Understanding Bike Part Diagrams for Better Maintenance
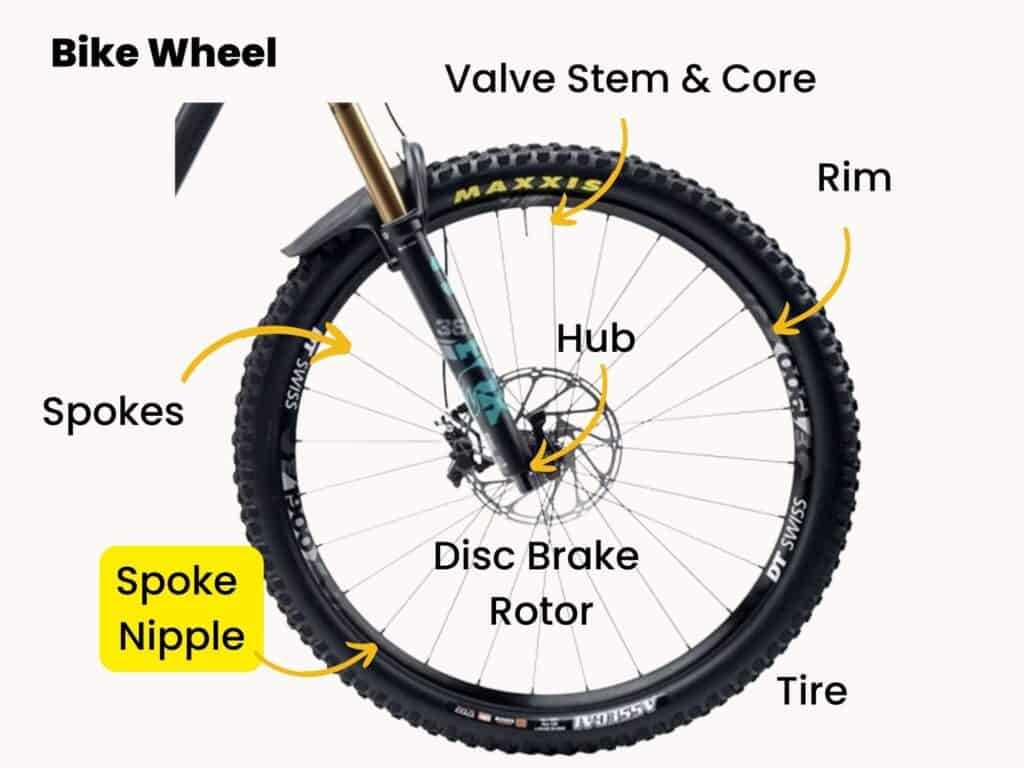
The intricate world of two-wheeled transport encompasses various components, each playing a crucial role in overall functionality. This exploration aims to clarify how these elements interact, contributing to a seamless riding experience. By breaking down the essentials, enthusiasts and novices alike can appreciate the design and engineering behind their favorite mode of transportation.
Each segment of this vehicle is designed with precision, ensuring efficiency and safety. Whether it’s the sturdy framework, the responsive control mechanisms, or the energy-efficient propulsion system, understanding these elements can enhance both performance and maintenance. Moreover, a deeper comprehension of these intricacies fosters a greater appreciation for the craftsmanship involved.
As we delve into this topic, we will uncover the ultimate relationship between these components, highlighting their interdependence and importance. This knowledge empowers riders to make informed decisions about upgrades, repairs, and overall care, enriching their experience on the road.
