2009 Honda Civic Parts Diagram Overview
Understanding the layout and configuration of essential mechanical elements is crucial for both maintenance and repair. Each section of a vehicle relies on the correct positioning and connection of various elements, working in unison to ensure smooth performance and reliability.
Having a clear reference to the structure and placement of these components can help identify the cause of potential issues and allow for quick and efficient troubleshooting. This guide offers insight into how different elements are interconnected within the engine, transmission, and other vital systems.
Whether you’re looking to replace worn-out pieces or upgrade specific areas, a detailed look at the arrangement of mechanical and electrical components will prove invaluable for proper installation and adjustments. This overview is designed to assist in locating each critical part to facilitate optimal operation and longevity.
2009 Honda Civic Component Layout Overview

The layout of key mechanical and electrical elements in this vehicle is thoughtfully designed to ensure accessibility and functionality. Each section is strategically organized to facilitate maintenance and optimize overall performance.
- Engine Bay: A central feature housing various essential systems, including fluid reservoirs and key mechanical components.
- Interior Console: The internal layout features easy access to critical controls, ensuring a user-friendly experience for drivers and passengers.
- Undercarriage: This area provides structural support and protection for important elements beneath the frame.
Each of these areas contains carefully placed components, ensuring smooth operation and straightforward maintenance when needed.
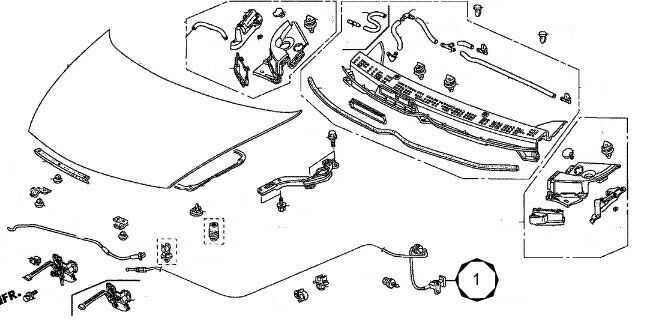
Engine Bay Parts Identification
The engine bay houses several essential components that work together to ensure the vehicle operates smoothly. Understanding the location and function of each part is crucial for maintaining and troubleshooting the system. This section provides a clear overview of key elements located under the hood, aiding in proper identification and comprehension of their roles.
| Component | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cooling System | Responsible for regulating the temperature of the engine to prevent overheating and maintain optimal performance. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intake System | Facilitates the flow of air into the engine for combustion, improving fuel efficiency and power output. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Battery | Supplies electrical power to start the vehicle and supports various electronic systems when the engine is off. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transmission | Transfers the engine’s power to the wheels, allowing the vehicle to move at different speeds and torque levels. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Component | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brake Pedal | The device that initiates the braking process when pressure is applied by the driver. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Master Cylinder | Converts the force from the pedal into hydraulic pressure, which is then distributed to the rest of the system. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brake Lines | These tubes carry the hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder to the braking mechanisms at each wheel. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brake Calipers | They
