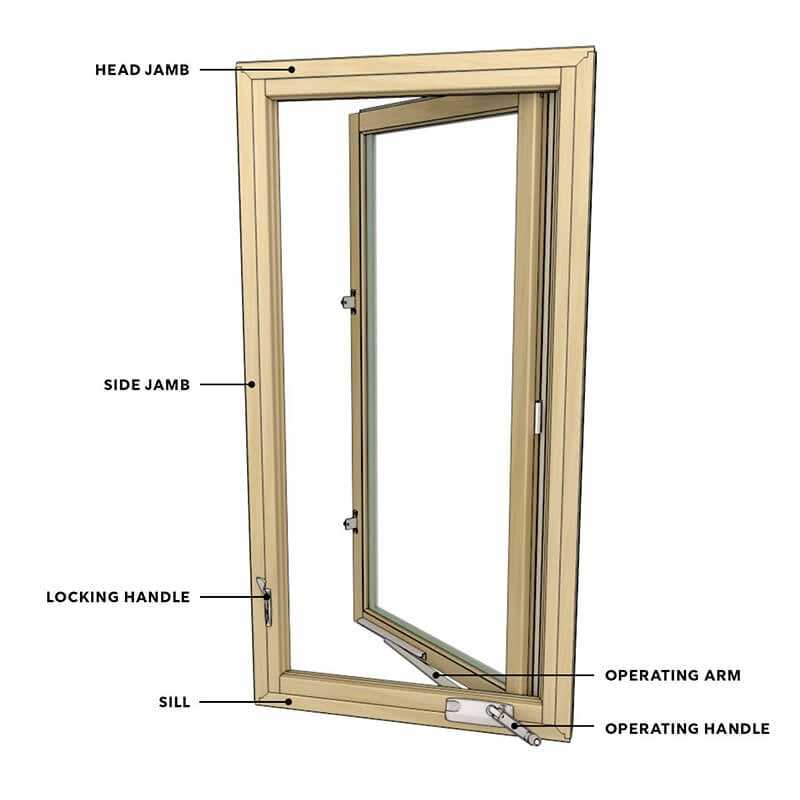
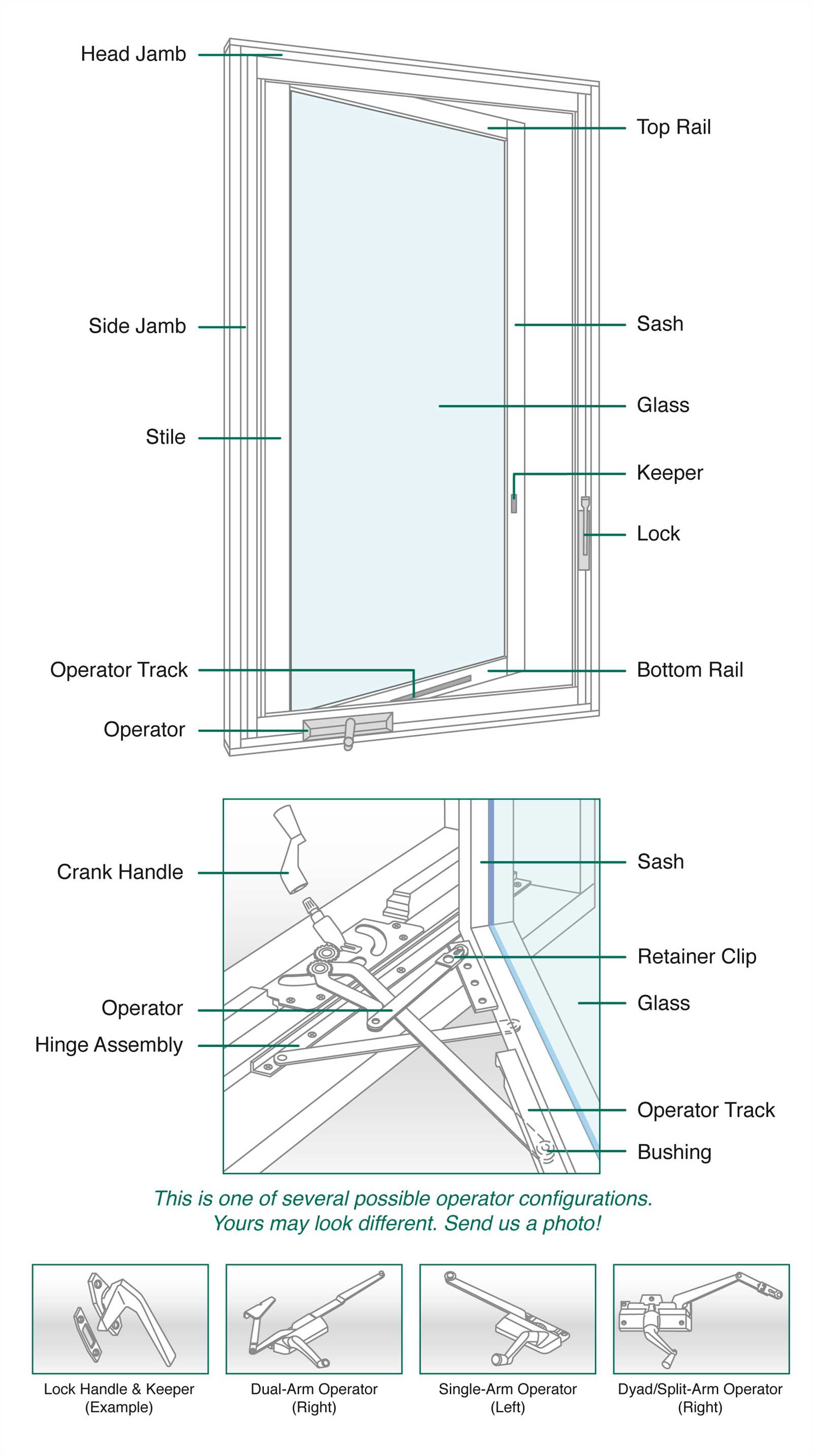
Understanding the Components of Casement Windows
Exploring the essential elements of a side-hinged opening reveals a sophisticated blend of functionality and design. Each component plays a crucial role in the overall operation, ensuring smooth performance and aesthetic appeal. From the framework to the mechanisms that facilitate movement, every aspect contributes to the integrity and usability of this architectural feature.
