Understanding the 2012 Ford Escape Parts Layout
Understanding the inner workings of a vehicle’s mechanical structure is essential for both maintenance and repairs. A clear representation of its individual systems allows enthusiasts and professionals alike to address any issues effectively. Each element, whether related to the engine, transmission, or electrical network, plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation of the automobile.
Detailed visual references provide a simplified way to grasp the intricacies of these components. They help in identifying specific areas that might require attention, from smaller parts to larger assemblies. By familiarizing oneself with the vehicle’s layout, one can save time and avoid unnecessary replacements.
Whether dealing with routine upkeep or major repairs, having a well-organized view of the various mechanisms can be an invaluable resource. In this guide, we’ll explore key elements, offering insights into the vehicle’s core systems to help you make informed decisions.
Understanding the Structure of Ford Escape 2012
The vehicle’s design is a complex combination of engineering and functionality, where each component plays a significant role in ensuring smooth operation and safety. To maintain optimal performance, it is important to have a clear understanding of how various sections are interconnected and support the overall functionality of the machine.
Main Components Overview
The key elements include the framework that supports the body, the powertrain responsible for movement, and the electronic systems that manage everything from safety features to driver assistance. Each of these parts works together harmoniously, contributing to the vehicle’s reliability and efficiency on the road.
Structural Layout and Integration
The layout is strategically designed to optimize space, strength, and aerodynamics. From the engine compartment to the rear suspension, the different sections are meticulously arranged, balancing performance with user comfort. Understanding the way these areas integrate can help owners and technicians maintain the vehicle with precision.
Key Components in the Engine Bay Layout
The engine bay houses a collection of critical elements that ensure the smooth operation and efficiency of the vehicle. Understanding the arrangement of these essential components can help with maintenance and troubleshooting. Each element plays a specific role in powering and regulating the performance of the vehicle’s core systems.
- Engine Block: The main structure that contains the combustion chambers, providing the foundation for power generation.
- Air Intake System: A vital part that directs air into the engine, ensuring the right amount of oxygen is mixed with fuel for combustion.
- Battery: Supplies electrical power necessary to start the vehicle and keep its electronic systems running.
- Cooling System: Consisting of a radiator and hoses, this system maintains the engine’s temperature, preventing overheating.
- Alternator: A generator that converts mechanical energy into electricity to recharge the battery and power the electrical components while driving.
- Fuse Box: Protects the vehicle’s electrical circuits from overload by housing fuses that can break the connection if necessary.
- Brake Fluid Reservoir: A container that stores the hydraulic fluid needed to operate the brake system effectively.
- Power Steering Pump: Assists in providing the hydraulic pressure needed to turn the steering wheel smoothly.
Each of these components is strategically placed within the engine bay for optimal performance, and their proper functioning ensures a reliable and efficient driving experience.
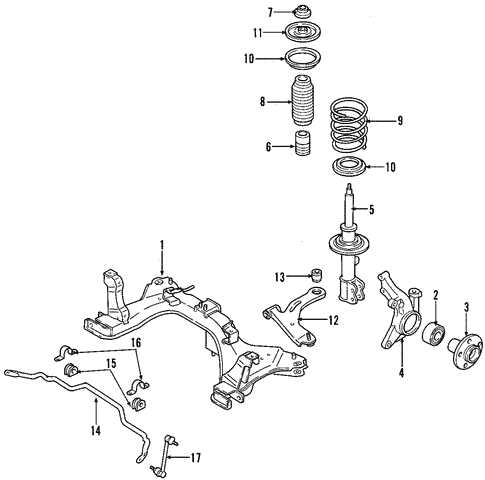
Exploring the Suspension and Steering System
The structure responsible for ensuring smooth rides and precise control plays a crucial role in any vehicle. It is composed of various components that work together to absorb road shocks, maintain stability, and ensure safe maneuvering. Understanding these elements is key to grasping how the system maintains balance and delivers responsiveness during driving.
- Shock Absorbers and Struts: These elements help cushion the impact of uneven road surfaces, ensuring a more comfortable experience and keeping the vehicle stable.
- Control Arms: Connected to the wheels and chassis, control arms help maintain proper alignment and facilitate controlled movement during driving.
