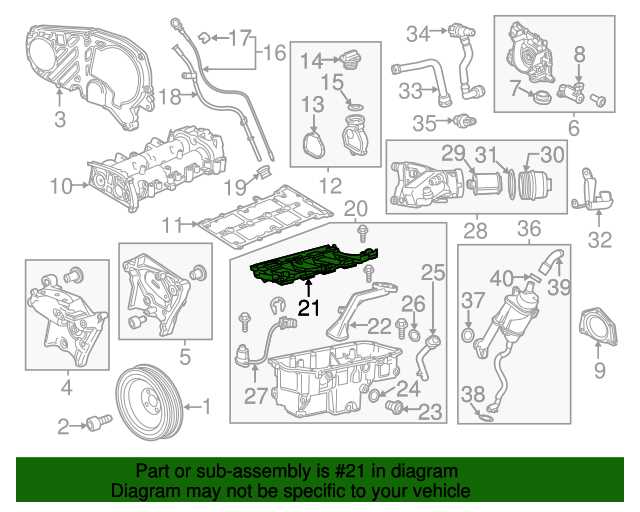
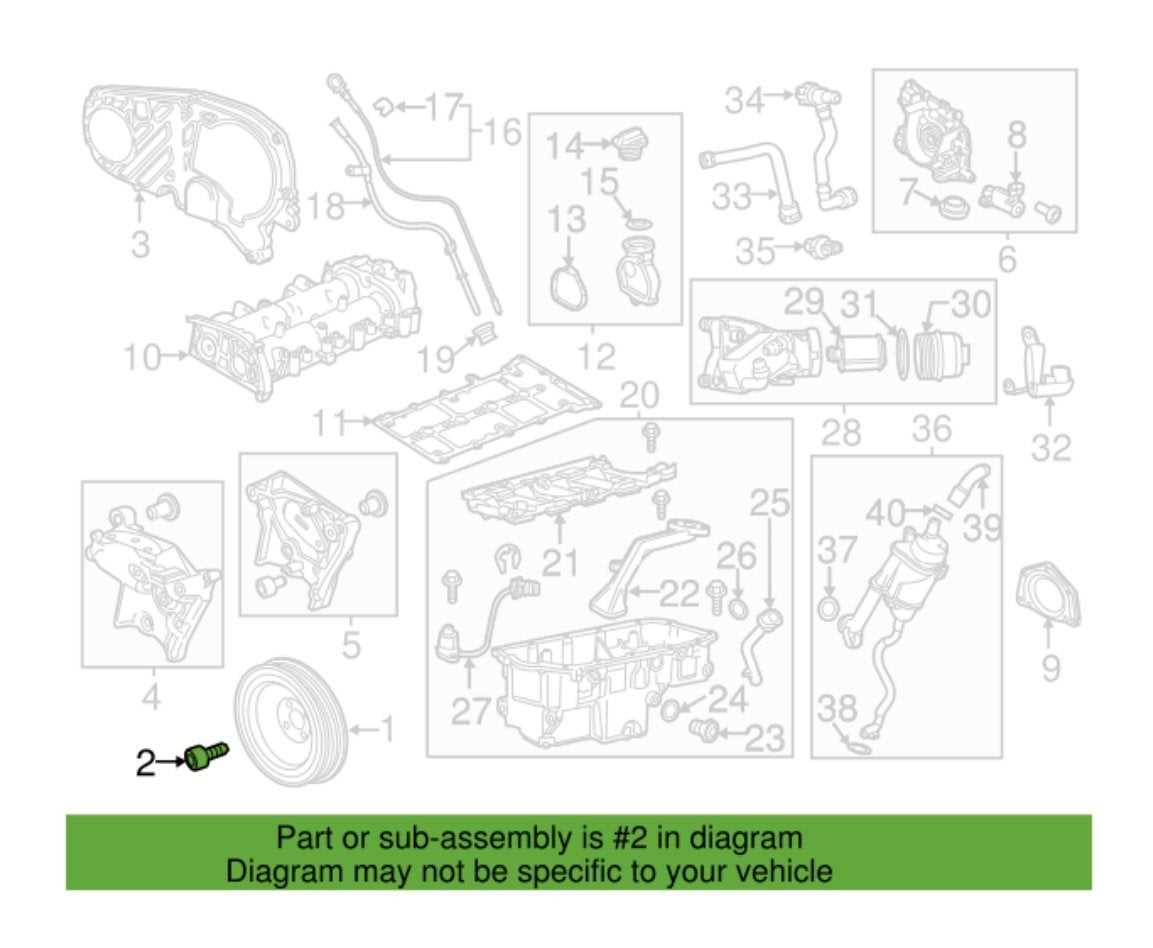
| Exploring the Engine’s Cooling System
The cooling mechanism of a vehicle plays a critical role in maintaining optimal performance by preventing overheating during operation. By regulating the temperature of key components, it ensures that heat generated from combustion is effectively dissipated. A well-functioning system allows the motor to run smoothly under various conditions, keeping temperatures within a safe range.
