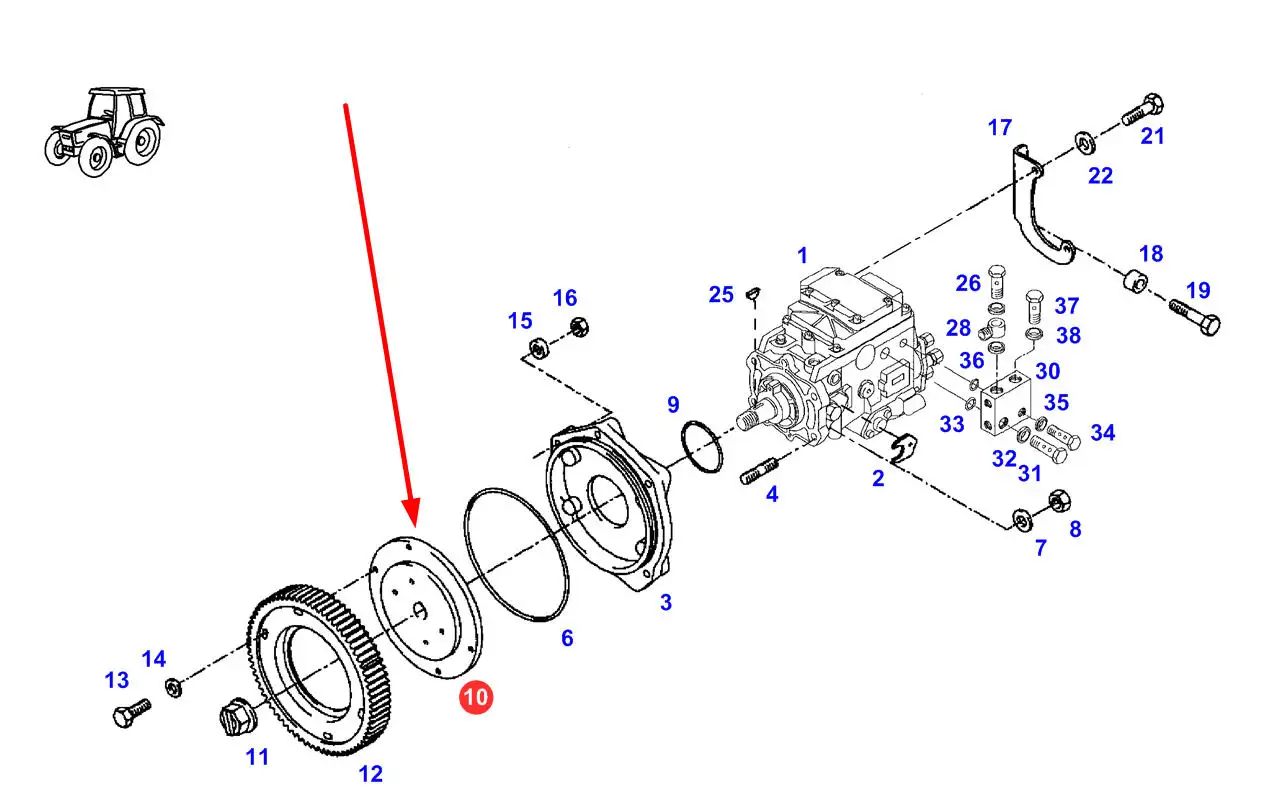
Pump Assembly Breakdown and Description
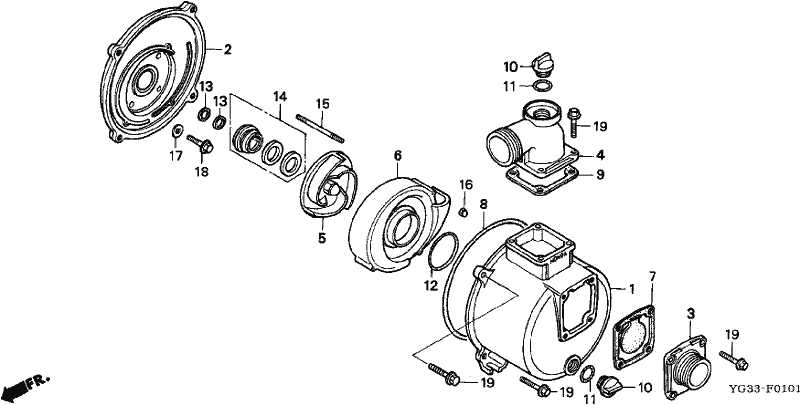
This section provides a detailed exploration of the internal structure of a water pump, highlighting how various components interact to ensure efficient fluid movement. Understanding the configuration of each element helps in maintenance, troubleshooting, and ensuring long-term reliability.
