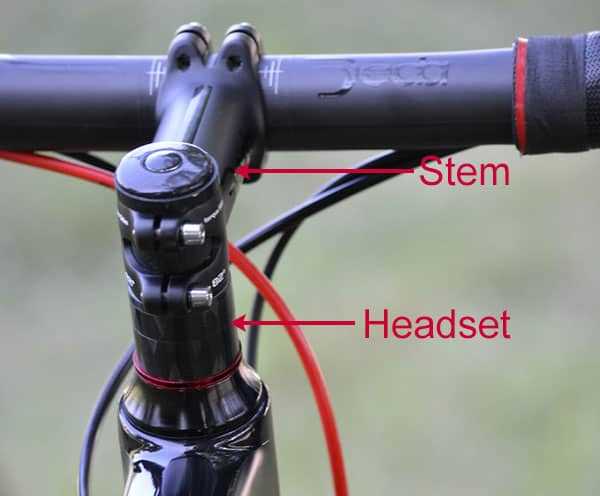
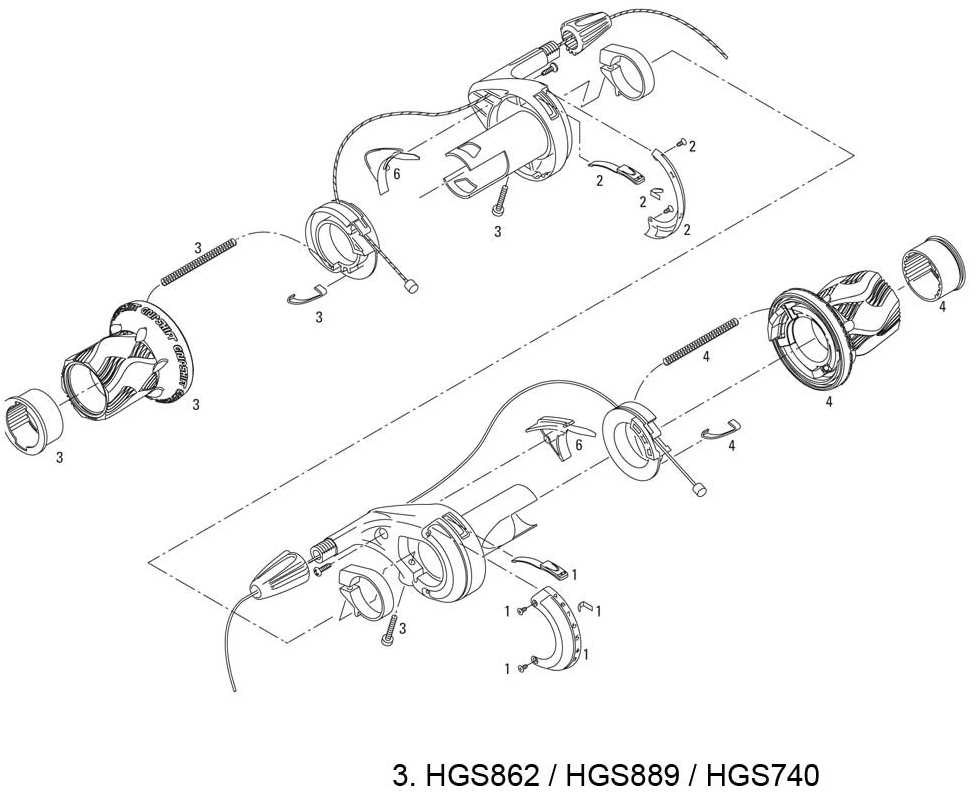
Understanding Bike Shifter Parts Diagram
Every mechanical system designed to control speed and performance relies on a combination of intricate elements working together. These components ensure smooth transitions and allow precise control during operation. In this section, we will explore how these mechanisms are structured and how each element contributes to a seamless experience.
Key components in this system are designed to ensure that adjustments are efficient and reliable. The ability to modify settings with precision is crucial, especially when operating under various conditions. By understanding the functionality of each part, one can maintain and optimize performance effectively.
Through this exploration, we will delve into the intricate workings of these mechanisms, highlighting the importance of each component in achieving smooth and responsive control.
