Understanding the Components of a Brake Master Cylinder Diagram
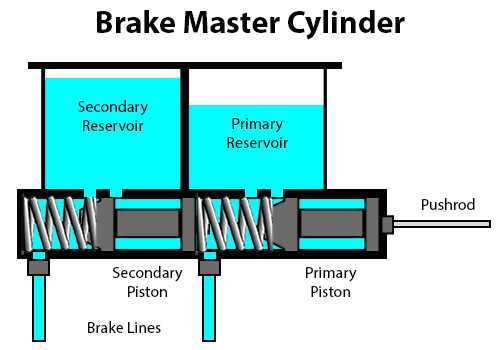
The functionality of any hydraulic system relies heavily on its crucial components, each playing a significant role in the overall operation. A thorough understanding of these elements can enhance maintenance practices and optimize performance, ensuring safety and efficiency.
In this section, we will explore the intricate relationships between various elements involved in the hydraulic mechanism. By delving into their structures and interactions, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview that facilitates better comprehension and troubleshooting.
Visual representations are invaluable in grasping the complexities of these components. They offer clarity, allowing enthusiasts and professionals alike to pinpoint issues and appreciate the engineering behind this vital system.
Understanding the Brake Master Cylinder
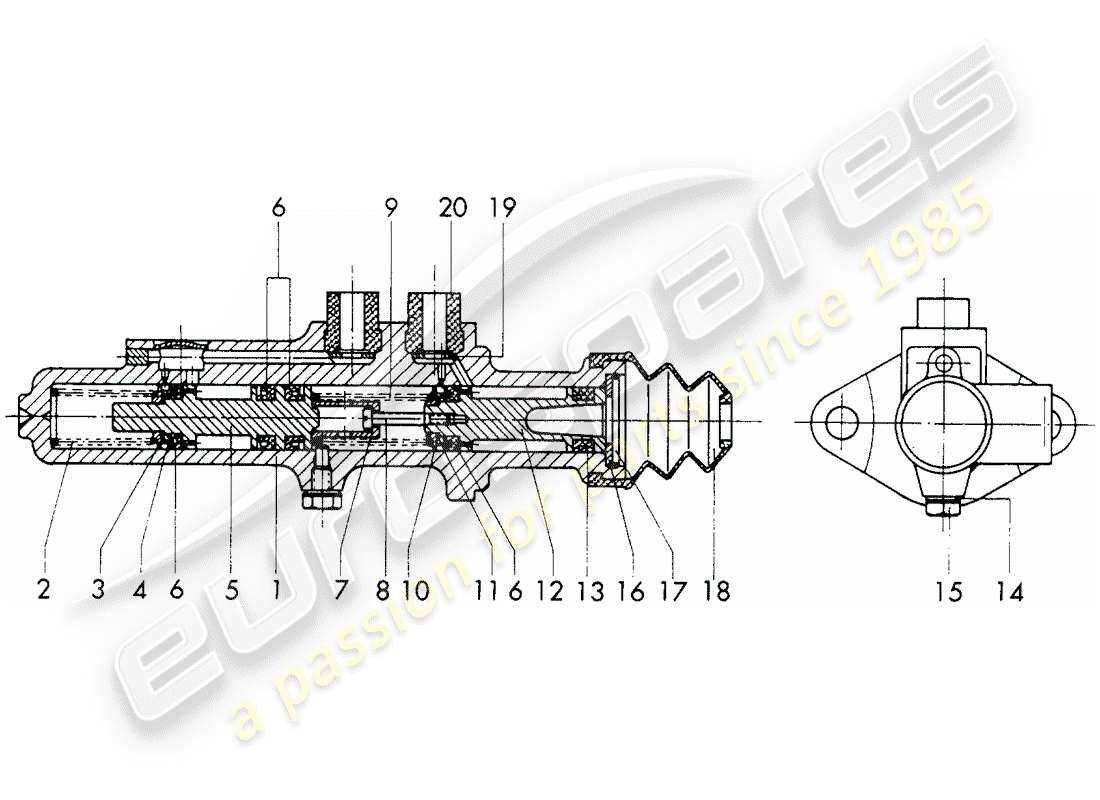
The hydraulic system that operates a vehicle’s stopping mechanism is crucial for safety and performance. This system is designed to convert force applied to the pedal into hydraulic pressure, enabling the wheels to slow down or come to a complete stop. A comprehensive understanding of this essential component is vital for maintaining vehicle efficiency and ensuring reliable operation.
