Understanding the Essential Components of E-Bike Diagrams

In the world of electric cycles, a comprehensive grasp of the essential elements is crucial for enthusiasts and newcomers alike. These intricate mechanisms work together to create a seamless riding experience, enhancing both performance and convenience.
Every segment plays a vital role in ensuring efficiency and reliability. From the propulsion system to the control mechanisms, each component contributes to the overall functionality, enabling riders to navigate diverse terrains with ease.
As we explore these fundamental elements, it becomes clear how they interact and support one another. Gaining insight into this structure not only enriches one’s knowledge but also paves the way for informed choices and enhancements in the realm of electric mobility.
Essential Components of E-Bikes
Electric cycles are composed of several crucial elements that work harmoniously to deliver a smooth and efficient riding experience. Understanding these fundamental components helps users appreciate the technology behind modern transportation solutions. Each element plays a significant role in enhancing performance, comfort, and overall functionality.
Power Source
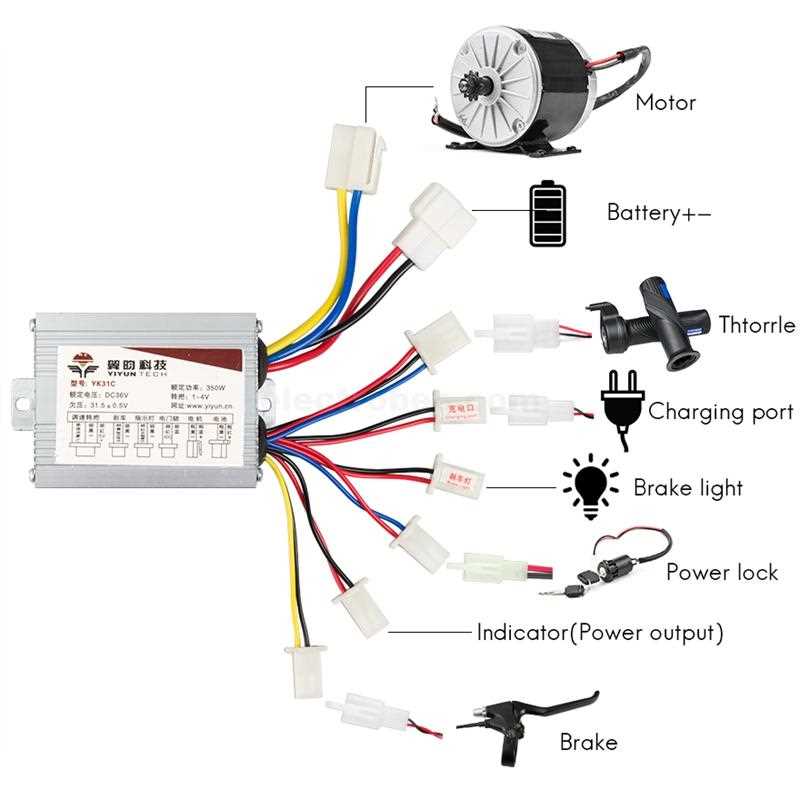
The heart of any electric vehicle is its power source. Typically, this consists of rechargeable batteries that store energy, allowing riders to travel longer distances without physical exertion. The capacity and efficiency of the battery significantly influence range and performance, making it a vital consideration for anyone looking to invest in an electric cycle.
Propulsion System
Equally important is the propulsion system, which often includes a motor that provides the necessary force to assist the rider. This component can be located in various positions, such as the front wheel, rear wheel, or even in the crankset. The choice of motor type and placement affects handling and the overall riding experience, enabling cyclists to navigate diverse terrains with ease.
Understanding E-Bike Battery Types
In the realm of electric transportation, the energy source plays a pivotal role in determining performance and efficiency. Different types of power storage solutions each come with unique characteristics that affect range, charging time, and overall user experience. A comprehensive understanding of these energy systems is essential for making informed decisions when selecting an electric vehicle.
