Caterpillar Body Parts Illustrated Diagram
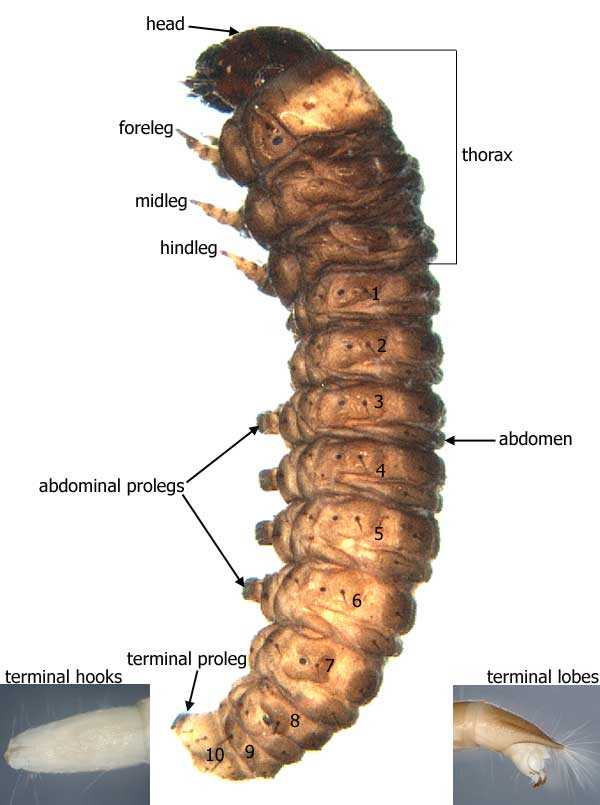
Exploring the intricate design of these remarkable creatures reveals a fascinating world of form and function. Each segment plays a vital role in the creature’s survival and development, showcasing nature’s ingenuity. By examining these components, we gain insight into the life cycle and adaptability of these organisms.
Learning about the various structures involved can enhance our appreciation for their complexity. From the way they move to how they interact with their environment, each feature serves a specific purpose. The arrangement and characteristics of these segments are crucial for growth and metamorphosis.
Moreover, understanding this unique configuration can illuminate broader ecological concepts, such as the relationships between different species and their habitats. By delving into this topic, we not only satisfy our curiosity but also foster a deeper connection with the natural world.
Understanding Caterpillar Anatomy
This section delves into the intricate structure of these fascinating larvae, highlighting their unique features and adaptations that facilitate their growth and survival. Recognizing the various components and functions of these organisms is essential for a deeper appreciation of their role in the ecosystem.
External Characteristics
The outer layer of these insects showcases a variety of colors and patterns, which serve multiple purposes, including camouflage and warning signals to potential predators. Each segment of their elongated form is equipped with specialized structures that aid in movement and feeding, allowing them to thrive in diverse environments.
Internal Systems
Internally, these creatures possess a complex network that supports vital functions. Their digestive system is specially adapted to process foliage efficiently, while the respiratory system allows for effective gas exchange, crucial for their growth. Understanding these internal mechanisms reveals the remarkable adaptations that enable them to fulfill their ecological roles.
Key Features of Caterpillar Structure
The anatomy of these fascinating larvae is characterized by several distinct elements that contribute to their adaptability and survival. Each component plays a vital role in their development, mobility, and feeding strategies. Understanding these characteristics is essential for appreciating the complexity of these creatures.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Segments | The segmented structure allows for flexibility and movement, facilitating crawling and climbing. |
| Legs | These are divided into true legs and prolegs, aiding in locomotion and stability. |
| Head | Equipped with mandibles, it is crucial for feeding on foliage and other plant materials. |
| Spiracles | These small openings enable respiration, allowing for efficient gas exchange. |
| Coloration | Many exhibit vibrant colors or patterns, serving as camouflage or warning signals against predators. |
Life Cycle Stages of Caterpillars
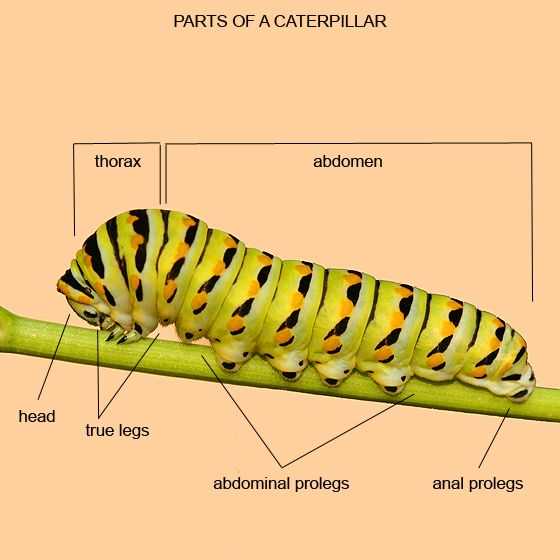
The journey of a certain insect from egg to maturity encompasses several fascinating transformations. Each stage is crucial for development, playing a unique role in the overall process. Understanding these phases provides insight into the remarkable adaptations and behaviors of this remarkable organism.
