Understanding the Parts of a Flower with Diagram Worksheets

Exploring the intricate structure of blooms reveals a world of complexity and beauty. Each component plays a crucial role in the reproduction and survival of plants, making the study of these elements both fascinating and essential for understanding botanical life. This section aims to delve into the various sections that contribute to the overall function and appearance of these natural wonders.
From vibrant petals that attract pollinators to the supportive structures that ensure stability, every element serves a unique purpose. By examining these characteristics closely, one gains insight into the evolutionary adaptations that have allowed plants to thrive in diverse environments. This exploration not only enhances our appreciation for nature but also aids in various scientific disciplines, including horticulture and ecology.
Engaging with visual aids enhances comprehension, making it easier to identify and memorize the specific roles of each segment. These resources are invaluable for students and enthusiasts alike, providing a clear representation of the relationships between different floral elements. Through careful observation and study, one can unlock the secrets held within the captivating world of blossoms.
Understanding Flower Anatomy
This section delves into the essential structures that constitute the reproductive organ of plants, emphasizing their roles in the life cycle and reproduction process. A comprehensive grasp of these components aids in appreciating the complexity and beauty of nature’s design.
Key Structures and Their Functions
The components of these reproductive entities are specialized, each contributing uniquely to the plant’s reproductive success. Understanding their functions allows us to see how they interact within the ecosystem.
| Structure | Function |
|---|---|
| Petals | Attract pollinators with vibrant colors and scents. |
| Stamens | Produce pollen, the male gametes. |
| Carpels | House ovules and facilitate fertilization. |
| Sepals | Protect the developing bud and support the bloom. |
Importance in Ecosystems
The intricate relationships between these structures and their pollinators foster biodiversity. Understanding these elements highlights their significance in sustaining various habitats and promoting the overall health of ecosystems.
Essential Components of a Flower
Understanding the fundamental elements that make up a blossom is crucial for grasping its role in reproduction and ecosystem dynamics. Each component plays a significant role in ensuring the successful propagation of the species and the overall health of the environment.
- Stamen: The male reproductive structure responsible for producing pollen.
- Pistil: The female reproductive part that houses the ovary and receives pollen.
- Petals: Often brightly colored, these structures attract pollinators and protect the reproductive organs.
- Sepals: Typically green, these leaf-like structures enclose and protect the developing bud.
- Nectaries: Glands that produce nectar to attract pollinators.
Each element works in harmony, contributing to the process of pollination and the eventual formation of seeds, thereby ensuring the continuation of plant life. Understanding these components enhances appreciation for biodiversity and the interdependence of species within ecosystems.
Function of Flower Parts

The various components of a blooming plant play essential roles in reproduction and survival. Each element contributes uniquely to processes such as pollination, seed development, and attracting pollinators, ensuring the continuation of species. Understanding these functions can enhance appreciation for the intricate systems of nature.
Key Functions
- Reproduction: The primary purpose is to facilitate the reproduction process, allowing for the creation of seeds and new plants.
- Pollinator Attraction: Bright colors and pleasant fragrances attract insects and birds, which are crucial for transferring pollen.
- Protection: Some structures provide shelter for reproductive organs, safeguarding them from environmental factors.
- Nourishment: Specific elements may store nutrients that support the growth of seeds after fertilization.
Supporting Roles
- Structural Support: Certain components maintain the integrity of the structure, allowing for stability and optimal positioning for pollination.
- Seasonal Adaptation: Some parts may change with seasons, ensuring the plant can thrive in various environmental conditions.
- Energy Storage: Specific areas may store energy in the form of sugars, aiding in the growth of new shoots and roots.
Visual Representation in Diagrams
Effective illustration plays a crucial role in enhancing comprehension and retention of information. Utilizing visual elements allows for complex concepts to be conveyed in an accessible manner, bridging the gap between textual descriptions and real-world understanding. By integrating imagery and symbols, learners can grasp intricate relationships and processes more easily.
Importance of Clarity
Clarity is paramount when it comes to visual aids. Well-organized representations reduce cognitive load, enabling viewers to focus on key ideas without unnecessary distractions. Clear labeling and logical structure further enhance the ability to interpret information swiftly and accurately.
Engagement and Retention
Engaging visuals not only attract attention but also facilitate better memory retention. When learners interact with appealing illustrations, they are more likely to internalize the content. This dynamic interaction fosters an environment conducive to exploration and inquiry, ultimately leading to deeper understanding.
Importance of Pollination in Plants
Pollination plays a crucial role in the reproductive success of many plant species, facilitating the transfer of genetic material necessary for the production of seeds and fruits. This process not only ensures the continuation of plant populations but also contributes significantly to biodiversity within ecosystems.
