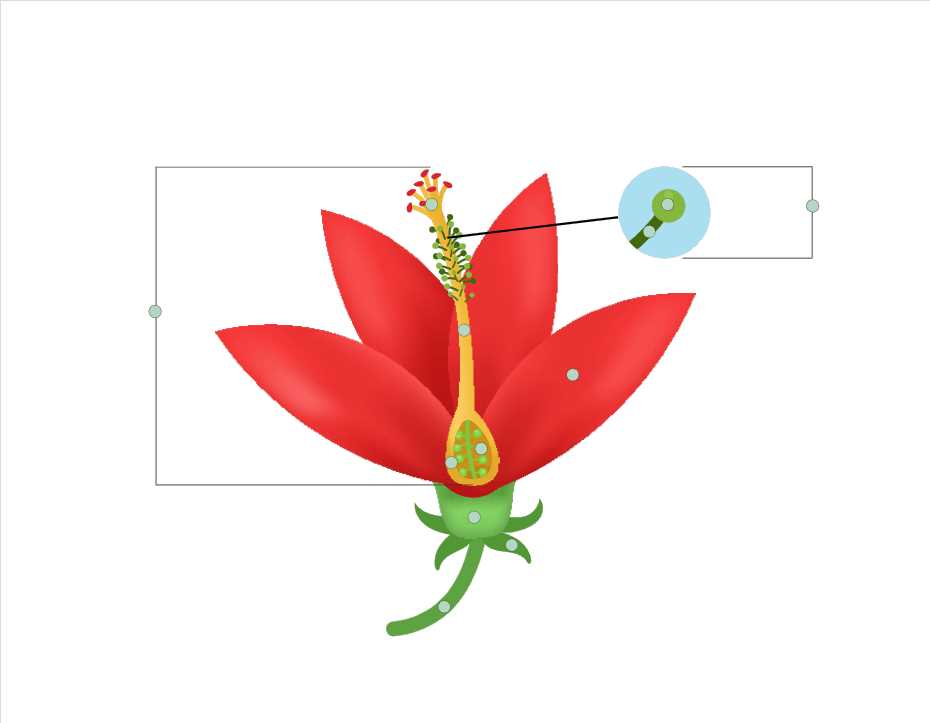
Key Components of Floral Anatomy
The intricate structure of a blossom is composed of several essential elements that work together in harmony to ensure its growth, reproduction, and survival. These elements vary in appearance, function, and significance, forming a complex yet balanced system. Understanding the core elements helps to appreciate the delicate processes within nature’s botanical creations.
The reproductive units include vital organs that play a crucial role in the propagation process. These units allow for the continuation of species through the production and distribution of seeds. Each segment has a distinct purpose, contributing to successful pollination and fertilization.
Supporting structures provide stability, protection, and nourishment. They help to anchor the organism in its environment, supply the necessary nutrients, and guard delicate components from external harm. These structures are fundamental to the overall health and functionality of the
Blank Diagrams for Botanical Study
Botanical studies often require visual aids to better understand the structures and characteristics of various plants. These illustrations, without pre-filled labels, serve as a valuable educational tool, allowing learners to identify and label specific features themselves. By engaging in this process, students develop a deeper understanding of plant morphology and gain practical experience in recognizing different elements in their natural environment.
Interactive learning is one of the key advantages of such illustrations. When individuals are tasked with labeling various plant structures, they are encouraged to actively recall information and apply their knowledge. This method enhances retention and promotes a hands-on approach to learning.
Additionally, customizable templates provide flexibility in botanical research and education, offering room for detailed annotations based on specific study needs. This adaptability ensures that learners at various levels can benefit from the use of these unmarked illustrations in their studies.
Exploring Reproductive Parts in Flowers
The intricate mechanisms of plant reproduction rely on specialized structures that ensure the continuation of species. These biological components, often visually distinct, play a pivotal role in the formation and distribution of seeds. Understanding these elements reveals the fascinating strategies that plants employ to adapt and thrive in various environments.
Male Reproductive Structures
The pollen-producing organs are central to the reproductive process, responsible for generating and dispersing the essential genetic material. Their unique design facilitates efficient transfer, often aided by natural agents such as wind or insects.