Stages of Development
The lifecycle unfolds in a series of distinct phases, each characterized by specific features and activities. Below is a brief overview of these stages:
| Stage | Description | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Egg | The initial stage where fertilized eggs are laid on host plants. | 3-10 days |
| Lava | The feeding stage where growth occurs rapidly, consuming foliage. | 2-4 weeks |
| Pupa | A transitional phase where the organism undergoes metamorphosis inside a protective casing. | 1-3 weeks |
| Adult | The final stage, emerging as a fully developed insect ready to reproduce. | Variable lifespan |
Significance of Each Stage
Each phase is not only vital for the individual’s growth but also plays an essential role in the ecosystem. For instance, the larval stage is crucial for nutrient cycling, while the adult phase contributes to pollination and biodiversity. Recognizing these stages allows for a deeper appreciation of the interconnectedness within nature.
Function of Each Body Part
The various sections of an insect serve distinct roles that contribute to its survival and development. Each region has evolved to fulfill specific tasks, ensuring efficiency in movement, feeding, and protection.
Feeding Mechanisms
- Mouthparts: Adapted for grasping and chewing foliage, allowing for effective nutrient intake.
- Salivary Glands: Produce enzymes that aid in breaking down plant material, facilitating digestion.
Locomotion and Sensory Perception

- Prolegs: Provide grip and support on surfaces, aiding in movement and stability.
- Antennas: Serve as sensory organs, detecting chemicals and vibrations in the environment.
- Segments: Allow for flexibility and mobility, enhancing the ability to navigate through various habitats.
Comparison with Other Insects
When examining the anatomy of various larval forms, interesting contrasts arise when juxtaposed with other arthropods. These distinctions can highlight the evolutionary adaptations that facilitate survival in diverse environments. Understanding these variations sheds light on the unique characteristics that define each group.
| Feature | Larval Forms | Beetles | Ants |
|---|---|---|---|
| Head Structure | Distinct with well-defined mouthparts | Compact with chewing mandibles | Reduced with minimal features |
| Segmentation | Soft and flexible, typically numerous | Less flexible, with fewer segments | Highly segmented, supporting movement |
| Locomotion | Utilizes a wriggling motion | Moves with a crawling gait | Employs a more coordinated movement pattern |
| Respiratory System | Tracheal system with spiracles | Similar tracheal structure | Utilizes spiracles for gas exchange |
These comparisons emphasize the diverse strategies employed by different species to adapt to their surroundings. Each group exhibits specific traits that reflect their ecological niches, revealing a fascinating tapestry of life within the insect world.
Common Caterpillar Species Overview
This section provides insights into various species of the larval stage of butterflies and moths, highlighting their distinctive characteristics and behaviors. Understanding these organisms is essential for both enthusiasts and researchers, as they play vital roles in ecosystems.
| Species Name | Habitat | Food Source | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eastern Tiger Swallowtail | Woodlands, gardens | Willow, cherry, tulip | Black and yellow coloration |
| Black Swallowtail | Fields, gardens | Carrots, parsley, dill | Green with yellow spots |
| Luna Moth | Forests | Walnut, hickory, sweetgum | Large size, pale green color |
| Hickory Horned Devil | Wooded areas | Walnut, hickory | Impressive size, horn-like projections |
| Viceroy | Wetlands, meadows | Willow, cottonwood | Similar to monarch, black stripe |
Unique Adaptations for Survival
The survival strategies of certain larvae showcase remarkable evolutionary traits that enhance their chances of thriving in various environments. These specialized features not only aid in evasion from predators but also facilitate effective feeding and growth. Understanding these adaptations offers insight into the complex interplay between organisms and their habitats.
Camo and Mimicry
One of the most fascinating adaptations is the ability to blend into surroundings. Many species exhibit coloration and textures that mimic foliage or bark, making them nearly invisible to potential threats. This camouflage not only protects them but also allows for more successful feeding as they remain undetected.
Defensive Mechanisms
Beyond visual adaptations, certain larvae have developed unique defense strategies. Some possess spines or hair-like structures that deter predators, while others release unpleasant odors or toxins when threatened. These mechanisms serve as effective deterrents, ensuring their survival until metamorphosis.
| Adaptation | Description |
|---|---|
| Camouflage | Mimics surroundings to avoid detection. |
| Spines and Hair | Physical deterrents against predators. |
| Toxins | Release of harmful substances when threatened. |
| Mimicry | Imitating other organisms for protection. |
Importance of Caterpillars in Ecosystems
These fascinating larval forms play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance. Their presence contributes to various processes that support the health of natural habitats. By engaging in specific interactions within their environments, they foster biodiversity and facilitate essential life cycles.