Enhancing Genetic Diversity: By promoting cross-fertilization, this process increases genetic variation, which is vital for the adaptability and resilience of plants. Diverse genetic traits enable populations to thrive under changing environmental conditions, making them less susceptible to diseases and pests.
Supporting Ecosystems: Many organisms depend on the products of this vital process. Animals, including humans, rely on fruits, vegetables, and nuts for sustenance. The intricate relationships formed between plants and their pollinators create balanced ecosystems, ensuring the survival of numerous species.
Economic Significance: In agricultural contexts, effective transfer of pollen is essential for crop yields. Many food crops are heavily dependent on this phenomenon, which underlines its importance not just for nature but also for global food security and economic stability.
In summary, pollination is an essential ecological service that supports life, sustains biodiversity, and underpins human agriculture.
Labeling Worksheets for Education
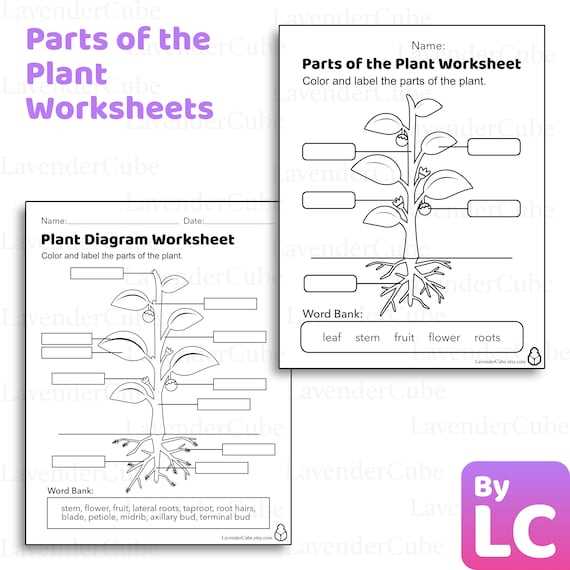
Educational resources that focus on identification and categorization play a crucial role in enhancing learners’ comprehension and retention. These activities encourage students to engage actively with content, fostering a deeper understanding of various subjects. By utilizing visual aids, educators can create an interactive environment that promotes curiosity and exploration.
Benefits of Labeling Activities

- Improves memory retention by associating terms with images.
- Enhances critical thinking as students analyze and categorize information.
- Encourages collaboration among peers during group activities.
- Develops fine motor skills through the act of writing and drawing.
Effective Strategies for Implementation
- Integrate these exercises into various subjects to provide a multi-disciplinary approach.
- Utilize technology by incorporating digital labeling tools for interactive learning.
- Adapt difficulty levels to cater to different age groups and learning abilities.
- Provide clear instructions and examples to guide students in their tasks.
Interactive Activities for Learning
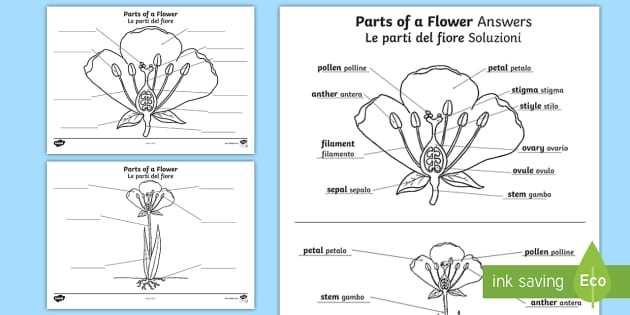
Engaging students through hands-on experiences can significantly enhance their understanding of complex concepts. Interactive tasks encourage exploration, critical thinking, and collaboration, making the learning process more enjoyable and effective. By incorporating various activities, educators can foster a deeper connection with the subject matter.
One effective method is the use of virtual simulations, allowing learners to manipulate elements in a controlled environment. These tools enable users to observe outcomes based on their actions, promoting inquiry-based learning. Another approach involves group projects where participants create models or presentations, facilitating teamwork and communication skills.
Incorporating games can also be beneficial. Educational challenges and quizzes not only motivate students but also reinforce knowledge through friendly competition. Additionally, outdoor activities related to the topic can provide a refreshing change of pace while solidifying understanding through real-world applications.
Finally, reflective practices, such as journaling or peer discussions, can help learners articulate their thoughts and insights. This process encourages self-assessment and deeper cognitive engagement with the material, ultimately leading to more meaningful retention of information.