Identifying these elements not only enhances our appreciation of their craftsmanship but also empowers homeowners and builders to make informed decisions during installation and maintenance. A clear understanding of how these components interact can lead to more efficient repairs and upgrades.
In this section, we will delve into the specific elements that constitute a side-hinged opening, highlighting their purposes and how they work together harmoniously. This knowledge is vital for anyone looking to enhance their living space or embark on a renovation project.
Understanding Casement Windows
These innovative openings have transformed the way we experience natural light and ventilation. Their design allows for maximum airflow, making them a popular choice in both traditional and modern architecture. Exploring the mechanics and components of these fixtures reveals their functionality and appeal.
Key Features
- Flexible operation that opens outward, enhancing air circulation.
- Seamless integration with various architectural styles.
- Exceptional energy efficiency when properly sealed.
Benefits of Choosing This Design
- Improved airflow, particularly in tight spaces.
- Enhanced visibility due to large glass surfaces.
- Customizable options for frame materials and finishes.
Understanding these unique openings reveals their potential to elevate both functionality and aesthetics in any setting.
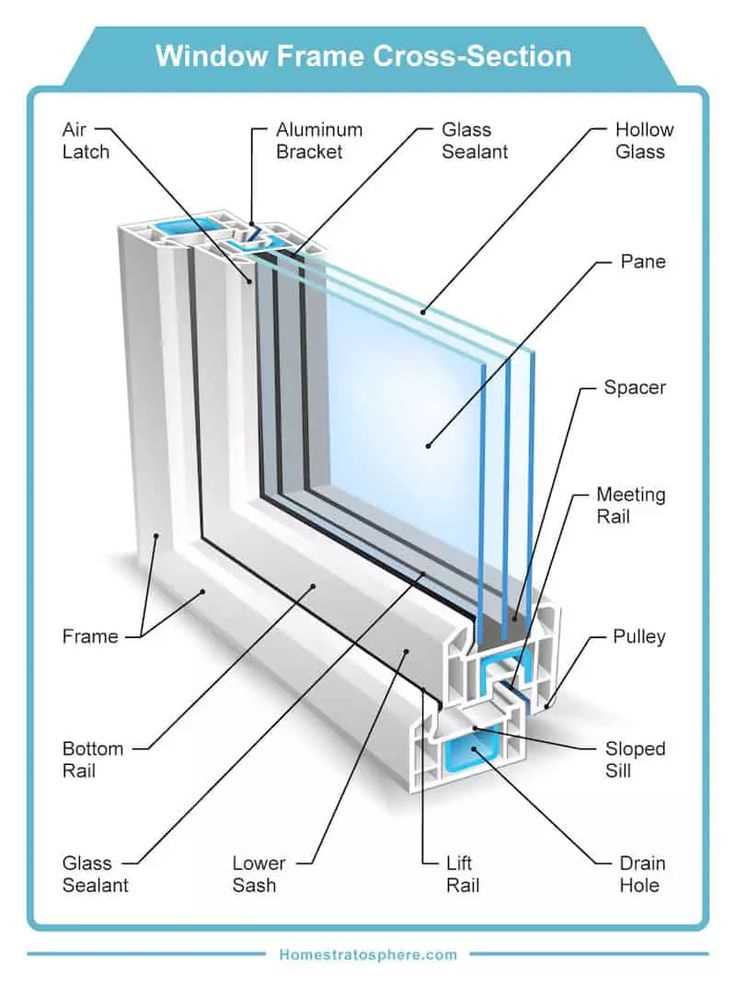
Essential Components of Casement Windows
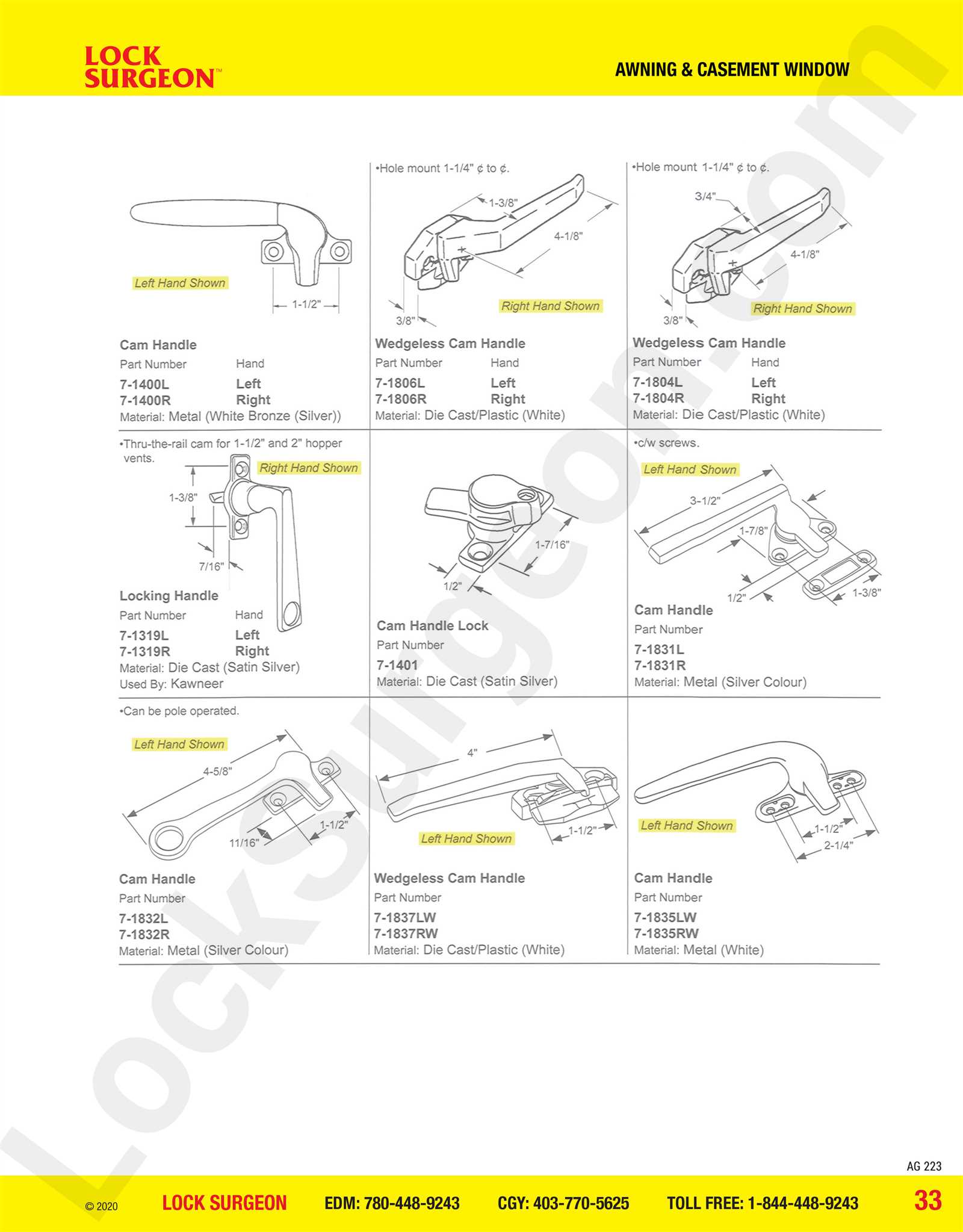
Understanding the key elements that contribute to the functionality and aesthetics of these architectural features is crucial. Each component plays a significant role in ensuring smooth operation, energy efficiency, and overall durability. Familiarity with these essential elements can aid in maintenance and enhance the performance of these installations.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Frame | The structural framework that supports the entire assembly, providing stability and shape. |