One significant aspect of their role is their function as a food source. Numerous predators rely on them for sustenance, which in turn helps regulate populations within the ecosystem. Furthermore, they contribute to nutrient cycling, aiding in the decomposition of organic matter and enriching the soil.
| Role | Impact |
|---|---|
| Food Source | Supports various species, maintaining predator-prey dynamics |
| Nutrient Cycling | Enhances soil quality and promotes plant growth |
| Pollination | Some contribute to the pollination of plants, aiding reproduction |
| Habitat Formation | Influence the structure of vegetation, providing habitats for others |
In summary, these creatures are not merely transitional stages in a lifecycle; they are integral to ecosystem functioning and resilience. Their preservation is vital for maintaining the intricate web of life that sustains our environment.
Illustrated Diagram of Caterpillar Parts
This section presents a visual representation of the various structures found in a larval stage of a lepidopteran. Understanding these elements is essential for studying their growth and development. Each component plays a vital role in their survival and transformation into mature insects.
Key Features
- Head: The foremost section equipped with sensory organs and mandibles for feeding.
- Thorax: The middle segment that houses muscles for movement and supports the locomotion appendages.
- Abdomen: The rear portion containing digestive and reproductive systems.
Additional Elements
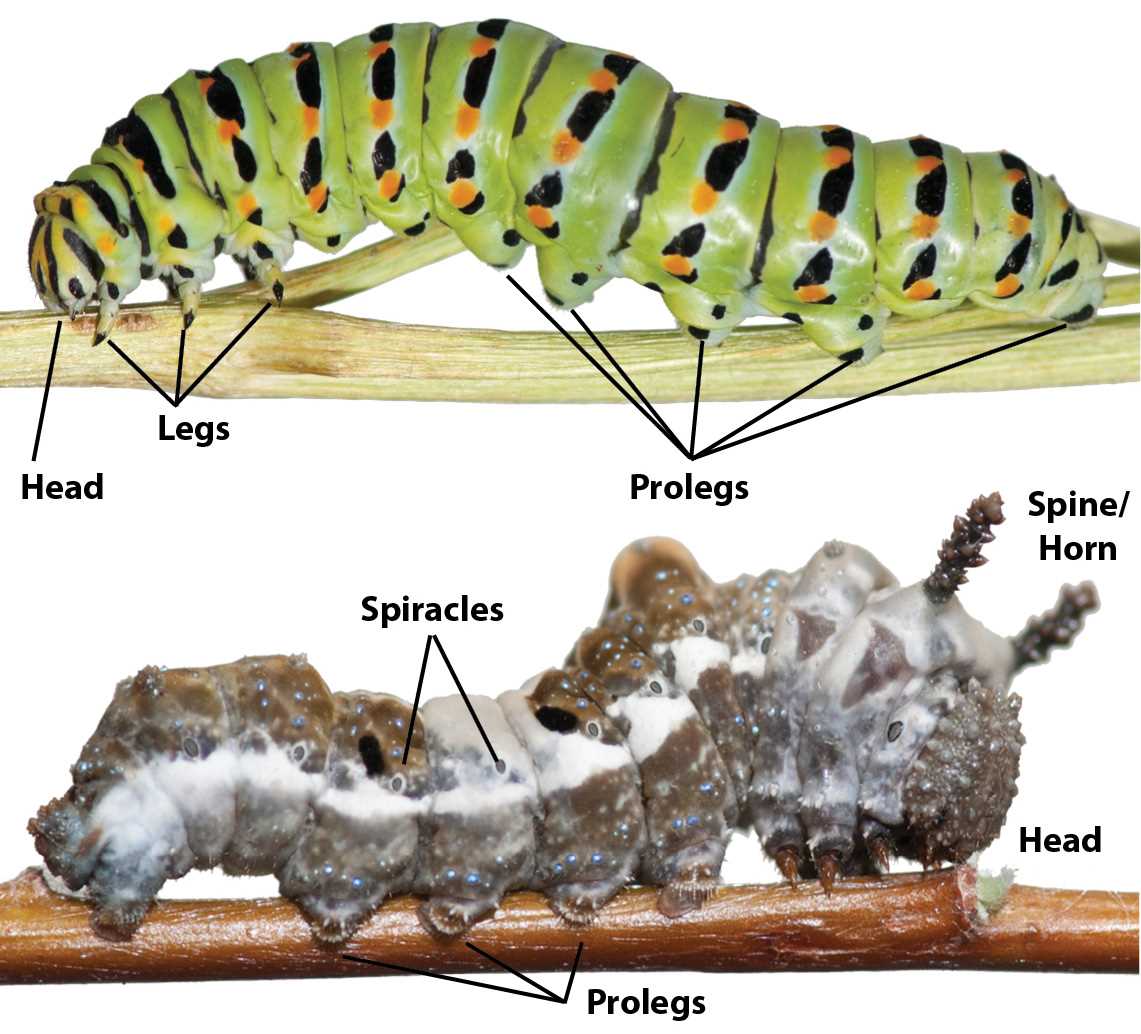
- Prolegs: Short, fleshy limbs that assist in gripping surfaces.