Understanding Bike Part Diagrams
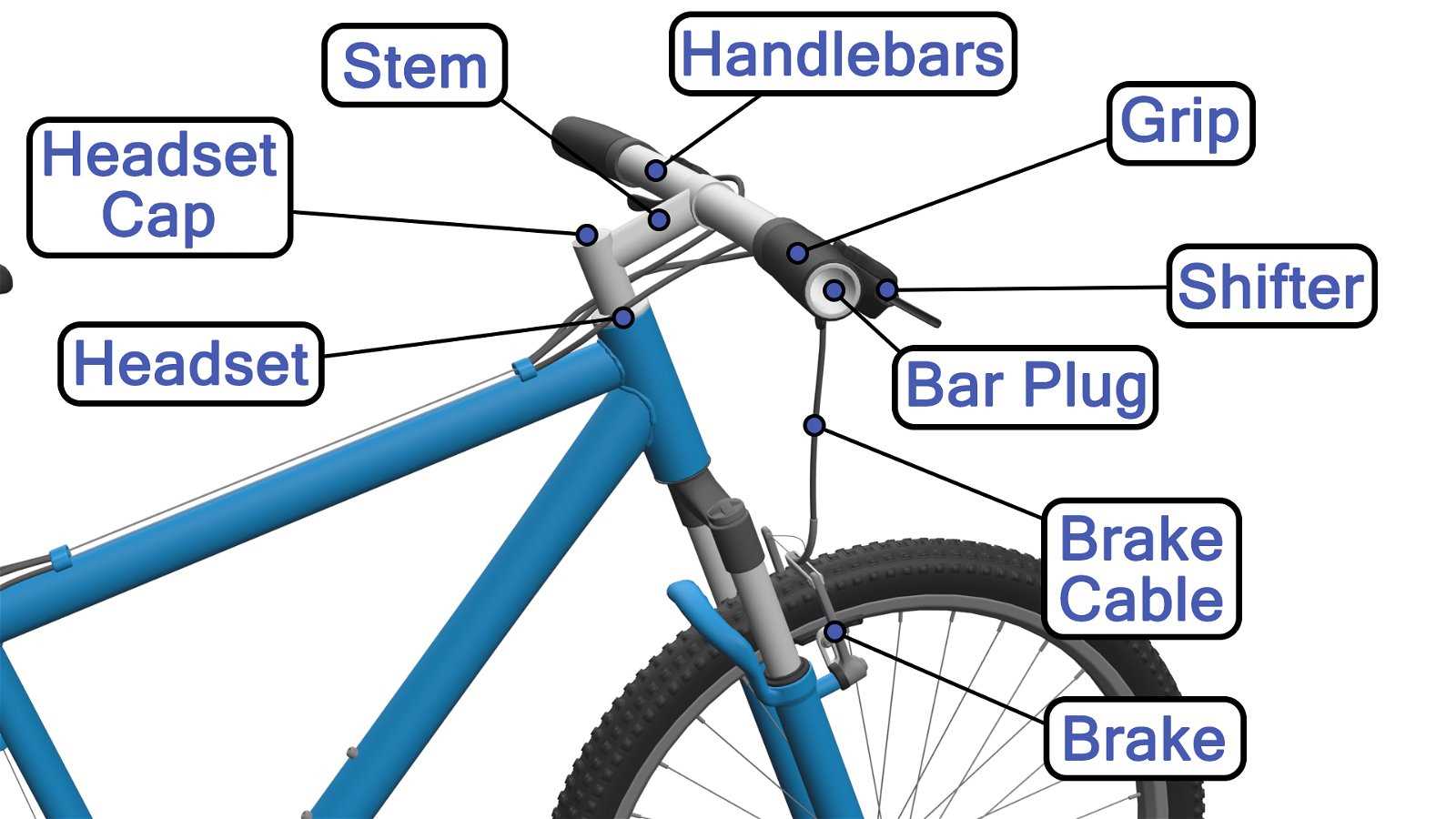
Grasping the components and their interconnections is essential for enthusiasts looking to enhance their cycling experience. Visual representations serve as invaluable tools, enabling users to identify each element and its role in overall functionality.
Key Components

- Frame: The backbone that supports all other elements.
- Wheels: Essential for motion and stability.
- Brakes: Crucial for safety and control.
- Drivetrain: Facilitates movement through gear adjustments.
Benefits of Visual Guides
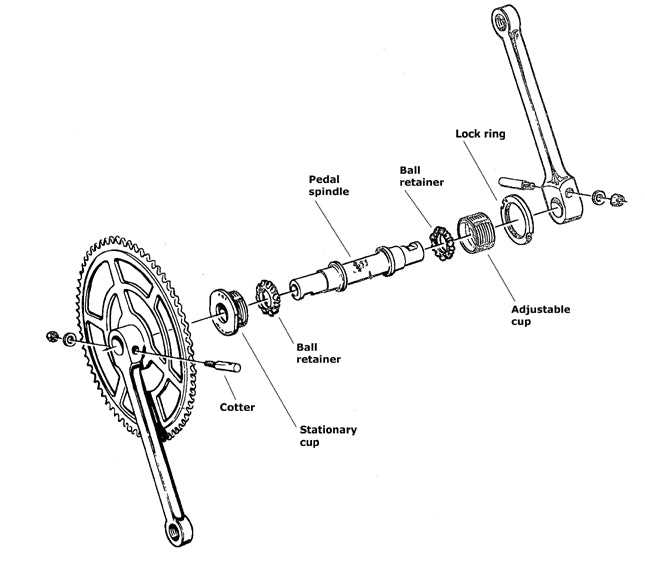
- Clarity: Simplifies complex structures.