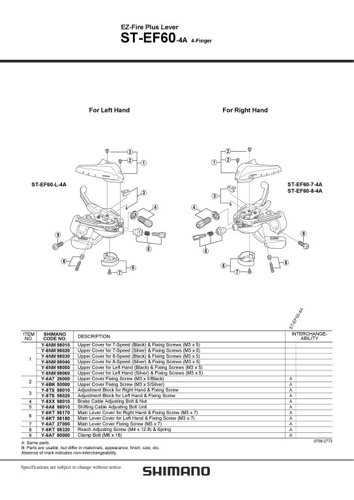
Comprehensive Guide to Bicycle Gear Mechanism
Understanding how a cycle’s gear system functions is essential for achieving smooth and efficient movement. This section provides an overview of the mechanical process that allows riders to adjust speed and control with ease.
Main Components of the Gear System
The system consists of several interconnected elements that work together to provide variable resistance and adaptability for different terrains. Below is a breakdown of the key components:
- Derailleur: Responsible for shifting the chain between different sprockets.
- Cassette: A set of gears attached to the rear wheel that offer varying levels of resistance.
- Chainrings: Front gears that interact with the chain to create tension for pedaling.
How the Mechanism Operates
The gear system operates through
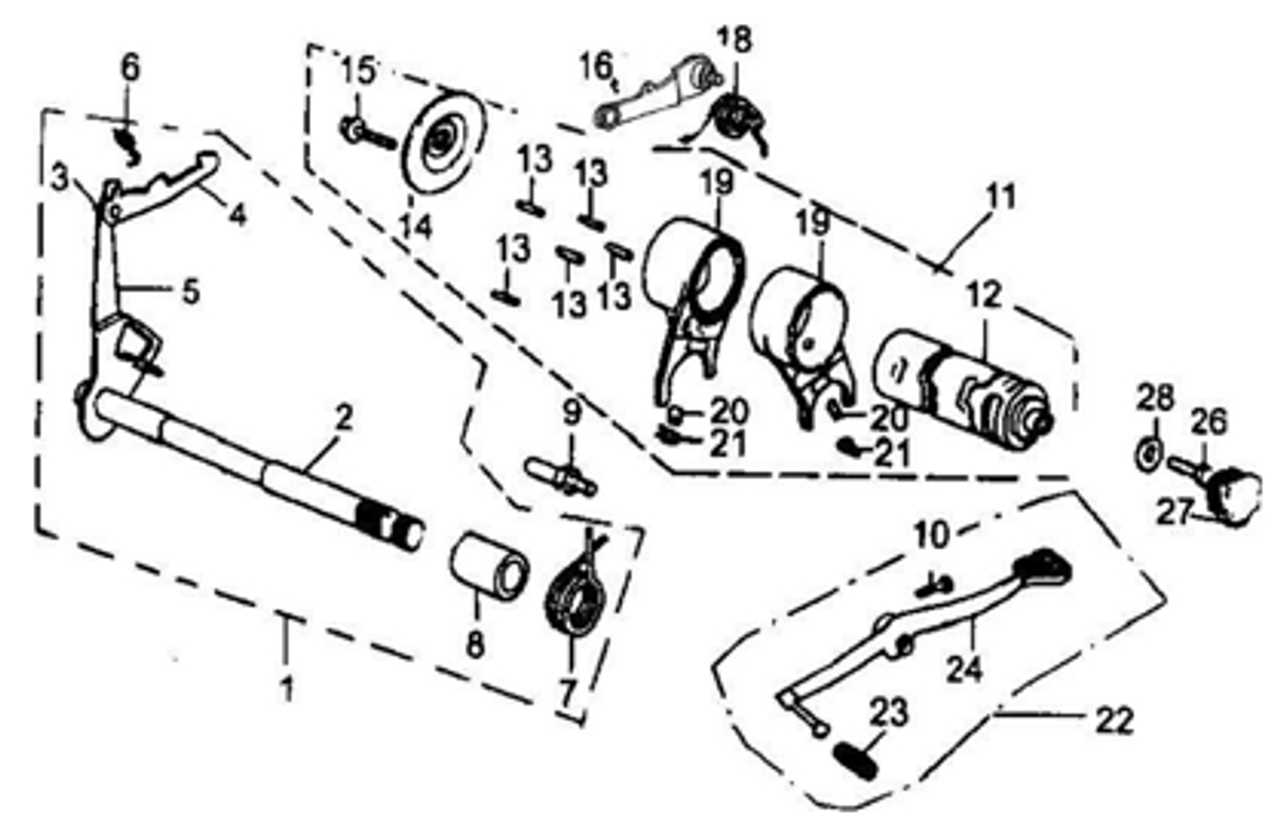
Understanding Bicycle Shifting Systems
Modern cycling requires a system that helps riders smoothly adjust their pedaling effort according to the terrain. These systems provide a way to change how force is applied, making riding more efficient and comfortable, whether on flat roads or challenging climbs. Learning how these mechanisms work is essential for anyone who wants to optimize their riding experience.