Female Reproductive Structures
The part responsible for receiving and nurturing the pollen is designed to protect and support the development of seeds. This component is vital for ensuring successful fertilization and seed formation, which eventually leads to the propagation of the species.
| Structure |
Function |
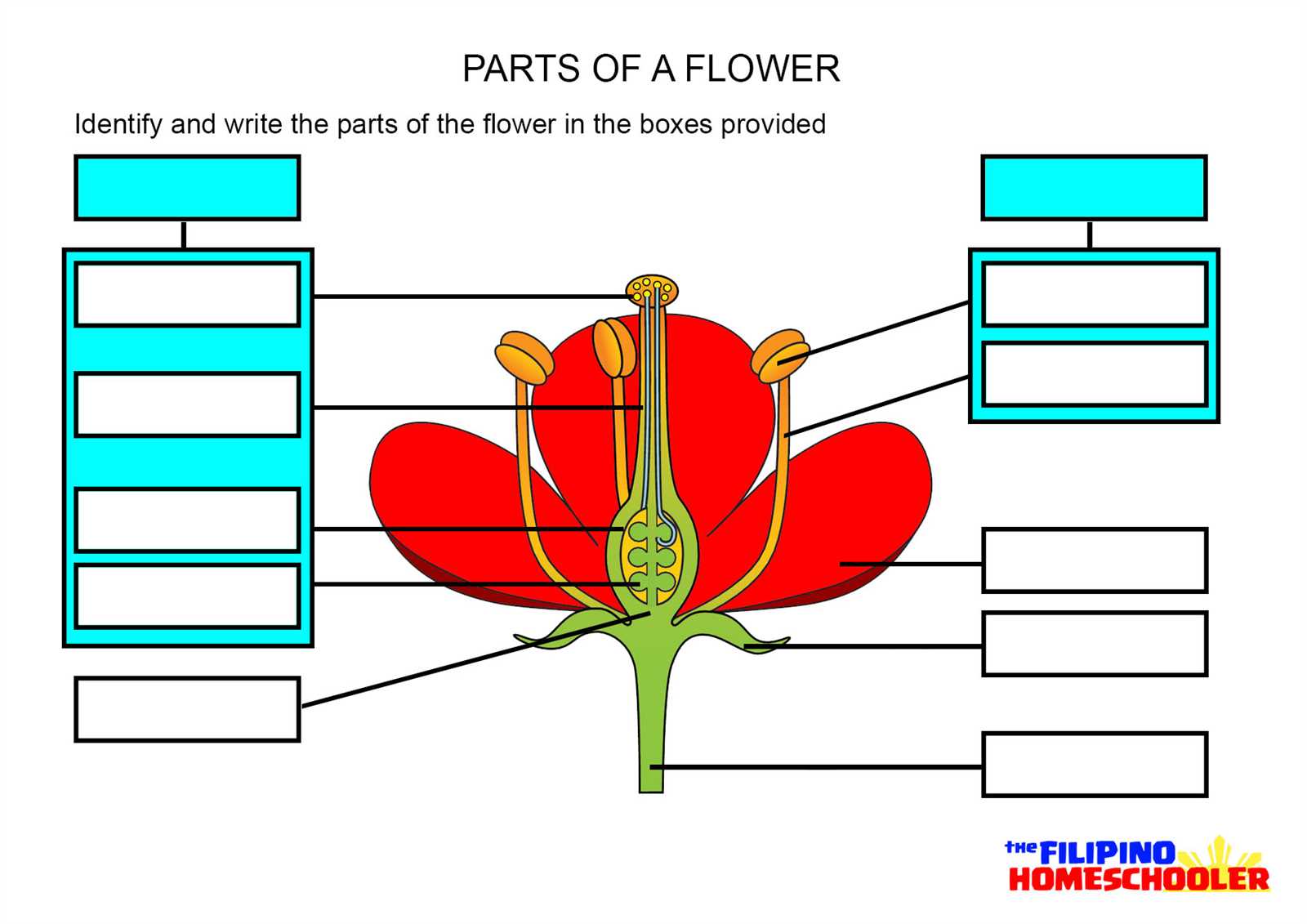
Labeling Techniques for Flower Diagrams
Creating visual representations often involves the process of clearly marking various components to enhance understanding. To ensure accuracy, a well-organized labeling strategy is essential. The approach to labeling can vary depending on the complexity of the illustration and the learning goals, but there are several methods that can help make the visual clear and educational.
