Understanding the Components of a John Deere 4200
In agricultural and industrial machinery, having a clear visualization of how various elements are interconnected is essential for maintenance and repairs. A detailed overview of a machine’s internal and external components ensures that users can identify specific elements with ease, streamlining the process of part replacement or repair.
Being familiar with the mechanical structure of your equipment aids in troubleshooting and enhances the overall efficiency of upkeep. This guide will provide a breakdown of essential systems and connections, offering users a clear perspective on how various sections interact and support each other during operation.
Whether addressing minor adjustments or more complex technical tasks, understanding the full scope of the equipment’s layout will ensure smoother operations and prolong the lifespan of the machine.
Essential Components of the John Deere 4200
The core elements of this versatile machinery are designed to ensure optimal performance and durability in various tasks. Understanding these key structures helps operators maintain efficiency and extend the equipment’s lifespan.
Power and Transmission Systems
The engine and transmission form the backbone, providing the necessary power for different operations. This combination delivers both speed and torque, making it suitable for a range of workloads.
- Reliable engine for consistent power output
- Efficient transmission system for smooth operation
- Multiple gears for adapting to different terrains
Hydraulics and Attachments
The hydraulic system plays a crucial role in managing attachments and lifting capacities. These connections allow the machine to handle heavy loads and various tools seamlessly.
- Strong hydraulic system for enhanced lifting power
- Attachment points for versatile tool use
- Flexible operations for both front and rear implements
Understanding the Tractor’s Engine Layout
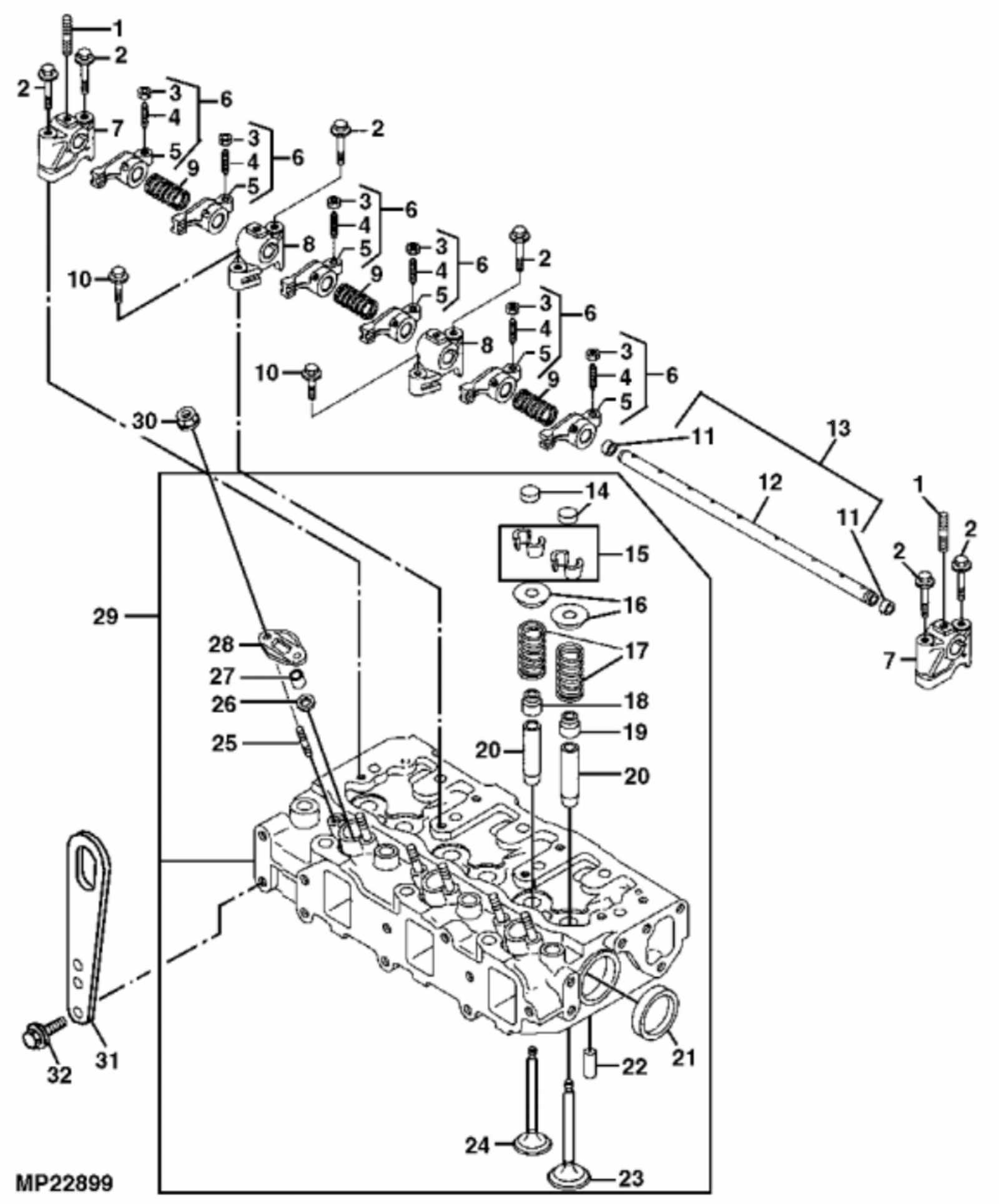
The internal configuration of a tractor’s engine is critical for its overall performance. Recognizing how various components work together helps in both maintenance and troubleshooting. This section provides an overview of the key elements that form the engine’s structure, focusing on the arrangement and function of essential systems without diving into specifics.
Key Components and Their Placement
At the heart of the engine, you’ll find several interconnected parts that drive the machine’s power. The cylinder block, which houses the pistons, is central to this setup. Surrounding it, various other systems, such as fuel injection and cooling mechanisms, play vital roles in maintaining efficient operation. Proper alignment and connection of these systems ensure smooth performance.