This intricate system consists of multiple components working together to circulate fluid and maintain balance. Pipes, pumps, and thermal controls ensure that coolant moves efficiently, reducing excess heat. Regular maintenance of this mechanism is essential to prevent malfunctions that could lead to costly repairs.
Functionality of the Timing Belt and Chain

The timing belt and chain play crucial roles in the smooth operation of a vehicle’s internal mechanisms. These components synchronize the movement of the crankshaft and camshaft, ensuring that the valves open and close at the correct intervals in relation to the piston movement. Their proper functioning is essential for optimal performance, efficiency, and longevity of the overall system.
Synchronization of Components
One of the primary functions of the timing belt and chain is to maintain precise synchronization between various mechanical elements. This synchronization is vital for effective combustion and power generation. A misaligned or malfunctioning timing mechanism can lead to serious issues, including engine misfires or catastrophic failures.
Durability and Maintenance
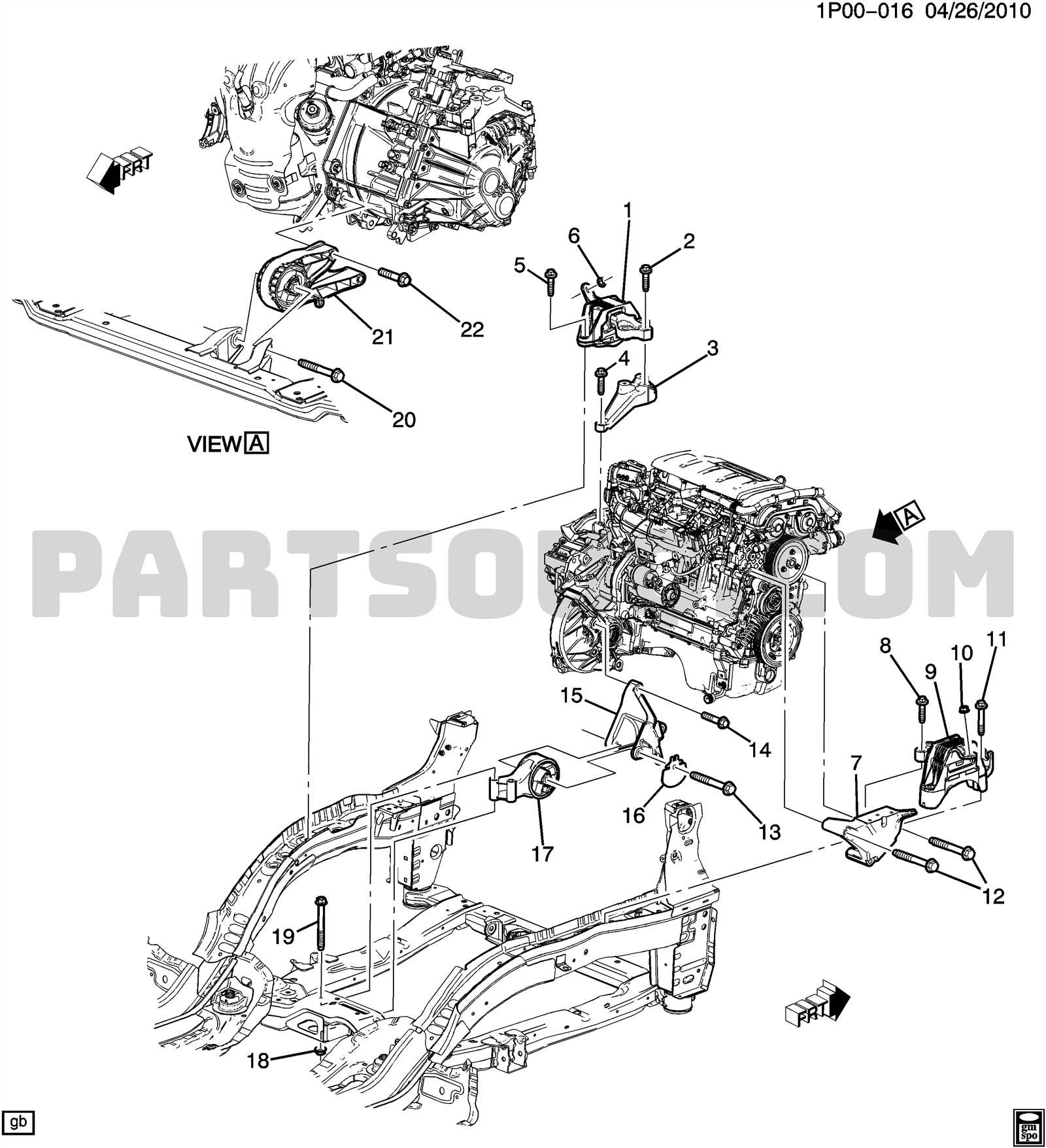
Regular maintenance of the timing system is essential to ensure durability and reliability. Over time, wear and tear can weaken these components, making periodic inspections and replacements necessary. Awareness of the signs of deterioration can help prevent extensive damage and costly repairs, keeping the overall system in peak condition.
Understanding the Exhaust System Layout
The exhaust system plays a crucial role in ensuring that harmful gases produced during combustion are effectively expelled from the vehicle. This system not only enhances performance by optimizing airflow but also contributes to the overall efficiency of the automobile. By understanding its components and layout, one can appreciate how this assembly works to minimize emissions and noise while maintaining engine performance.
Key Components of the Exhaust Assembly