Comparing Flower Structures Across Species
Understanding the diversity of reproductive structures among various plant species reveals fascinating insights into their evolutionary adaptations. These variations not only influence pollination strategies but also play critical roles in the ecological interactions of plants. By examining the unique characteristics found in different species, researchers can uncover patterns that highlight the complexity of plant life.
| Species | Structure Type | Pollination Mechanism | Color Variations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rose (Rosa) | Petals with multiple layers | Insect pollination | Red, pink, yellow |
| Orchid (Orchidaceae) | Complex, intricate shapes | Attracts specific insects | White, purple, striped |
| Daisy (Bellis perennis) | Simple, radial symmetry | Wind and insect pollination | White with yellow center |
| Sunflower (Helianthus annuus) | Large, prominent head | Bees and other insects | Yellow, orange |
By comparing these structures, it becomes evident how adaptations serve to optimize reproduction across different environments. The interplay between form and function in reproductive organs is a key area of study for botanists and ecologists alike, contributing to a deeper understanding of biodiversity.
Common Mistakes in Flower Diagrams
Understanding the components of a bloom is essential for accurate representation and analysis. However, there are frequent errors that individuals encounter, leading to misconceptions and incomplete knowledge. These pitfalls can hinder effective learning and appreciation of botanical structures.
One prevalent error is the mislabeling of structures. It is crucial to correctly identify and name each element, as confusion can arise from similar appearances. For example, confusing the stamen with the pistil can significantly alter the comprehension of reproductive functions.
Another mistake often seen is the neglect of scale and proportion. Accurately depicting sizes relative to one another is vital for clarity. When dimensions are exaggerated or minimized, it can distort the viewer’s understanding of the organism’s biology.
Additionally, omitting key features is a common oversight. Failing to include critical elements such as sepals or bracts can lead to an incomplete picture, undermining the educational value of the representation.
Finally, using vague or ambiguous terms can create confusion. Precision in language helps convey clear information, ensuring that learners grasp the intricate details of each component.
Creative Uses of Flower Worksheets
Exploring the beauty of nature can be both engaging and educational. Activities focused on botanical studies offer a wealth of opportunities for creativity and learning. Here are some innovative ways to utilize these resources effectively.
- Art Projects: Encourage students to create their own artistic interpretations using colors and textures inspired by nature.
- Science Integration: Combine these resources with lessons on pollination, plant biology, or ecosystems to enhance understanding.
- Interactive Games: Transform learning into play by developing matching or identification games that challenge students to recognize various species.
In addition to these activities, consider the following ideas:
- Group Collaborations: Foster teamwork by assigning group projects that involve research and presentations on different aspects of botany.
- Outdoor Exploration: Take the learning outside by organizing field trips where students can observe and document real-life examples.
- Creative Writing: Prompt students to write stories or poems inspired by their observations and artistic creations.
Utilizing these educational tools in diverse ways not only enhances comprehension but also ignites a passion for the natural world among learners.
Integrating Technology in Flower Education
Incorporating modern tools into botanical studies opens new avenues for understanding and engagement. By leveraging innovative resources, educators can enhance the learning experience, making it more interactive and accessible for students. This approach not only enriches knowledge but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the natural world.
Interactive Learning Tools
Utilizing digital platforms, such as virtual simulations and educational apps, allows learners to explore biological concepts in an immersive manner. These tools can provide a dynamic way to visualize complex structures, enhancing retention and understanding. Additionally, online resources enable collaborative projects, encouraging teamwork and peer learning.
Assessment and Feedback
Technology also plays a vital role in evaluating student progress. Through digital quizzes and interactive assessments, educators can receive immediate feedback, tailoring instruction to meet individual needs. This adaptability ensures that all students are engaged and supported in their educational journey, paving the way for a more effective learning environment.
Benefits of Hands-On Learning Techniques
Experiential learning approaches offer a range of advantages that enhance the educational experience. By engaging students through direct involvement and practical application, these methods foster a deeper understanding of concepts and improve retention of information.
One significant benefit is the development of critical thinking skills. When learners participate in activities that require problem-solving and decision-making, they cultivate analytical abilities that are essential in real-world scenarios. This active engagement encourages them to think independently and creatively.
Additionally, hands-on methods promote collaboration among peers. Group activities enable students to share ideas, communicate effectively, and build teamwork skills. This social interaction not only enriches the learning experience but also prepares individuals for future professional environments where collaboration is key.
Moreover, these techniques can increase motivation and enthusiasm for learning. When students are actively involved, they often find the material more relevant and interesting, leading to greater investment in their educational journey. The tangible nature of practical tasks can ignite curiosity and inspire further exploration of subjects.
Finally, hands-on experiences often cater to diverse learning styles. By incorporating various sensory modalities, these approaches accommodate visual, auditory, and kinesthetic learners alike, ensuring a more inclusive educational atmosphere that meets the needs of all students.