| Sash | The moveable part that holds the glazing, allowing for opening and closing functionality. |
| Glazing | The glass pane that allows light to enter while providing insulation against the elements. |
| Hinge | A pivot mechanism that enables the sash to swing outward or inward, facilitating easy access. |
| Locking Mechanism | A device that secures the sash in place when closed, enhancing security and weather resistance. |
| Weatherstripping | A sealing material that prevents air and water infiltration, improving energy efficiency. |
| Operator | A handle or crank that allows for manual operation of the opening mechanism. |
How Casement Windows Function
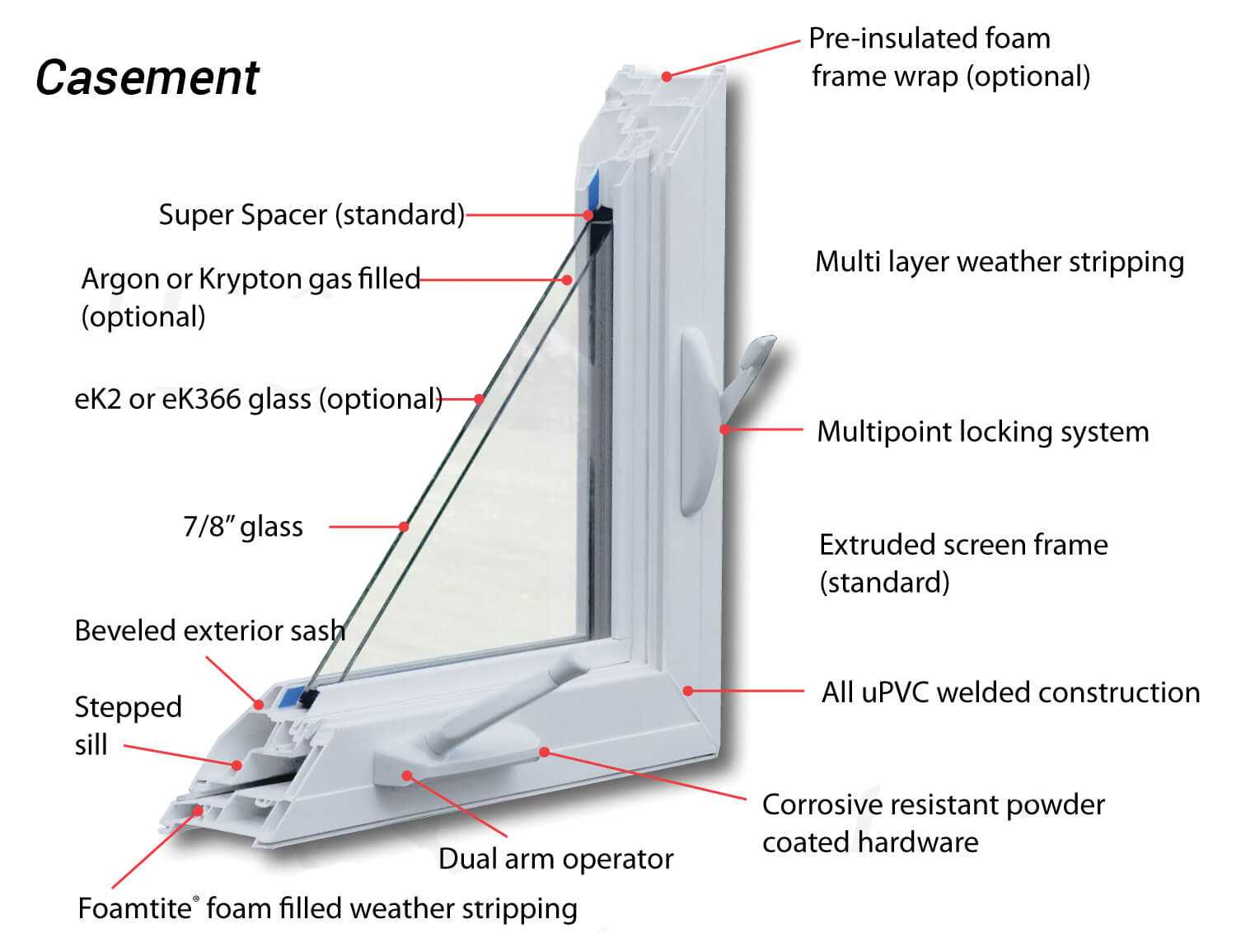
These architectural elements are designed to open outward, providing excellent ventilation and unobstructed views. The mechanism relies on a combination of hinges and a handle, allowing for easy operation. When engaged, the unit swings open like a door, enabling fresh air to flow into the interior space.
One of the key components is the hinge, which is securely fastened to the frame, ensuring stability and durability. As the handle is turned, it activates the movement of the structure, creating a seamless transition between indoor and outdoor environments. This functionality not only enhances airflow but also contributes to energy efficiency, as it allows for controlled ventilation.
Additionally, the design often includes a locking mechanism that provides security when closed. This feature is essential for maintaining safety while also allowing for peace of mind. The overall simplicity and effectiveness of the system make it a popular choice in various architectural styles.
Benefits of Using Casement Windows