- Maintenance: Assists in identifying parts needing attention.
- Customization: Aids in planning upgrades and modifications.
Essential Components of a Bicycle
Understanding the key elements of a two-wheeled vehicle is crucial for both enthusiasts and casual riders. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring functionality, safety, and overall performance. This section explores the fundamental pieces that make up this mode of transportation, providing insights into their significance and interaction.
Frame and Structure

The frame serves as the backbone, providing stability and support. Typically constructed from materials such as aluminum, steel, or carbon fiber, it is designed to withstand various stresses. The geometry of the frame influences the ride quality, agility, and comfort. Attention to detail in the frame design ensures that the entire assembly operates harmoniously.
Wheels and Tires
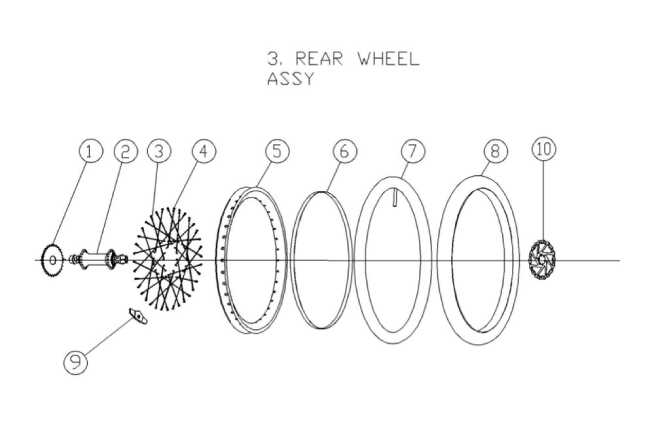
The wheels are crucial for mobility, featuring rims, spokes, and hubs that contribute to overall strength and efficiency. Tires, available in different sizes and tread patterns, affect traction and control. Selecting the right combination of wheels and tires can enhance performance on diverse terrains, from smooth pavements to rugged trails. Proper maintenance of these components is essential for a smooth and safe riding experience.
How to Read Bike Part Diagrams
Understanding technical illustrations of cycling components can greatly enhance your maintenance and repair skills. These visuals provide a simplified view of various elements, allowing for easier identification and comprehension of their functions and relationships within the whole system.
Key Components to Look For
When examining these illustrations, focus on the following elements to gain insights into the structure and mechanics:
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Labels | Indicate the names of components for easy reference. |
| Numbers | Often used to refer to specific items in a corresponding list or legend. |
| Lines | Show connections or relationships between different elements. |
| Color Coding | Helps differentiate between various types of components or functionalities. |
Interpreting Connections and Functions
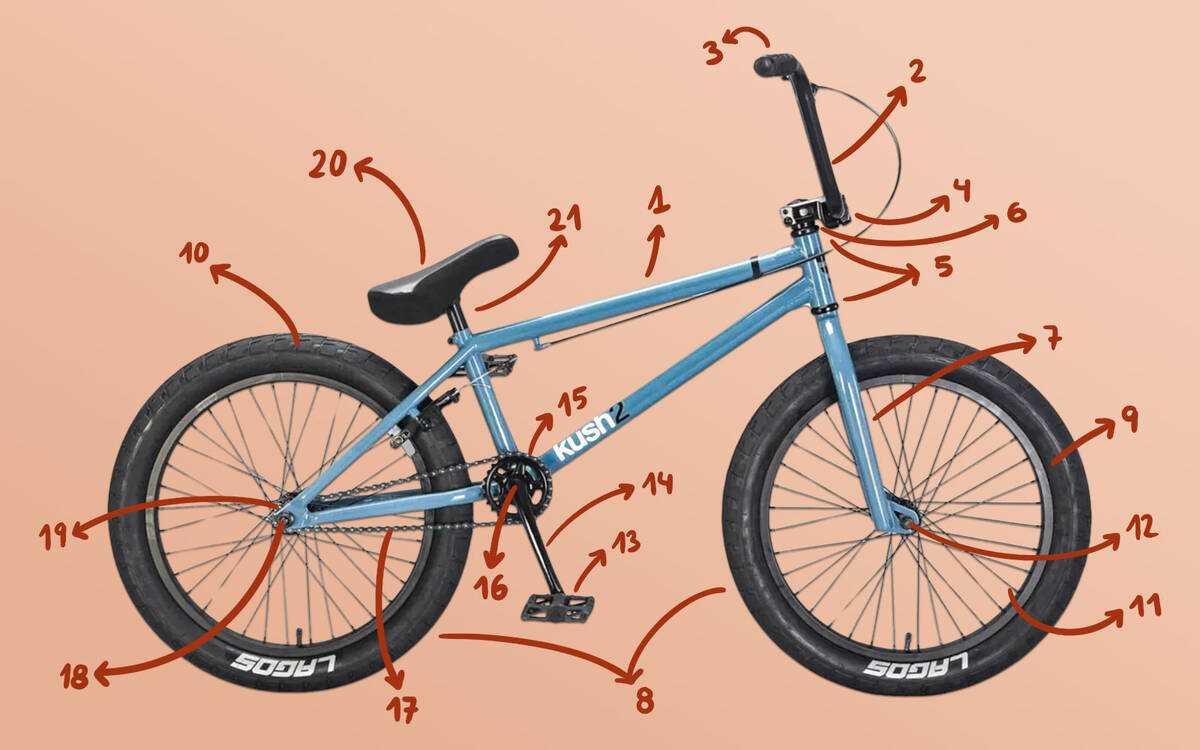

Pay attention to how the components are connected, as this reveals their interactions and how they work together to achieve optimal performance. Analyzing these relationships will provide a deeper understanding of the mechanics at play, facilitating troubleshooting and enhancements.