- Impeller: The central rotating element that creates the necessary flow by pushing water outward through centrifugal force.
- Casing: Encloses the impeller and directs water from the inlet to the outlet, preventing leaks and ensuring optimal flow.
- Inlet and Outlet Valves: Regulate water entry and exit, preventing backflow and maintaining consistent pressure levels.
- Shaft: Connects the motor to the impeller, ensuring efficient transfer of rotational energy.
- Seals and Bearings: Minimize friction and protect the assembly from contaminants, extending the pump’s operational life.
Each part plays a specific role in the operation, and any wear or failure in one element can affect overall performance. Regular inspection and replacement of worn-out components are crucial for uninterrupted service and to avoid costly
Key Features of the Impeller System
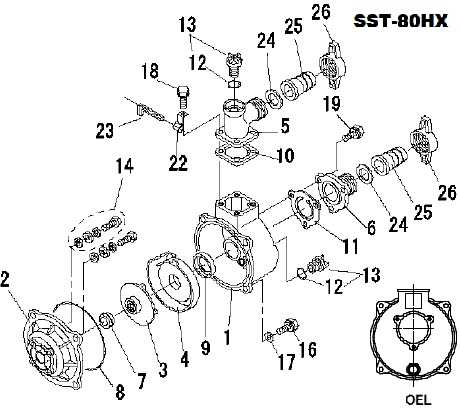
The impeller system plays a pivotal role in maintaining efficient fluid movement within pumping equipment. Its design directly influences the flow rate, pressure levels, and overall performance of the device. Understanding the primary components and their functions ensures smooth operation and reduces wear over time.
Optimized Flow Design
An optimized flow design ensures that water or other fluids move with minimal resistance through the system. The curvature and placement of each blade are calculated to reduce turbulence, resulting in higher efficiency. This streamlined flow also helps to lower energy consumption during prolonged use.
Durable Construction Materials
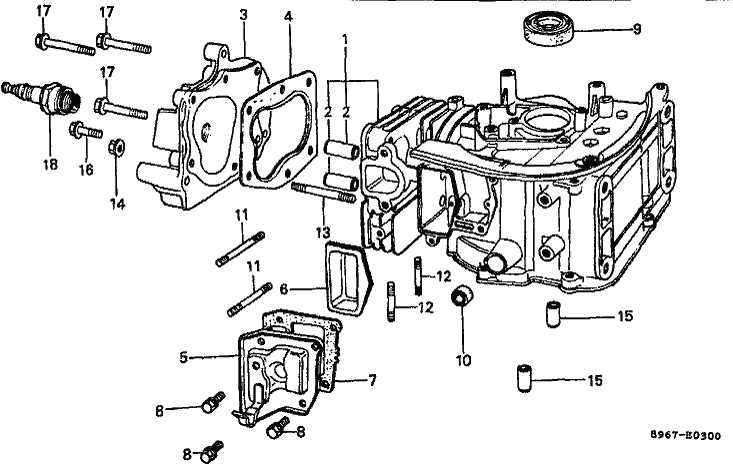
Impeller systems are typically constructed from corrosion-resistant alloys or high-grade plastics, ensuring longevity in various environments. Whether exposed to abrasive substances or continuous operation, the materials offer resilience, reducing the need for frequent maintenance. Additionally, the lightweight nature of certain materials minimizes strain on connected components.