Common Types of Energy Storage
Among the prevalent options, lithium-ion batteries stand out due to their lightweight design and high energy density. They are widely favored for their longevity and rapid charging capabilities. In contrast, lead-acid batteries, while heavier and less efficient, can offer a lower initial cost, making them a consideration for budget-conscious users. Nickel-metal hydride batteries present another alternative, providing a balance between performance and cost but with a shorter lifespan compared to lithium variants.
Factors to Consider
When choosing an energy source, several factors come into play. Capacity indicates how much energy can be stored, directly impacting the distance covered on a single charge. Weight affects the overall maneuverability of the vehicle, while charging speed determines how quickly one can return to the road. Understanding these elements will enable users to align their needs with the appropriate energy storage solution.
Motor Varieties in Electric Bicycles
In the realm of electrified two-wheeled vehicles, understanding the different types of propulsion systems is essential for enthusiasts and users alike. These systems significantly influence performance, efficiency, and overall riding experience. Exploring the nuances of these variations can help riders make informed choices tailored to their preferences.
Hub Motors
Hub motors are commonly found in many models, offering simplicity and ease of installation. Positioned in the wheel hub, they provide direct power to the wheels, ensuring a smooth ride. This type is often favored for urban commuting due to its stealthy operation and low maintenance needs.
Mid-Drive Motors
On the other hand, mid-drive motors are integrated into the bike’s frame, delivering power directly to the crankshaft. This design enhances weight distribution and allows for better climbing capabilities, making it an ideal choice for off-road and hilly terrain. Riders seeking an ultimate balance of performance and handling might find mid-drive systems particularly appealing.
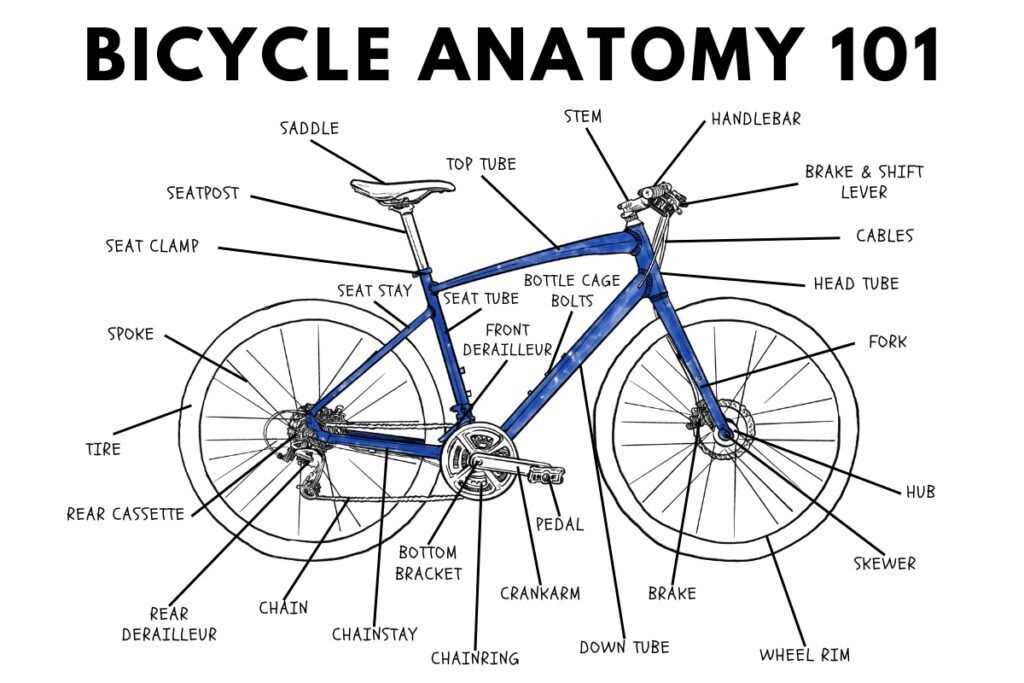
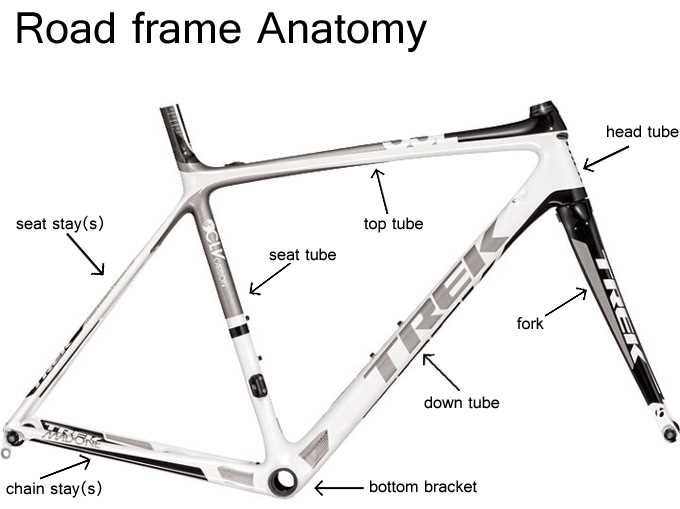
Frames: Choosing the Right Material
When selecting a structure for your electric two-wheeler, the choice of material plays a crucial role in performance, durability, and comfort. Each option has its own advantages and limitations, making it essential to understand how these factors align with your riding style and needs.
Here are some common materials used for crafting structures:
- Aluminum: Lightweight and resistant to corrosion, aluminum is a popular choice for many riders. It provides a good balance between strength and weight, making it ideal for urban commuting and recreational use.
- Carbon Fiber: Known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, carbon fiber offers superior performance and shock absorption. However, it can be more expensive and less forgiving when it comes to impacts.
- Steel: Renowned for its durability and repairability, steel structures provide a comfortable ride due to their ability to absorb vibrations. They may be heavier, but they are often favored for touring and long-distance travel.
- Titanium: This material combines the best of both worlds–lightweight and incredibly strong. Though typically pricier, titanium offers excellent longevity and a smooth ride, appealing to enthusiasts looking for premium quality.
When making a decision, consider factors such as weight, riding conditions, and personal budget. Each material type caters to different preferences and styles, so it’s vital to align your choice with your specific requirements.
Importance of E-Bike Controllers
The controller serves as the brain of an electric vehicle, playing a crucial role in managing various functions and ensuring smooth operation. It interprets signals from the user and other components, translating them into precise actions that enhance the riding experience.
Key Functions of E-Bike Controllers
- Power Management: Efficiently regulates energy from the battery to the motor, optimizing performance and extending range.
- Speed Control: Adjusts the motor output based on the rider’s input, allowing for seamless acceleration and deceleration.
- Safety Features: Incorporates mechanisms such as over-current protection, preventing potential damage to components.
- Communication: Facilitates interaction between various parts, ensuring they work harmoniously together.
Impact on Riding Experience

A well-designed controller can significantly enhance the overall experience for the user. By providing responsive handling and intuitive feedback, it contributes to:
- Improved Efficiency: Ensures energy is used wisely, leading to longer trips.
- Enhanced Control: Offers precise adjustments for different terrains and conditions.
- Increased Comfort: Minimizes abrupt changes in power delivery, making rides smoother.
In summary, the significance of the controller cannot be overstated, as it is essential for ensuring reliability, efficiency, and enjoyment in electric mobility solutions.