Common Symbols in Bicycle Diagrams
Understanding the visual language used in illustrations of cycling components is essential for both enthusiasts and mechanics. These symbols provide a standardized way to convey information quickly and efficiently, allowing users to identify parts and their functions with ease.
Key Symbols
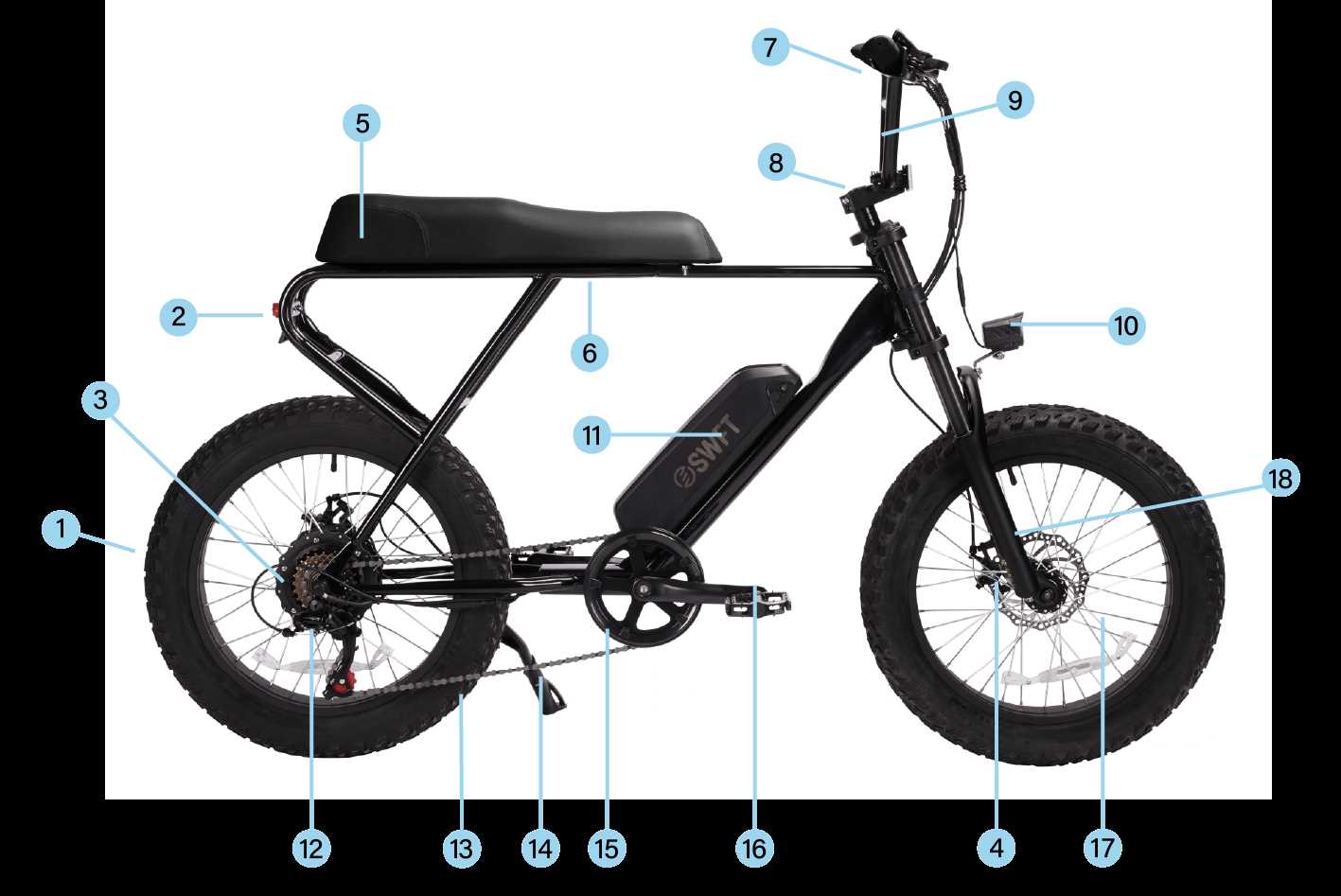

- Circle: Often represents rotation or wheels.
