Understanding Flower Parts Through Diagrams and Worksheets
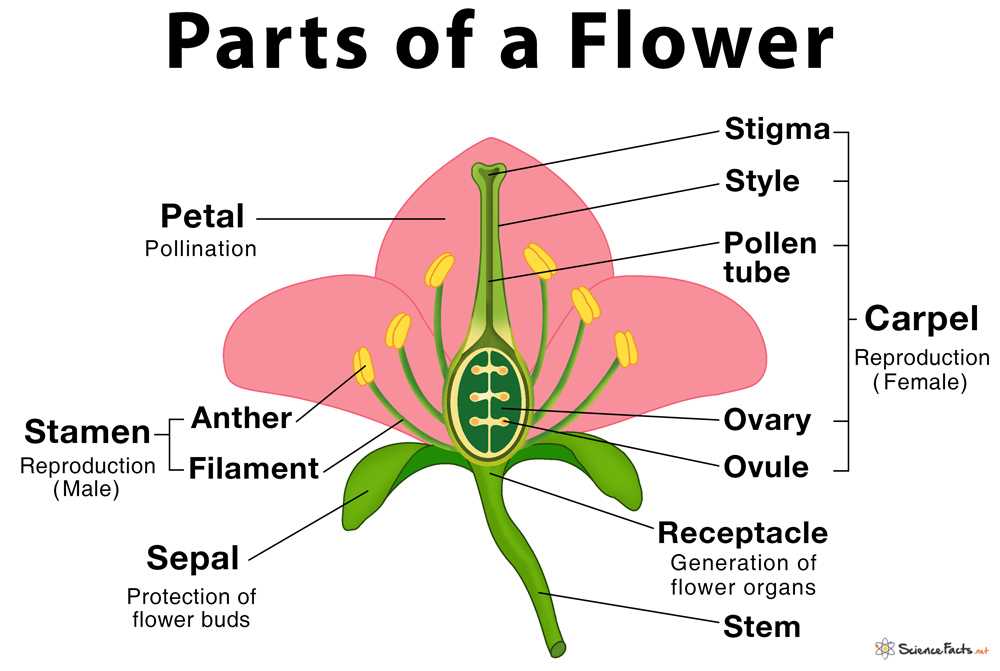
Exploring the intricate components of flowering organisms reveals the marvels of nature’s design. Each element plays a crucial role in the lifecycle and reproduction, showcasing a blend of functionality and beauty. Gaining insight into these elements enhances our appreciation of biodiversity.
Recognizing and labeling these features can be a rewarding educational journey. Engaging with visual representations allows learners to grasp complex concepts more effectively. By mapping out these structures, one can ultimately deepen their understanding of how these organisms thrive and interact with their environment.
This knowledge not only serves academic purposes but also fosters a greater connection to the natural world. As we delve into the specifics, we uncover the essential relationships that sustain life and promote ecological balance.
Understanding Flower Anatomy Basics
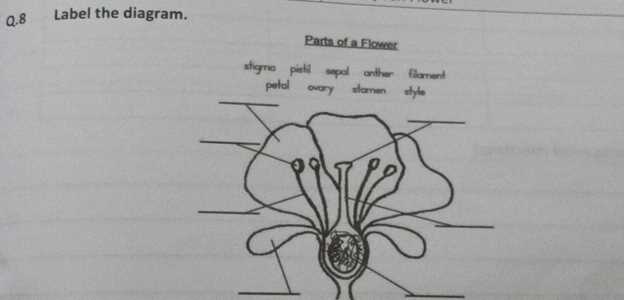
Grasping the structure of botanical reproductive systems is essential for comprehending their functions and roles in ecosystems. Each component plays a vital role in reproduction, pollination, and seed development, contributing to the diversity of plant life. By exploring these components, one gains insights into how plants thrive and adapt to their environments.
Key Components
Central elements include the reproductive and non-reproductive structures. The reproductive elements are crucial for the fertilization process, while non-reproductive features often serve protective and supportive roles. Together, they form a complex yet harmonious system that ensures successful propagation.
Importance of Structure

Understanding these structures helps in fields such as botany, agriculture, and ecology. Knowledge of how these components interact can lead to better cultivation practices and conservation efforts, ultimately enhancing biodiversity and ecological health.
