Understanding the Human Body Parts Through Diagrams
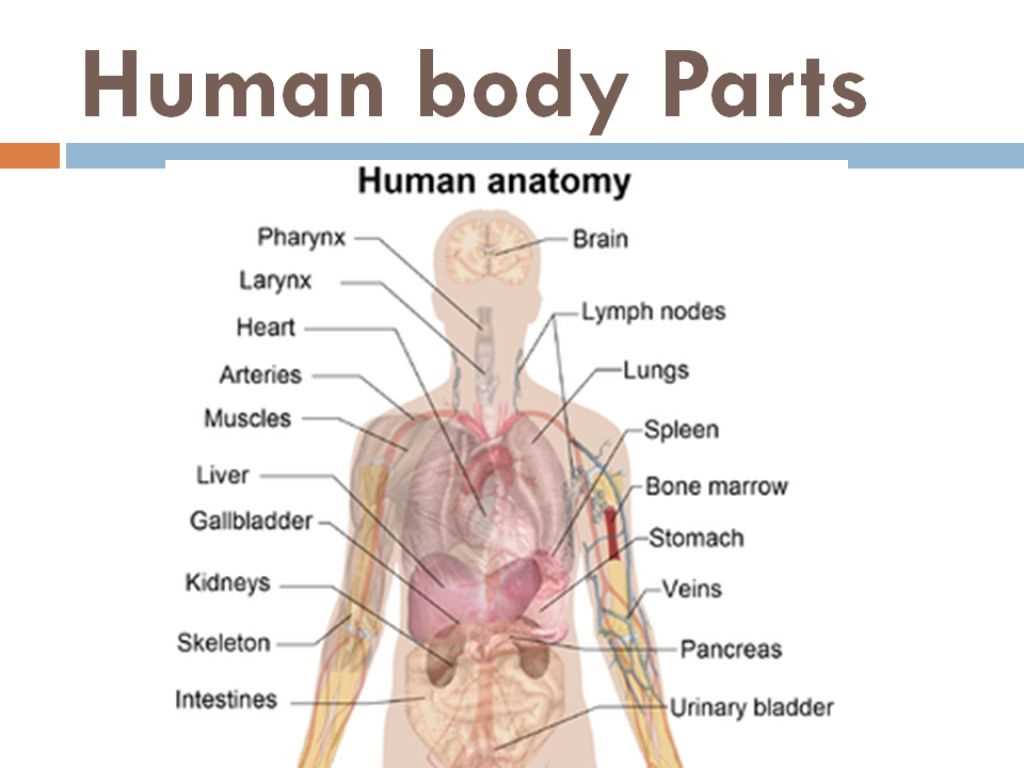
The intricate design of the organism reveals a fascinating interplay of systems and structures, each playing a crucial role in overall functionality. Understanding these elements enhances our appreciation of life itself and promotes insights into health and wellness.
In this exploration, we will delve into the various components that contribute to movement, sensation, and vital processes. Each element has its unique characteristics and significance, forming a cohesive unit that supports daily activities.
With the ultimate goal of fostering awareness, we will highlight the essential features and relationships among these components. This knowledge not only empowers individuals but also encourages a deeper connection to the marvels of living beings.
Understanding Human Anatomy Basics
Exploring the structure and function of living organisms is essential for grasping how they operate. This field of study reveals the intricate systems that work together to sustain life, highlighting the complexity and interdependence of various components. By examining these elements, one can appreciate the remarkable design that underpins vitality and health.
Anatomical knowledge serves as a foundation for numerous disciplines, including medicine, biology, and physiology. It encompasses various categories, such as skeletal frameworks, muscular systems, and neural networks, each playing a critical role in maintaining overall functionality. Understanding these categories allows for better insights into health, disease, and treatment approaches.
Moreover, the study of these systems not only enhances our comprehension of physical attributes but also fosters a deeper connection to wellness. By recognizing how each segment contributes to the greater whole, individuals can make informed choices that promote longevity and quality of life.
