Understanding Human Body Parts with Diagrams
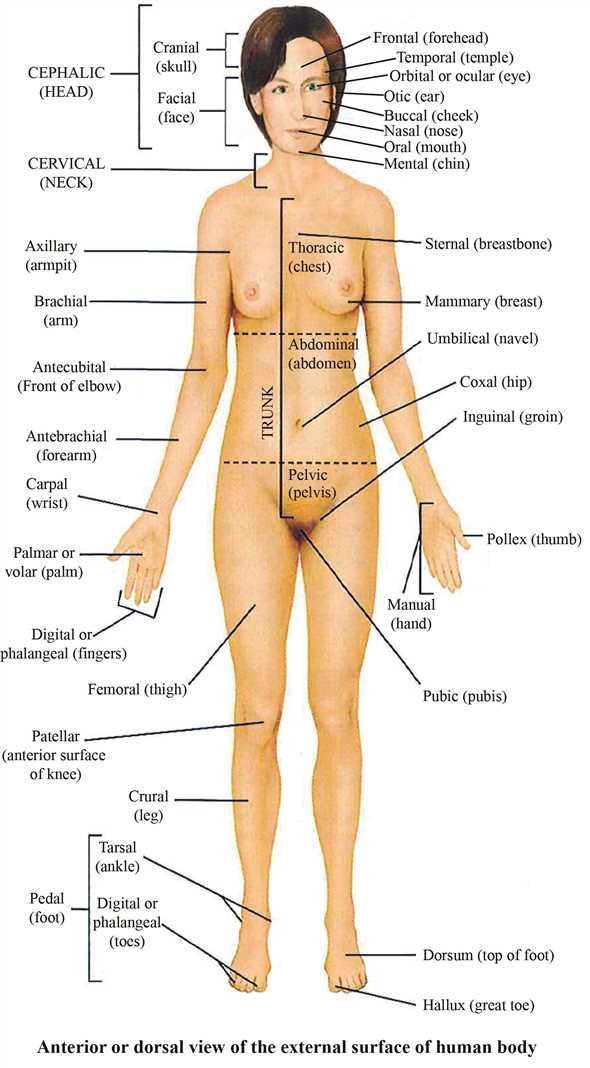
The intricate structure of our form encompasses a vast array of components, each serving a unique function. Understanding these elements is essential for grasping the complexity of our physical existence. From the smallest to the most significant, every segment plays a crucial role in our overall well-being.
In this section, we will delve into the terminology associated with various elements of anatomy. By examining these names, we aim to enhance our comprehension of how these components work together harmoniously. Additionally, visual aids will support our exploration, offering a clearer perspective on the relationships between different structures.
Through this journey, you will gain insights into the terminology that describes these vital segments, enriching your knowledge and appreciation of the magnificent design of life. Prepare to embark on an enlightening experience that highlights the ultimate connection between form and function.
Understanding Human Anatomy Basics
Grasping the fundamentals of the structure of living organisms is essential for various fields, including medicine, biology, and health sciences. This knowledge allows individuals to appreciate how different systems interact and function together, forming a cohesive entity. An introduction to these elements can enhance one’s understanding of overall well-being and physical capabilities.
Key Components of the Structure
The essential elements include various systems that work collaboratively to sustain life. These systems comprise distinct features that each play a specific role, from supporting movement to regulating internal processes. Recognizing these components helps in understanding how they contribute to the functionality and resilience of the organism.
Interconnected Systems
Each system is intricately linked, demonstrating the complexity of life. The interplay between them highlights the importance of holistic health approaches, emphasizing that any disruption in one area can affect others. A comprehensive understanding fosters a deeper appreciation for the delicate balance required for optimal health.
Key Functions of Body Parts
The intricate design of the anatomical structures in organisms serves a multitude of essential roles that enable survival and interaction with the environment. Each segment is specialized to perform distinct activities, contributing to the overall functionality and well-being of the organism.
Essential Roles
From locomotion to sensory perception, various regions exhibit unique capabilities. These functions are crucial for daily activities, communication, and adaptation to different scenarios. Understanding these functions highlights the complexity and harmony within living systems.