Braking Systems for Electric Bikes
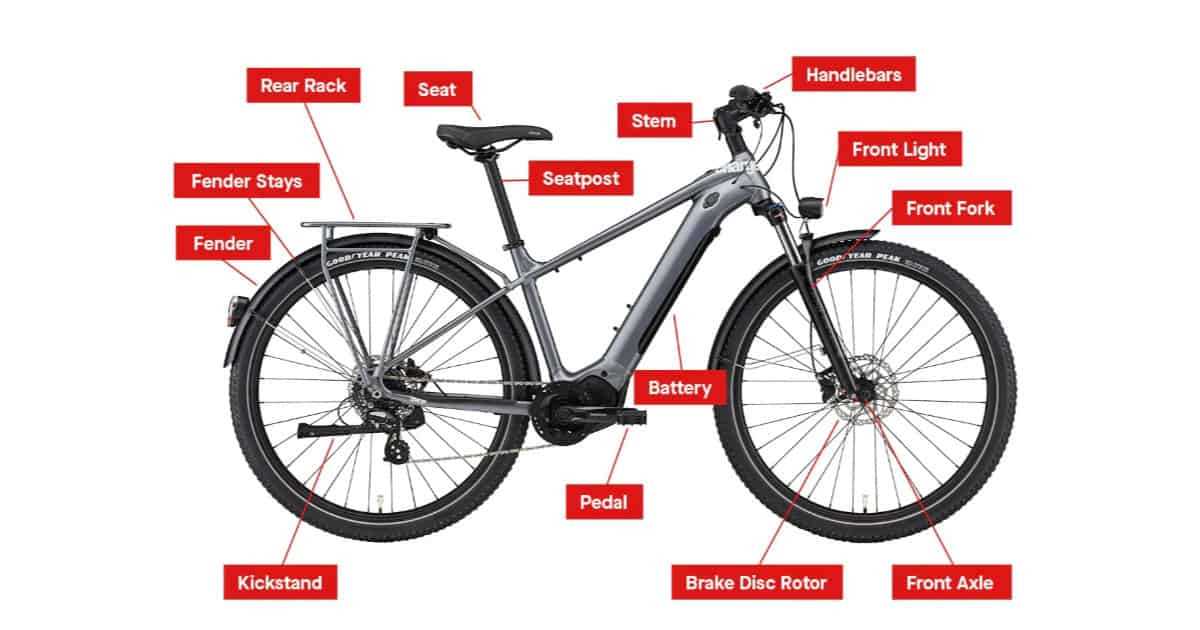
Effective stopping mechanisms are crucial for ensuring safety and performance in electric two-wheelers. These systems are designed to provide reliable deceleration while accommodating the unique demands of electric propulsion.
There are several types of stopping systems commonly utilized:
- Disc Brakes: Known for their excellent stopping power and heat dissipation.
- Drum Brakes: These provide consistent performance in various weather conditions.
- Regenerative Braking: This innovative approach recovers energy during deceleration, enhancing overall efficiency.
Each type offers distinct advantages, making it essential to choose based on specific riding needs and conditions.
Wheels and Tires: Key Features
The significance of wheels and tires in electric cycles cannot be overstated, as they serve as the primary contact points with the terrain. Their design and construction influence performance, comfort, and overall riding experience. Understanding their essential characteristics is crucial for optimizing functionality and safety.
Material and Construction
The choice of materials affects both weight and durability. Aluminum and carbon fiber are popular for their strength-to-weight ratio, while steel offers robustness at the expense of weight. Tire construction also varies, with options like tubeless systems providing better puncture resistance.