Essential Organs and Their Functions
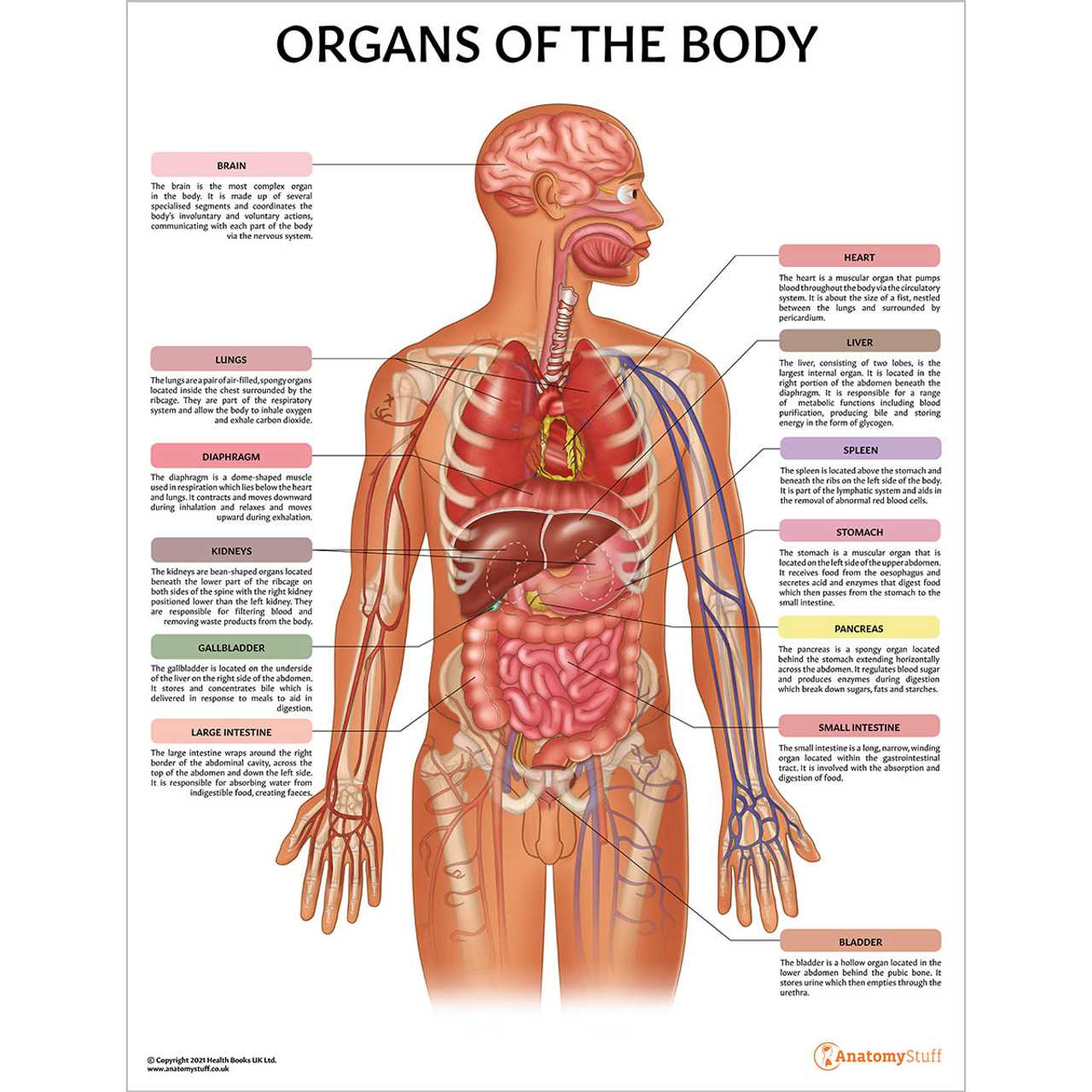
Understanding the vital components of the physical structure is crucial for appreciating how various systems operate and sustain life. Each essential element plays a unique role, contributing to overall functionality and well-being.
- Heart: Pumps blood, supplying oxygen and nutrients to tissues.
- Lungs: Facilitate gas exchange, providing oxygen and removing carbon dioxide.
- Liver: Processes nutrients, detoxifies substances, and produces bile.
- Kidneys: Filter waste products from blood and regulate fluid balance.
- Brain: Controls bodily functions and processes information.
Each of these organs works in harmony to ensure optimal performance and health.
Overview of Skeletal System Components
The skeletal structure serves as a critical framework that supports and protects vital systems. It consists of various elements that work in harmony to enable movement and provide stability.
- Bones: The primary constituents that provide structure and strength.
- Cartilage: A flexible tissue that cushions joints and supports various structures.
- Joints: The connections between bones that facilitate movement.
- Ligaments: Fibrous tissues that connect bones to one another.
- Tendons: Connective tissues that attach muscles to bones.
Understanding these components allows for a deeper appreciation of their roles and interactions in overall functionality.
