2007 Ford Escape Parts Diagram Overview
Understanding the layout of various elements in a vehicle can significantly improve maintenance efficiency. Whether you are working on enhancing the performance or simply ensuring that everything is running smoothly, having a clear overview of the component organization is essential for any vehicle enthusiast or mechanic.
In this section, we’ll explore the detailed arrangement of mechanical and electrical components, focusing on key areas that require frequent attention. Knowing the structure of these elements can help with troubleshooting, repairs, and upgrades, ensuring a smoother workflow for both routine and complex tasks.
For those looking to extend the lifespan of their vehicle, having access to clear and well-organized technical schematics is invaluable. With the right information, you can confidently approach any repair, replacement, or upgrade, minimizing errors and saving time.
Essential Components of a 2007 Ford Escape
The structure and functionality of this vehicle depend on several crucial elements, ensuring smooth performance and safety. These elements work together to deliver a reliable driving experience while maintaining the durability and efficiency of the car. Below are some of the most important systems and parts that contribute to the overall performance.
Powertrain and Drivetrain
- Engine: The heart of the vehicle, designed to provide the necessary power for movement.
- Transmission: A vital system that controls the power distribution to the wheels.
- Drive Axle: Ensures that torque is delivered from the transmission to the wheels for movement.
Suspension and Steering
- Shock Absorbers: These components maintain comfort by reducing vibrations and jolts on uneven roads.
- Steering Gear: Facilitates smooth control over the vehicle’s direction.
- Control Arms
Front Suspension and Steering System Overview
The front suspension and steering system is responsible for maintaining stability and control during vehicle operation. It ensures a smooth ride by absorbing road irregularities and allows the driver to direct the vehicle with precision.
Main Components of the Suspension
The suspension includes key elements such as the struts, control arms, and coil springs, all of which work together to manage the vehicle’s movement over uneven surfaces. These components reduce the impact of bumps and dips, ensuring both comfort and safety.
Steering Mechanism Functions
The steering system enables the driver to change direction by using parts like the rack and pinion, tie rods, and other essential components. This system ensures that the vehicle responds accurately to the driver
Engine Bay Parts Layout
The engine compartment is designed to house several key components, each playing an essential role in ensuring the vehicle’s performance and functionality. Understanding the placement and purpose of these elements is crucial for maintaining and servicing the system efficiently.
- Power source block – The primary element responsible for powering the vehicle, located centrally within the engine bay.
- Cooling system – Positioned towards the front, this ensures optimal temperature regulation to prevent overheating.
- Battery – Typically mounted near the side, providing electrical energy to start the vehicle and power various systems.
- Air intake system – Responsible for directing airflow into the power source, ensuring efficient combustion, often placed near the front.
- Fluid reservoirs – Various tanks for coolant, windshield washer fluid, and brake fluid are located at accessible points
Brake System Components Identification
The brake system is a crucial part of a vehicle’s safety, involving multiple interconnected components that work together to ensure effective stopping power. Understanding the layout and function of each element is essential for diagnosing issues or performing maintenance. This section will guide you through the identification of key components, highlighting their roles in the braking process.
Brake Pads and Rotors: These are central to the braking mechanism. The pads create friction when pressed against the rotors, slowing the wheels. Regular inspection of wear is necessary for optimal performance.
Calipers: These devices house the brake pads and use hydraulic pressure to push them against the rotors. Proper caliper function is essential for consistent braking force.
Interior Dashboard and Console Diagram
The interior layout of the dashboard and central console offers a well-organized setup for the driver and passengers. It includes essential control panels, various compartments, and integrated technology for convenient access to vehicle functions. The arrangement is designed to ensure ergonomic handling and a visually appealing design.
Main Console Features

The central console typically includes climate control switches, multimedia controls, and storage options. These elements are positioned for easy reach, allowing the driver to maintain focus on the road while operating essential systems. Additionally, certain models may offer auxiliary power outlets and connectivity ports for electronic devices.
Instrument Panel Layout
The instrument cluster behind the steering wheel displays vital driving information such as speed, fuel levels, and engine performance indicators. The gauges are strategically placed to provide clear
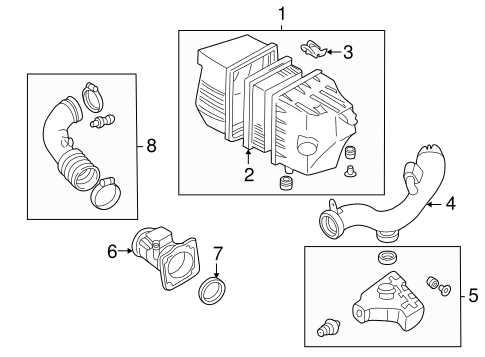
Exhaust System and Muffler Placement
The exhaust assembly plays a crucial role in directing harmful gases away from the engine and into the atmosphere. Proper positioning of the components is essential for optimal performance and to minimize noise levels. This section outlines the critical elements of the exhaust setup, focusing on the placement of the silencer and related parts.