The exhaust assembly consists of several critical components that work together seamlessly. These include the manifold, which collects exhaust gases from the cylinders, and the catalytic converter, which facilitates the conversion of harmful pollutants into less harmful emissions. Additionally, the muffler serves to reduce noise, while the pipes transport gases away from the vehicle. Each of these elements is designed with precision to ensure optimal flow and efficiency.
Flow Path and Functionality
The layout of the exhaust system is engineered to create a clear pathway for exhaust gases. The gases flow from the manifold through the catalytic converter and into the muffler before being expelled through the tailpipe. This route is designed to minimize back pressure, which can hinder engine performance. Understanding this flow path helps in diagnosing issues related to performance and emissions, ensuring that the vehicle operates efficiently.
Fuel System Parts and Diagram
The fuel delivery mechanism in vehicles plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient combustion and optimal performance. This section provides an overview of the components involved in transporting and regulating fuel flow within the system. Understanding these elements is essential for diagnosing issues and performing maintenance effectively.
At the core of the fuel delivery system is the fuel tank, which stores the gasoline or diesel until needed. Fuel is drawn from the tank by the fuel pump, which pressurizes the liquid and sends it through the system. The fuel filter is another vital component, ensuring that impurities do not enter the engine, which can lead to damage and reduced efficiency.
The pressurized fuel travels through lines to the fuel injector or carburetor, where it is atomized and mixed with air for combustion. In modern systems, fuel rails distribute the fuel evenly to each injector, enhancing performance. Additionally, the pressure regulator maintains optimal pressure within the system, allowing for consistent fuel delivery under varying engine conditions.