- Ball Joints: These pivot points allow the steering and suspension components to move freely while keeping the structure intact.
- Steering Rack and Pinion: This mechanism translates the driver’s input from the steering wheel into the actual movement of the wheels, allowing for accurate directional control.
- Stabilizer Bar: Also known as an anti-roll bar, this component reduces body roll during turns, enhancing stability and safety.
Maintaining these parts in optimal condition ensures smooth handling and improved driving performance, significantly contributing to the overall driving experience.
Transmission Assembly Overview and Function
The transmission system is a crucial component in the operation of a vehicle, responsible for managing the transfer of power from the engine to the wheels. Its role is to ensure the optimal balance between speed and torque, adapting to various driving conditions and demands. Understanding the structure and function of this mechanism provides insights into its efficiency and performance.
The assembly is composed of multiple interconnected elements that work in harmony to shift gears and control movement. Below is an outline of the main sections involved in this process:
- Gearbox: The core of the system, it contains a series of gears that adjust speed and force, depending on the driving situation.
- Clutch or Torque Converter: These components help to engage or disengage the engine from the transmission, allowing smooth shifting or stopping.
- Drive Shafts: These are responsible for transmitting rotational power from the transmission to the wheels, enabling motion.
- Hydraulic System: Used in automatic setups, this system controls the shifting of gears and fluid pressure within the assembly.
- Electronic Control Unit (ECU): This unit monitors and adjusts the operation, ensuring that the assembly functions efficiently under varying conditions.
Each of these components plays a vital role in ensuring that the vehicle operates smoothly, providing a balance between power output and fuel efficiency. Proper maintenance and understanding of this system can help in diagnosing issues and enhancing performance.
Brake System Components and Their Roles
The braking mechanism is a crucial part of any vehicle, ensuring safety and control during driving. Understanding how each element works together helps to highlight its importance in maintaining the overall functionality of the system. This section delves into the key components responsible for slowing down and stopping the vehicle effectively.
Main Components of the Braking Mechanism
The braking setup typically consists of several core elements, each performing a distinct function. The brake pedal initiates the entire process by applying pressure that is transmitted through the system. The master cylinder then amplifies this force, directing hydraulic fluid to each wheel. This fluid, working within the brake lines, delivers pressure to the wheel-based elements, triggering the physical stopping mechanism.
Stopping Components and Their Roles
At the wheels, two main components take on the final task of deceleration. The brake calipers clamp down on the rotors, creating friction that gradually reduces speed. Alternatively, in vehicles using drum-based systems, brake shoes press outward against the drum’s surface to achieve a similar effect. The combined action of these components ensures a smooth and controlled stop, preventing sudden or uneven braking.
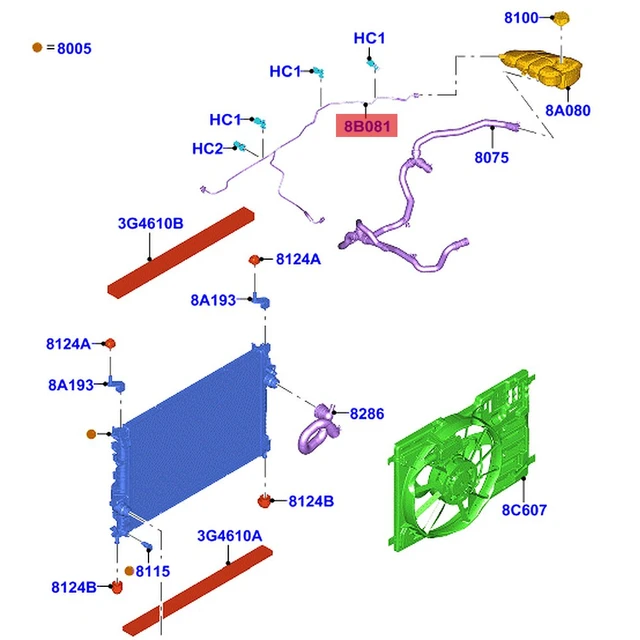
Cooling System Parts Breakdown
The cooling mechanism of a vehicle plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal engine temperature, preventing overheating, and ensuring efficient performance. Understanding the components involved in this system is essential for proper maintenance and repairs. Below is a detailed overview of the main elements that make up the cooling system.