Engine Performance and Efficiency
Every part of the engine layout is designed with efficiency in mind. The distribution of elements, from the intake to the exhaust, is engineered to reduce friction and maximize output. Understanding this layout is key to optimizing the engine’s longevity and ensuring consistent, powerful performance under varying conditions.
Hydraulic System: Key Parts and Functions
The hydraulic system in modern machinery is a critical component that ensures efficient power transmission and precise control of various mechanical movements. Its design integrates several essential elements that work together to operate different functions, contributing to the machine’s overall performance and reliability.
Main Hydraulic Components
- Pumps: Responsible for generating the flow of hydraulic fluid necessary to create pressure within the system.
- Valves: Control the direction, flow, and pressure of the fluid, ensuring that the correct force is applied where needed.
- Hydraulic Cylinders: Convert the fluid pressure into mechanical force to drive motion in various parts of the machine.
- Reservoir: Stores the hydraulic fluid and helps to dissipate heat generated during operation.
Hydraulic System Functions
- Power Transmission: The system allows for smooth transmission of energy, ensuring efficient use of mechanical force in different tasks.
- Precision Control: With carefully calibrated components, the system provides fine-tuned control ove
Transmission Assembly Breakdown
The transmission system is a crucial component of any machinery, ensuring the proper transfer of power from the engine to the wheels. Understanding its internal structure allows for better maintenance and troubleshooting, leading to extended equipment longevity and efficiency.
Main Gear Components
The transmission is built around a series of gears that handle various speed settings and torque adjustments. These gears are designed to withstand significant force while smoothly shifting power. High-performance bearings and gear synchronizers play a vital role in reducing friction and ensuring seamless transitions during operation.
Hydraulic and Mechanical Integration
Hydraulic systems often complement mechanical components, allowing for smoother gear shifts and improved control over the machine’s movement. Proper alignment and lubrication of the hydraulic lines are essential for maintaining optimal performance and preventing system wear.