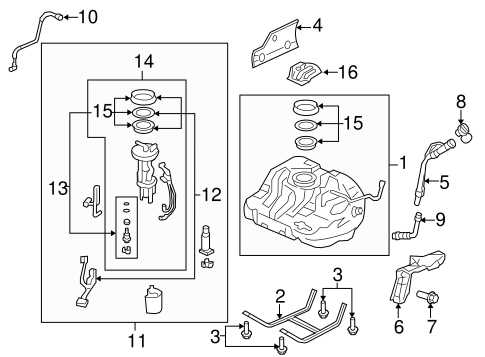
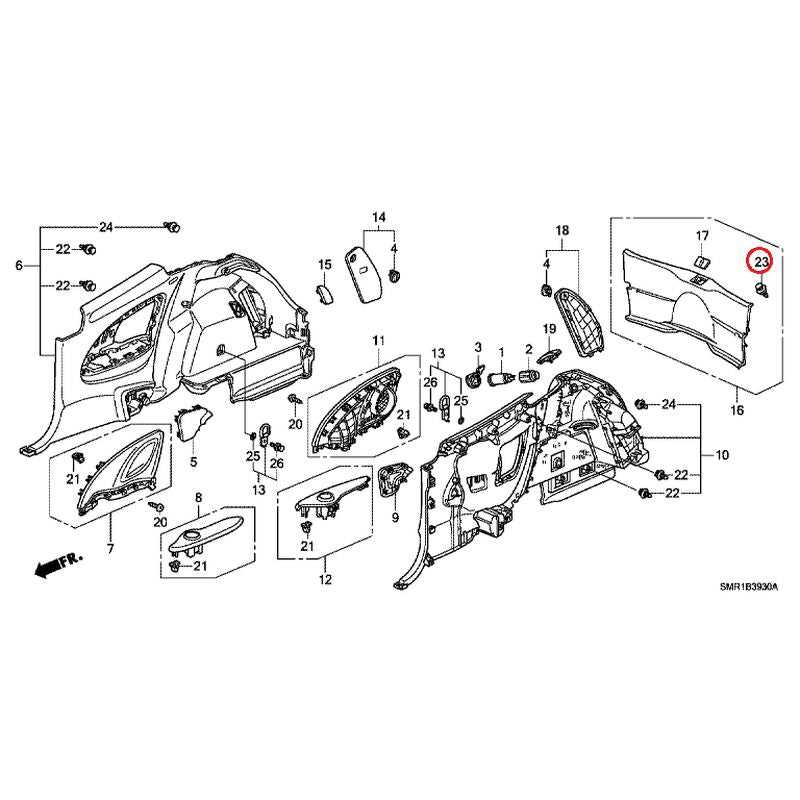
Suspension Elements and Their PlacementThe arrangement of key components responsible for absorbing road impact and maintaining vehicle stability plays a critical role in ensuring a smooth and safe ride. These elements work together to provide a balance between comfort and handling, responding to various driving conditions and terrain types. Understanding their positioning and function is essential for proper maintenance and optimal performance. Main ComponentsSeveral vital components are involved in this system. These include shock absorbers, which reduce the impact of road irregularities, and control arms that help guide the wheel’s motion. Together, they form a complex structure that enhances both comfort and control. Placement and FunctionalityEach component is strategically placed to handle specific loads and forces. For example, the springs are positioned to bear the weight of the vehicle, while the stabilizer Interior Equipment and Controls MappingThe layout of the vehicle’s cabin is designed to ensure easy access to essential controls and features, promoting convenience and safety for both the driver and passengers. Understanding the arrangement of various interior components allows for efficient use of the system during operation.
Understanding the interplay between these components is essential for troubleshooting issues related to overheating and coolant leaks. Regular maintenance of the cooling assembly ensures the engine operates within a safe temperature range, preventing damage and enhancing performance. Air Conditioning and HVAC Components
In modern vehicles, maintaining a comfortable environment is crucial, and the climate control system plays a vital role in achieving this. This system consists of various elements that work together to regulate temperature, humidity, and air quality inside the cabin. Understanding these components can enhance the efficiency of the system and aid in troubleshooting any issues that may arise.
Each of these components plays a significant role in ensuring optimal performance of the climate control system. Regular maintenance and inspections can prevent potential failures and enhance the longevity of the entire system. Body Panels and Exterior Trim
The external components of a vehicle play a crucial role in both aesthetics and functionality. These elements not only define the overall look of the automobile but also serve to protect internal mechanisms and improve aerodynamic performance. Understanding the various parts that make up the outer shell is essential for maintenance and repair. Key Components
Exterior Trim Elements
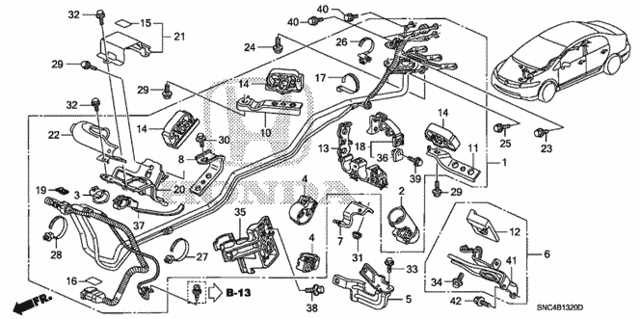
Maintaining these exterior features is vital for both the performance and appearance of the vehicle. Regular inspections can help identify wear and tear, ensuring longevity and safety. Lighting and Signal Components DiagramThis section explores the various elements associated with illumination and signaling systems in vehicles. Understanding the configuration of these components is crucial for maintaining optimal visibility and ensuring safe communication with other road users. Each element serves a specific function, contributing to the overall performance of the vehicle’s lighting system. Key Components
Functional RelationshipsEach component interacts with others to create a cohesive lighting system. Understanding these relationships enhances the ability to diagnose issues and perform effective repairs.
|