In summary, this assembly of components ensures the proper flow and quality of fuel, which is essential for achieving the desired power output and efficiency in vehicles.
Air Intake and Filtration System Breakdown
The air intake and filtration setup plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal performance and efficiency in vehicles. This system is designed to ensure that the engine receives clean air for combustion, which is essential for smooth operation. Understanding the various components of this system can help in diagnosing issues and performing maintenance effectively.
Key components of the air intake and filtration system include:
- Air Filter: This element traps dirt, debris, and contaminants from the air before it enters the combustion chamber.
- Intake Manifold: A crucial part that distributes the air to the cylinders, ensuring an even flow for combustion.
- Throttle Body: This component controls the amount of air entering the engine, playing a vital role in engine performance.
- Mass Air Flow Sensor: This sensor measures the amount of air entering the system and helps adjust the fuel delivery for optimal combustion.
- Air Ducts and Hoses: These pathways transport air from the filter to the engine, ensuring a steady airflow.
Regular maintenance of this system is essential for preventing performance issues and prolonging the lifespan of the vehicle. Routine inspections and timely replacements of the air filter and other components can lead to improved efficiency and overall vehicle health.
Detailed View of the Engine Block
The heart of a vehicle’s performance lies within its core structure, which plays a crucial role in the overall functionality and efficiency. This assembly houses several essential components that work together to convert fuel into motion, ensuring optimal operation under various conditions.
In this section, we will explore the various elements that make up this critical assembly, focusing on their roles and interactions. Understanding these features can enhance comprehension of how they contribute to the overall system.
- Structure: The main framework that supports other components and withstands high levels of stress and heat.
- Cylinders: Hollow chambers where combustion occurs, generating the power needed for movement.
- Cooling passages: Channels designed to circulate coolant, helping to regulate temperature and prevent overheating.
- Oil galleries: Pathways that distribute lubricating oil to reduce friction and wear on moving parts.
- Mounting points: Locations where various systems and accessories attach, ensuring stability and integration with the overall design.
Each of these elements plays a significant role in the functionality and longevity of the assembly. Understanding their purpose and how they interconnect allows for better maintenance and troubleshooting, leading to enhanced performance and reliability.
Electrical Connections in the Engine Bay
The system of electrical linkages within the front compartment is crucial for ensuring the smooth operation of various components. These connections facilitate the flow of power and signals, allowing different parts to communicate effectively. Understanding these linkages can help in troubleshooting issues and maintaining overall vehicle performance.
Key Electrical Components
- Battery: Provides the initial power needed to start the vehicle.
- Alternator: Charges the battery and powers electrical systems when the engine is running.
- Fuses: Protect electrical circuits from overloads by breaking the circuit when current exceeds safe levels.
- Relays: Act as switches that control high-current circuits with low-power signals.
Common Connection Types
- Connector Blocks: Multi-pin connectors that join multiple wires for streamlined connections.
- Terminal Ends: Individual points where wires connect to components, providing a secure interface.
- Ground Connections: Ensure that electrical systems have a safe return path, preventing shorts and ensuring stability.
Lubrication System: Key Components
The lubrication mechanism plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth operation and longevity of a vehicle’s internal machinery. It is designed to reduce friction between moving elements, thereby minimizing wear and tear. This system is vital for maintaining optimal performance, preventing overheating, and protecting components from damage due to lack of proper lubrication.
| Component |
Function |
| Oil Pump |
Circulates lubricant throughout the system, ensuring all components receive adequate lubrication. |
| Oil Filter |
Removes contaminants and debris from the lubricant, maintaining cleanliness and preventing damage to moving parts. |
| Oil Pan |
Holds the lubricant when the system is not in operation, acting as a reservoir and providing access for the pump. |
| Lubrication Lines |
Channels through which the lubricant travels, delivering it to various components needing protection and support. |
| Oil Pressure Switch |
Monitors the lubricant pressure within the system, providing alerts for potential issues if the pressure drops below normal levels. |
|