Identifying Steering Mechanism Components
Understanding the elements of the steering system is crucial for maintaining optimal functionality. This section focuses on recognizing the key components that make up the steering mechanism. Each part plays a vital role in ensuring smooth and responsive handling of the machine.
Steering Wheel: The main interface through which the operator controls the direction of the vehicle. It is connected to the steering column and provides the leverage necessary for turning the wheels.
Steering Column: This component links the steering wheel to the rest of the system, allowing for the transfer of movement. It typically houses mechanisms for tilt and adjustment, ensuring comfort and proper control for the operator.
Steering Linkages: These are the connecting rods and joints that transmit the motion from the steering column to the wheels. Their condition is essential for precise and responsive steering.
Hydraulic Cylinders: In some setups, hydraulic cylinders assist in turning the wheels, providing added force and reducing manual effort. They are integral in ensuring smooth and efficient steering, especially in larger machines.
Proper identification and maintenance of these parts can prevent costly repairs and extend the longevity of the machine.
Electrical System: Wiring and Key Parts
The electrical system of a machine plays a vital role in its overall functionality. Understanding the components and their connections is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Wiring Harness: A network of wires that connects various electrical components, ensuring seamless communication and power distribution.
- Battery: Provides the necessary energy to start the engine and power electrical accessories.
- Starter Motor: Engages the engine during ignition, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy.
- Alternator: Charges the battery while the engine runs, maintaining the electrical system’s power supply.
- Fuses: Protect circuits from overload by breaking the connection when excessive current flows.
- Relays: Act as switches to control high-power components with low-power signals.
By delving into these key elements, users can ensure the efficient operation of the electrical system and enhance the longevity of their machinery.
Fuel System Overview and Diagram
The fuel mechanism in agricultural machinery plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. This section provides insights into the various components involved in the fuel delivery process, highlighting their functions and interconnections. Understanding this system is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting, ultimately enhancing the longevity of the equipment.
Key Components of the Fuel Mechanism
The primary elements of the fuel system include the fuel tank, pump, filters, injectors, and lines. Each part works in harmony to transport fuel from the tank to the engine, where it is transformed into energy. Below is a brief overview of these components:
Component Function Fuel Tank Stores fuel until it is needed by the engine. Fuel Pump Moves fuel from the tank to the engine at the required pressure. Filters Remove impurities and contaminants from the fuel to protect engine components. Injectors Atomize fuel for efficient combustion within the engine cylinders. Fuel Lines Connect all components, allowing the fuel to flow smoothly. Understanding Fuel Flow
The flow of fuel begins at the tank, where it is drawn by the pump. Once pressurized, the fuel passes through filters that catch any debris, ensuring that only clean fuel reaches the injectors. The injectors then disperse the fuel into the engine, facilitating combustion and powering the machinery. Regular inspection and maintenance of these components are essential for uninterrupted operation.
Cooling System Parts and Their Roles
The cooling mechanism in agricultural machinery plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal operating temperatures, preventing overheating, and ensuring efficient performance. Each component within this system contributes to the overall functionality, working in harmony to manage heat generated by the engine during operation. Understanding these elements and their specific duties is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Main Components
The primary elements of the cooling system include a variety of key components that each serve distinct functions to regulate temperature effectively.
Component Function Radiator Dissipates heat from the coolant into the air, lowering the temperature of the fluid before it returns to the engine. Water Pump Circulates coolant throughout the system, ensuring constant flow and preventing hot spots. Thermostat Regulates coolant flow based on temperature, opening and closing to maintain optimal engine heat. Coolant Reservoir Stores excess coolant and allows for thermal expansion, ensuring the system remains full and efficient. Hoses Transport coolant between components, facilitating the flow of fluid throughout the cooling system. Importance of Regular Maintenance
Brake System Structure and Components
The brake system in agricultural machinery plays a crucial role in ensuring safety and control during operation. It comprises various elements that work together to slow down or stop the vehicle effectively. Understanding the structure and function of these components is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting.