- Arrow: Indicates direction of movement or flow.
- Square: Typically denotes connection points or junctions.
Additional Notations
- Dashed Lines: Suggest a hidden or internal component.
- Text Labels: Clarify specific elements or functions.
- Color Coding: Differentiates various systems, like braking or gearing.
Benefits of Using Diagrams for Repairs
Visual representations serve as invaluable tools in the maintenance and restoration of equipment. They enhance understanding and streamline processes, ensuring that tasks are completed with greater accuracy and efficiency. By providing a clear outline of components and their relationships, these visuals help both novices and experts navigate complex repairs.
Enhanced Clarity
Utilizing visual aids simplifies intricate instructions, breaking down complicated procedures into manageable steps. This clarity minimizes confusion and reduces the likelihood of errors, making the repair process smoother and more straightforward.
Time Efficiency
Reference materials can significantly expedite the repair journey. With a clear visual guide, individuals can quickly identify the necessary components, reducing the time spent searching for information and allowing for quicker resolutions.
Types of Bicycles and Their Parts
Understanding the various styles of two-wheeled vehicles is essential for enthusiasts and casual riders alike. Each design serves a specific purpose and features distinct components tailored to enhance performance, comfort, and usability. This section explores the different categories of cycles and highlights the essential elements that contribute to their functionality.
Common Types of Cycles
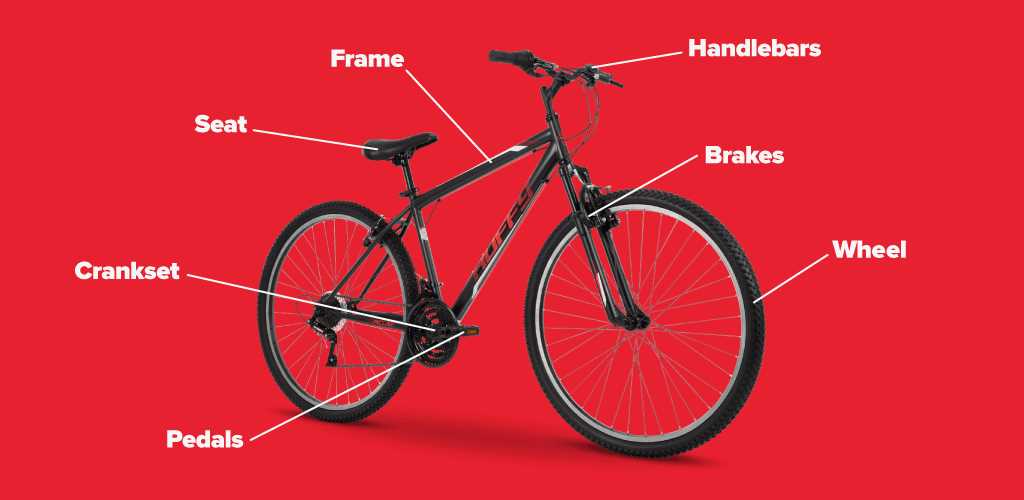

The classification of these vehicles generally revolves around their intended use, terrain compatibility, and design characteristics. Below are some prevalent types:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Road | Lightweight with thin tires, designed for speed on paved surfaces. |
| Mountain | Sturdy and robust, built for rugged trails and off-road adventures. |
| Hybrid | A blend of road and mountain styles, suitable for a variety of terrains. |
| Electric | Equipped with a motor to assist with pedaling, ideal for longer distances. |
| Folding | Compact design for easy transport and storage, perfect for urban environments. |
Key Components
Each style incorporates essential elements that enhance performance and rider experience. Here are some critical components commonly found in various types:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Frame | The main structure that supports all other components. |
| Wheels | Facilitate movement and stability; size and type vary by design. |
| Brakes | Ensure safe stopping and control while riding. |
| Gear System | Allows for changing resistance, improving efficiency on different terrains. |
| Saddle | Provides comfort during rides, with variations to suit rider preferences. |
Identifying Issues Through Diagrams
Visual representations serve as valuable tools in recognizing and analyzing problems within complex systems. They allow individuals to pinpoint anomalies and understand interactions between components more effectively.
