Diagram of Human Body Parts with Names

Understanding the various components of the human figure is essential for numerous fields, including medicine, biology, and art. This section provides a comprehensive overview of the significant elements that constitute our physical structure. By recognizing these vital elements, individuals can enhance their knowledge of human physiology and improve their overall health literacy.
In addition to fostering a deeper appreciation for our own anatomy, this visual representation serves as a valuable resource for students and professionals alike. Whether for educational purposes or personal interest, familiarity with these essential structures promotes a greater awareness of how our bodies function. Knowledge of anatomical features is not only beneficial for those pursuing careers in health-related fields but also enriches the understanding of the intricate design of the human form.
As you explore the various components depicted in this illustration, take a moment to reflect on the remarkable complexity and harmony that exists within the human figure. Each element plays a unique role, contributing to the overall functionality and movement of our physical being.
This section aims to explore the complexity and functionality of various components that make up the human anatomy. Through a structured approach, we will delve into different categories, enhancing comprehension of each element’s significance and interrelation within the entire system.
- Overview of Human Anatomy
- Essential Structures and Their Functions
- Categories of Major Organ Systems
- Understanding Musculoskeletal Framework
- Overview of Circulatory Mechanisms
- Exploring Respiratory Functions
- Nervous System Insights
- Digestive Process Explanation
- Understanding Sensory Mechanisms
- Integration of Endocrine Signals
- Role of Immune Defenses
Anatomy Overview and Importance
Understanding the structure and function of living organisms is essential for various fields, including medicine, biology, and health sciences. This knowledge allows for better diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases, as well as a deeper appreciation for the complexities of life. A comprehensive grasp of biological systems is fundamental for students, healthcare professionals, and researchers alike.
Significance in Medical Science
A thorough understanding of biological structures is crucial in medical science. It aids healthcare providers in diagnosing conditions, developing treatment plans, and performing surgical procedures. Knowledge of how different systems interact helps in identifying the root causes of ailments and implementing effective interventions.
Educational Value
Studying the arrangement and functions of living entities provides invaluable insights for students and researchers. It lays the groundwork for advanced studies in related disciplines and promotes critical thinking and analytical skills essential for scientific inquiry.
| Field | Importance |
|---|---|
| Medicine | Diagnosis and treatment planning |
| Biology | Understanding life processes |
| Education | Foundation for advanced studies |
Major Body Systems Explained
This section delves into the essential systems that facilitate the functioning of living organisms. Each system plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and homeostasis, working in harmony with others to support various physiological processes. Understanding these intricate networks can enhance one’s knowledge of how the organism operates and responds to different stimuli.
The circulatory system is responsible for transporting vital substances, such as oxygen and nutrients, throughout the organism. The respiratory system works closely with it to ensure efficient gas exchange, allowing cells to perform their functions effectively. Additionally, the digestive system processes food to extract necessary energy and nutrients, while the excretory system removes waste products to maintain internal balance.
The nervous system coordinates actions and responses, acting as the body’s control center. Simultaneously, the musculoskeletal system provides structure and enables movement, essential for interaction with the environment. Each of these systems plays a distinctive role, collectively contributing to the organism’s survival and well-being.