Muscle Types and Their Roles
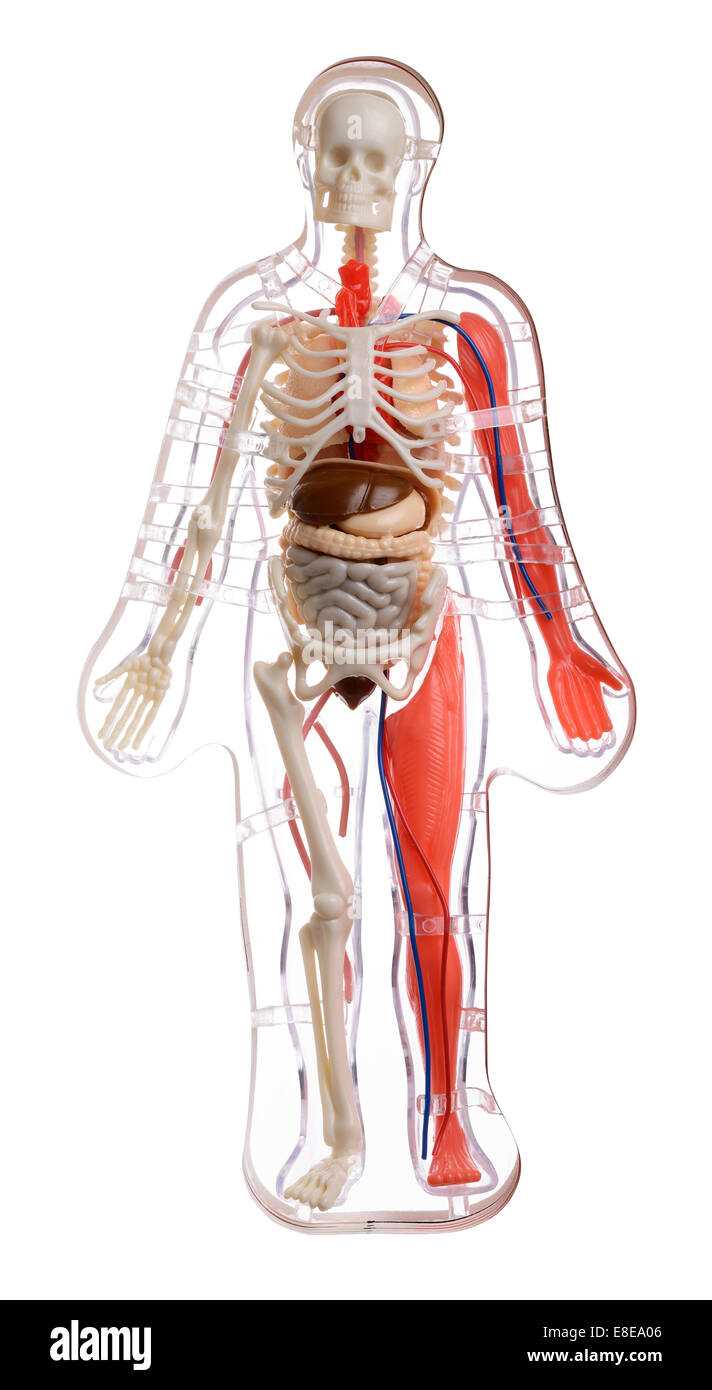
Understanding the different classifications of muscular tissue is essential for grasping their unique functions and contributions to movement and stability. Each type plays a crucial role in enabling various physical activities and maintaining overall performance.