Utilizing these illustrations can lead to the following benefits:
- Enhanced clarity in understanding relationships.
- Quick identification of malfunctioning elements.
- Facilitated communication among team members.
- Streamlined troubleshooting processes.
By carefully examining these visuals, one can delve into potential sources of difficulty and work toward finding the ultimate solutions efficiently.
Diagram vs. Actual Bicycle Assembly
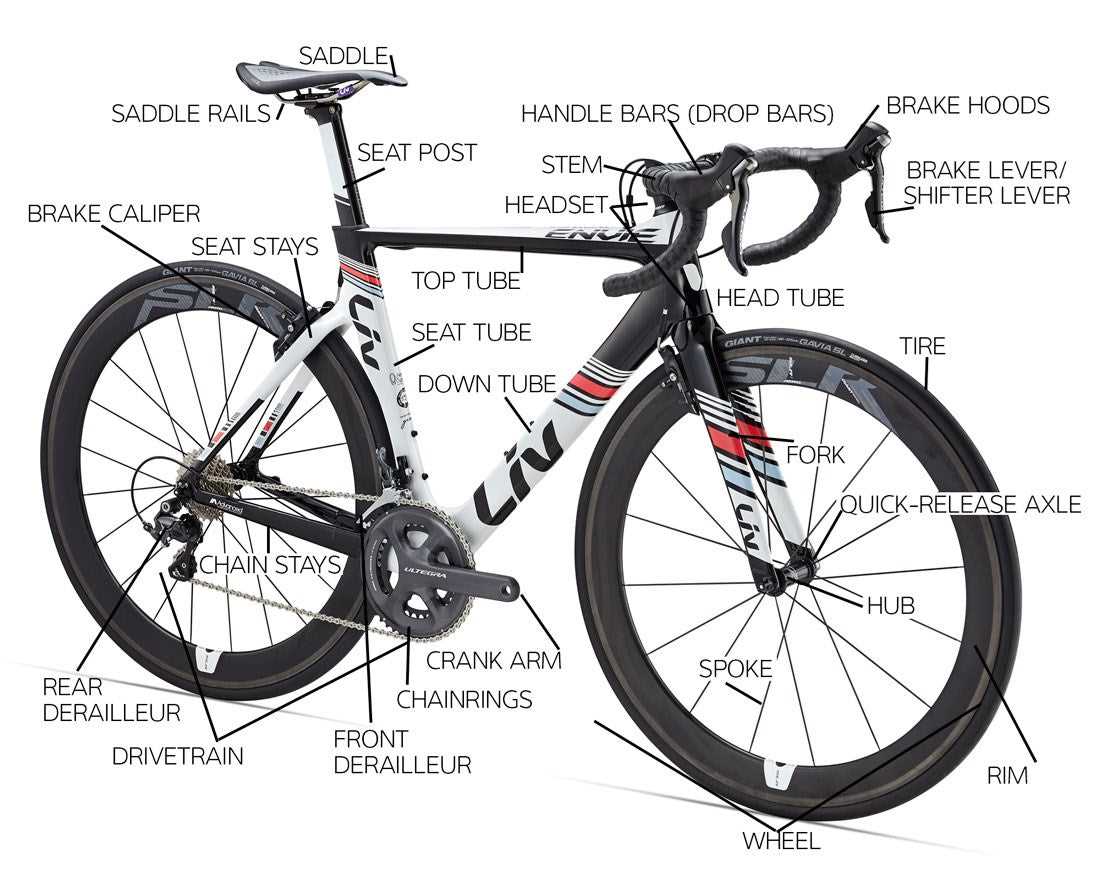
Understanding the relationship between visual representations and tangible constructions is essential for anyone interested in the intricacies of two-wheeled vehicles. While illustrations can provide clarity on components and their placements, the real-world assembly process often reveals nuances that aren’t captured in static images.