Tread Patterns and Sizes
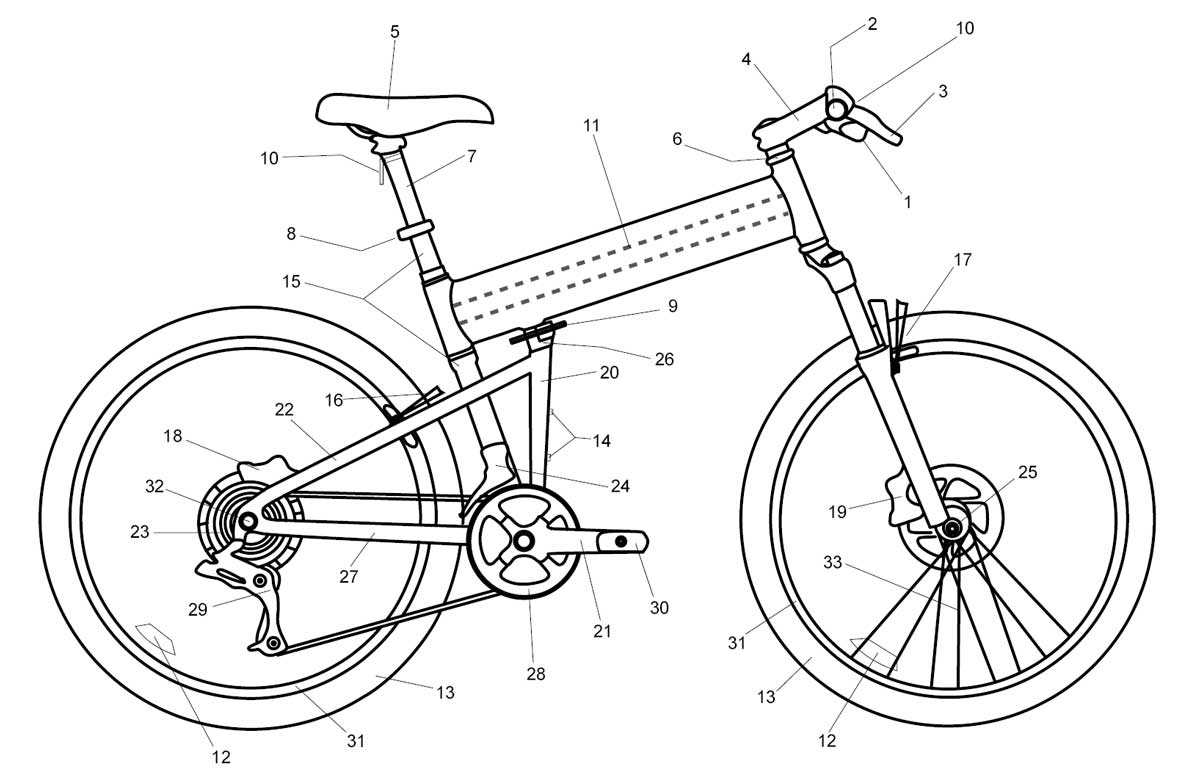
Tread patterns play a pivotal role in traction and control. Knobby designs excel in off-road conditions, while slick tires are ideal for urban environments. Additionally, the size of both wheels and tires affects acceleration, stability, and comfort, making it essential to choose wisely based on intended use.
Suspension Options for Comfort
When it comes to enhancing the riding experience, selecting the right suspension system can significantly impact overall comfort. Various types of systems are designed to absorb shocks and vibrations, providing a smoother journey over diverse terrains. Understanding the available options allows users to make informed decisions tailored to their needs.
| Type of Suspension | Advantages | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Rigid | Simple design, low maintenance, lightweight | Less shock absorption, may cause discomfort on rough surfaces |
| Hardtail | Improved stability, efficient power transfer | Limited rear suspension, less comfort on uneven terrain |
| Full Suspension | Superior shock absorption, increased traction, enhanced comfort | Heavier, more complex maintenance, higher cost |
| Air Suspension | Adjustable pressure for different conditions, lightweight | Requires regular maintenance, potential for leaks |
| Spring Suspension | Consistent performance, reliable under heavy loads | Can be heavier, less adjustable compared to air systems |
Each suspension type offers unique benefits and challenges. The choice depends on riding style, terrain, and personal comfort preferences, ultimately enhancing the overall experience.
Lighting Systems for Safety
Effective illumination is crucial for enhancing visibility and ensuring the safety of riders during low-light conditions. A well-designed lighting setup not only helps in navigating roads but also makes a significant difference in being seen by others. Various options exist to cater to diverse needs and preferences, providing both functionality and security.
