Understanding the Parts of a Daffodil Diagram

The structure of a bloom reveals the intricate design of nature, showcasing a fascinating interplay of elements that contribute to its beauty and function. Each component plays a vital role in the plant’s lifecycle, ensuring reproduction and the continuation of species.
In this exploration, we will uncover the essential features that make up this enchanting floral specimen. From the vibrant outer layers that attract pollinators to the hidden reproductive organs, every part has its significance, ultimately leading to the flower’s purpose.
By delving into these characteristics, we can appreciate not only the aesthetic value but also the ecological importance of this botanical wonder. Understanding these elements enhances our connection to nature and deepens our knowledge of plant biology.
Understanding Daffodil Structure
This section explores the intricate design of a specific flowering plant, highlighting its unique components and their functions. Each element plays a crucial role in the plant’s overall beauty and reproductive success, contributing to its captivating nature.
Key Components
The main features of this bloom include the colorful crown, the supportive stem, and the leaf structure. Each of these aspects is essential for growth, attracting pollinators, and ensuring the plant’s vitality throughout its life cycle.
Functionality and Adaptations
This flowering species showcases remarkable adaptations that enhance its ability to thrive in various environments. The specialized structures not only provide stability but also optimize processes like photosynthesis and reproduction, demonstrating nature’s ingenuity.
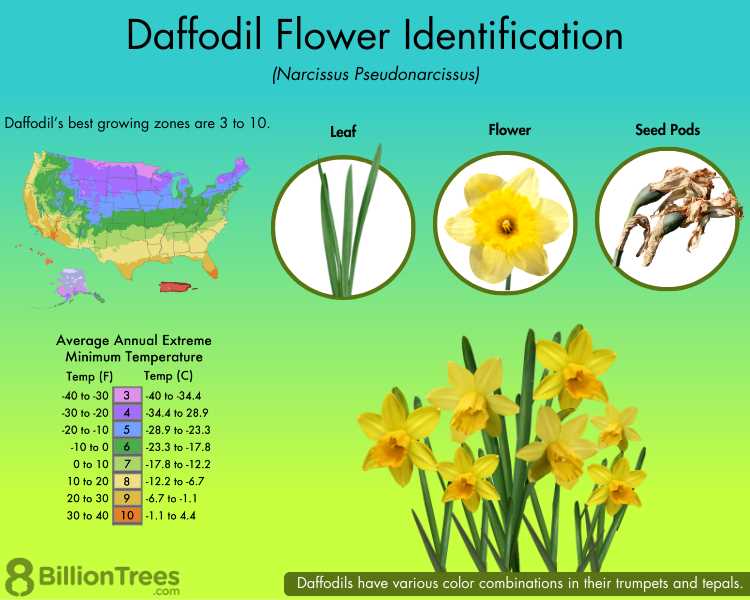
Key Features of Daffodil Flowers
The vibrant blooms of this springtime favorite exhibit a range of remarkable characteristics that enhance their appeal. Known for their striking appearance and cheerful hues, these blossoms are a symbol of renewal and beauty in gardens worldwide.
Color Variety: The petals showcase a spectrum of colors, from bright yellows to creamy whites and even vibrant oranges, making them a focal point in any floral arrangement.
Unique Shape: Their distinct trumpet-like structure captivates admirers, creating an eye-catching silhouette that stands out in natural landscapes.
Fragrance: Many varieties exude a subtle yet delightful aroma, adding another sensory layer to their charm.
Growth Habit: These plants are perennial, returning each year to spread joy and color, often forming delightful clusters that enhance garden aesthetics.
Parts of a Daffodil Explained
This section delves into the essential components of a specific flowering plant, exploring their roles and characteristics. Each element contributes to the overall beauty and functionality of the blossom, playing a crucial role in its reproduction and appeal.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Petals | The colorful outer parts that attract pollinators and provide visual appeal. |
| Cup | The central structure that holds reproductive organs and often enhances the flower’s attractiveness. |
| Stamens | Male reproductive components that produce pollen, essential for fertilization. |
| Carpels | Female reproductive structures that house the ovules, playing a key role in seed development. |
| Leaves | Green structures that provide nourishment through photosynthesis, supporting the entire plant. |
Function of the Daffodil Bulb

The underground structure of this flowering plant serves a vital role in its growth and survival. Acting as a reservoir of nutrients, it ensures the sustenance of the above-ground parts during various stages of development. This essential component allows the plant to endure unfavorable conditions while preparing for the next blooming cycle.
Nutrient Storage
One of the primary functions of the bulb is to store energy in the form of carbohydrates. This stored energy is crucial during the initial growth phase in spring when the plant emerges from dormancy. As the weather warms, the bulb provides the necessary fuel for the formation of leaves and flowers, facilitating a robust and vibrant display.