Fuel System Structure and Components
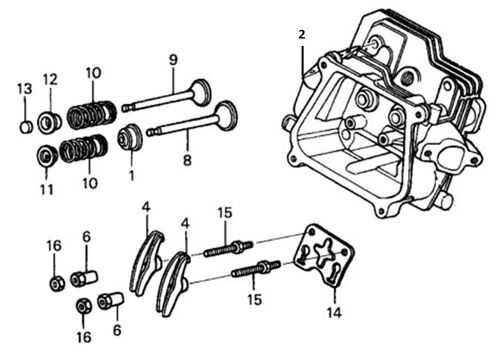
The fuel system ensures the continuous supply of energy to the engine by managing the flow and filtering of fuel. Its layout involves several interconnected elements working together to optimize combustion and enhance performance. Understanding these elements allows for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Main Components Overview
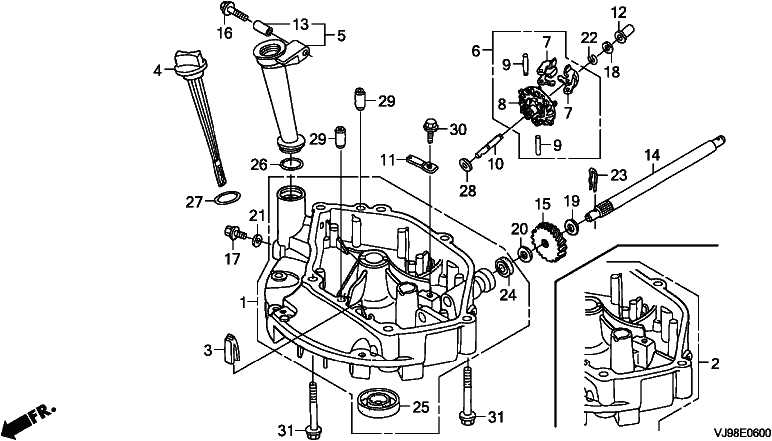
This system relies on several key components to regulate fuel delivery. Each part plays a distinct role in ensuring efficiency, from filtering impurities to controlling pressure levels throughout the flow path.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Fuel Tank | Stores fuel and allows gravity or pumps to deliver it to other parts. |
| Fuel Filter | Removes contaminants to protect the engine from blockages or damage. |
| Fuel Pump | Transfers fuel from the tank to the engine at required pressure levels. |
| Carburetor | Mixes fuel with air in precise ratios to ensure efficient combustion. |
Maintenance of the Air Intake Parts
Proper upkeep of the air intake components is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the equipment. Regular attention to these parts not only enhances efficiency but also prevents potential issues that may arise from neglect. This section will cover crucial aspects of maintaining air intake elements, including inspection, cleaning, and replacement procedures.
Inspection Procedures
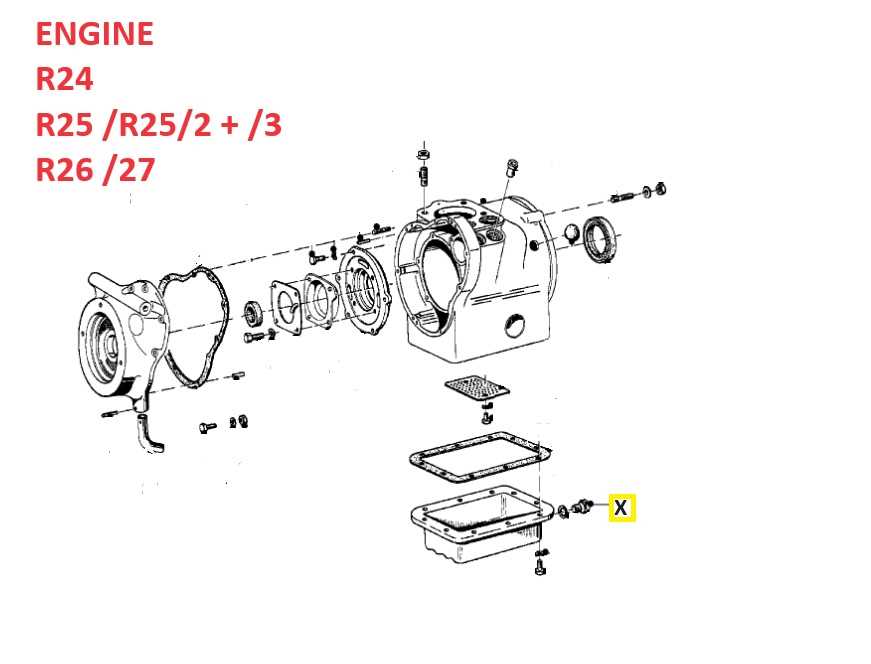
Regular inspections are vital for identifying wear or damage to the air intake components. Follow these steps for effective evaluation:
- Check for any visible cracks or signs of deterioration.
- Inspect seals and gaskets for proper sealing and integrity.