Choosing the right type of opening for your home can significantly impact both aesthetics and functionality. The design in question offers a range of advantages that enhance comfort, energy efficiency, and overall appeal.
1. Optimal Ventilation: The unique outward-swinging mechanism allows for maximum airflow. This feature is especially beneficial on warm days, as it can catch breezes more effectively than many other styles.
2. Energy Efficiency: With tight seals when closed, this type of fixture can reduce drafts and maintain indoor temperatures. This results in lower energy bills and a more comfortable living environment.
3. Unobstructed Views: The design typically features larger panes of glass, offering clear, expansive views of the outdoors. This can create a brighter, more inviting atmosphere inside.
4. Easy Operation: The simple crank mechanism makes it easy to open and close, even for those with limited strength. This accessibility is a major advantage for all age groups.
5. Enhanced Security: When fully closed, these fixtures can be quite secure. The locking mechanisms can deter intruders, making them a safer choice for your home.
6. Versatile Aesthetics: Available in various styles and finishes, this option can complement any architectural design, adding charm and character to your property.
In conclusion, opting for this particular style can lead to numerous benefits that enhance the overall experience of living in your space.
Common Materials for Casement Frames
When considering the structure that provides functionality and aesthetic appeal to any opening, the choice of materials plays a crucial role. Different substances offer varying benefits, influencing durability, maintenance, and energy efficiency. Here are some of the most commonly used materials for these frameworks.
1. Wood
Wood is a traditional choice, known for its natural beauty and insulating properties. It can be easily customized to fit different styles and finishes.