Main Components
- Radiator: This component dissipates heat from the coolant before it returns to the engine.
- Water Pump: Circulates coolant through the engine and radiator, ensuring efficient heat exchange.
- Thermostat: Regulates the flow of coolant based on the engine’s temperature, opening and closing as needed.
- Coolant Reservoir: Stores excess coolant and allows for expansion and contraction within the system.
- Hoses: Flexible tubes that transport coolant to and from various components within the cooling assembly.
Additional Elements
- Cooling Fan: Helps to maintain airflow through the radiator, especially during low-speed operation.
- Heater Core: Provides heat for the cabin by using hot coolant from the engine.
- Bypass Hose: Facilitates coolant flow around the thermostat when it is closed.
By familiarizing oneself with these components, vehicle owners can better understand their role in the overall functionality of the engine’s cooling system and take proactive measures for upkeep.
Fuel System Layout and Connections

The fuel delivery mechanism is a critical component of any vehicle’s operation, ensuring that the engine receives the appropriate amount of fuel for optimal performance. Understanding the configuration and interconnections within this system is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. This section provides an overview of the layout and connections that make up the fuel delivery infrastructure.
Key Components of the Fuel Delivery System
The fuel delivery system comprises several integral elements, including the fuel tank, pump, injectors, and lines. Each of these components plays a significant role in ensuring the efficient transfer of fuel from storage to the engine.
Connection Overview
Each component is interconnected through a series of hoses and fittings, designed to maintain a secure flow and prevent leaks. Proper understanding of these connections is vital for any repair or replacement work.
| Component | Description | Connection Type |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Tank | Storage for the fuel supply | Seamless Connection to the Fuel Pump |
| Fuel Pump | Pumps fuel from the tank to the engine | Electrical and Mechanical Connections |
| Fuel Injectors | Injects fuel into the combustion chamber | High-Pressure Lines |
| Fuel Lines | Transfers fuel between components | Hoses and Fittings |
Electrical System Diagram and Wiring
The electrical framework of a vehicle is essential for its overall functionality and performance. Understanding the layout and connections within this system can greatly assist in troubleshooting and repair processes. This section delves into the intricate network of wires, connectors, and components that make up the electrical infrastructure, providing insights into how each element interacts within the broader system.
Key components of the electrical system include:
- Batteries
- Alternators
- Fuses and relays
- Wiring harnesses
- Switches and sensors
When examining the wiring aspects, it is crucial to note the following:
- Wiring colors often indicate their specific functions, aiding in identification.
- Proper insulation and routing of wires prevent electrical shorts and interference.
- Connectors must be secured to ensure reliable electrical flow and prevent disconnections.
To maintain the integrity of the electrical system, regular inspections should be conducted. This includes checking for:
- Frayed or damaged wires
- Corrosion at connection points
- Faulty switches or sensors
Understanding the electrical layout enables effective maintenance, enhances safety, and improves the overall efficiency of the vehicle. Familiarity with the components and their interconnections ensures that any issues can be quickly diagnosed and resolved.
Interior Cabin Components and Features
The interior of a vehicle plays a crucial role in ensuring comfort, functionality, and aesthetic appeal. Within the cabin, various elements work in harmony to create an inviting atmosphere while also providing essential utilities for drivers and passengers. This section delves into the significant components and features that enhance the overall driving experience.
Seating: The seats are designed to offer support and comfort for extended periods. They often come with adjustable settings, allowing individuals to find their preferred position. High-quality materials enhance both durability and aesthetic value, contributing to the overall cabin ambiance.
Dashboard: This central area houses essential controls and displays, ensuring that information is easily accessible. With a well-organized layout, drivers can navigate various functions without distraction. The integration of modern technology, such as touchscreens and voice commands, further enhances usability.
Storage Solutions: Efficient use of space is key to a practical cabin design. Various compartments, including glove boxes, center consoles, and door pockets, provide ample storage for personal items and travel essentials. Clever organization features help keep the interior clutter-free.
Climate Control: A reliable climate control system is vital for maintaining comfort in diverse weather conditions. Features may include automatic temperature adjustments, heated seats, and ventilation options, ensuring an enjoyable environment for all occupants.