Overview of Functions
| Structure | Function |
|---|---|
| Heart | Pumps blood, supplying oxygen and nutrients to cells |
| Lungs | Facilitate gas exchange, allowing oxygen intake and carbon dioxide removal |
| Brain | Coordinates thoughts, processes information, and regulates bodily functions |
| Stomach | Breaks down food, aiding digestion and nutrient absorption |
| Muscles | Enable movement and provide strength for various activities |
Major Organ Systems Overview
The intricate network of vital systems within living organisms works harmoniously to sustain life. Each system comprises specialized components that perform essential functions, contributing to overall health and well-being. Understanding these systems offers insight into how various functions interconnect and maintain balance.
Circulatory System
The circulatory system is responsible for the transport of nutrients, gases, and waste products throughout the organism. Comprising the heart, blood vessels, and blood, this system plays a crucial role in delivering oxygen to tissues and removing carbon dioxide. Effective circulation is vital for maintaining homeostasis and supporting cellular processes.
Nervous System
Acting as the control center, the nervous system coordinates responses to internal and external stimuli. It consists of the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. This intricate system processes information, enabling communication between different parts of the organism, thereby facilitating movement, reflexes, and sensory perceptions.
Common Terminology for Anatomy
The study of anatomy involves a rich vocabulary that facilitates precise communication about the structure and function of living organisms. Understanding this terminology is essential for professionals in healthcare and related fields, as it allows for clear discussion and documentation.
Directional Terms are critical in describing the location of various elements. Terms such as superior, inferior, medial, and lateral provide clarity in spatial orientation.
Regional Terms designate specific areas, allowing for a focused approach to study. Common examples include thoracic for the chest area and abdominal for the stomach region.
Lastly, Structural Terms refer to the components themselves, encompassing categories like organs, tissues, and systems. Mastery of this terminology is fundamental for effective engagement in anatomical discussions.
External Body Features and Terms
The various attributes that define our outer appearance play a crucial role in identity and interaction. Understanding these features enhances our appreciation of individuality and serves as a foundation for effective communication.
Head: This uppermost section houses essential sensory organs, including the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth. Each component is vital for perception and expression.
Neck: Serving as a connector, this area links the head to the torso, facilitating movement and housing important structures such as the trachea and esophagus.
Chest: This region contains critical organs like the heart and lungs, protected by the rib cage. Its expansion and contraction are essential for respiration.
Arms: These limbs provide dexterity and strength, enabling a wide range of activities from fine motor skills to heavy lifting.
Hands: An extension of the arms, hands are intricately designed for grasping, manipulating, and interacting with the environment.
Abdomen: Located between the chest and pelvis, this area contains vital digestive organs and plays a role in overall health and function.
Legs: These lower limbs are fundamental for mobility, supporting weight and enabling movement through walking, running, and jumping.
Feet: Acting as the foundation of movement, feet provide balance and support, playing a crucial role in daily activities.
Each feature contributes to the overall functionality and aesthetic of the individual, highlighting the complexity and beauty of physical form.
Internal Organs and Their Locations
Understanding the vital components housed within an organism is essential for grasping overall health and functionality. Each element plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis and supporting various physiological processes.
Heart: Positioned centrally in the chest, this muscular organ pumps blood throughout the circulatory system.
Lungs: Located on either side of the heart, these paired organs facilitate gas exchange, allowing oxygen to enter the bloodstream and carbon dioxide to be expelled.
Stomach: Found in the upper abdomen, it serves as a storage site for food, initiating digestion through enzymatic action.
Liver: Situated in the right upper quadrant, this large organ is vital for metabolism, detoxification, and bile production.
Kidneys: These bean-shaped structures are located towards the back, filtering blood and producing urine to eliminate waste.
Intestines: The small and large varieties reside in the abdominal cavity, playing key roles in nutrient absorption and waste elimination.
Spleen: Positioned to the left of the stomach, it is involved in immune response and the recycling of red blood cells.
Muscular System and Its Components
The muscular system plays a vital role in the overall functionality and movement of the organism. It consists of various elements that work in harmony to facilitate motion, maintain posture, and generate heat. Understanding this intricate network enhances our appreciation of how movement is achieved and the importance of each component within the system.
The key components of this system can be categorized as follows:
- Skeletal Muscles: These are the muscles attached to the skeleton, responsible for voluntary movements. They are characterized by their striated appearance and are under conscious control.