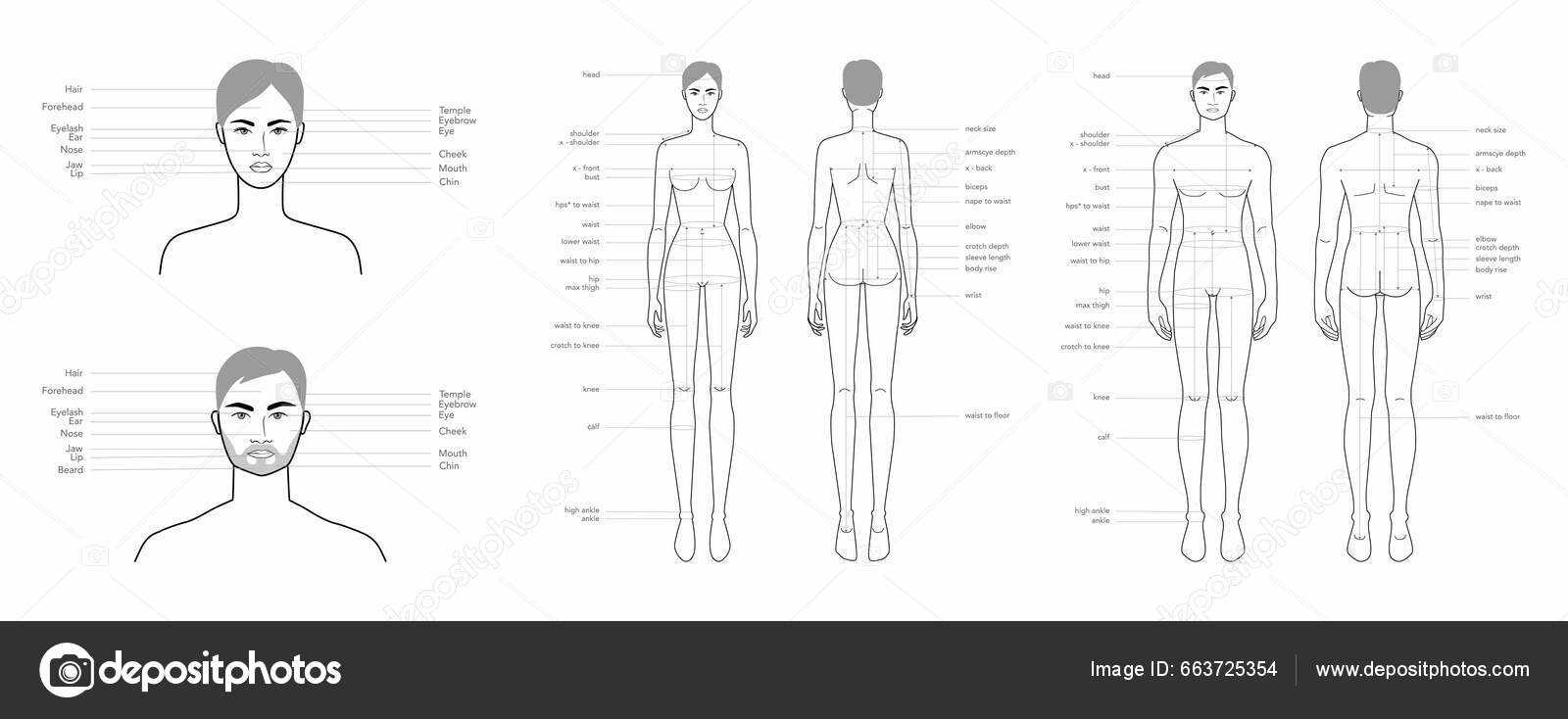
Head and Neck Structure
The head and neck region plays a crucial role in human anatomy, housing essential components that support various functions. This area is intricately designed to facilitate movement, protect vital organs, and enable communication. Understanding its complexity is fundamental to grasping how these elements interact and contribute to overall well-being.
The head comprises various structures, including the skull, which encases the brain, and facial features that are vital for expression and sensory perception. The neck serves as a vital conduit, linking the head to the torso while supporting important arteries, veins, and nerves.
Key structures within this region include the cervical spine, which provides stability and flexibility, and the larynx, essential for voice production. Overall, the harmonious interplay of these elements is vital for many daily activities, from speaking to breathing.
Upper Limb Components
The upper limb is a complex structure essential for various functions and activities. It encompasses a range of elements that work together to enable movement, manipulation, and interaction with the environment. Understanding these components is crucial for recognizing their roles in daily tasks and overall physical performance.
This section will explore the main elements of the upper limb, including the shoulder region, forearm, and hand. Each component has its unique characteristics and functions, contributing to the versatility and adaptability of this part of the anatomy. By examining these structures, one can appreciate the intricate design and functionality of the upper limb.
Torso and Its Functions
The torso serves as a vital central structure, housing essential organs and providing support for various bodily systems. It plays a key role in protecting the internal mechanisms while facilitating numerous functions critical to overall health and well-being.