The Role of Gear Mechanisms
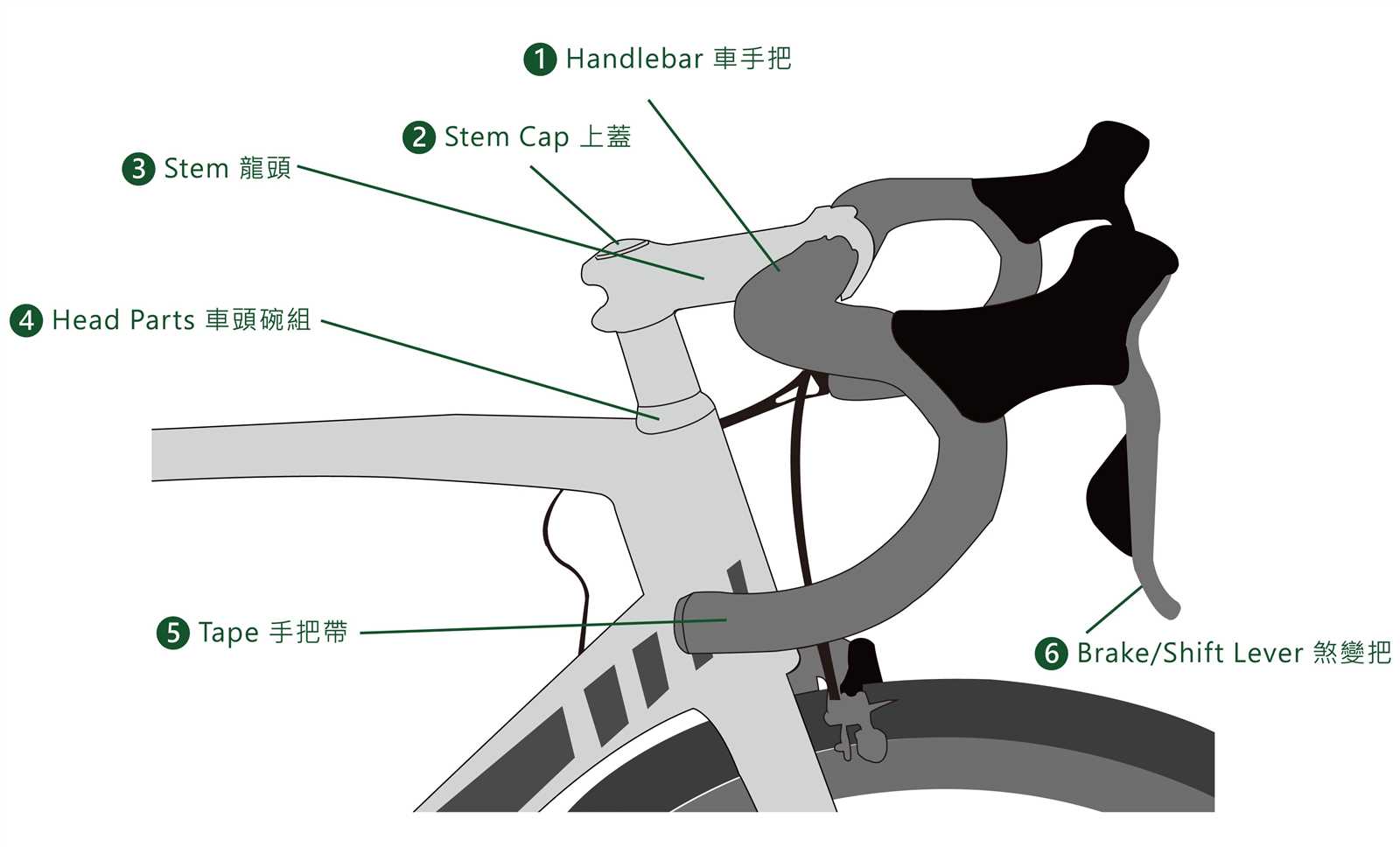
Gears play a crucial role in adapting the effort needed to move forward. They allow riders to increase or decrease resistance, helping manage energy and speed. Understanding the relationship between the different gears is key to mastering the control these systems offer.