- Ensure that there are no obstructions in the air passages.
- Look for signs of dirt accumulation or blockage.
Cleaning and Replacement Guidelines
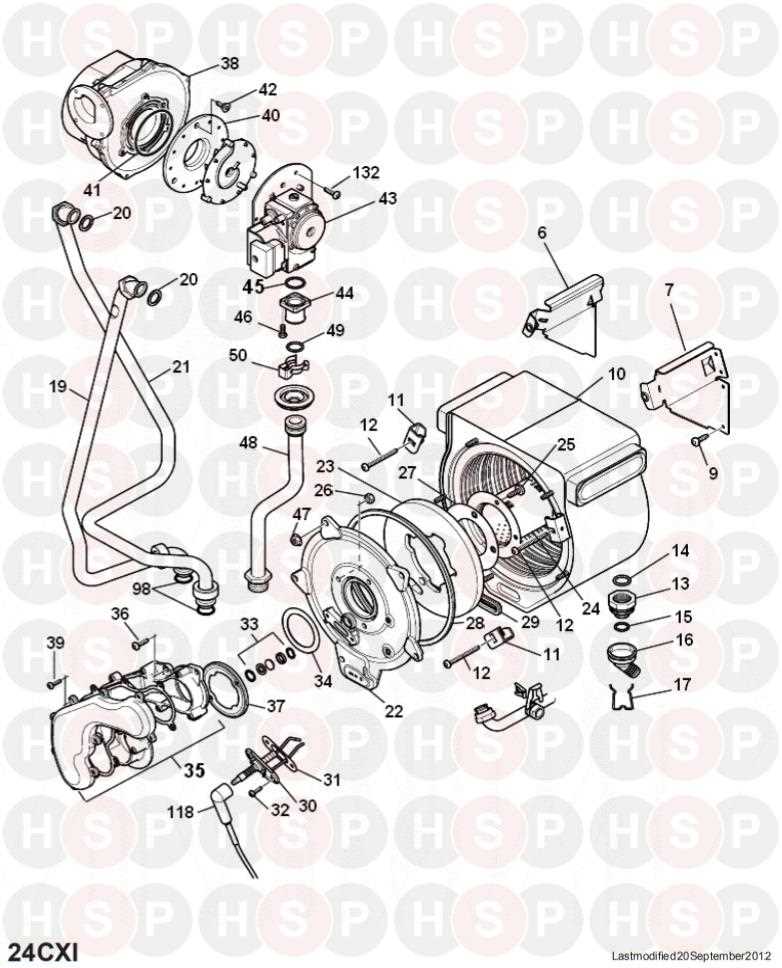
Cleaning and timely replacement of air intake elements contribute to the optimal functioning of the equipment. Consider the following recommendations:
- Remove dirt and debris from the air filter using compressed air or a gentle wash.
- Replace filters that show signs of excessive wear or damage.
- Clean intake manifolds with appropriate cleaning solutions to eliminate carbon buildup.
- Replace worn gaskets to prevent air leaks.
Casing and Frame Design Insights
The structural integrity and aesthetic appeal of machinery largely depend on the design of its casing and frame. These components not only protect internal mechanisms from external factors but also contribute to the overall functionality and efficiency of the equipment. Understanding the design principles behind these elements can enhance the performance and durability of the entire system.
Incorporating high-quality materials and innovative engineering techniques is essential in creating a robust casing. The choice of material significantly impacts weight, strength, and resistance to wear and tear. Additionally, the frame design must allow for effective heat dissipation and provide adequate support for all internal parts.
| Design Element | Material | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Casing | Aluminum | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant |
| Frame | Steel | High strength and durability |
| Insulation | Thermal foam | Enhanced temperature control |
Moreover, the design should prioritize ease of assembly and disassembly, facilitating maintenance and repairs. A well-thought-out casing and frame not only extend the lifespan of machinery but also ensure optimal performance in various operating conditions.
Connections and Hose Fittings Explained

The efficiency of any mechanical system often relies on the integrity of its connections and hose fittings. These components play a crucial role in ensuring the seamless transfer of fluids within the machinery, preventing leaks and maintaining optimal performance. Understanding the various types of fittings and their applications can enhance maintenance practices and prolong the lifespan of equipment.