- Advantages: Aesthetic appeal, good insulation, renewable resource.
- Disadvantages: Requires regular maintenance, susceptible to rot and pests.
2. Vinyl
Vinyl is a popular modern alternative due to its affordability and low maintenance. It is resistant to moisture and does not require painting.
- Advantages: Cost-effective, durable, energy-efficient.
- Disadvantages: Limited color options, can warp in extreme heat.
3. Aluminum
Aluminum is known for its strength and lightweight properties. It is often used in contemporary designs for its sleek appearance.
- Advantages: Low maintenance, resistant to rust, long-lasting.
- Disadvantages: Poor insulator compared to wood and vinyl, may require thermal breaks for energy efficiency.
Choosing the right material involves weighing these factors against personal preferences and the specific requirements of your project.
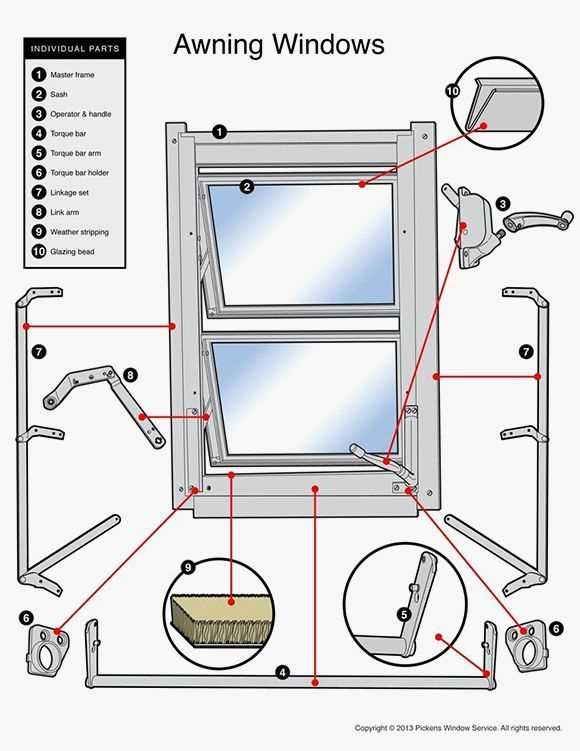
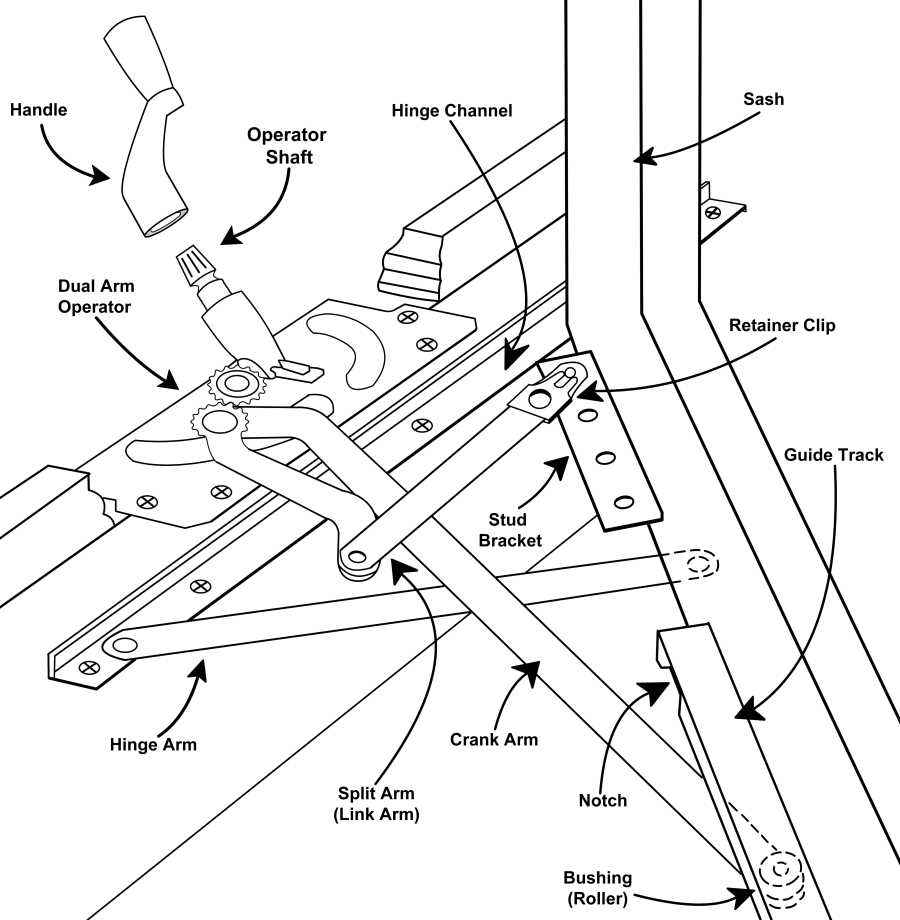
Window Operation Mechanisms Explained
Understanding the mechanisms that allow for the effective opening and closing of structures designed for ventilation and light is essential. These systems enable smooth functionality and contribute to the overall user experience. This section explores various operational methods employed in these fixtures, highlighting their unique characteristics and advantages.