Component Description Brake Pedal Initiates the braking process when pressed by the operator. Brake Cylinder Transforms the pedal force into hydraulic pressure. Brake Lines Transport hydraulic fluid from the cylinder to the brakes. Brake Shoes Press against the drum to create friction and reduce speed. Drum/Disc Provides a surface for the brake shoes to contact and apply force. Front Axle Assembly and Its Parts
The front axle assembly plays a crucial role in the overall functionality of agricultural machinery. It is designed to support the weight of the vehicle, provide stability during operation, and facilitate smooth steering. Understanding its components is essential for maintenance and optimal performance.
Key Components of the Front Axle
This assembly consists of several integral elements, each contributing to its efficiency and durability. Key components include the axle housing, kingpins, and bearings, among others.
Component Description Axle Housing Encloses and protects internal parts, ensuring structural integrity. Kingpins Pivot points for steering, allowing for smooth directional changes. Bearings Support rotational movement, reducing friction between moving parts. Maintenance Tips
Regular inspection and lubrication of the axle assembly are vital to prevent wear and extend its lifespan. Proper care ensures that the vehicle maintains its performance and reliability in various conditions.
Rear Drive System and Key Elements
The rear drive mechanism is a crucial component in ensuring optimal performance and efficiency in agricultural machinery. Understanding its structure and functionality is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting. This section delves into the primary elements that comprise this system, highlighting their roles and importance.
Key Components
- Transmission: This unit transmits power from the engine to the rear wheels, enabling movement and control.
- Axles: They connect the wheels to the transmission and facilitate the transfer of torque, playing a vital role in stability and handling.
- Differential: This component allows for the independent rotation of wheels, enhancing maneuverability, especially during turns.
- Drive Shafts: These shafts connect the transmission to the axles, transferring power efficiently to the wheels.
Maintenance Considerations
- Regularly check fluid levels in the transmission to ensure smooth operation.
- Inspect axles for signs of wear or damage, replacing them as necessary.
- Lubricate the differential to prevent overheating and ensure longevity.
- Examine drive shafts for any signs of misalignment or wear.
Maintaining these key components is essential for the reliability and performance of the machinery. Understanding their functions allows operators to make informed decisions regarding maintenance and repairs.
Loader Attachments and Relevant Parts
Understanding the various accessories that can be utilized with compact machinery is essential for maximizing efficiency in agricultural and construction tasks. Each attachment serves a specific purpose, enhancing the capabilities of the equipment and allowing operators to tackle a range of activities with ease.
Types of Loader Attachments
- Bucket Attachments
- Forks
- Bale Spears
- Snow Plows
- Grapples
These accessories not only improve productivity but also offer versatility, allowing for quick changes based on the job requirements. Each type of attachment comes with unique components that may require maintenance or replacement over time.
Essential Components for Maintenance
- Hydraulic Cylinders
- Mounting Brackets
- Lift Arms
- Connection Pins
- Seals and Gaskets
Regular inspection and timely replacement of these essential components ensure that the loader operates smoothly and effectively, minimizing downtime and enhancing performance. Familiarity with these attachments and their maintenance needs can lead to better decision-making for operators.
Maintenance Tips for Essential Components
Proper upkeep of crucial machinery elements is vital for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Regular attention to these components can prevent costly repairs and enhance efficiency. Below are essential tips to maintain various integral parts effectively.
- Lubrication: Regularly apply appropriate lubricants to moving parts to minimize friction and wear. Ensure that you use the recommended types specific to each component.
- Filters: Change air, oil, and fuel filters at regular intervals. Clogged filters can lead to decreased performance and increased fuel consumption.
- Batteries: Check battery connections for corrosion and ensure terminals are clean. Regularly test battery charge levels to avoid unexpected failures.
In addition to these tips, consider the following practices for enhanced maintenance:
- Inspect belts and hoses for signs of wear or damage. Replace them as needed to prevent breakdowns.
- Keep the exterior clean to avoid dirt accumulation that can affect performance.
- Adhere to the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule for inspections and service.
By following these guidelines, you can significantly improve the reliability and efficiency of your machinery, ensuring it operates smoothly for years to come.