- Cardiac Muscle: This specialized muscle is found in the heart. It operates involuntarily and is essential for pumping blood throughout the circulatory system.
- Smooth Muscle: Present in various internal organs, smooth muscle is responsible for involuntary movements, such as the contraction of blood vessels and digestive tract.
Additionally, the muscular system relies on several supporting elements:
- Tendons: These connective tissues attach muscles to bones, enabling movement.
- Fascia: This layer of connective tissue surrounds muscles and groups them into functional units.
- Muscle Fibers: The basic units of muscle tissue, responsible for contraction and relaxation.
Each component contributes to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the muscular system, highlighting the complexity and beauty of movement in living organisms.
Human Skeleton Structure Explained
The framework of the physical form serves as a vital support system, providing structure, protection, and mobility. It consists of various elements that work together harmoniously, ensuring the overall stability and function of the organism. Understanding this intricate assembly is essential for appreciating how it contributes to movement and overall health.
Components of the Framework
The skeleton is primarily composed of the following types of structures:
- Long bones: These are crucial for movement and support, found in limbs.
- Short bones: Typically providing stability and some movement, these are located in wrists and ankles.
- Flat bones: These structures protect internal organs and are found in the skull and rib cage.
- Irregular bones: Unique shapes that serve various functions, such as vertebrae.
- Sesamoid bones: These small bones develop within tendons, often found in joints like the knee.
Functions of the Framework
The skeletal framework performs several crucial roles:
- Support: It provides the necessary structure to maintain the body’s shape.
- Protection: Vital organs, such as the brain and heart, are safeguarded by various bony structures.
- Movement: Muscles attach to the bones, allowing for coordinated motion.
- Mineral storage: It serves as a reservoir for essential minerals, including calcium and phosphorus.
- Blood cell production: Certain bones contain marrow, which is responsible for generating blood cells.
Cardiovascular System in Detail
The cardiovascular system plays a crucial role in sustaining life, ensuring the circulation of vital substances throughout the organism. This intricate network is essential for delivering oxygen and nutrients while removing waste products, maintaining overall health and vitality.
Anatomy of the System
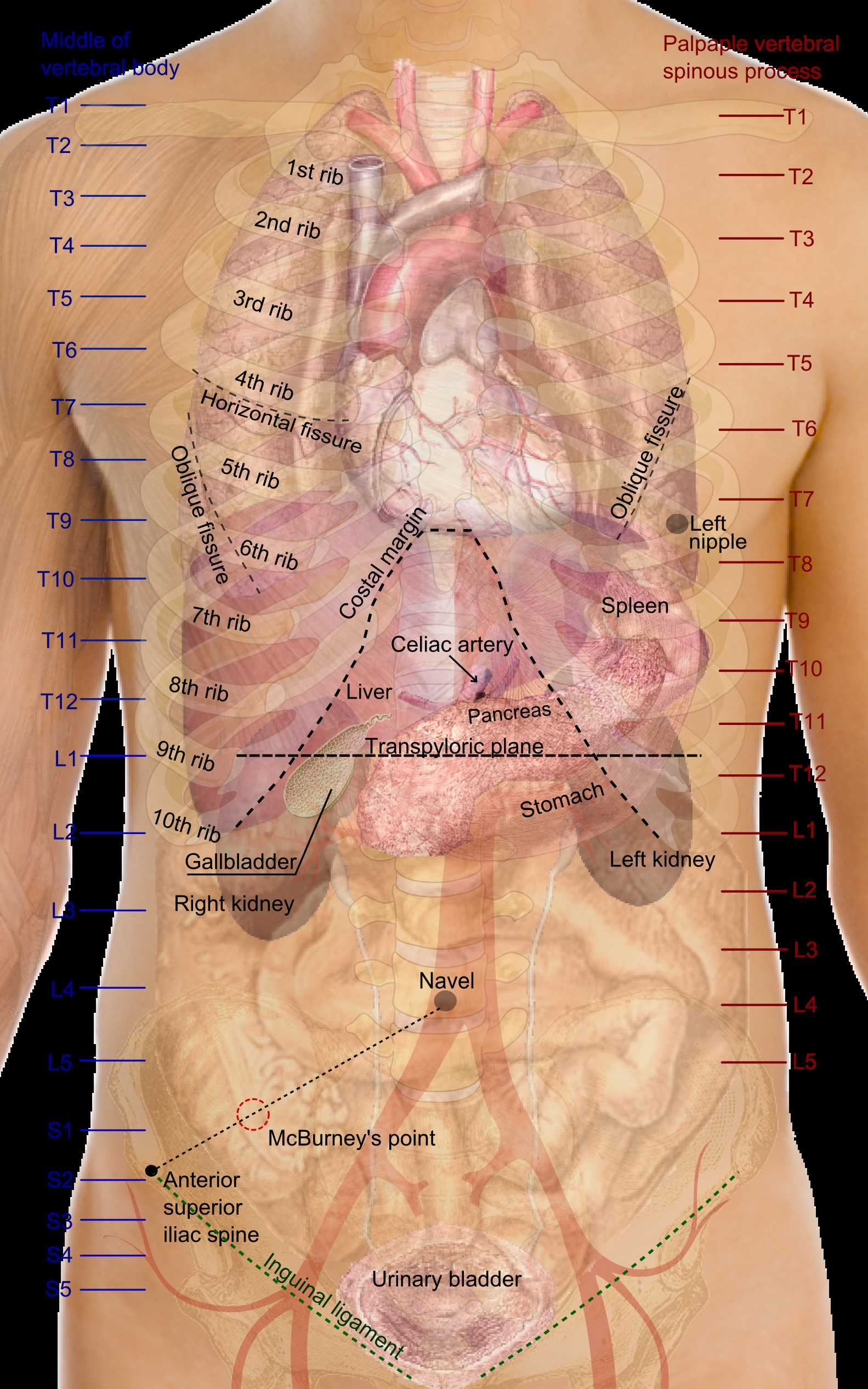
At its core, this network comprises the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The heart serves as the central pump, propelling blood through a series of arteries, veins, and capillaries. Each vessel type has distinct functions, contributing to efficient circulation and regulating blood pressure.
Function and Importance