This assembly consists of several key elements that work in harmony to facilitate the transfer of force. When the pedal is depressed, a piston within the unit moves, creating pressure in the fluid contained inside. This pressure is then transmitted through the lines to the stopping mechanisms at each wheel, ensuring a balanced and effective reduction in speed.
Moreover, this unit is equipped with various features that enhance its functionality and safety. For instance, it may include a reservoir for the hydraulic fluid, ensuring a steady supply for optimal operation. Additionally, certain models are designed with safety mechanisms that prevent failure, ensuring that the system continues to operate even if one part becomes compromised.
Regular inspection and maintenance of this crucial component are essential. Over time, wear and tear can affect its efficiency, leading to potential safety hazards. Understanding the components and their functions can help in identifying issues early and ensuring the system remains in top condition.
Components of the Brake System
The braking system of a vehicle consists of several crucial elements that work together to ensure effective stopping power and safety. Each component plays a specific role, contributing to the overall performance and reliability of the mechanism.
The primary element is the hydraulic actuator, which converts pedal pressure into fluid force, transmitting it to other system parts. This process is essential for generating the necessary pressure to engage the stopping mechanism.
Next, the fluid reservoir holds the hydraulic fluid, ensuring a steady supply for efficient operation. This element is vital for maintaining optimal fluid levels and preventing air from entering the system.
The connecting lines serve as pathways for the hydraulic fluid, linking various components and facilitating fluid movement. Proper maintenance of these conduits is crucial to avoid leaks and ensure a consistent response.