Smooth Transitions for Effective Riding
A well-functioning shifting system ensures a seamless transition between resistance levels. Proper use can preven
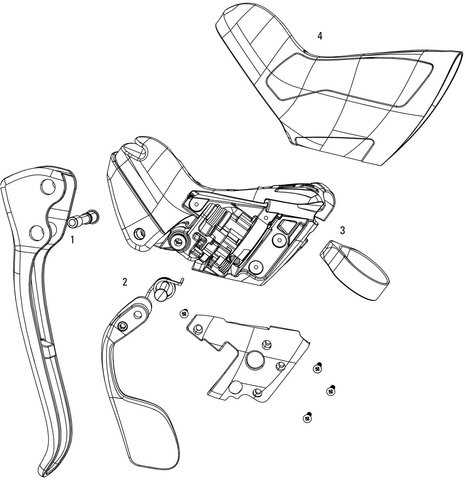
Main Components of Gear Shifters
The mechanism that allows smooth and efficient changes in speed relies on several interconnected elements. These elements work together to ensure a reliable transition between various levels of resistance, helping the user maintain control over different terrains.
Control Lever
The control lever is an essential part of this system, allowing the user to engage different speed settings. With a simple push or twist, it adjusts the tension, guiding the system to a new position
Types of Bike Gear Levers
Gear levers come in various forms, each designed to suit different riding preferences and mechanical systems. These controls allow cyclists to switch between different gears, providing an optimal riding experience based on terrain or speed. The design and functionality of these components vary, offering both simplicity and advanced control depending on the model.
Trigger Levers
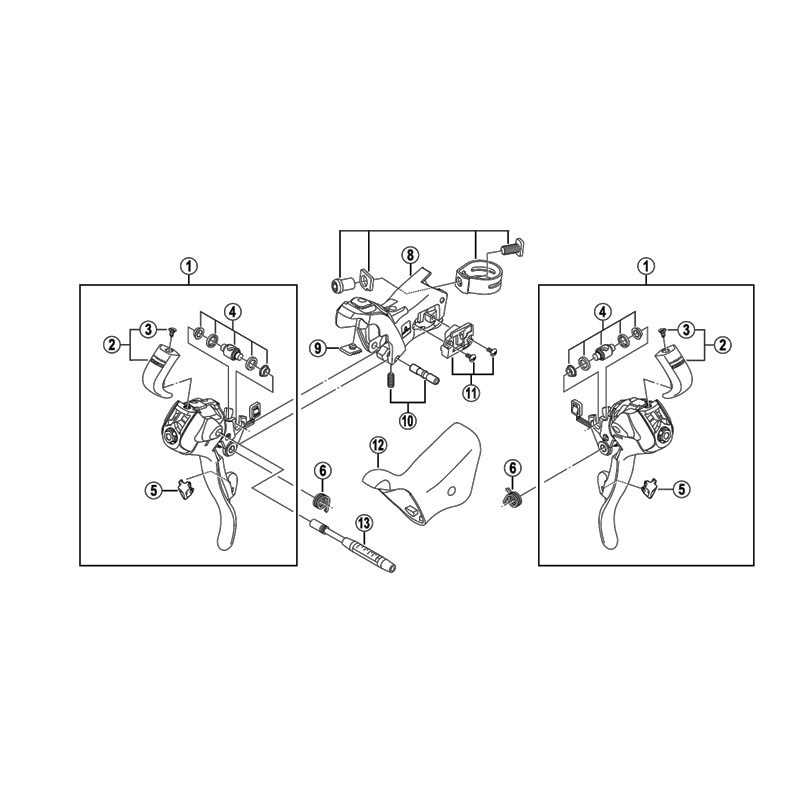
Trigger levers are popular for their precision and ease of use. With a simple push or pull of the levers, riders can quickly change gears. These are typically found in mountain and hybrid cycles, offering reliable performance in challenging conditions.