Types of Illumination Solutions
- Front Lights: Essential for illuminating the path ahead, these lights help riders spot obstacles and hazards early.
- Rear Lights: Designed to increase visibility from behind, they alert other road users to the presence of a rider.
- Reflective Accessories: Adding reflective materials to clothing or gear enhances visibility without requiring power.
- Integrated Systems: Some modern vehicles come with built-in lighting that synchronizes with other safety features.
Features to Consider
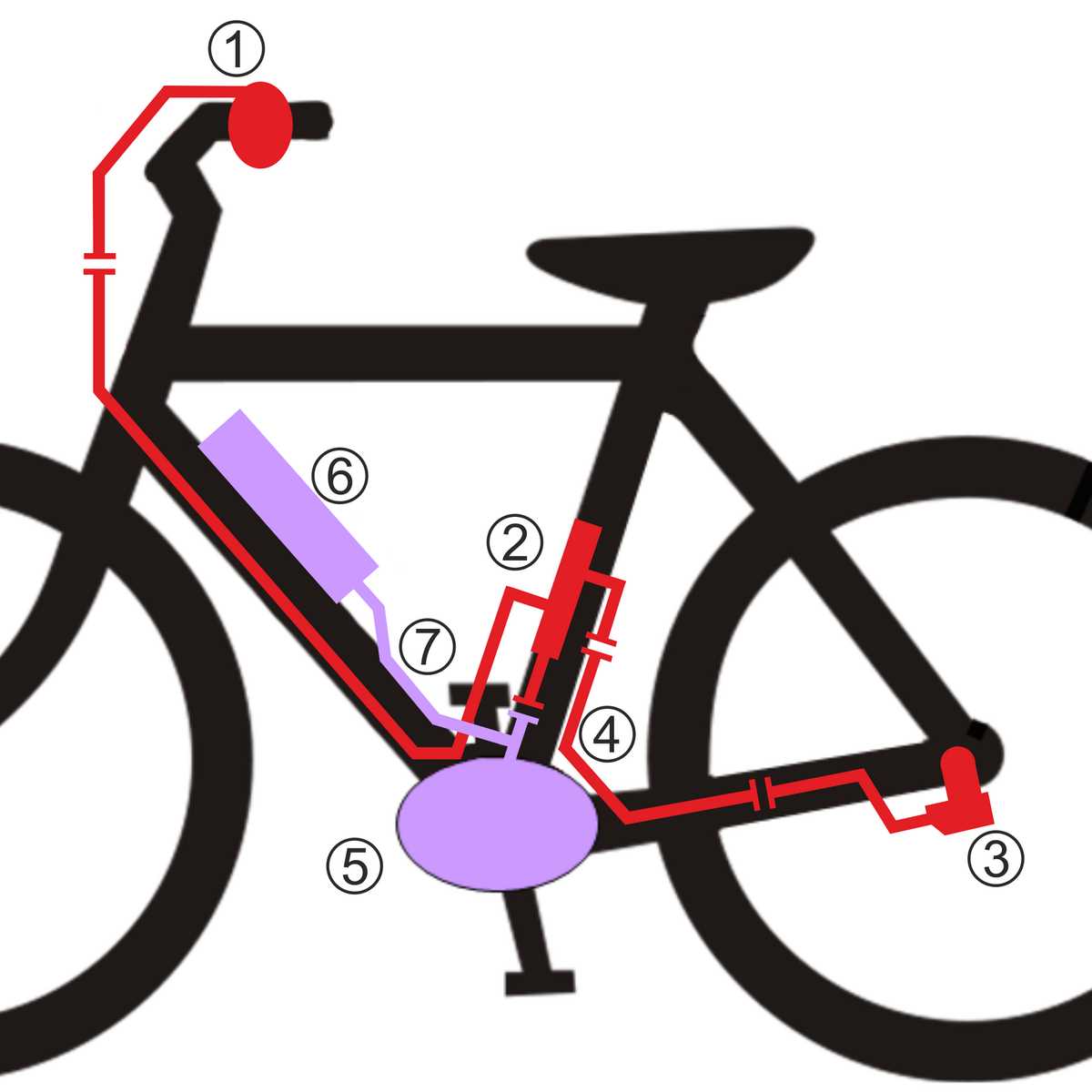
- Brightness Levels: Opt for adjustable brightness settings to adapt to varying conditions.