Finally, the engagement devices apply friction to the rotating elements of the vehicle, effectively reducing speed. Their design and material selection are key factors in achieving optimal stopping performance and durability.
Functionality of the Master Cylinder
The component in question plays a crucial role in the hydraulic system of a vehicle, ensuring efficient transmission of force. Its design allows for the generation of pressure needed to activate various mechanisms, ultimately contributing to the vehicle’s safety and performance. Understanding its function helps in grasping how other elements interact within the system.
Operational Mechanism
When the driver engages the pedal, this unit compresses hydraulic fluid within the system. This action creates pressure that is transmitted through the lines, resulting in the activation of the braking assemblies at each wheel. The entire process is vital for ensuring responsive and reliable stopping capabilities.
Key Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Pressure Generation | Transforms mechanical input into hydraulic pressure. |
| Fluid Management | Regulates the flow of hydraulic fluid to ensure consistent performance. |
| System Integration | Works in conjunction with other components for effective operation. |
Common Types of Master Cylinders
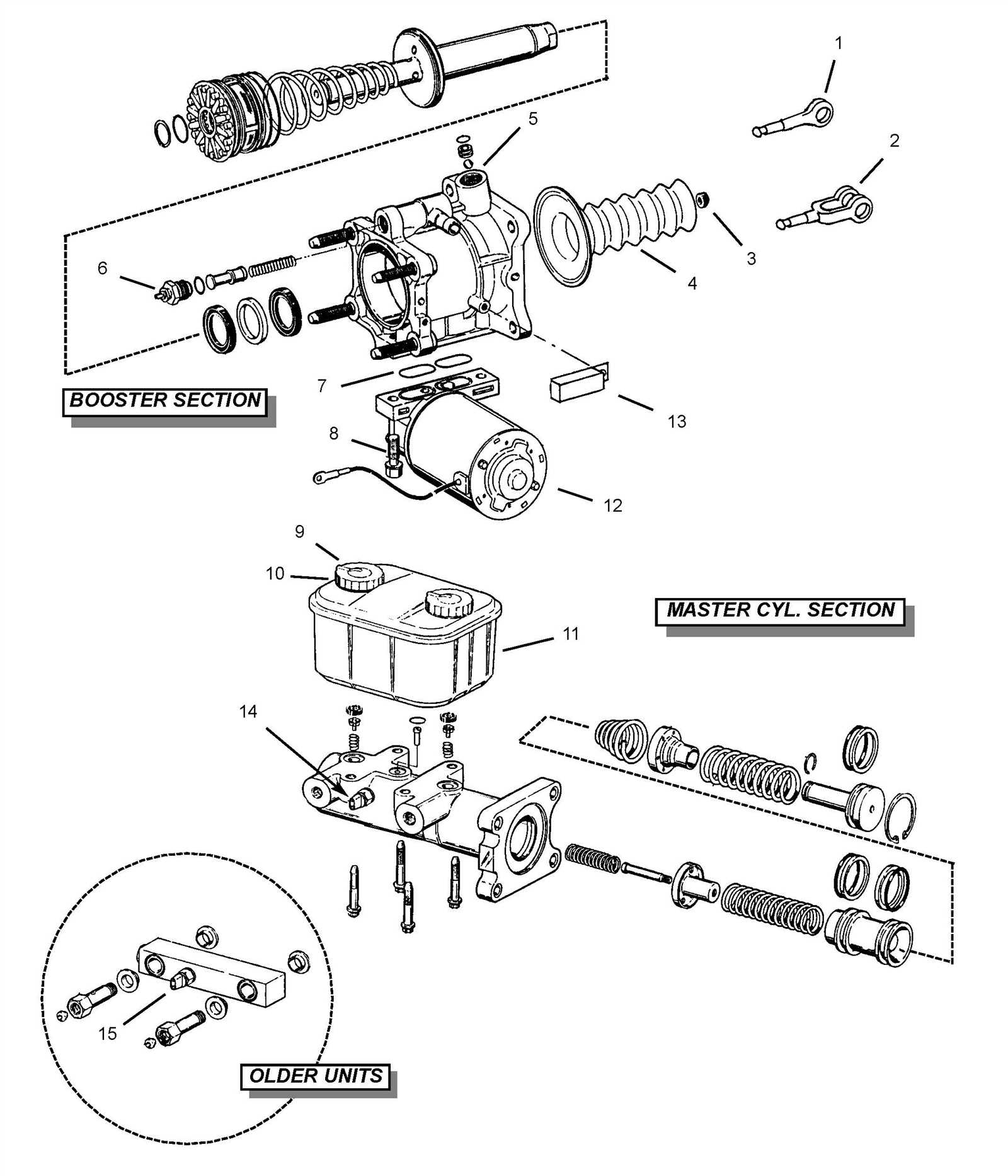
Understanding the different variations of hydraulic actuation systems is crucial for effective vehicle maintenance and performance. These mechanisms play a vital role in the overall functionality of braking systems, and each type has unique characteristics tailored to specific applications.
Types Based on Design
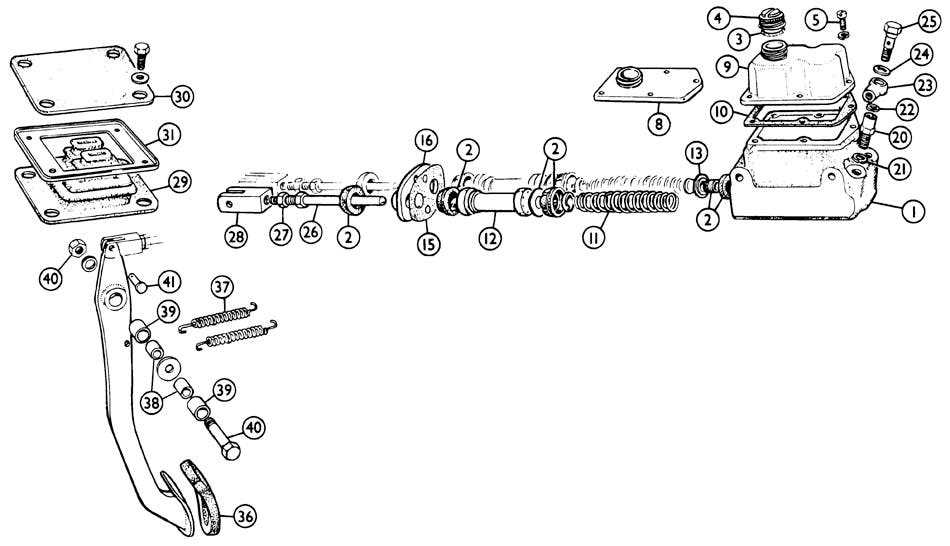
- Single Circuit: A straightforward system designed for basic functionality.
- Dual Circuit: Enhances safety by providing two independent circuits.
- Multi-Piston: Offers increased efficiency through multiple actuation points.
Types Based on Application
- Passenger Vehicles: Typically utilize simpler designs for everyday use.
- Heavy-Duty Trucks: Require more robust systems to handle greater loads.