Sound System: An advanced audio system transforms the cabin into an entertainment hub. Quality speakers and connectivity options for smartphones enhance the listening experience, allowing passengers to enjoy music, podcasts, or navigation instructions seamlessly.
Lighting: Ambient lighting contributes to the overall atmosphere of the interior. Adjustable brightness levels and strategically placed lights enhance visibility while creating a welcoming environment, especially during nighttime travel.
In conclusion, the components within the cabin significantly impact comfort, usability, and overall satisfaction. Understanding these features can enhance the appreciation of vehicle design and functionality.
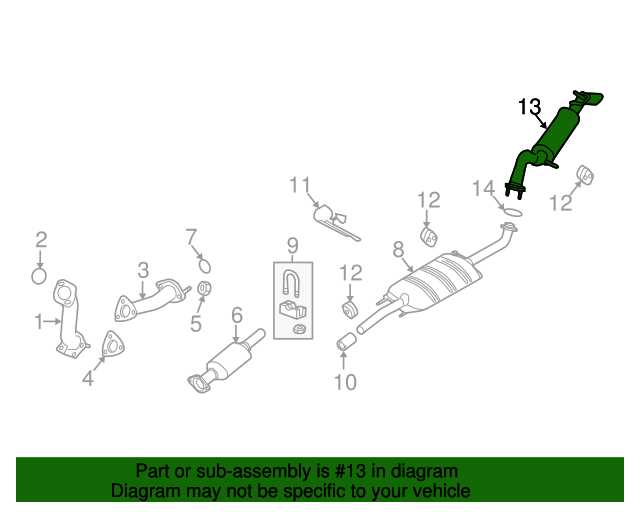
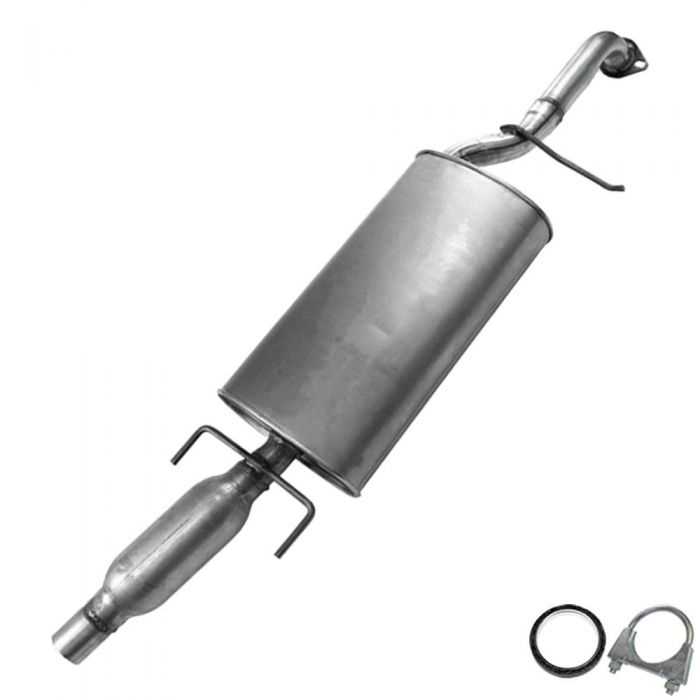
Exhaust System Elements and Pathway
The exhaust system is a crucial component of an automobile, designed to expel gases produced during combustion while minimizing noise and harmful emissions. This system plays a vital role in enhancing performance and ensuring that the engine operates efficiently. Understanding its elements and the pathway of exhaust gases can provide insights into its functionality and maintenance.
Main Components
The main components of the exhaust system include the manifold, catalytic converter, muffler, and tailpipe. Each element has a specific function that contributes to the overall effectiveness of the system.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Manifold | Collects exhaust gases from the engine’s cylinders and directs them into the system. |
| Catalytic Converter | Reduces harmful emissions by converting toxic gases into less harmful substances. |
| Muffler | Reduces engine noise and vibrations by dissipating sound waves. |
| Tailpipe | Expels treated gases into the atmosphere, completing the exhaust pathway. |
Pathway of Exhaust Gases
The pathway of exhaust gases begins at the manifold, where gases are collected from the engine. From there, they flow through the catalytic converter, where harmful substances are processed. Afterward, the gases move to the muffler, where sound is dampened. Finally, the exhaust exits through the tailpipe, releasing it into the environment. This pathway not only ensures efficient gas removal but also promotes compliance with environmental standards.