Types of Operating Mechanisms
- Hinged Systems: These involve a pivot point, allowing the unit to swing open or closed. Typically mounted on one side, they provide ease of use and accessibility.
- Sliding Systems: This mechanism allows components to move horizontally along a track. They save space and are ideal for areas with limited clearance.
- Folding Mechanisms: These designs consist of multiple sections that fold inwards or outwards, maximizing the opening area while minimizing the footprint.
- Rotary Systems: In these configurations, elements rotate around a central axis, offering a unique approach to ventilation.
Advantages of Different Mechanisms
- Space Efficiency: Sliding and folding options often require less room when operated, making them perfect for compact environments.
- Ease of Operation: Hinged varieties are straightforward and intuitive, allowing for quick adjustments.
- Enhanced Ventilation: Certain designs facilitate greater airflow, optimizing indoor climate control.
- Versatility: Many mechanisms can be customized to suit various architectural styles and functional needs.
In summary, the operational mechanisms used in these fixtures play a crucial role in their effectiveness and user-friendliness. Selecting the right type can greatly enhance both functionality and aesthetics in any setting.
Maintenance Tips for Casement Windows
Ensuring the longevity and functionality of your openings is essential for a comfortable living environment. Regular upkeep not only enhances their aesthetic appeal but also prevents potential issues that could lead to costly repairs. Below are some practical tips to keep these fixtures in optimal condition.
Regular Cleaning
Clean the surfaces frequently to remove dirt and grime. Use a mild detergent mixed with water and a soft cloth to wipe down both the interior and exterior. For hard-to-reach areas, consider using a soft brush to dislodge any buildup. Make sure to dry all surfaces to prevent moisture accumulation, which can lead to deterioration over time.
Check and Lubricate Hardware
Inspect the mechanical components, including hinges and locks, regularly. If they feel stiff or do not operate smoothly, apply a light lubricant. Silicone spray or a similar product works well for this purpose. Additionally, ensure that all screws are tightened to maintain structural integrity and ease of operation.
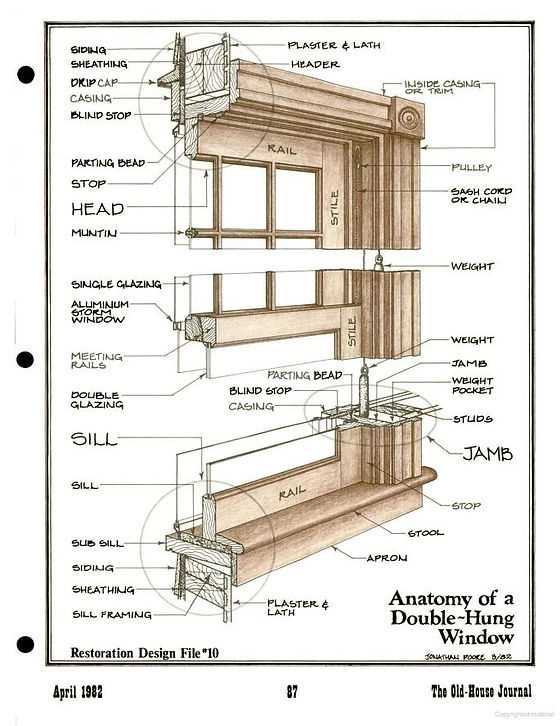
Comparing Casement and Double-Hung Windows
When considering different types of ventilation solutions for a home, it’s essential to weigh the benefits and drawbacks of various designs. Each option offers unique functionality and aesthetic appeal, influencing not only airflow but also energy efficiency and ease of maintenance. Understanding these differences can help homeowners make informed choices based on their specific needs and preferences.
One of the primary distinctions lies in the way these openings operate. The first type typically swings outward on hinges, allowing for unobstructed views and maximum airflow when fully opened. In contrast, the second option slides vertically, which can be beneficial in spaces where outward swing is impractical, such as in tight areas or near walkways.
Another important aspect to consider is maintenance. The hinged design usually allows for easier cleaning from the interior, while the sliding mechanism may require reaching out from the outside, which can be cumbersome. Additionally, the materials and construction of each type can impact their longevity and resistance to weather conditions.
In terms of energy efficiency, both styles can be designed to minimize air leakage, but their performance can vary based on installation and quality of materials. Homeowners should evaluate their climate and energy costs when deciding which style will provide the best long-term benefits.
Ultimately, the choice between these two styles should reflect individual priorities, whether they be aesthetic preferences, functionality, or maintenance considerations. By thoroughly assessing each option, one can ensure a suitable and effective addition to their living space.
Energy Efficiency of Casement Designs
The effectiveness of architectural openings in energy conservation is a crucial aspect in modern construction. When designed thoughtfully, these structures can significantly reduce energy consumption, enhance comfort, and contribute to sustainability efforts. This section explores how certain features and materials influence thermal performance and overall efficiency.
Sealing and Insulation: A vital component in minimizing heat transfer is the quality of seals around the structure. Properly fitted units reduce drafts and prevent energy loss. Advanced materials such as weatherstripping and foam seals play an essential role in maintaining temperature stability inside the building.