Survival Mechanism
During adverse weather conditions, such as extreme cold or drought, the bulb acts as a protective mechanism. It remains dormant underground, shielding itself from harsh elements. This survival strategy enables the plant to remain viable until conditions are favorable for growth, ensuring the continuation of the species.
In summary, the underground structure is not merely a storage unit; it is a crucial element that supports life and resilience, allowing the flowering plant to thrive across seasons.
Unique Aspects of Daffodil Leaves
The foliage of this springtime bloom possesses distinctive characteristics that contribute to its charm and functionality. Its structure and coloration not only enhance aesthetic appeal but also play a crucial role in the plant’s overall health and growth cycle.
Structure and Texture
The leaves are typically long and narrow, exhibiting a smooth texture that aids in water retention. Their lanceolate shape allows for optimal sunlight capture, which is essential for photosynthesis, enabling the plant to thrive during its blooming period.
Coloration and Adaptability
Rich green hues dominate the foliage, signaling vitality and strength. This vibrant coloration can vary slightly based on environmental conditions, showcasing the adaptability of the plant to different climates while maintaining its essential functions.
The Role of Daffodil Stems
The elongated structures of this flower play a crucial role in its overall development and vitality. They serve as the main support, elevating the bloom above the ground and allowing it to receive ample sunlight. Additionally, these stalks facilitate the transportation of essential nutrients and water from the roots to the vibrant petals.
These vertical elements also contribute to the plant’s stability, anchoring it against environmental factors such as wind and rain. Their strength and flexibility enable the flower to adapt to various conditions while maintaining its beauty. Ultimately, these components are vital for the flourishing of the plant and the production of seeds.
Importance of Daffodil Petals
The delicate outer segments of these spring blooms play a crucial role in their overall appeal and functionality. They not only enhance the aesthetic beauty of the flower but also serve essential purposes in the reproductive process.
Attracting Pollinators: The vibrant colors and alluring shapes of the flower’s petals are specifically designed to captivate bees, butterflies, and other pollinators. This attraction is vital for successful fertilization and the continuation of the species.
Providing Protection: The petals also act as a protective barrier for the inner reproductive structures. By shielding them from environmental elements and potential predators, they ensure a higher chance of reproductive success.
Enhancing Genetic Diversity: By facilitating the attraction of various pollinators, these floral elements contribute to cross-pollination, which is essential for genetic diversity within the population. This diversity enhances resilience and adaptability in changing environments.
In summary, the outer segments of these vibrant flowers are not merely decorative; they are integral to the lifecycle and sustainability of the plant species. Their multifaceted roles underline their significance in both ecological and aesthetic contexts.
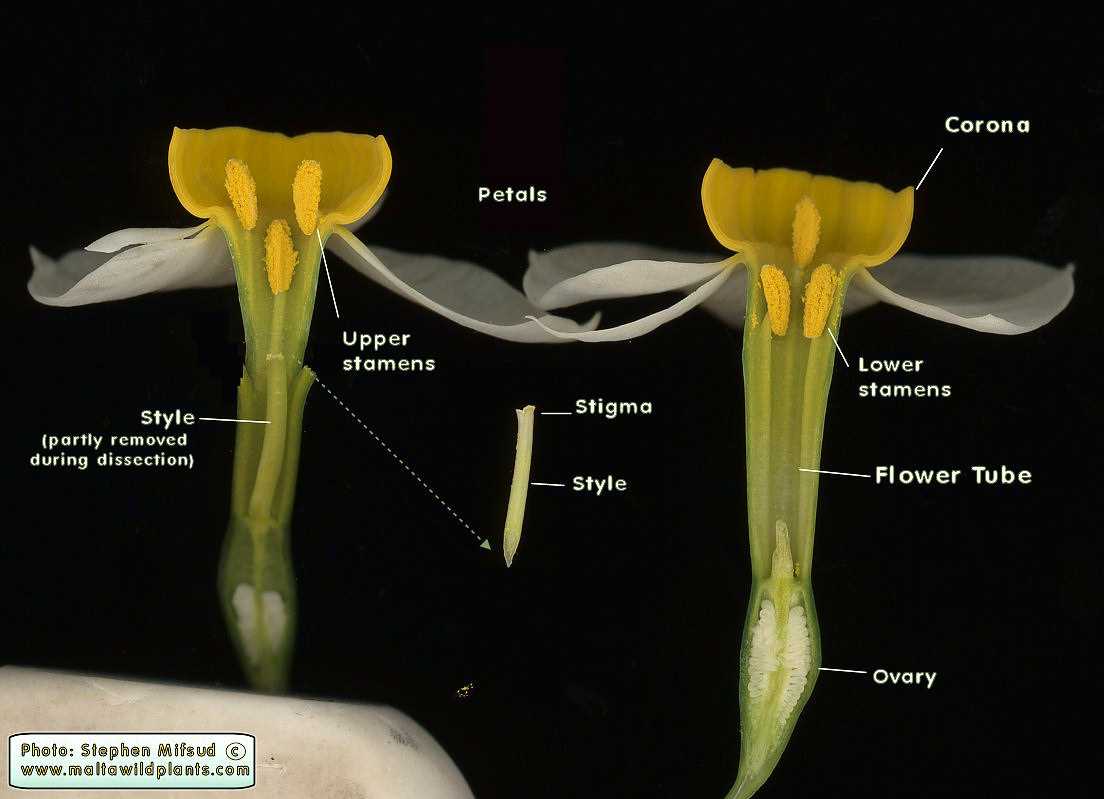
Daffodil Reproductive Organs Overview
This section provides a comprehensive look at the structures responsible for reproduction in this beautiful flowering plant. Understanding these components is essential for appreciating the intricate processes involved in pollination and seed formation.