| Muscle Type | Characteristics | Functions |
|---|---|---|
| Skeletal | Striated, voluntary control | Facilitates movement, posture maintenance |
| Cardiac | Striated, involuntary control | Pumps blood, maintains circulation |
| Smooth | Non-striated, involuntary control | Regulates internal organs, aids digestion |
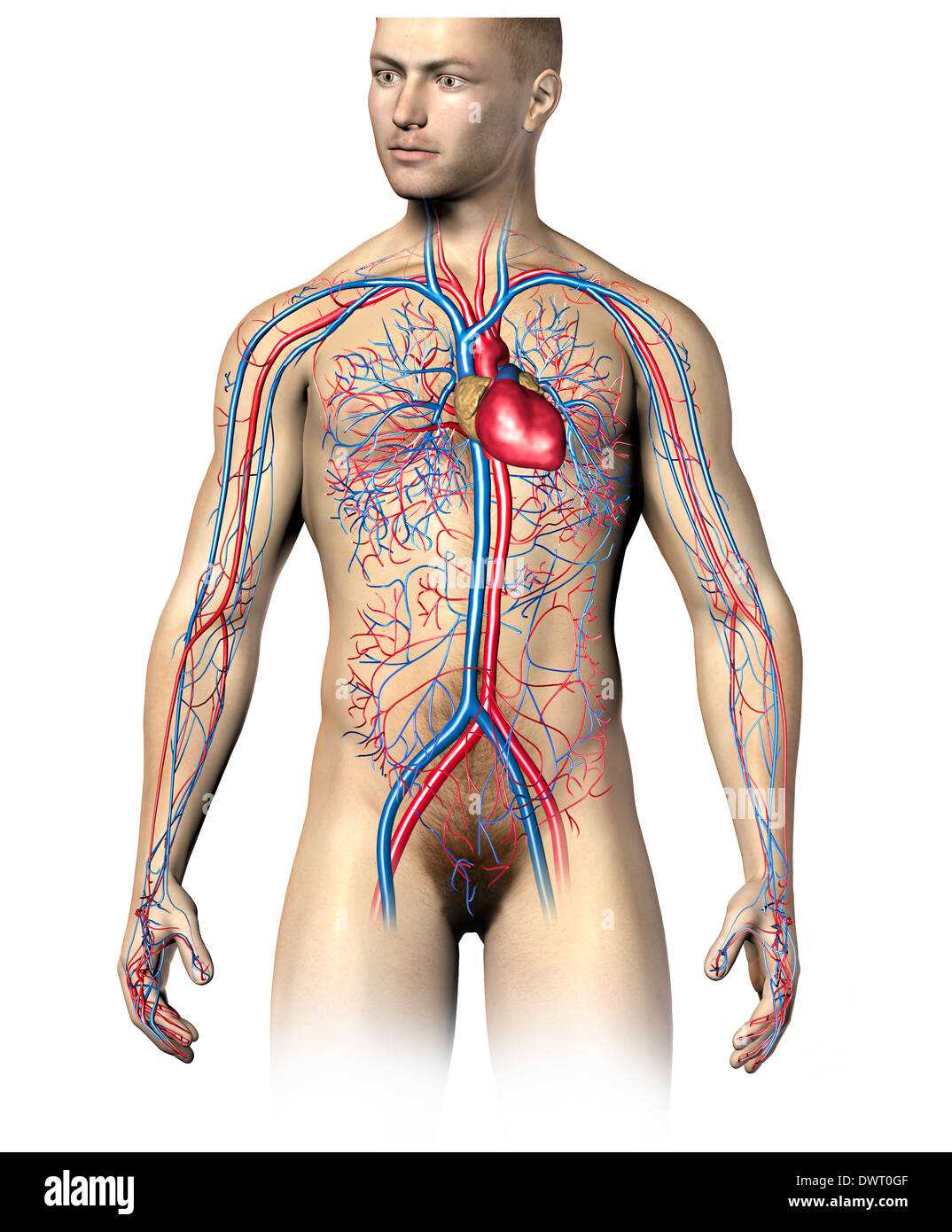
Circulatory System Explained in Detail
The intricate network responsible for the transport of essential substances throughout an organism plays a crucial role in maintaining life. This system facilitates the movement of nutrients, gases, and waste products, ensuring that every cell receives what it needs to function optimally.
Components of the Circulatory Network
Key elements of this system include the heart, blood vessels, and fluid, each contributing to the overall efficiency of circulation. The heart acts as a powerful pump, while arteries, veins, and capillaries form a vast pathway for the flow of life-sustaining materials.
Functions and Importance
This network not only distributes oxygen and nutrients but also plays a vital role in thermoregulation and immune responses. Understanding its functions can provide insights into overall health and potential medical conditions.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Heart | Pumps blood throughout the system |
| Arteries | Carry oxygenated blood away from the heart |
| Veins | Return deoxygenated blood to the heart |
| Capillaries | Facilitate exchange of gases and nutrients |
Nervous System: Key Elements and Functions
This intricate network is essential for coordinating actions and responses, acting as the communication hub of the organism. It facilitates interaction with the environment and maintains internal balance.
Key components include:
- Neurons: Specialized cells that transmit signals.
- Glial Cells: Supportive cells that protect and nourish neurons.
- Synapses: Junctions where communication occurs between neurons.
The functions of this system are vital for survival and can be categorized as follows:
- Motor Control: Enables voluntary and involuntary movements.
- Sensory Processing: Interprets sensory information from the environment.
- Cognitive Functions: Facilitates learning, memory, and decision-making.
Understanding these elements is crucial for appreciating the overall functioning of the organism.
Respiratory System: How It Works
The respiratory system plays a crucial role in sustaining life by facilitating the exchange of gases essential for energy production and overall health. This intricate network ensures that oxygen enters the system while carbon dioxide is expelled.