In most configurations, the exhaust system begins at the engine and extends to the rear of the vehicle, ensuring a smooth flow of gases. Mufflers are strategically located along this pathway to reduce noise created by the escaping gases. Their placement is vital to achieving the desired sound levels while also preventing back pressure that could hinder engine efficiency.
It is essential to consider factors such as clearance, alignment, and support when installing these components. Proper mounting not only enhances performance but also prolongs the lifespan of the exhaust system. Regular inspections can help identify any issues related to wear or misalignment, ensuring the assembly functions effectively and efficiently.
Fuel System and Tank Configuration
The fuel system plays a critical role in the performance and efficiency of a vehicle. This section explores the various components that make up the fuel system and their arrangement, which is essential for the proper delivery of fuel to the engine.
Key elements of the fuel system include:
- Fuel Tank: The primary storage unit for fuel, designed to ensure safety and prevent leaks.
- Fuel Pump: Responsible for transporting fuel from the tank to the engine under appropriate pressure.
- Fuel Filter: Removes contaminants from the fuel before it reaches the engine, ensuring clean operation.
- Fuel Injectors: Precision devices that atomize the fuel, allowing for optimal combustion in the engine.
- Fuel Lines: Tubing that connects the fuel tank, pump, filter, and injectors, facilitating the flow of fuel.
Understanding the layout and function of these components helps in diagnosing issues and performing maintenance efficiently.
In terms of configuration, the arrangement of the fuel system is designed to maximize efficiency and minimize the risk of fuel-related problems. Factors such as the placement of the fuel pump and the routing of the fuel lines are crucial for maintaining optimal pressure and flow.
Regular inspections and maintenance of the fuel system can prevent potential failures and enhance the vehicle’s overall performance. Be sure to consult the relevant service manuals for detailed information on specifications and procedures.
Rear Axle and Suspension Parts
The rear axle and suspension system play a crucial role in maintaining stability and ride quality. This section delves into the components that contribute to these systems, ensuring optimal performance and comfort during driving.
Key Components of the Rear Suspension
- Shock Absorbers: Essential for dampening the impact from road irregularities, providing a smooth ride.
- Springs: These support the vehicle’s weight and absorb shocks from uneven surfaces.
- Control Arms: Important for maintaining the position of the axle while allowing for vertical movement.
- Stabilizer Bar: Helps reduce body roll during cornering, enhancing stability.
Rear Axle Assembly
- Differential: Distributes power to the wheels while allowing them to rotate at different speeds, especially during turns.
- Axle Shafts: Connect the differential to the wheels, transmitting power for movement.
- Wheel Bearings: Facilitate smooth rotation of the wheels, reducing friction.
- Brake Components: Ensure effective stopping power, critical for safety.
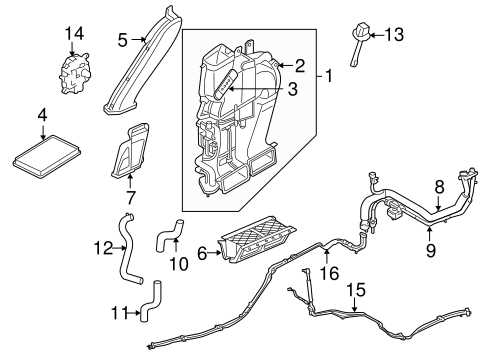
Cooling System and Radiator Parts Breakdown
The cooling system plays a vital role in maintaining the optimal operating temperature of the engine. It consists of various components that work together to regulate heat and prevent overheating. Understanding the functions and interconnections of these elements is crucial for effective maintenance and repairs.
The radiator serves as the primary component, dissipating heat from the engine coolant. It allows the heated liquid to cool down before circulating back to the engine. Additionally, the thermostat regulates coolant flow, ensuring that the engine reaches its ideal temperature quickly. Water pumps are essential for circulating coolant throughout the system, while hoses connect different parts, facilitating the flow of fluid. Regular inspection of these components is vital for identifying potential issues and ensuring the system operates efficiently.
Moreover, coolant reservoirs store excess liquid, providing a buffer for the system. The expansion tank plays a key role in managing pressure changes within the cooling system. Any leaks or blockages in these areas can lead to overheating or reduced performance. Therefore, maintaining each component and understanding their roles can significantly enhance the lifespan and reliability of the engine’s cooling system.