Visual guides serve as helpful tools, offering a blueprint for enthusiasts to follow. They outline the positioning and interaction of each element, allowing for a theoretical comprehension of the assembly. However, when one engages in the physical assembly, various challenges may arise that require adaptability and problem-solving skills, which diagrams may not fully anticipate.
Moreover, the experience of handling actual components adds a layer of understanding that illustrations alone cannot convey. The tactile feedback and the need to adjust based on fit and functionality are critical aspects of the assembly process. This hands-on experience often leads to a deeper appreciation of the mechanics involved.
In conclusion, while visual representations are invaluable in providing a foundational understanding, the reality of assembling a two-wheeled vehicle is a complex and enriching endeavor that demands both theoretical knowledge and practical skill.
Tools Needed for Bicycle Repairs
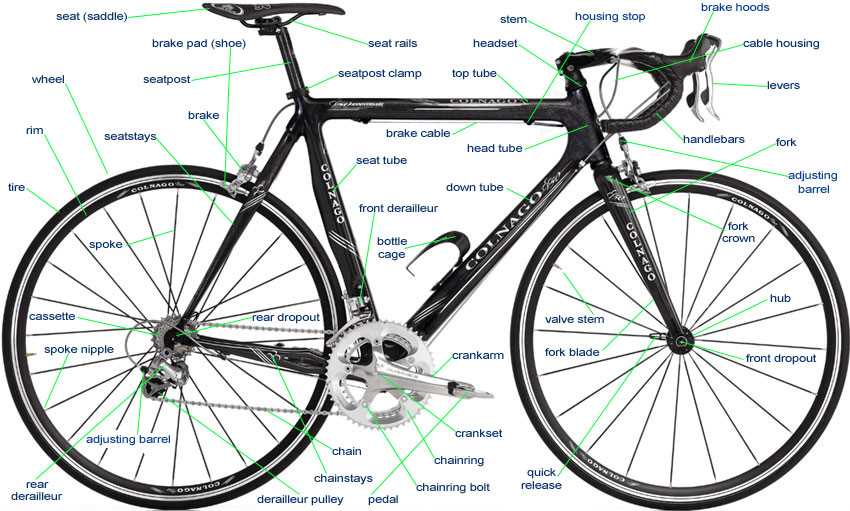
Having the right equipment is essential for effective maintenance and repair of your two-wheeled vehicle. Whether you are performing routine checks or tackling more complex issues, specific tools can significantly simplify the process and enhance your experience.
- Wrenches: Adjustable and fixed wrenches are crucial for loosening and tightening nuts and bolts.
- Screwdrivers: A set of both flat-head and Phillips screwdrivers will help with various components.
- Hex Keys: Also known as Allen wrenches, these are essential for many modern fittings.
- Tire Levers: These tools make it easier to remove and replace tires without damaging them.
- Patch Kit: Useful for repairing punctures, a patch kit can save you from being stranded.
Investing in these tools can lead to a smoother repair experience and extend the lifespan of your vehicle.
Maintenance Tips for Bicycle Parts
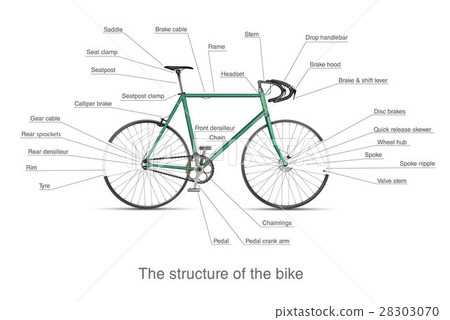
Proper upkeep of essential components can significantly enhance performance and longevity. Regular checks and timely interventions can prevent issues and ensure a smoother riding experience. Here are some vital suggestions to keep in mind.
Routine Inspections

Conducting frequent examinations of various elements is crucial. Look for signs of wear, such as fraying cables or uneven tire pressure. Addressing small problems before they escalate can save time and money.
Cleaning and Lubrication
Regular cleaning helps remove dirt and debris that can hinder functionality. Use appropriate cleaners and lubricants on moving parts to maintain efficiency and reduce friction. This practice not only improves performance but also extends the life of components.