Key components involved in this process include:
- Lungs
- Trachea
- Bronchi
- Alveoli
The process can be broken down into several steps:
- Inhalation: Air is drawn in through the nose or mouth, traveling down the trachea.
- Gas Exchange: Oxygen moves from the alveoli into the bloodstream, while carbon dioxide moves from the blood into the alveoli.
- Exhalation: Carbon dioxide-rich air is expelled from the lungs.
Through these mechanisms, the respiratory system efficiently supports vital functions, ensuring that cells receive the oxygen they need to thrive.
Digestive Process and Organ Functions
The intricate sequence of breaking down nutrients involves several specialized structures, each contributing to the transformation of food into essential energy and materials. Understanding this process reveals the remarkable efficiency of these components working in harmony.
The journey begins in the mouth, where initial breakdown occurs. Key structures include:
- Teeth: Mechanically grind food into smaller pieces.
- Salivary Glands: Release enzymes that initiate digestion.
As the mixture travels down the esophagus, it reaches the stomach, a crucial site for further processing:
- Stomach: Mixes food with gastric juices, continuing chemical breakdown.
- Chyme: The semi-liquid mixture formed here is essential for nutrient absorption.
Next, the chyme enters the small intestine, where most nutrient absorption occurs:
- Duodenum: Receives digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the liver.
- Villi: Tiny projections that maximize nutrient absorption into the bloodstream.
Finally, the remaining material moves into the large intestine, focusing on water reabsorption and waste formation:
- Colon: Extracts water and compacts waste.
- Rectum: Stores waste until elimination.
This intricate system underscores the ultimate efficiency of nutrient processing and the vital roles each structure plays in maintaining overall wellness.
Endocrine System: Hormones and Glands
The endocrine system plays a crucial role in regulating various functions within an organism through the secretion of specific substances. These powerful chemical messengers influence processes such as growth, metabolism, and mood, ensuring that numerous systems operate harmoniously.
Glands within this intricate network release hormones directly into the bloodstream, where they travel to target tissues to elicit particular responses. Each gland has a unique function, contributing to the overall balance of physiological activities.
Hormones can vary significantly in their effects, ranging from stimulating growth to regulating energy levels. This diverse array of substances highlights the complexity and ultimate significance of the endocrine system in maintaining homeostasis.
Integumentary System: Skin’s Importance
The outer covering serves as a vital barrier and plays a crucial role in overall well-being. This complex structure not only protects against external threats but also maintains essential functions that contribute to health and homeostasis.
Among its many responsibilities, the integumentary system regulates temperature, provides sensory information, and facilitates the synthesis of important substances. Each layer contributes uniquely to these essential tasks, ensuring that the organism functions optimally.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Protection | Acts as a shield against pathogens, chemicals, and physical injuries. |
| Temperature Regulation | Maintains thermal balance through sweat production and blood flow adjustment. |
| Sensory Perception | Contains receptors that detect touch, pain, temperature, and pressure. |
| Synthesis of Vitamin D | Facilitates the production of vitamin D upon exposure to sunlight, vital for calcium absorption. |
Understanding the significance of this outer layer highlights its role not only in physical defense but also in maintaining internal equilibrium, ultimately influencing overall health and quality of life.
Human Body Diagram: Visual Learning Tools
Visual representation of anatomical structures plays a crucial role in enhancing comprehension and retention of complex information. By utilizing various illustrative techniques, learners can engage with intricate details more effectively. This approach caters to different learning styles and fosters a deeper understanding of physiological functions.
Several tools are available to facilitate this educational journey:
- Charts and Posters: Colorful and detailed illustrations can be displayed in classrooms or study spaces, providing constant reference points.
- Interactive Software: Digital platforms offer interactive experiences, allowing users to explore structures in three dimensions.
- Mobile Applications: On-the-go resources enable learners to access visual content anytime, enhancing flexibility in study habits.
- Video Tutorials: Dynamic presentations help visualize processes and systems, making complex concepts more relatable.
Incorporating these visual tools can significantly improve the learning experience, making the study of anatomical elements engaging and accessible.
When selecting resources, consider the following:
- Quality of Illustrations: Ensure that visuals are accurate and well-labeled.
- User Engagement: Look for interactive features that encourage exploration.
- Accessibility: Choose materials that are easy to obtain and use across various devices.
- Educational Support: Opt for tools that come with additional resources, such as quizzes or explanatory notes.
By leveraging these innovative methods, learners can develop a comprehensive understanding of anatomical systems, ultimately fostering a greater appreciation for the complexities of life.