Glass Technology: The choice of glazing also impacts energy efficiency. Double or triple-glazed panels with low-emissivity coatings reflect heat back into the interior during colder months and reduce solar heat gain during warmer periods. This technology not only enhances comfort but also lowers energy bills.
Orientation and Design: Strategic placement can optimize natural light and reduce reliance on artificial lighting. By considering the orientation of the openings, designers can harness passive solar heating, further boosting energy efficiency.
In conclusion, integrating these elements into the design process leads to structures that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also environmentally responsible and cost-effective in the long run.
Installation Process for Casement Windows

The installation of a specific type of opening structure is a critical task that ensures optimal functionality and aesthetics. This guide outlines the essential steps to achieve a seamless and secure fitting.
- Preparation
- Gather all necessary tools and materials.
- Ensure the opening is clean and free from debris.
- Check for any structural damage that may need repair.
- Measurement
- Accurately measure the dimensions of the opening.
- Confirm the size of the unit to ensure a proper fit.
- Placement
- Position the structure within the opening.
- Use shims to adjust for level and plumb.
- Check that the unit operates smoothly before securing.
- Securing
- Fasten the unit using screws or brackets as required.
- Ensure it is tightly sealed to prevent air and water leaks.
- Finishing Touches
- Install trim or casing around the opening.
- Apply caulk to any gaps for added insulation.
- Test the operation to confirm functionality.
Following these steps will result in a well-installed unit that enhances both the appearance and energy efficiency of your space.
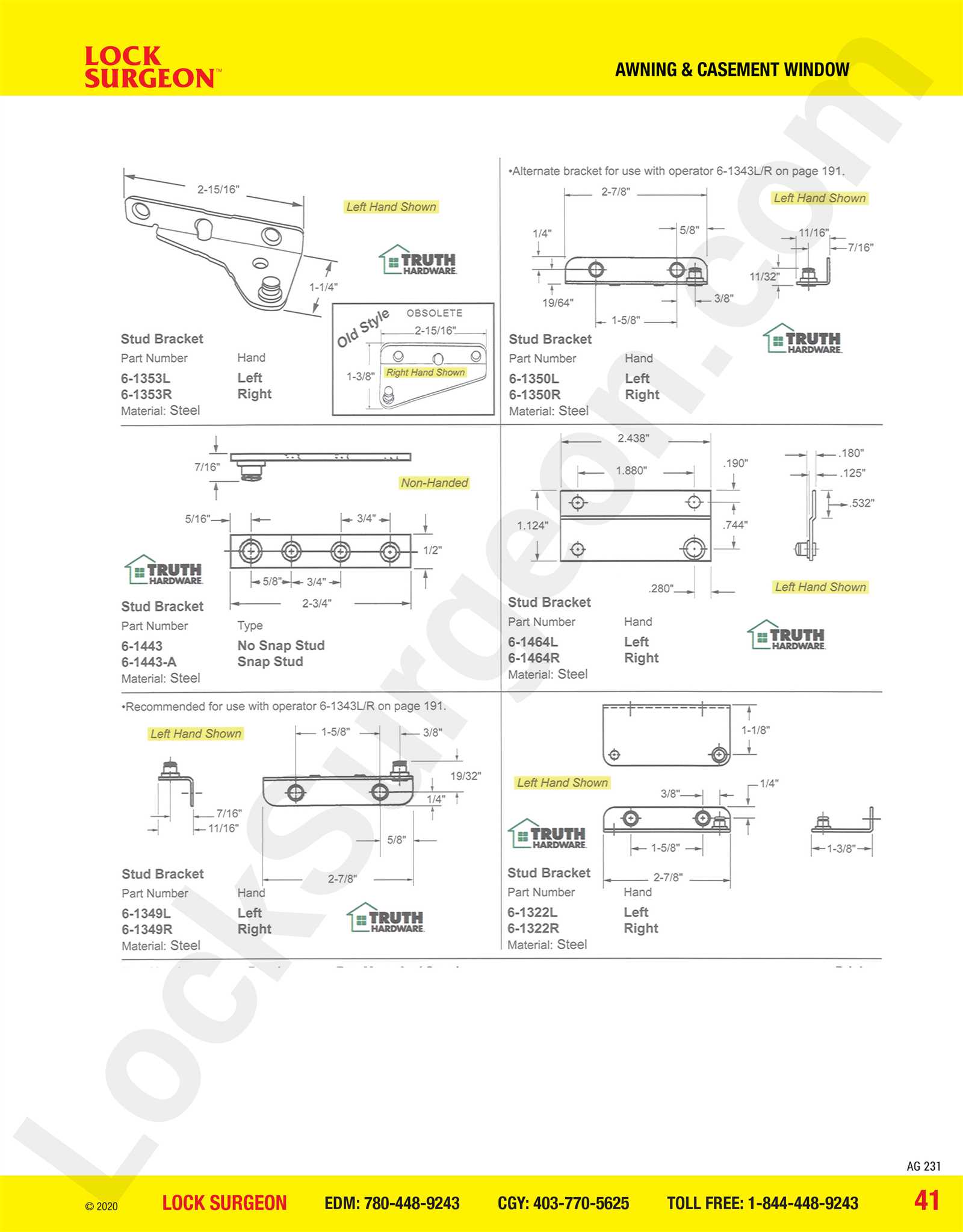
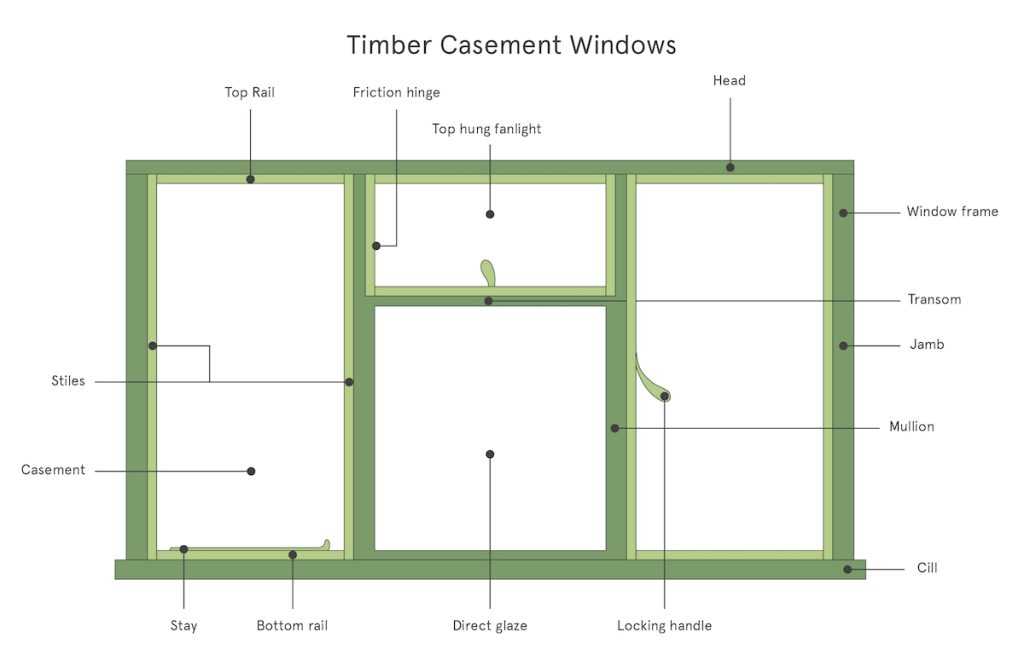
Identifying Parts in Diagrams
Understanding the components illustrated in visual representations is crucial for effective analysis and implementation. Recognizing each element allows for better comprehension of functionality and design. This knowledge empowers individuals to make informed decisions and facilitates maintenance or upgrades.
When examining these representations, consider the following key aspects:
- Labels: Look for clear annotations that indicate the name and purpose of each component.
- Shapes: Different shapes often correspond to specific functions, aiding in quick identification.
- Connections: Pay attention to how elements are interconnected, as this reveals their relationship and interaction.
To enhance understanding, follow these steps when analyzing:
- Begin with an overview to grasp the overall structure.
- Identify and note each labeled element one by one.
- Understand the functionality by referring to accompanying descriptions or guides.
- Practice by comparing various representations to recognize common features.