- Battery Life: Ensure that the power source lasts long enough for your typical journeys.
- Mounting Options: Look for flexible mounting systems that allow easy installation and removal.
- Weather Resistance: Choose durable solutions that can withstand different weather conditions.
Investing in a reliable lighting system enhances safety and confidence for all riders. Proper visibility contributes significantly to preventing accidents and ensuring a more enjoyable experience on the road.
Pedal Assist Mechanisms Explained
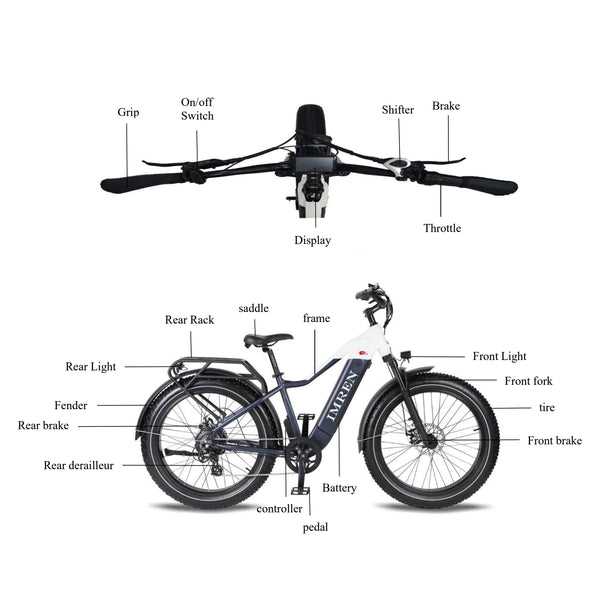

Understanding the functionality of various support systems in electric vehicles enhances the riding experience, offering a seamless blend of human effort and technological aid. These mechanisms are designed to amplify the user’s input, making journeys more efficient and enjoyable.
Types of Assist Systems
There are several prominent types of assistance systems, each with unique attributes and advantages. These systems can be categorized based on their operational characteristics and responsiveness to rider input.
| System Type | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Torque Sensor | Measures the force applied to the pedals and adjusts assistance accordingly. | Provides a natural feel, mimicking traditional cycling. |
| Cadence Sensor | Focuses on the pedaling speed to determine the level of support. | Easy to use, suitable for varied terrain. |
| Combined System | Utilizes both torque and cadence measurements for optimal support. | Offers a balanced and responsive riding experience. |
Conclusion
Pedal assist technologies represent a significant advancement in transportation, encouraging longer journeys and reducing fatigue. By delving into the specifics of each mechanism, users can select the ideal system for their needs, ensuring the ultimate riding experience.