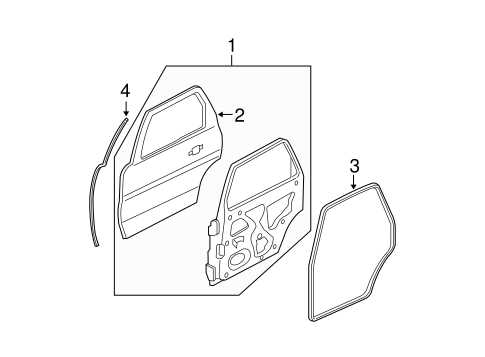
Body Frame and Exterior Parts Overview
The body structure and outer components of a vehicle play a critical role in its overall functionality and aesthetic appeal. These elements not only contribute to the design but also provide essential protection and support for various systems within the automobile. Understanding the composition and arrangement of these components is crucial for maintenance, repair, and enhancement of performance.
Key Components of the Body Frame
- Chassis: The foundational structure that supports all other components.
- Subframe: A secondary framework that provides additional strength and support.
- Crossmembers: Horizontal supports that enhance rigidity and stability.
- Mounting Points: Specific areas designed to attach various systems such as suspension and drivetrain.
Exterior Features
- Fenders: Panels that encase the wheels, protecting the vehicle’s body and components from debris.
- Hood: The cover over the engine compartment, providing access for maintenance.
- Doors: Entry points that contribute to safety and accessibility.
- Bumpers: Front and rear components designed to absorb impact and enhance safety.
- Windows: Glass panels that provide visibility while contributing to the vehicle’s aerodynamics.
Lighting System Parts and Placement
The lighting system of a vehicle plays a crucial role in ensuring visibility and safety during operation. Proper arrangement and functionality of the components are essential for optimal performance. Understanding the various elements and their positions can significantly aid in maintenance and troubleshooting.
The key components of a typical automotive lighting system include:
- Headlights
- Taillights
- Turn signal indicators
- Fog lights
- Interior lighting
- License plate lights
Each component serves a specific purpose and is strategically placed to maximize effectiveness:
- Headlights: Positioned at the front, they illuminate the road ahead and are vital for night driving.
- Taillights: Located at the rear, they signal the presence of the vehicle to those behind, enhancing safety.
- Turn Signal Indicators: Found on both front and rear sections, these lights indicate directional changes.
- Fog Lights: Positioned lower on the front of the vehicle, they provide additional illumination in poor visibility conditions.
- Interior Lighting: Located within the cabin, these lights improve visibility for occupants.
- License Plate Lights: Situated above the license plate, they ensure the plate is visible in low light.
Each element must be regularly inspected to ensure it is functioning correctly, as this impacts overall safety and compliance with traffic regulations. Understanding their layout and role will facilitate effective maintenance and enhance driving experience.
Commonly Replaced Parts in Ford Escape 2012
Vehicle maintenance often involves the replacement of specific components due to wear and tear. Certain elements in this particular model are frequently subject to service, ensuring optimal performance and safety. Understanding these commonly exchanged items can help owners manage repairs effectively.
- Brakes
- Battery
- Alternator
- Spark Plugs
- Oil Filter
- Fuel Pump
Braking systems are vital for safety, and pads and rotors often require replacement to maintain proper stopping power. Batteries typically have a limited lifespan, leading to regular changes to ensure reliable starts.
- Brake Components: Essential for safety, these parts often wear out and need replacement to prevent accidents.
- Electrical Systems: Batteries and alternators are crucial for vehicle operation; hence, they are commonly swapped out as needed.
- Engine Accessories: Components like spark plugs and filters are vital for performance and efficiency, leading to frequent exchanges.
Routine checks on fuel systems can help identify the need for a pump replacement, ensuring efficient fuel delivery. Being aware of these common replacements can aid in proactive vehicle care.