Key Components of Flower Structure
The intricate design of a blooming organism is a marvel of nature, showcasing various elements that work in harmony to ensure reproduction and continuation of species. Each segment plays a vital role, contributing to the overall functionality and beauty of the organism. Understanding these essential components is crucial for appreciating their biological significance.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Petals | Often brightly colored, these structures attract pollinators and play a key role in reproduction. |
| Sepals | Typically green and leaf-like, they protect the developing bud and support the petals when in bloom. |
| Stamens | The male reproductive organs, consisting of an anther and filament, responsible for producing pollen. |
| Pistil | The female reproductive structure, comprising the stigma, style, and ovary, vital for fertilization. |
| Nectar | A sweet substance secreted by glands, enticing pollinators and aiding in the process of pollination. |
Importance of Flower Parts in Pollination
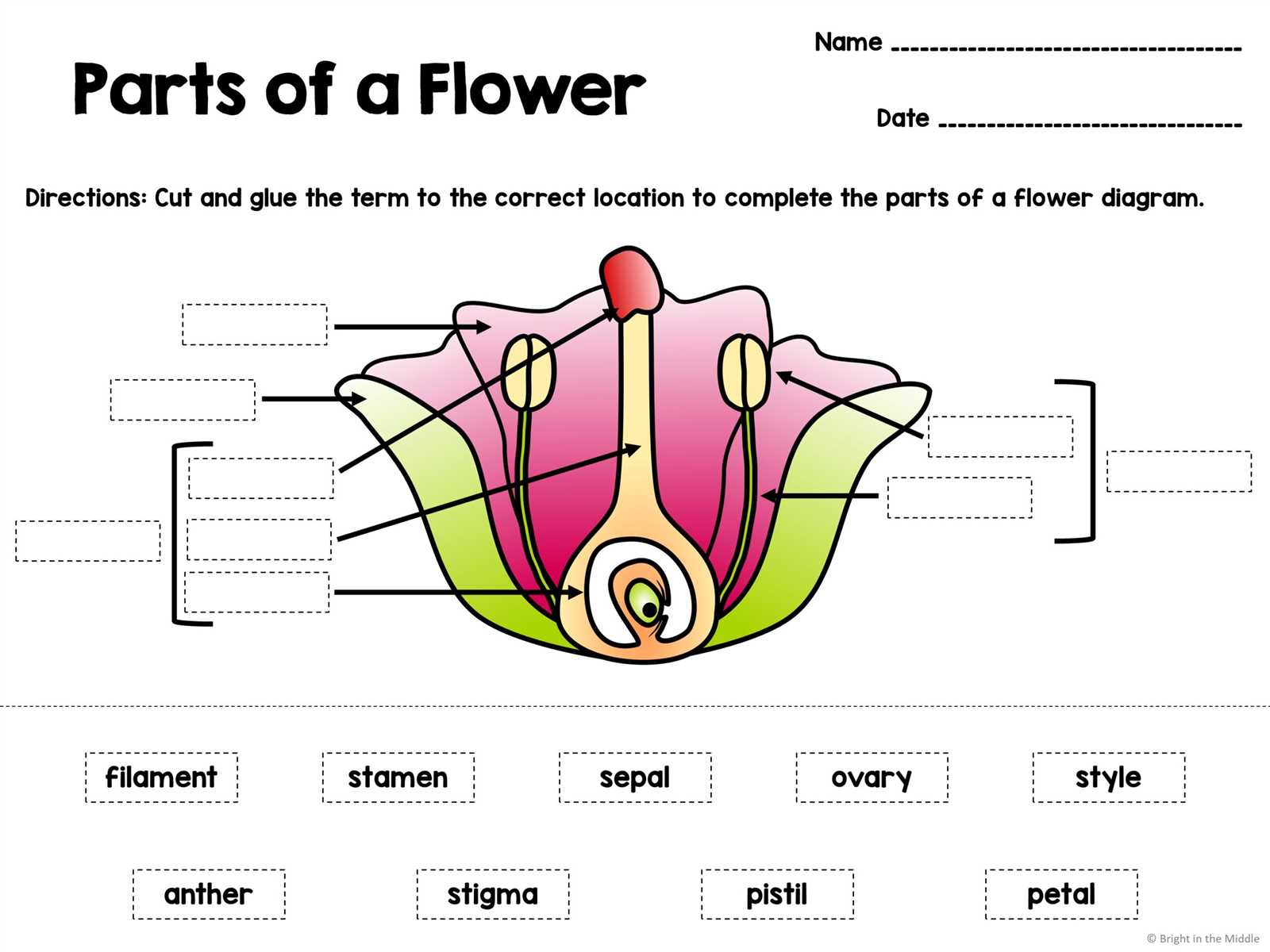
The various components of a blossom play a crucial role in the reproductive process of plants, facilitating the transfer of genetic material. Understanding their functions is essential for grasping how plants ensure their continuation and the vital interactions with pollinators.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Stamens | Produce pollen, the male gamete |
| Pistils | Receive pollen and house ovules for fertilization |
| Petals | Attract pollinators with color and scent |
| Sepals | Protect the developing bud |
These elements work synergistically, ensuring that pollinators are guided to the right locations, enhancing the likelihood of successful fertilization and ultimately contributing to biodiversity.