The ultimate goal of this system is to ensure that every cell receives the necessary substances for optimal functioning. It adapts to various conditions, responding to physical demands and environmental changes, thereby highlighting its significance in maintaining homeostasis.
Nervous System Essentials and Functions
The intricate network responsible for communication within the organism plays a crucial role in coordinating activities and responding to environmental stimuli. This system integrates signals from various sources, ensuring efficient operation and interaction across different regions.
Components of the System
This intricate structure consists of two primary divisions: the central and peripheral elements. The central segment includes the brain and spinal cord, while the peripheral aspect encompasses all the nerves that branch out throughout the organism, linking the central unit to limbs and organs.
Functions and Importance
The essential functions include processing sensory information, regulating movements, and facilitating cognitive functions. It acts as the ultimate control center, influencing behavior, emotions, and reflexes, thereby sustaining overall well-being and adaptability.
Diagrammatic Representation of Anatomy
This section explores the visual interpretation of the intricate systems that compose living organisms. Through the use of illustrations, we can gain insights into the structure and function of various elements, enhancing our understanding of their relationships and roles.
Diagrams serve as valuable tools in education, providing clarity and facilitating the learning process. By depicting the arrangement and connection of different components, these visuals aid in the comprehension of complex biological concepts.
Illustrations can range from simple sketches to detailed renderings, each designed to highlight specific features. They not only enrich academic material but also support healthcare professionals in conveying essential information to patients.
Effective visualization fosters a deeper appreciation for the complexity of life forms, allowing us to recognize the elegance in their design. Whether for scholarly pursuits or practical applications, these representations play a crucial role in our exploration of anatomy.
Significance of Accurate Body Part Names
Understanding the precise terminology associated with anatomical structures plays a crucial role in effective communication within medical and educational contexts. Clear definitions facilitate accurate diagnosis, treatment, and learning, minimizing misunderstandings among practitioners and students alike.
Utilizing correct terminology fosters a shared language among professionals, enhancing collaboration in healthcare and research. Furthermore, it aids in the development of educational materials, ensuring that learners grasp complex concepts without ambiguity.
Moreover, precise labeling contributes to improved patient care. When individuals are informed about their own physiology using proper terms, it promotes better understanding of health conditions, treatments, and procedures, ultimately leading to more engaged patients.