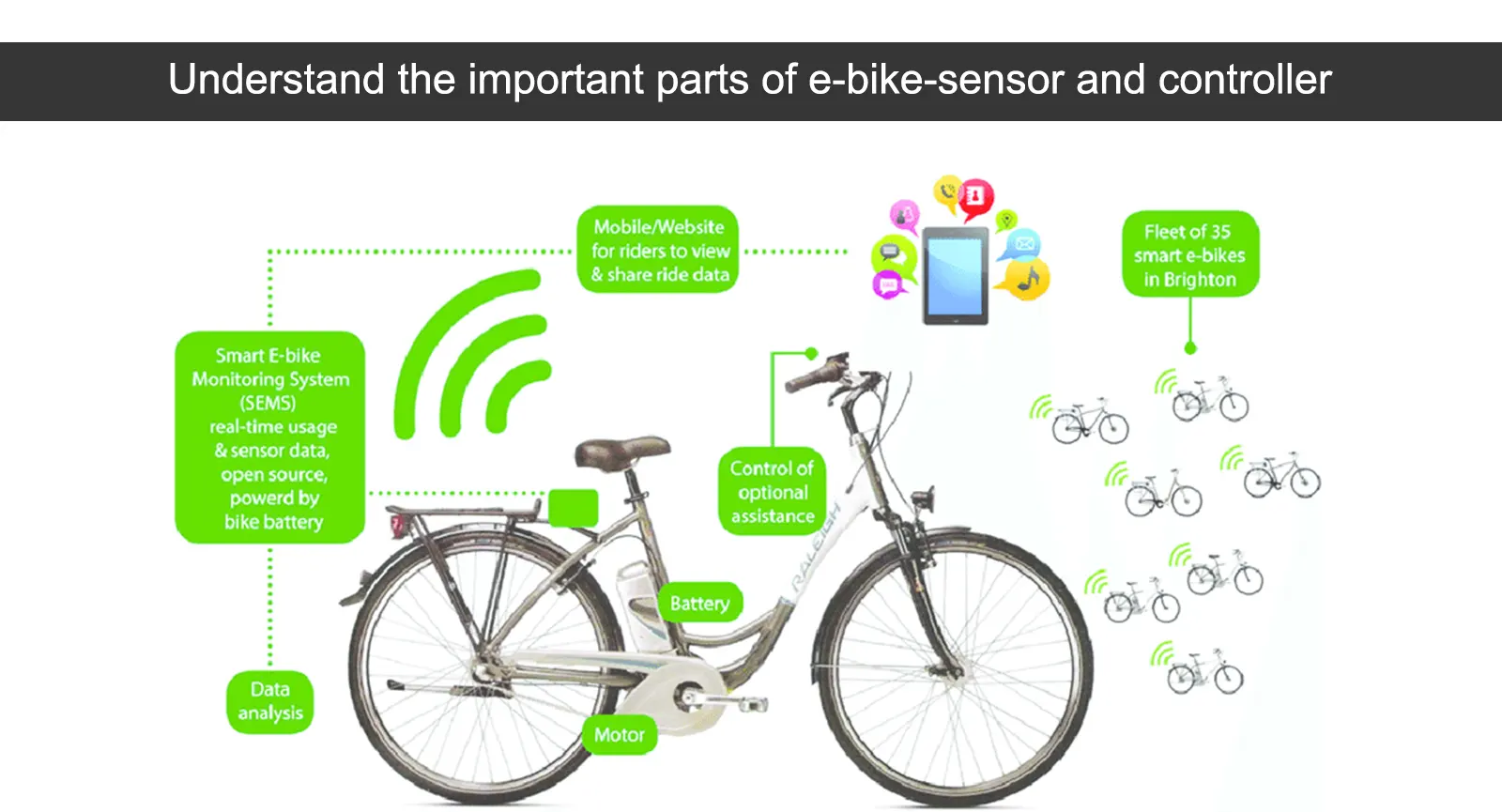
Integrating Smart Technology in E-Bikes
The fusion of intelligent systems within electric vehicles has revolutionized the way users interact with their rides. This advancement enhances not only performance but also safety and convenience, offering a more immersive experience for riders.
Enhanced Connectivity
Modern electric rides now feature seamless connectivity, allowing users to link their devices for navigation, fitness tracking, and real-time diagnostics. This integration provides valuable insights into performance and helps in maintaining optimal conditions.
Smart Safety Features
Incorporating advanced safety technologies such as automatic lights, anti-theft systems, and collision alerts significantly boosts user confidence. These innovations contribute to a safer journey, ultimately transforming the perception of riding in urban environments.