Types of Connections: Connections can be classified into several categories, including threaded, quick-disconnect, and push-fit types. Each type has its specific uses and advantages, contributing to the overall functionality of the system. For instance, threaded connections provide a secure, leak-proof seal, while quick-disconnect fittings offer ease of use during maintenance and repair tasks.
Hose Fittings and Their Importance: Hose fittings are essential for connecting hoses to different components of the machinery. They ensure that the flow of fluids is uninterrupted and that pressure is maintained. High-quality fittings can withstand various pressures and temperatures, making them vital for operational safety.
Maintenance Tips: Regular inspection of connections and fittings is essential for detecting wear and preventing potential failures. Ensure that all fittings are properly tightened and check for signs of corrosion or damage. Replacing worn-out components promptly will help maintain system efficiency and avoid costly downtime.
Lubrication System Parts and Usage
The lubrication system plays a crucial role in maintaining the efficiency and longevity of machinery. This system ensures that all moving components operate smoothly by minimizing friction and wear. Understanding the various components involved and their functions is essential for optimal performance and maintenance.
Key Elements of the Lubrication System include the oil pump, filters, and delivery lines. The oil pump is responsible for circulating lubricant throughout the engine, ensuring that all critical areas receive adequate lubrication. Filters are vital for removing contaminants, thus protecting sensitive parts from damage. Delivery lines transport the lubricant from the pump to various components, ensuring that every moving part is adequately supplied.
Regular maintenance of the lubrication system is essential for preventing breakdowns. This includes monitoring oil levels, replacing filters, and inspecting the pump for any signs of wear or failure. By adhering to a proper maintenance schedule, operators can ensure that the lubrication system functions effectively, contributing to the overall health of the machinery.
Electrical Components in the WB30XT Model
The electrical system of this engine model is crucial for its operation and efficiency. It consists of various elements that work together to ensure proper functionality and reliability. Understanding these components can help in maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Ignition System: This includes the spark plug and ignition coil, responsible for starting the engine by creating a spark at the right moment.
- Battery: Provides the necessary power to start the engine and supports the electrical components when the engine is not running.
- Alternator: Charges the battery and supplies power to the electrical system while the engine is running, ensuring a consistent energy supply.
- Wiring Harness: A network of wires that connects all electrical components, allowing for efficient communication and energy distribution.
- Fuse Box: Contains fuses that protect the electrical circuits from overload, preventing potential damage to the system.
Regular inspection and maintenance of these electrical components are essential for the longevity and performance of the engine. Identifying and addressing any issues promptly can prevent costly repairs and ensure optimal operation.
Compatible Replacement Parts Selection
When it comes to ensuring the optimal performance of your equipment, selecting suitable replacement components is essential. Properly matching compatible items can enhance functionality and extend the lifespan of the machine. This process involves careful consideration of specifications and quality to achieve the best results.
Identifying Quality Alternatives: One of the primary steps in this selection process is to identify high-quality alternatives that meet the necessary standards. Evaluating the materials, durability, and reliability of these components is crucial. Reliable suppliers often provide detailed information regarding compatibility, which aids in making informed decisions.
Compatibility Checks: Conducting compatibility checks ensures that the selected items fit perfectly with existing systems. It is advisable to refer to manufacturer specifications and consult with professionals when in doubt. This attention to detail can prevent issues such as improper fitting or performance deficits.
Benefits of Using Equivalent Components: Utilizing equivalent components can lead to cost savings while maintaining performance. Many aftermarket suppliers offer quality alternatives at competitive prices. However, it is vital to ensure that these items meet the necessary standards to guarantee safety and efficiency.
Common Wear Issues and Solutions
Wear and tear is a common concern for various types of machinery, impacting performance and longevity. Identifying these issues early can prevent more extensive damage and costly repairs. Below are some frequently encountered problems along with their potential remedies.
Frequent Problems
- Overheating components due to inadequate lubrication.
- Worn seals leading to fluid leaks.
- Corrosion from exposure to harsh environmental conditions.
- Degraded gaskets resulting in air leaks.
- Excessive vibrations caused by imbalanced parts.
Solutions and Maintenance Tips
- Regularly check and change lubricants to ensure optimal operation.
- Inspect seals and gaskets periodically; replace them as necessary.
- Utilize protective coatings to combat corrosion.
- Ensure all components are properly aligned to reduce vibration.
- Conduct routine inspections and maintenance to catch issues early.