- Spiracles: Small openings for respiratory functions located along the sides.
- Setae: Tiny bristle-like structures that provide sensory feedback.
Comprehending these structures enhances our knowledge of their ecological roles and life cycles, contributing to a greater appreciation of biodiversity.
How Caterpillars Move and Feed
The method of locomotion and feeding in these larval creatures is a fascinating aspect of their biology. Their movements are finely tuned to navigate their environment while effectively seeking nourishment. This interplay between mobility and sustenance is crucial for their growth and development into mature insects.
Locomotion Techniques
These larvae primarily use a unique form of crawling to traverse their surroundings. Utilizing a combination of muscle contractions and specific movements, they propel themselves forward. The rhythmic alternation of different segments allows for smooth navigation, making it easier to avoid predators and obstacles.
Nourishment Strategies
When it comes to feeding, these creatures exhibit a remarkable ability to consume various plant materials. Their specialized mouthparts enable them to efficiently chew and digest leaves, facilitating optimal nutrient absorption. This feeding behavior is vital for their rapid growth, preparing them for the next stage of their life cycle.
Role of Caterpillars in Food Chains
Within ecosystems, certain organisms play crucial roles that influence the balance of life. Among these, a specific larval stage of insects serves as an essential link in various ecological webs, facilitating energy transfer and nutrient cycling.
These larvae primarily function as herbivores, consuming a wide array of plant material. By feeding on foliage, they contribute to plant health by promoting new growth. Additionally, their feeding habits help regulate plant populations, ensuring biodiversity in their habitats.
As they progress in their life cycle, these organisms become vital prey for numerous predators, including birds, small mammals, and other insects. This makes them integral to maintaining the populations of these predators, thereby enhancing ecosystem stability. The interplay between these larvae and their predators exemplifies the interconnectedness of life forms in nature.
Furthermore, when these larvae undergo metamorphosis, they not only transform into beautiful winged insects but also enrich the environment as pollinators, thereby continuing their role in the food web. Their life cycle illustrates a remarkable process of energy flow and ecological balance.
In summary, the significance of this larval stage extends beyond its immediate existence. It embodies a crucial component of the food chain, supporting both plant life and various animal species, ultimately fostering a rich and diverse ecosystem.
Threats to Caterpillar Populations
Numerous factors jeopardize the survival of these essential organisms within ecosystems. Understanding these challenges is crucial for preserving their diversity and, by extension, the health of the environments they inhabit.
Habitat loss stands as one of the most significant threats, driven primarily by urbanization, agriculture, and deforestation. As natural environments are replaced with human infrastructure, the availability of food sources and suitable living conditions diminishes.
Additionally, climate change is impacting temperatures and precipitation patterns, which in turn affect the lifecycle and distribution of these creatures. Shifts in climate can lead to mismatches between the timing of development and the availability of host plants.
Pesticide use poses another serious risk. Chemicals designed to control pests often inadvertently harm non-target species, disrupting local populations and leading to declines. The ripple effects of these toxins can alter entire food webs.
Moreover, invasive species can outcompete native organisms for resources, leading to further declines. These newcomers may also introduce new diseases that can devastate local populations.
In conclusion, addressing these threats requires concerted efforts in conservation and sustainable practices. By fostering awareness and implementing protective measures, we can help ensure the survival of these vital creatures and the ecosystems they support.
Conservation Efforts for Caterpillars
Preserving the life cycle of these fascinating insects is crucial for maintaining ecological balance. Various initiatives aim to safeguard their habitats and promote awareness of their importance in nature. By understanding the threats they face, we can implement effective strategies to ensure their survival.
Threats to Their Survival
- Habitat loss due to urbanization and agriculture
- Climate change affecting food sources
- Pesticide use leading to population declines
- Invasive species disrupting ecosystems
Conservation Strategies
- Creating protected areas to preserve natural habitats.
- Implementing sustainable agricultural practices that reduce chemical use.
- Promoting native plant gardens to support local populations.
- Engaging communities through educational programs about their role in ecosystems.
Through collaborative efforts, we can contribute to the well-being of these vital creatures and the environments they inhabit.