Twist Grips
Twist grips are another common option, known for their intuitive design. By rotating the grip on the handlebar, the user can easily adjust the gears. These are
Common Materials Used in Shifter Construction
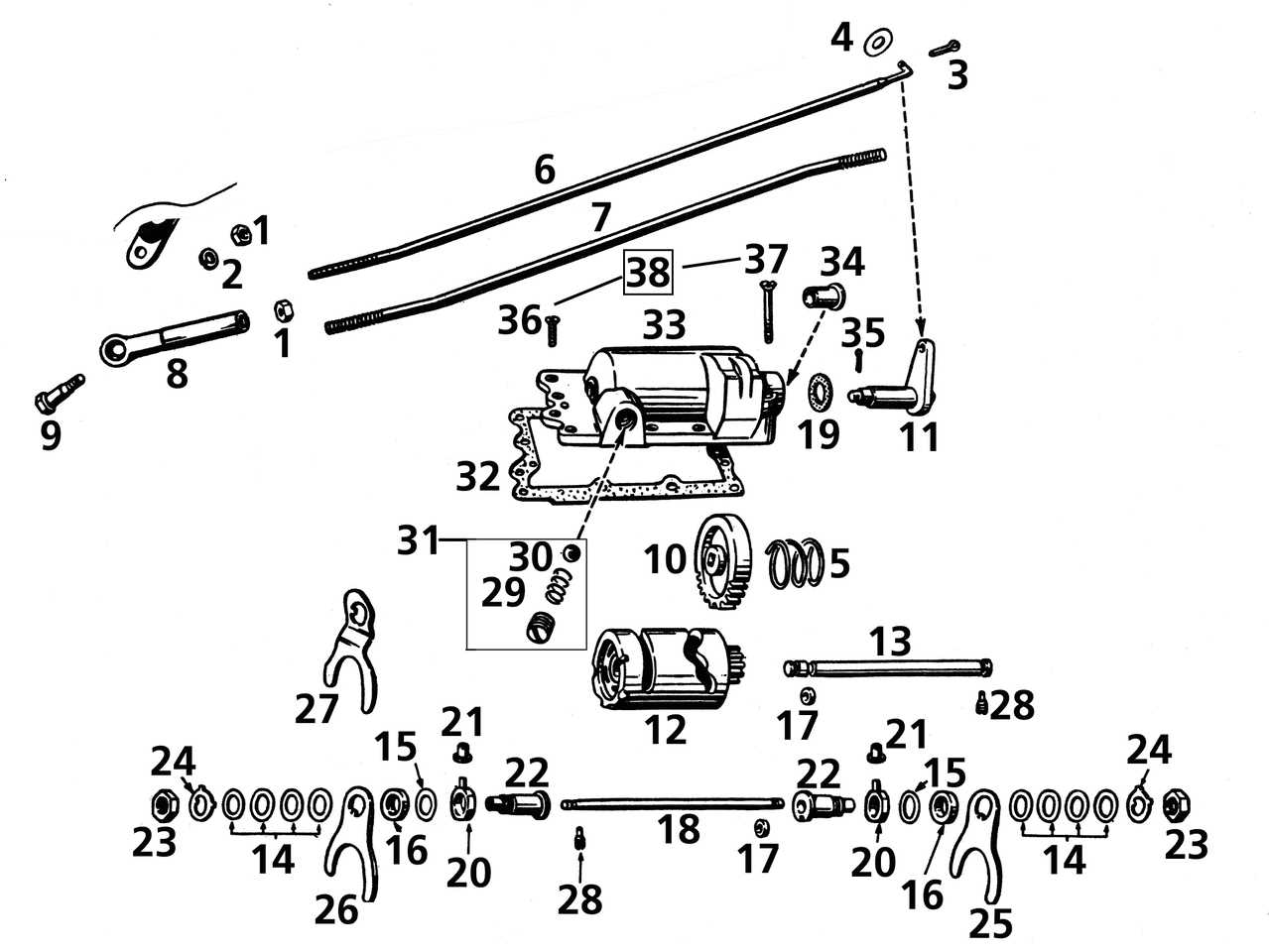
Various mechanisms designed for changing gear rely on a range of materials that provide both durability and smooth performance. These materials are selected for their ability to withstand frequent use, exposure to the elements, and wear over time, while maintaining efficiency and precision.