This section delves into the primary functions of the torso, highlighting its importance in both movement and vital processes.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Protection | Safeguards vital organs such as the heart and lungs. |
| Support | Provides structural support for the upper body and aids in posture. |
| Movement | Facilitates motion through muscles connected to the rib cage and spine. |
| Respiration | Enables breathing by expanding and contracting during inhalation and exhalation. |
Lower Limb Anatomy

The lower limb is a complex structure designed for mobility and stability, playing a crucial role in locomotion and support. It consists of various components that work together seamlessly to enable a wide range of movements.
Understanding the anatomy of this region is essential for comprehending its function and common conditions that may affect it. The main components include:
- Thigh
- Knee
- Leg
- Ankle
- Foot
Each of these segments consists of multiple structures that contribute to their overall functionality. Key elements include:
- Muscles: Responsible for movement and stability.
- Bones: Provide support and structure.
- Joints: Allow for flexibility and range of motion.
- Tendons: Connect muscles to bones.
- Ligaments: Stabilize joints by connecting bones.
Grasping the layout and interrelation of these elements is vital for those studying human anatomy or addressing related health issues.
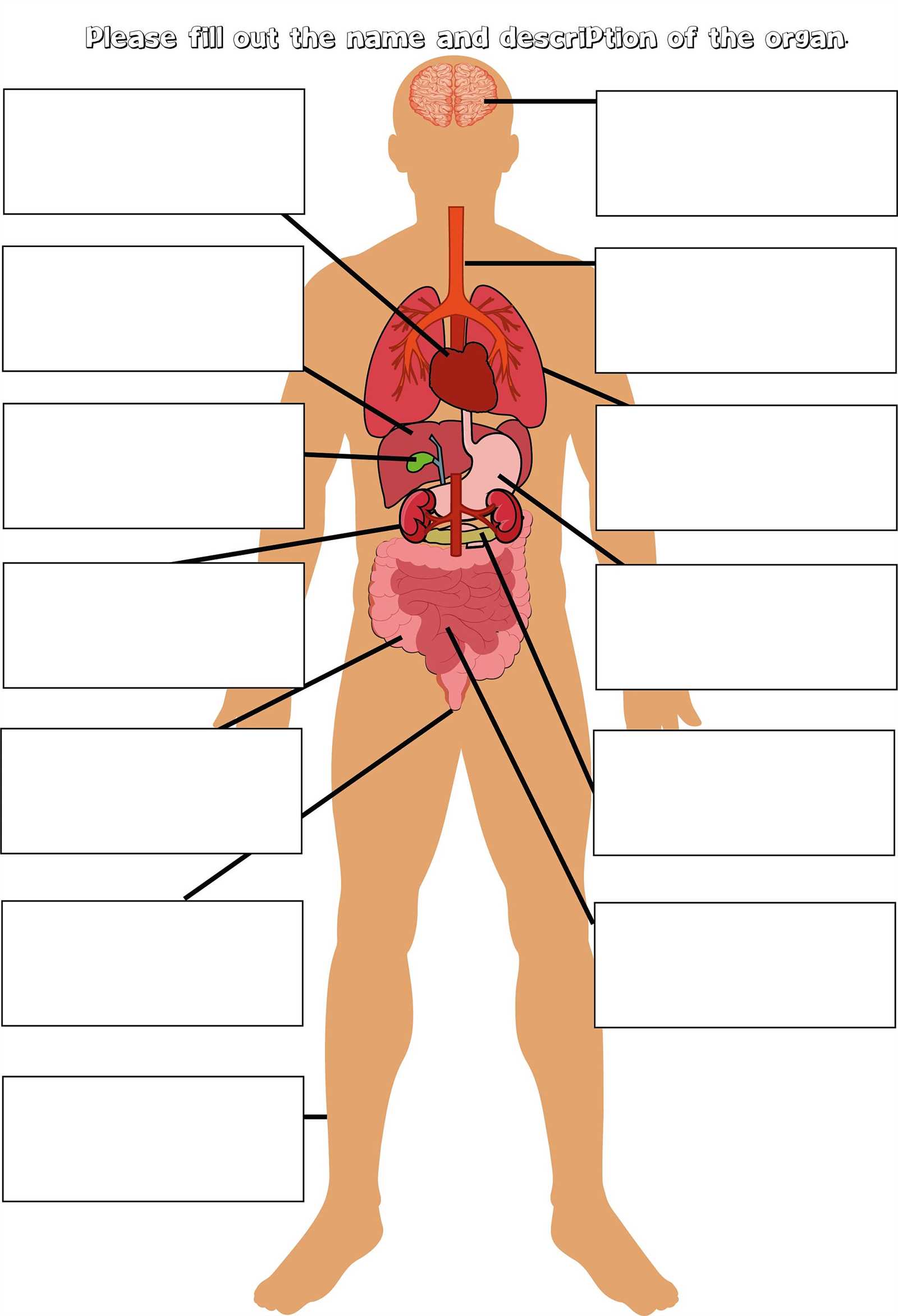
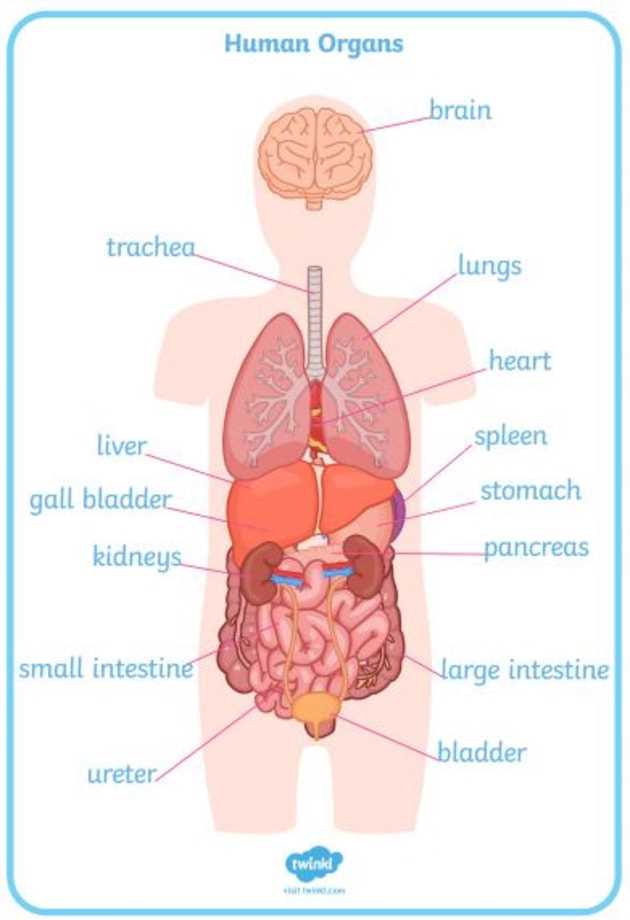
Internal Organs and Their Roles
The complex system of internal structures plays a vital role in maintaining the overall health and functionality of an organism. Each component contributes uniquely to various physiological processes that are essential for survival.
Heart serves as the central pump, circulating blood throughout the body and ensuring the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to cells. Lungs facilitate gas exchange, providing oxygen to the bloodstream while expelling carbon dioxide. Liver processes nutrients, detoxifies harmful substances, and produces essential biochemicals for digestion.
Moreover, kidneys are crucial for filtering blood, removing waste, and regulating fluid balance. The stomach and intestines work together to digest food, allowing the absorption of nutrients necessary for energy and growth. Each of these components interacts harmoniously, supporting the intricate balance required for optimal function.
Skin: The Body’s Shield
The skin serves as a vital barrier that protects the inner mechanisms from external threats. It plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being by shielding sensitive structures from harmful elements. This protective covering is essential for regulating various bodily functions and responding to environmental changes.
Functions of the Skin
- Protection against pathogens and harmful substances
- Regulation of temperature through sweating and insulation
- Sensory perception for touch, pressure, and temperature
- Production of vitamin D upon exposure to sunlight
Layers of the Skin
- Epidermis – The outermost layer, providing a protective barrier.
- Dermis – The middle layer, containing connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerve endings.
- Hypodermis – The innermost layer, consisting of fat and connective tissue, helping to insulate and cushion.