- Performance Vehicles: Often employ specialized configurations for enhanced responsiveness.
Importance of Brake Fluid Selection
The choice of hydraulic fluid is crucial for the overall performance and safety of a vehicle. It influences the effectiveness of the stopping system, as well as the longevity of various components involved in the operation. Selecting the appropriate fluid ensures optimal functionality and responsiveness in critical situations.
Compatibility with system materials is essential. Different fluids can react adversely with seals and hoses, leading to leaks and potential failure. Thus, understanding the properties of the fluid and its interactions with components is vital for maintaining integrity.
Performance characteristics such as boiling point and viscosity also play a significant role. Fluids with high boiling points help prevent vapor lock under extreme conditions, ensuring consistent pressure transmission. Meanwhile, appropriate viscosity allows for effective movement within the system at varying temperatures.
In summary, selecting the right hydraulic fluid not only enhances safety but also extends the lifespan of the entire system. Regular assessment and adherence to manufacturer recommendations are key to achieving ultimate reliability.
Visualizing the Parts Diagram
Understanding the components of a hydraulic system is essential for effective maintenance and repair. A visual representation serves as a valuable tool, helping to demystify the intricate relationships between various elements. By examining these illustrations, one can gain insights into the functionality and assembly of the system, leading to improved troubleshooting and performance enhancement.
Key Components to Observe
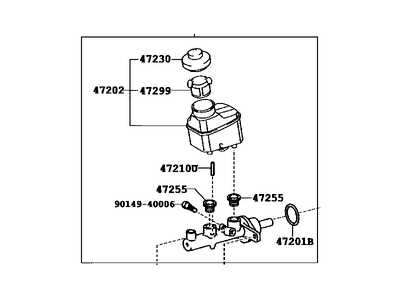
- Reservoir: Stores the hydraulic fluid, ensuring a constant supply.
- Actuator: Converts hydraulic pressure into mechanical movement.
- Piston: Plays a crucial role in generating pressure within the system.
- Seals: Prevent leaks and maintain pressure integrity.
- Connectors: Facilitate fluid transfer between components.
Benefits of Visual Representation
- Enhances comprehension of system layout.
- Facilitates easier identification of potential issues.
- Guides assembly and disassembly procedures.
- Aids in instructional and training contexts.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Proper upkeep is essential for ensuring the extended lifespan of hydraulic components within vehicles. Regular attention can prevent common issues and enhance overall performance.
- Inspect fluid levels frequently to ensure optimal functionality.
- Replace hydraulic fluid according to manufacturer recommendations to prevent contamination.
- Check for leaks in the system and address any issues immediately.
- Maintain clean connections and components to avoid dirt buildup.
In addition to regular inspections, consider the following:
- Monitor the performance during driving to detect unusual behavior.
- Seek professional assistance for deep inspections if you notice any irregularities.
- Keep a maintenance log to track services and fluid changes.
By following these guidelines, you can significantly enhance the longevity of your vehicle’s hydraulic system.
Signs of a Failing Master Cylinder
Recognizing the signs of a failing hydraulic actuator is crucial for maintaining the safety and performance of your vehicle. When this vital component begins to malfunction, it can lead to a range of issues that affect overall driving experience. Awareness of these warning signals can help you address potential problems before they escalate.
Common Indicators
- Poor Responsiveness: Delayed or sluggish response when pressing the pedal can signal underlying issues.
- Fluid Leaks: Spots or puddles of fluid under the vehicle may indicate a compromised seal or connection.
- Warning Light: Dashboard indicators may illuminate, prompting immediate attention.
- Unusual Noises: Strange sounds while engaging the pedal can suggest internal wear or damage.
- Pedal Feel: A soft or spongy feeling when pressing the pedal can indicate air in the system or fluid issues.
Consequences of Neglect
If left unaddressed, a failing actuator can lead to severe safety risks, including:
- Increased stopping distances, jeopardizing safety.
- Complete loss of hydraulic pressure, rendering the system ineffective.
- Potential damage to connected components, leading to costly repairs.
Monitoring these signs can ensure your vehicle remains in optimal condition, providing peace of mind on the road.