Structured Labeling Methods
- Sequential Numbering: This approach assigns numbers to each element, which are then cross-referenced with a legend, providing clarity without overcrowding the image.
- Direct Annotation: For simpler designs, labels can be placed next to the elements, ensuring an immediate connection between the label and the feature.
Using Colors and Symbols

Color-coding is another technique that can greatly enhance the visual appeal and ease of identification. Different shades or symbols can represent specific features, helping viewers quickly distinguish between them.
- Assign unique colors to each item.
- Use symbols or patterns when colors aren’t practical.
By employ
How to Draw Floral Structures
Creating detailed representations of botanical forms requires attention to the shape and arrangement of individual components. By observing the natural design of these forms, you can sketch a clear and structured visual. Focus on capturing the overall symmetry and subtle variations present in the natural world.
Begin with the center, marking the core of the structure. This will help you maintain balance as you add more intricate details. From there, extend outward with curves and lines that follow the flow of the natural pattern, gradually building up the structure’s complexity.
Refining the outlines and adding subtle shading will bring depth and clarity to your illustration. Remember, practice and keen observation are key to mastering this technique.
Visualizing Flower Components without Labels
When studying the structure of botanical elements, focusing on a visual representation without textual hints can be an effective way to enhance comprehension. This method encourages observers to engage more deeply with the form and arrangement, improving their ability to recognize and categorize different sections by their physical characteristics alone.
Enhancing Learning through Visual Focus
By removing written identifiers, individuals are prompted to rely solely on their observation skills. This fosters a deeper connection to the subject matter, as attention is directed toward shapes, symmetry, and patterns within the natural structure. The visual approach supports the retention of this knowledge over time.
Exploration and Identification Practice
This strategy not only challenges memory but also helps in understanding how various segments interact. Without names attached, learners must engage critically, enhancing their ability to identify components based on unique features, such as size, texture, or placement.
The Role of Petals and Sepals
Petals and sepals play crucial roles in the life cycle of plants. Their appearance and structure contribute significantly to various processes, particularly those involving external factors. These components work together to ensure the proper development and protection of key elements.
Protection and Support
Sepals often act as a shield, forming an outer layer that safeguards against environmental challenges. This layer provides vital support during initial growth stages, ensuring that delicate inner parts are protected from damage.
Attraction and Interaction
Petals, with their diverse shapes and colors, serve a different function. They are primarily responsible for attracting external forces, often guiding these toward specific goals. Their visual and olfactory signals create an environment conducive to interaction, which is essential for continued development.
- Sepals form a protective layer in the early stages.
- Petals enhance interaction through visual and scent cues.
- Both components work in tandem to support
Blank Diagram Use in Classrooms
Utilizing unfilled visuals in educational settings fosters an interactive learning environment. These resources encourage students to engage actively with the content, promoting retention and comprehension. By incorporating such visuals, educators can enhance lessons across various subjects.
Implementing these tools has numerous advantages:
- Encourages critical thinking by prompting students to analyze and fill in information.
- Facilitates collaborative learning as students work together to complete the visuals.
- Supports diverse learning styles, allowing visual learners to engage meaningfully with the material.
- Promotes creativity as students can express their understanding in unique ways.
In addition, employing these resources can streamline assessments. Teachers can gauge comprehension by reviewing the completed visuals, identifying areas where students may need further assistance.
Ultimately, integrating unfilled representations in classroom activities cultivates a dynamic atmosphere that nurtures exploration and understanding among learners.
Breaking Down the Stamen and Pistil
The reproductive structures within blooming plants play a crucial role in the process of reproduction. Understanding these components is essential for comprehending how these organisms propagate and ensure their survival through generations.