Resources for Finding Bike Diagrams
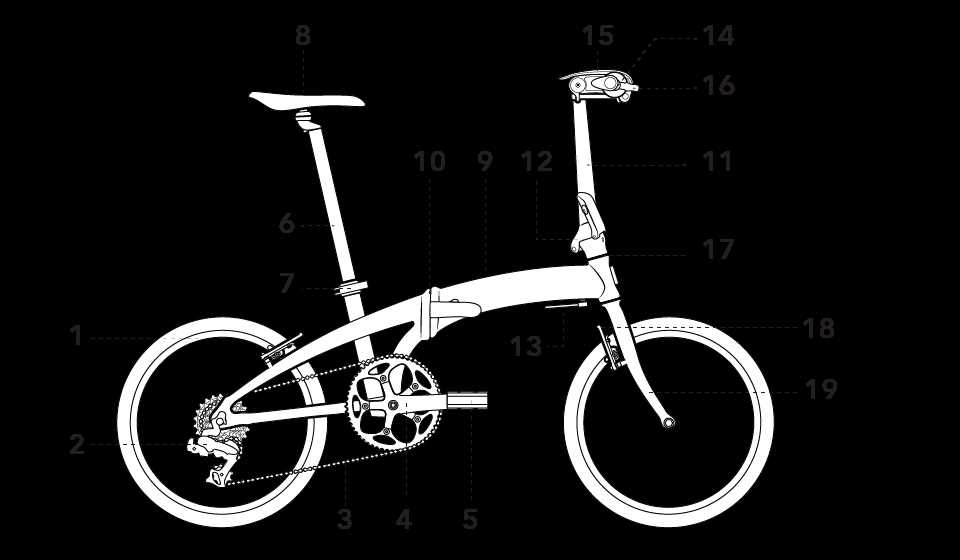

Accessing accurate visual representations is essential for enthusiasts and professionals alike. Various platforms provide valuable insights and resources to help individuals understand components and assemblies effectively.
Online Platforms
- Manufacturer Websites: Many brands offer detailed visuals and manuals.
- Community Forums: Engaging with fellow enthusiasts can yield unique resources.
- Educational Websites: Some sites focus on teaching technical skills, often featuring illustrations.
Printed Materials
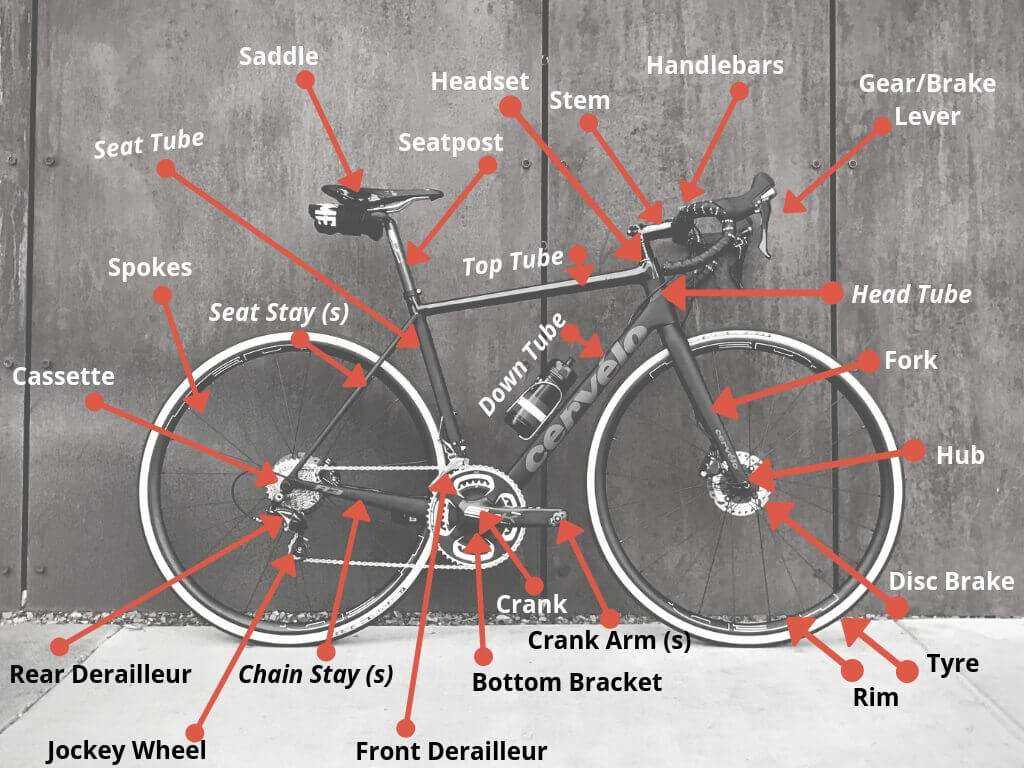
- Repair Manuals: Comprehensive guides that often include exploded views.
- Magazines: Specialty publications frequently contain feature articles with visuals.
- Books: Technical books provide in-depth information and illustrations.