Different Types of Flowers Explained
In the world of botany, the variety of blossoms showcases an incredible diversity that fascinates enthusiasts and scientists alike. Each species exhibits unique characteristics, contributing to the beauty and complexity of nature. Understanding these distinctions enriches our appreciation of these natural wonders.
Monocots represent a group distinguished by their single embryonic leaf. Examples include lilies and orchids, which often display intricate structures and vibrant hues. Their anatomical features, such as parallel leaf veins, make them stand out in various ecosystems.
Dicots, on the other hand, possess two embryonic leaves. Roses and daisies fall into this category, showcasing diverse forms and arrangements. The presence of net-like leaf venation and varied flower formations highlights their adaptability and beauty.
Inflorescences further diversify the spectrum, bringing together clusters of blooms. This arrangement can be seen in sunflowers and hydrangeas, where multiple florets create a striking visual impact. These groupings often play a crucial role in attracting pollinators, enhancing their reproductive success.
Understanding these categories not only deepens our botanical knowledge but also enhances our ability to cultivate and appreciate these incredible specimens in various settings.
Role of Sepals in Flower Protection
In the natural world, certain structures play a critical role in safeguarding reproductive elements. One such component serves as a protective barrier during the early stages of development. This section delves into the significance of this feature in ensuring the survival and integrity of the reproductive cycle.
Protection from Environmental Factors
These protective layers shield delicate components from harsh environmental conditions. They help prevent damage caused by extreme temperatures, moisture fluctuations, and harmful pests. By acting as a physical barrier, these structures enhance the chances of successful pollination and seed production.
Support During Growth
Beyond mere protection, these structures also provide essential support to the developing reproductive organs. They help maintain structural integrity, allowing the organism to focus energy on growth and maturation. This dual role underscores their importance in the overall health and vitality of the plant.
In summary, the protective feature serves as both a safeguard against external threats and a support system during crucial developmental phases, playing an invaluable role in the lifecycle of flowering organisms.
Functions of Petals in Attracting Pollinators

The vibrant and often fragrant structures of certain plants play a crucial role in enticing various creatures that aid in the process of reproduction. Their colors, patterns, and scents create a visual and olfactory appeal, drawing in beneficial visitors to ensure successful transfer of genetic material.
Visual Attraction

Bright hues and intricate designs serve as signals for potential pollinators, guiding them to the source of nectar. These visual cues are tailored to the preferences of specific species, enhancing the likelihood of interaction.