Exploring the Stamen
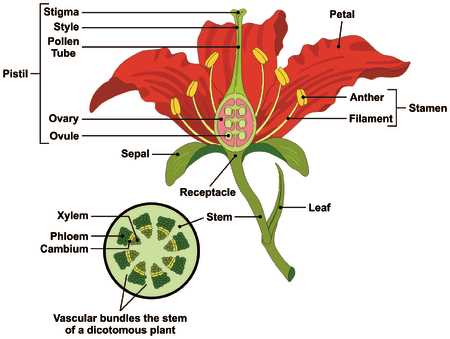
The stamen serves as the male reproductive element, primarily responsible for producing pollen. Composed of two main parts, the anther and the filament, it facilitates the transfer of genetic material necessary for fertilization.
Understanding the Pistil
In contrast, the pistil is the female counterpart, which includes the stigma, style, and ovary. This structure is vital for receiving pollen and housing ovules, which ultimately develop into seeds following successful fertilization. The intricate relationship between these two elements is fundamental to the reproductive cycle of many plant species.
Common Mistakes in Flower Diagrams
When illustrating the structure of plants, several errors can frequently occur, leading to misunderstandings of their anatomy. These inaccuracies can stem from a lack of attention to detail, mislabeling, or oversimplifying components. It is essential to recognize and address these pitfalls to ensure clarity and accuracy in visual representations.
One prevalent mistake is the inaccurate representation of individual components. For instance, the dimensions and arrangements of elements may be distorted, creating confusion about their functions. Additionally, failing to include essential features or misrepresenting their locations can mislead viewers, resulting in a lack of comprehension of the overall structure.
Another common error is inconsistent labeling. When terms are not used uniformly, it can create ambiguity and hinder effective communication. Proper terminology is crucial for understanding, and inconsistent use can result in significant misunderstandings. Furthermore, neglecting to include contextual information may lead to a lack of insight into how various components interact within the larger system.
Lastly, oversimplification is a frequent issue. While it is tempting to create a simplified version for ease of understanding, this can lead to the omission of critical details that are vital for a comprehensive grasp of the subject. Striking a balance between simplicity and accuracy is key to effective educational resources.
Creating Your Own Flower Diagram
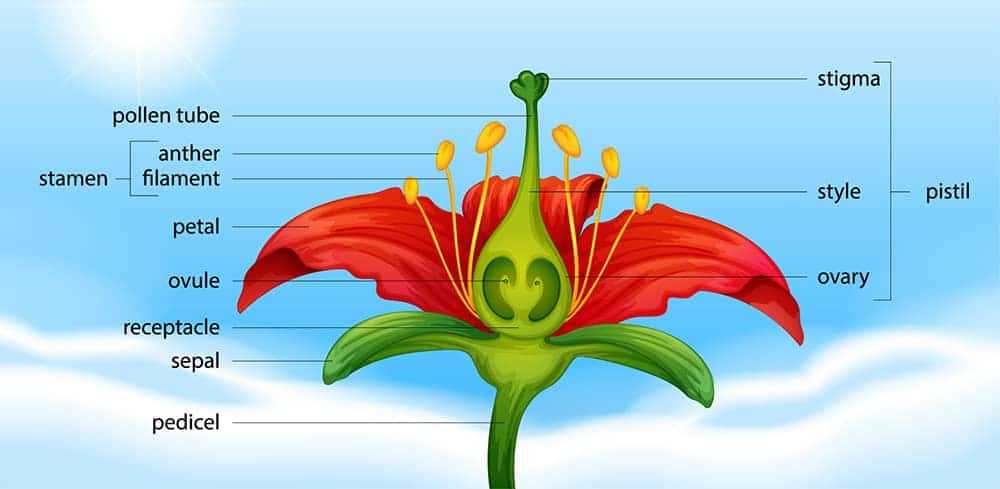

Designing your own representation of a botanical structure can be an engaging and educational experience. By understanding the various components that make up these living entities, you can enhance your grasp of their functions and significance in nature.
Materials Needed
- Paper or drawing software
- Colored pencils or markers
- Reference images
- Ruler
Steps to Create Your Representation

- Begin by selecting a reference image to understand the layout and elements of the organism.
- Use a ruler to draw the outline of the shape you wish to represent.
- Label each section with its corresponding name using clear lettering.
- Color each part distinctly to highlight differences and aid in identification.
- Review your creation and make any necessary adjustments to improve accuracy.
By following these steps, you can craft a personal illustration that showcases your understanding of these beautiful organisms. Enjoy the process of learning and creating!