| Material | Properties | Advantages | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloy | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Long-lasting, minimal weight impact | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Steel | High strength, durable | How to Properly Adjust a Shifter
Achieving optimal performance from your transmission mechanism involves precise adjustments. This process ensures smooth transitions between gear settings, enhancing overall riding efficiency. Understanding the fundamental steps is crucial for maintaining the functionality of the shifting system. Begin by examining the cable tension. Too much slack can hinder shifting responsiveness, while excessive tension may prevent proper engagement. Adjust the barrel adjuster on the handle to fine-tune this aspect, allowing for seamless operation. Next, check the alignment of the derailleur. It should be positioned accurately in relation to the gears. If misaligned, it can lead to inaccurate shifting. Use a small screwdriver to adjust the limit screws, ensuring the mechanism operates within the intended range.
Finally, test the entire mechanism by shifting through all available settings. This will help identify any remaining issues, allowing for additional fine-tuning as needed. Regular maintenance and proper adjustments will prolong the life of your transmission system. Diagnosing Issues with Gear ChangesEnsuring smooth transitions between different speeds is crucial for optimal performance. When users encounter difficulties in shifting, it can lead to frustration and inefficiency. Understanding the common symptoms and their underlying causes can assist in troubleshooting these issues effectively. Common Symptoms of Gear Change ProblemsSeveral indicators may suggest complications with gear changes. These include unexpected slipping between speeds, difficulty in engaging the desired ratio, or unusual noises during shifting. Each of these signs can provide valuable insights into what might be malfunctioning. Troubleshooting TechniquesTo address these complications, start by examining the adjustment of the mechanism. Proper tension in the cable or chain is essential for reliable performance. Additionally, inspecting the alignment of components can reveal misalignments that might hinder proper operation. Regular maintenance can prevent many issues from arising in the first place. Upgrading and Replacing Gear Shifters
Improving and changing transmission control mechanisms can significantly enhance your cycling experience. Whether you are looking to boost performance, ensure smoother transitions, or simply replace worn-out components, understanding the process is essential for any enthusiast. This section will guide you through the key considerations and steps involved in upgrading and replacing these crucial elements. Choosing the Right ComponentsWhen selecting new transmission controls, it’s important to consider compatibility with your existing setup. Ensure that the new mechanisms match the specifications of your current drivetrain. Additionally, consider the intended use; different styles are designed for various types of terrain and riding conditions. Installation StepsBegin by removing the old components carefully, ensuring not to damage surrounding areas. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the new mechanisms, paying attention to alignment and secure fitting. Once installed, test the functionality to ensure smooth operation. Regular maintenance will prolong the lifespan of these components, providing a better riding experience. Comparing Mechanical and Electronic ShiftersIn the world of cycling, the choice between traditional and modern shifting mechanisms plays a crucial role in performance and user experience. Each system offers distinct advantages and drawbacks that cater to different preferences and riding styles. Advantages of Traditional Systems
Conventional systems are often praised for their simplicity and reliability. These mechanisms typically require minimal maintenance and can function effectively in various conditions. Additionally, many enthusiasts appreciate the tactile feedback provided during operation, allowing for precise gear changes. Benefits of Modern SystemsOn the other hand, contemporary systems offer enhanced convenience and precision. The automated features reduce the physical effort required for shifting, making them ideal for longer rides. Furthermore, advancements in technology have led to improvements in battery life and overall performance, which can enhance the overall cycling experience.
|