Joint Types and Their Movements
The human skeletal system comprises various connections that enable a wide range of motion. Understanding the different classifications of these connections helps in grasping how movement is facilitated in the body. Each type is designed to allow specific actions, contributing to overall flexibility and function.
| Joint Type | Description | Examples | Movements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hinge | Allows movement in one plane, similar to a door. | Knees, elbows | Flexion, extension |
| Ball-and-Socket | Permits rotational movement in multiple directions. | Shoulders, hips | Flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, rotation |
| Pivot | Enables rotation around a single axis. | Neck, forearm | Rotation |
| Saddle | Allows movement in two planes, similar to a rider on a saddle. | Thumb | Flexion, extension, abduction, adduction |
| Ellipsoidal | Facilitates movement in two planes, but with less rotation. | Wrist | Flexion, extension, abduction, adduction |
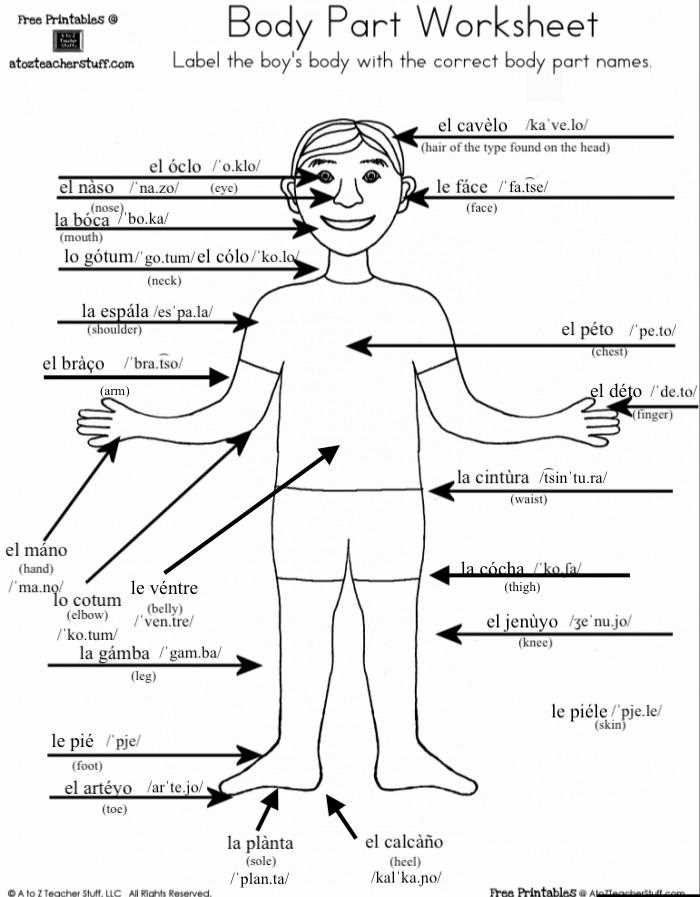
Common Body Part Terminology
Understanding the terminology related to human anatomy is essential for effective communication in various fields, including medicine, education, and fitness. This section explores frequently used terms that describe different regions and structures, enhancing one’s ability to discuss and comprehend related concepts.
Various regions of the human form are often categorized into specific groups to simplify identification. These designations can apply to the upper and lower sections, as well as the central area, each comprising a range of distinct structures.
Common terminology includes limbs, which refer to the arms and legs, as well as torso, denoting the central part of the physique. Furthermore, features such as the head, neck, and abdomen are also crucial for a comprehensive understanding of anatomical references.
Visual Aids in Anatomy Learning
Effective resources play a crucial role in the comprehension of complex structures and systems within the human form. Utilizing graphical representations enhances understanding and retention, making it easier for learners to grasp intricate details. Visual tools provide clarity and simplify the study of various systems, facilitating a more engaging educational experience.
Importance of Illustrations
Illustrations are essential in educational contexts, as they bridge the gap between theory and practical application. By visually depicting various elements, learners can better relate abstract concepts to real-life situations, fostering deeper insights into functionality and interrelationships.
Types of Visual Resources
Different types of visual aids can be employed to enhance the learning process. Each type serves distinct purposes and caters to various learning preferences, ensuring a comprehensive educational approach.
| Type of Visual Aid | Description |
|---|---|
| Illustrations | Detailed drawings highlighting specific structures. |
| Charts | Graphical representations showing relationships and functions. |
| Models | Three-dimensional representations for tactile learning. |
| Videos | Dynamic content demonstrating processes and interactions. |