How to Diagnose Issues
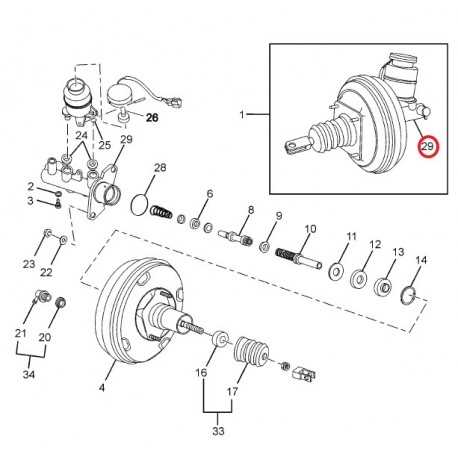
Identifying problems within a hydraulic system requires a systematic approach. By examining symptoms and using specific techniques, you can pinpoint the source of the malfunction effectively.
Common Symptoms
- Inconsistent pressure when operating
- Unusual noises during activation
- Fluid leaks around connections
- Unresponsive controls
Diagnostic Steps
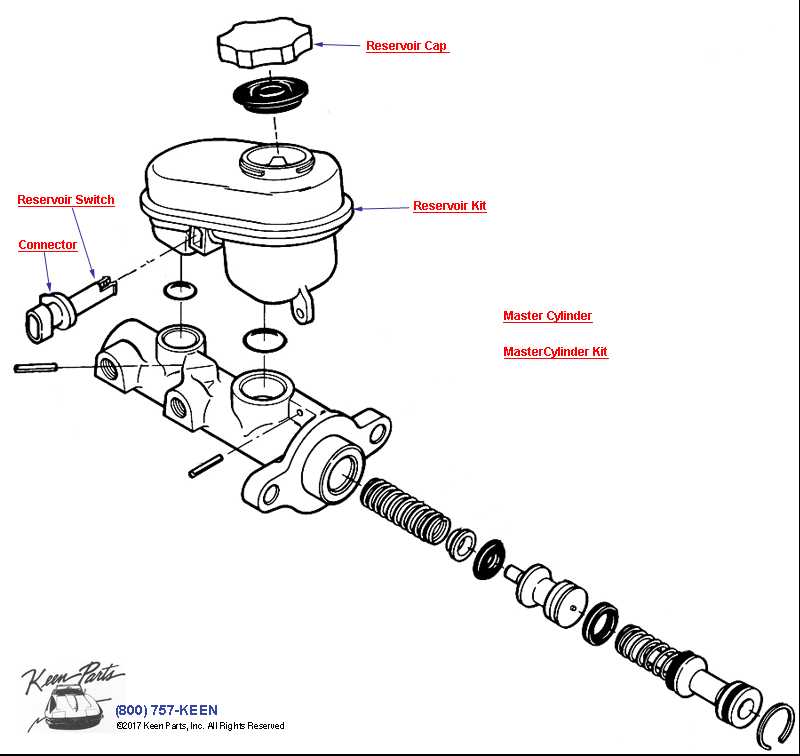
- Check fluid levels and top off if necessary.
- Inspect for leaks in hoses and connections.
- Listen for abnormal sounds when engaged.
- Test the responsiveness of the system.
- Consult a repair manual for specific troubleshooting guidelines.
Replacing the Master Cylinder
When it’s time to swap out a crucial component of your vehicle’s hydraulic system, proper procedure is essential. Ensuring efficiency and safety during the process can help maintain optimal performance on the road.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Gather necessary tools and replacement components. |
| 2 | Locate the component and disconnect fluid lines. |
| 3 | Remove mounting hardware and take out the unit. |
| 4 | Install the new component and secure it in place. |
| 5 | Reconnect fluid lines and bleed the system to remove air. |
Following these steps will help ensure that the new component functions effectively, enhancing your vehicle’s hydraulic capabilities.
Safety Precautions During Repairs
When engaging in maintenance work on vehicle hydraulic systems, it is crucial to prioritize safety to prevent accidents and injuries. Proper precautions not only protect the technician but also ensure the integrity of the vehicle components being serviced. Adhering to established guidelines will facilitate a smooth and secure repair process.
Personal Protective Equipment
Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and steel-toed boots. Gloves will safeguard your hands from harmful substances, while goggles protect your eyes from debris and splashes. Additionally, steel-toed boots provide essential foot protection against heavy objects.
Work Environment Considerations
Ensure your workspace is well-ventilated and organized. Keep tools and materials within reach to minimize movement around the area. Proper lighting is essential for visibility, allowing you to detect potential hazards and work more efficiently. Always have a first aid kit readily accessible in case of emergencies.