By systematically identifying and understanding each element, you will improve your overall grasp of the design and functionality, ultimately leading to more effective engagement with the subject matter.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Understanding the frequent problems that can arise with these types of openings is essential for maintaining their functionality and longevity. Addressing issues promptly can prevent more significant complications and ensure optimal performance over time.
1. Difficulty in Operation
One of the most common challenges is encountering resistance when trying to open or close the fixture. This issue may stem from debris accumulation in the tracks or hinges, or from misalignment due to wear and tear. Regular cleaning and lubrication can often resolve this. If misalignment is suspected, checking the alignment of the frame and making necessary adjustments can restore smooth operation.
2. Air and Water Leaks
Another prevalent concern is the presence of air or moisture intrusion. Over time, seals can degrade, allowing elements to penetrate. To address this, inspect the weatherstripping and replace it if damaged. Additionally, ensure that the mechanism is properly closed to minimize gaps. Regular maintenance checks can help identify and rectify these issues before they escalate.
Historical Context of Casement Windows
The design and functionality of hinged openings have played a significant role in architectural evolution. These structures have not only served practical purposes but have also reflected cultural and aesthetic values throughout history. Their versatility has made them a staple in various building styles, adapting to different climates and architectural trends over the centuries.
Origins and Early Usage
The roots of hinged openings can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where they were crafted from natural materials such as wood and stone. Early examples can be found in:
- Roman architecture, which featured large openings for ventilation and light.
- Medieval structures that incorporated smaller, more secure designs for safety and warmth.
- Renaissance buildings, where aesthetics began to play a more significant role, leading to ornate designs.
Evolution Through the Ages
As architectural styles evolved, so did these hinged features. The following points highlight key developments:
- The introduction of glass in the 16th century allowed for larger, more elaborate openings, enhancing natural light and views.
- The Industrial Revolution brought advancements in manufacturing, making these structures more accessible and diverse in design.
- In the 20th century, modernist movements embraced simplicity, leading to minimalistic forms that emphasized functionality.
This historical journey illustrates how these elements have continuously adapted, influencing both residential and commercial architecture across different regions and periods.