Olfactory Signals
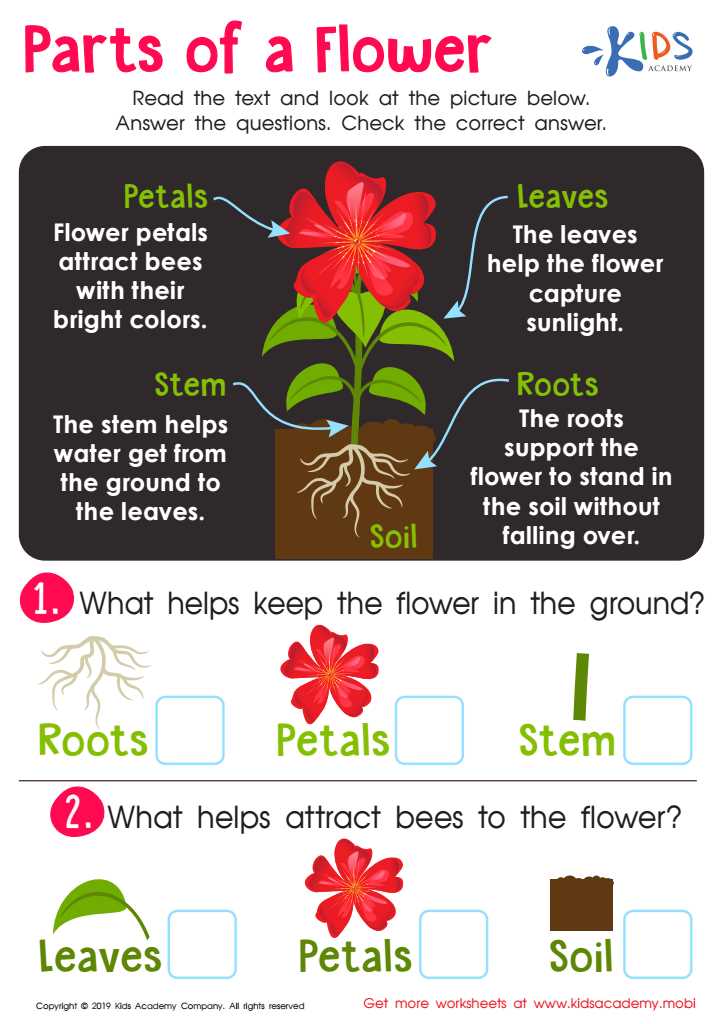
The scents emitted by these colorful structures are equally important, as they can attract a wide range of pollinators, from bees to butterflies. The chemical compounds released often mimic natural food sources, further enhancing the allure.
| Pollinator Type | Color Preference | Fragrance Type |
|---|---|---|
| Bees | Blue, Yellow | Sweet, Fruity |
| Butterflies | Red, Orange | Sweet, Floral |
| Birds | Bright Red, Orange | Neutral |
Stamens: The Male Reproductive Organs
The male reproductive structures play a crucial role in the life cycle of plants, contributing to the process of pollination and fertilization. Understanding these components is essential for grasping the overall reproductive strategies of various species.
Key components include:
- Anther: The pollen-producing part that releases male gametes.
- Filament: The slender stalk that supports the anther and connects it to the plant.
These structures work together to ensure successful reproduction by:
- Producing and dispersing pollen.
- Facilitating the transfer of pollen to female reproductive organs.
Overall, the understanding of these organs enhances our appreciation of plant biology and the intricate processes involved in reproduction.
Pistils: The Female Reproductive Structures
Pistils represent a crucial element in the reproductive system of certain plants, playing an essential role in the process of reproduction. These structures are specifically designed to facilitate fertilization and the development of seeds, showcasing nature’s intricate design and functionality. Understanding their anatomy and function is vital for comprehending the life cycle of these organisms.
Anatomy of the Pistil
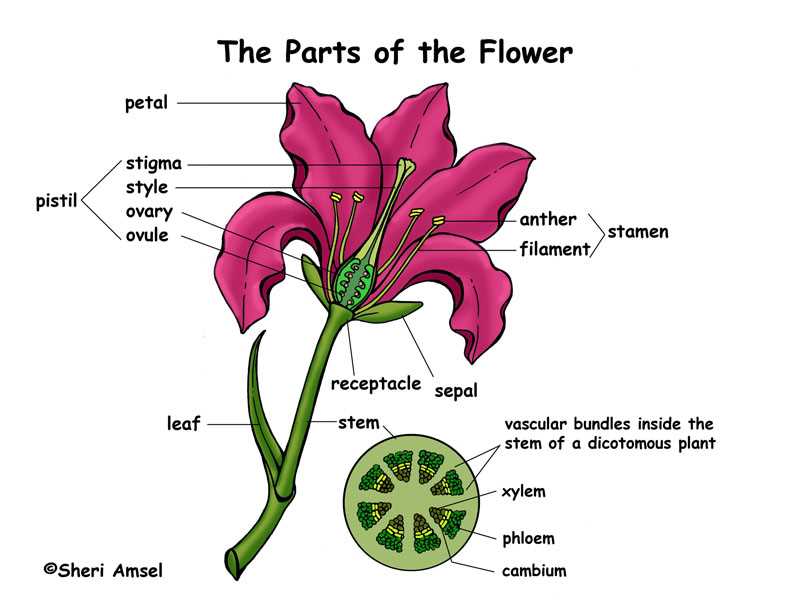
The pistil is primarily composed of three key components: the stigma, style, and ovary. Each part has a distinct function that contributes to the overall reproductive process.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Stigma | The sticky surface that captures pollen grains, initiating the fertilization process. |
| Style | A slender structure that connects the stigma to the ovary, providing a pathway for pollen tubes. |
| Ovary | The swollen base containing ovules, which develop into seeds after fertilization. |
Functionality in Reproduction

The functionality of pistils is central to the reproductive strategy of many species. Upon successful pollination, pollen grains adhere to the stigma, where they germinate and grow through the style to reach the ovary. This process ultimately leads to the formation of seeds, ensuring the continuation of the plant’s lineage. The design and efficiency of pistils are key to the reproductive success of numerous plant species.