Electrical Wiring and Fuse Box Layout
The organization of electrical connections and the layout of the fuse enclosure play a crucial role in the functionality and reliability of a vehicle’s electrical system. Understanding the arrangement of wires and the positioning of fuses can help ensure proper operation and facilitate troubleshooting when issues arise.
Typically, the wiring system is designed to provide power to various components, including lights, sensors, and entertainment systems. Each circuit has a designated fuse that protects it from overloads and short circuits. Below are key aspects of the electrical wiring and fuse box layout:
- Wiring Harness: A collection of wires bundled together to connect different electrical components throughout the vehicle.
- Fuse Types:
- Blade Fuses: Commonly used due to their ease of replacement.
- Mini Fuses: Smaller versions suitable for compact applications.
- Maxi Fuses: Designed for high-current circuits.
- Fuse Box Location: Typically found under the dashboard or in the engine compartment, providing easy access for maintenance.
Understanding the layout of the electrical system is essential for effective diagnostics and repair. By referencing the schematic and identifying the proper fuse locations, vehicle owners can manage electrical issues more efficiently.
In addition to the fuse box, it is important to regularly inspect wiring for wear or damage, ensuring that all connections remain secure and free from corrosion. This preventive maintenance can help extend the life of the vehicle’s electrical components.
Transmission System Diagram
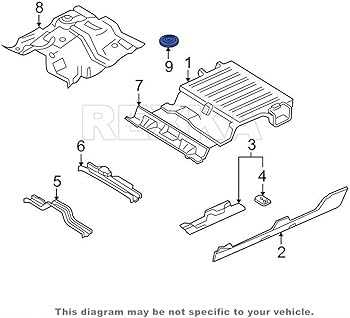
The transmission system plays a crucial role in the functionality of a vehicle, ensuring the effective transfer of power from the engine to the wheels. This section will explore the components and layout of the transmission system, providing a comprehensive overview of its structure and operation.
Key Components of the Transmission System
- Transmission Case: Houses and protects the internal components.
- Gear Sets: Alter the torque and speed delivered to the wheels.
- Clutch Assembly: Engages and disengages the engine from the transmission.
- Shift Mechanism: Allows the driver to change gears manually or automatically.
- Torque Converter: Transfers engine power to the transmission fluid for smooth acceleration.
Understanding the Functionality
The transmission system functions by adapting the engine’s output to various driving conditions. It manages the speed and torque required for optimal performance. By shifting gears, the system enables the vehicle to accelerate efficiently while maintaining fuel economy. This intricate network of components works together to provide a seamless driving experience.
Body Panels and Exterior Parts Overview
The outer shell of a vehicle plays a crucial role in both aesthetics and functionality. It comprises various components that not only enhance the appearance but also protect internal mechanisms and improve aerodynamics. Understanding these elements is essential for maintenance, repair, or customization purposes.
Types of Body Panels
Common types of external panels include the front and rear fenders, doors, and hoods. Each part serves specific functions, from shielding against environmental factors to providing access to vital components within the vehicle. Quality materials are essential for durability and resistance to wear and tear.
Exterior Accessories
In addition to panels, exterior elements like bumpers, grills, and mirrors contribute significantly to the overall design and performance. These accessories not only enhance visual appeal but also play vital roles in safety and functionality, helping to absorb impacts and improve visibility.
Air Conditioning and Heating System Components
The climate control system in vehicles plays a vital role in ensuring passenger comfort by regulating temperature and air quality. Understanding its various elements is essential for proper maintenance and repair.
Key Components of the Climate Control System
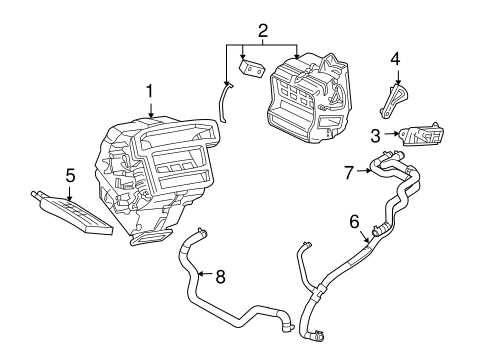
- Compressor: The heart of the air conditioning system, responsible for circulating refrigerant.
- Condenser: This unit cools the refrigerant, allowing it to return to a liquid state.
- Evaporator: Located inside the cabin, it absorbs heat and cools the air that enters the passenger compartment.
- Expansion Valve: Controls the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator, ensuring optimal cooling performance.
- Blower Motor: Circulates air through the system and into the cabin.
Heating Elements

- Heater Core: Functions like a small radiator, heating the air that is blown into the cabin.
- Thermostat: Regulates the engine temperature, ensuring that the heating system operates efficiently.
- Control Panel: Allows passengers to adjust temperature settings and airflow direction.