Key Structures Involved
The reproductive cycle is primarily facilitated by specific male and female components. The male structure produces pollen, which is crucial for fertilization, while the female counterpart houses the ovary where seeds develop post-pollination. Together, these elements create a system that enables the continuation of the species.
Pollination Process
Pollination occurs when pollen from the male structures is transferred to the female components, often aided by various pollinators. This interaction is vital for genetic diversity and the successful propagation of new plants, ensuring the survival of the species across different environments.
Pollination Process in Daffodils
The process of transferring pollen from the male structures to the female parts is crucial for the reproduction of this flower species. This intricate mechanism ensures the continuation of genetic diversity and the development of seeds, which play a vital role in the life cycle of the plant.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Pollen Release | The male structures release fine grains into the air or onto visiting pollinators. |
| Pollen Transfer | Pollinators, such as bees, collect pollen and transport it to another bloom. |
| Fertilization | The pollen grain lands on the stigma, allowing fertilization to occur. |
| Seed Development | Following fertilization, seeds begin to form, completing the reproductive cycle. |
Environmental Impact on Daffodil Growth
The growth and development of this springtime bloom are intricately tied to various ecological factors. These influences can significantly alter the flowering cycle, health, and overall vibrancy of the plant. Understanding these aspects is essential for gardeners and enthusiasts who wish to cultivate healthy specimens.
| Environmental Factor | Impact on Growth |
|---|---|
| Soil Quality | Nutrient-rich soil promotes vigorous growth and flowering. |
| Light Exposure | Optimal sunlight is crucial for photosynthesis and blooming. |
| Water Availability | Proper hydration is vital; both excess and deficiency can hinder development. |
| Temperature | Extreme temperatures can affect flowering time and plant health. |
Varieties of Daffodil Flowers
Exploring the diverse types of these stunning blooms reveals a world of colors, shapes, and sizes. Each variety offers unique characteristics, appealing to enthusiasts and gardeners alike. Understanding these differences enhances appreciation for their beauty and adaptability.
Classic Types
The classic varieties are known for their striking appearance and resilience. Among them, the Trumpet type stands out with its long, elegant petals and central trumpet-like corona, while the Large-Cupped variety showcases a prominent cup surrounded by broad petals, creating a captivating visual.
Unusual Variations
Some blooms present unusual features that delight collectors. The Split-Cupped varieties exhibit a distinctive split in their cups, offering a quirky twist, while the Jonquilla type is recognized for its smaller, fragrant clusters, perfect for adding charm to any garden.
Caring for Daffodils in Gardens
Proper maintenance is essential for ensuring vibrant blooms and healthy foliage in your garden. With a few key practices, you can create an ideal environment for these beautiful spring flowers to thrive and flourish year after year.
To begin with, consider the following aspects of care:
- Soil Quality: Ensure the soil is well-draining and rich in organic matter. Adding compost can enhance nutrient levels.
- Watering: While these plants are drought-tolerant, they benefit from consistent moisture during the growing season. Water deeply but infrequently.
- Light Exposure: Position them in a spot that receives full sun to partial shade. Adequate sunlight is crucial for robust growth.
- Fertilization: Use a balanced fertilizer in early spring to promote healthy development. Avoid excessive nitrogen, which can hinder flowering.
After the blooming period, proper care continues:
- Deadheading: Remove spent flowers to prevent seed formation and encourage energy conservation for the bulbs.
- Foliage Maintenance: Allow the leaves to remain until they turn yellow. This process helps the bulbs store energy for the next season.
- Dividing Bulbs: Every few years, lift and separate overcrowded bulbs to maintain vigor and prevent disease.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that these delightful flowers bring beauty to your garden for many seasons to come.