Creating Effective Flower Diagrams
Visual representations are crucial for conveying complex biological concepts clearly and efficiently. Crafting an engaging illustration that highlights the essential components of a plant’s reproductive system can significantly enhance understanding. A well-designed sketch not only aids in memorization but also facilitates discussions and analysis in educational settings.
Start with Clarity: The first step in creating a successful illustration is to ensure that each element is clearly labeled. Using distinct colors and shapes can help differentiate between various structures, making it easier for viewers to grasp their functions.
Incorporate Annotations: Adding brief descriptions alongside each component can provide context. These notes can explain the role of each structure, enriching the viewer’s knowledge and making the illustration more informative.
Consider the Audience: Tailor the complexity of the illustration based on the intended audience. For younger students, simpler visuals with basic labels may be more effective, while advanced learners might benefit from intricate details and technical terms.
Utilize Space Effectively: Balance the layout to prevent overcrowding. Adequate spacing allows for better readability and ensures that each element stands out. A well-organized presentation can significantly enhance comprehension.
Engage with Interactive Elements: If possible, consider using interactive features that allow users to explore each part. This can make the learning experience more engaging and memorable, fostering a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
In conclusion, by focusing on clarity, annotation, audience engagement, spatial organization, and interactivity, you can create a compelling visual that not only informs but also inspires curiosity and further exploration.
Educational Uses of Flower Worksheets
Utilizing visual aids in teaching promotes a deeper understanding of botanical structures and functions. Engaging with interactive materials enhances students’ grasp of concepts while fostering curiosity about nature. These tools serve as valuable resources in various educational settings, making complex ideas more accessible.
Interactive Learning

Incorporating these resources encourages hands-on activities that boost retention. Students can explore the significance of various components through creative exercises, allowing for an immersive learning experience. This approach not only solidifies knowledge but also nurtures critical thinking skills.
Assessment and Evaluation
These materials can also serve as effective assessment tools. Educators can gauge understanding through quizzes and projects that utilize visual elements, providing a comprehensive evaluation of student progress. This method allows for tailored feedback, ensuring that each learner’s needs are met.
Tips for Teaching Flower Anatomy
Understanding the structure of blooming plants can be an engaging experience for learners. To facilitate this process, it’s important to create a dynamic learning environment that encourages exploration and curiosity. Utilizing various teaching methods will cater to different learning styles and enhance retention of knowledge.
Incorporate hands-on activities, such as dissection or modeling, to allow students to physically interact with specimens. This tactile experience can deepen their understanding and create lasting memories associated with the subject. Encourage group discussions where learners can share observations and insights, fostering collaboration and critical thinking.
Visual aids are essential for illustrating complex concepts. Utilize clear illustrations or digital resources that highlight key features and their functions. Consider incorporating technology, such as interactive applications, that allow students to visualize the anatomy in 3D.
Connecting the material to real-world applications can increase relevance. Discuss how different structures contribute to pollination, reproduction, and ecosystem health. Field trips to botanical gardens or nature reserves can provide practical examples and inspire appreciation for biodiversity.
Finally, assess understanding through varied evaluation methods. Creative projects, presentations, or quizzes can help gauge knowledge and reinforce learning in a fun way. By combining these strategies, educators can create an engaging and informative experience that cultivates a love for the study of plant structures.