Tulip Flower Parts Illustrated Guide
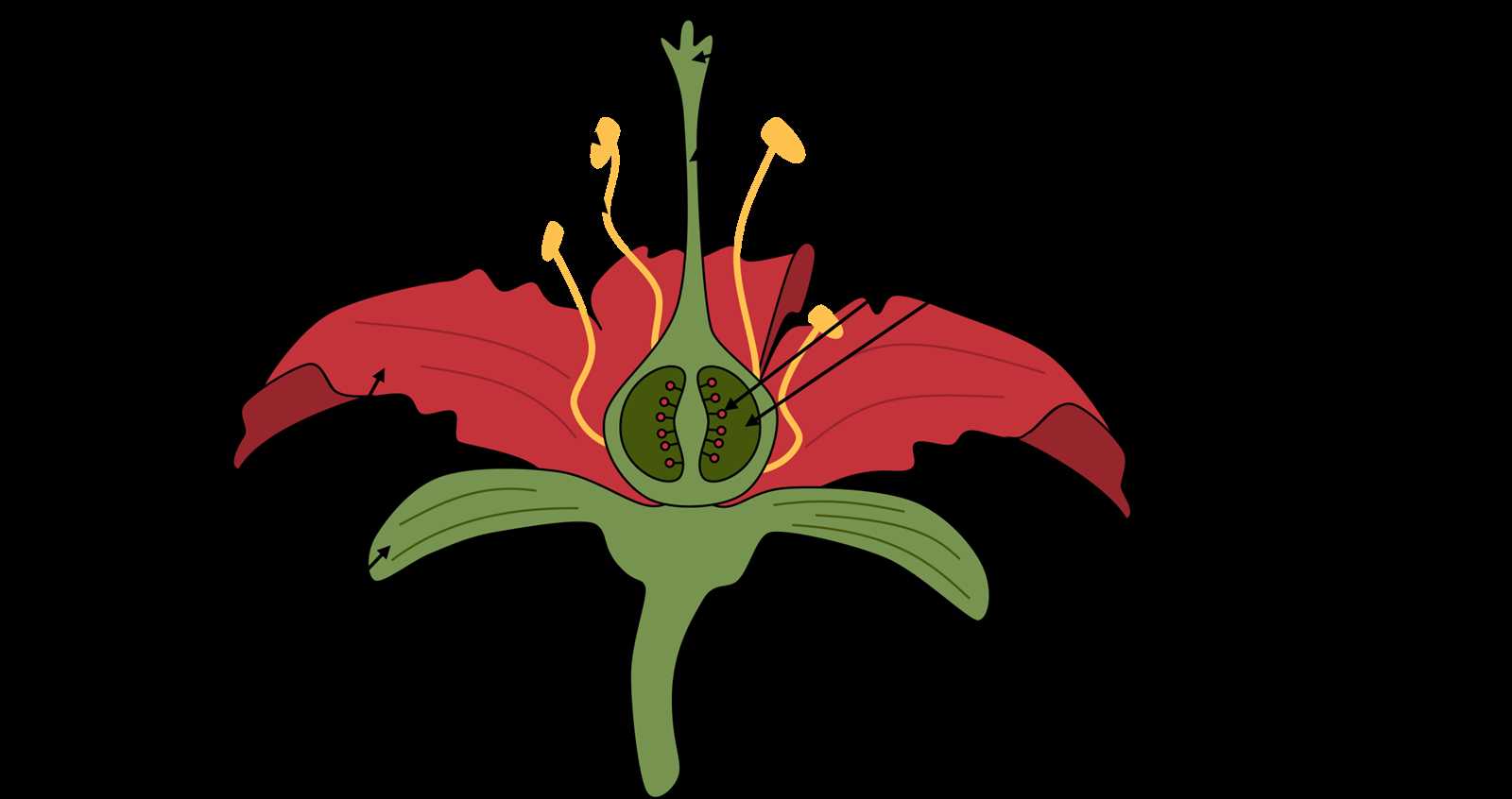

The intricate structure of a beloved garden specimen reveals a fascinating world that combines beauty and functionality. Each element plays a significant role in the reproductive process, ensuring the continuation of its species. By delving into this natural wonder, we can appreciate the complexity that lies beneath its vibrant exterior.
Examining the various components highlights their unique characteristics and interconnections. From the delicate protective layers to the essential reproductive organs, each feature contributes to the overall harmony and efficiency of the organism’s life cycle. Understanding these elements allows for a deeper appreciation of nature’s design.
Moreover, this exploration not only enriches our knowledge but also enhances our ability to cultivate and care for these natural treasures. Recognizing the significance of each section aids gardeners and enthusiasts in making informed decisions to support healthy growth and flourishing displays. Such insights foster a profound connection between people and the natural world.
Understanding Tulip Anatomy
This section explores the intricate structure of a beloved spring bloom, highlighting its essential components and their functions. By examining these elements, one gains insight into how this plant thrives and contributes to its environment.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Petals | Brightly colored structures that attract pollinators and provide protection for reproductive organs. |
| Stamens | Male reproductive organs that produce pollen, crucial for fertilization. |
| Carpels | Female reproductive parts that house ovules and develop into seeds post-fertilization. |
| Leaves | Green structures that perform photosynthesis, providing energy for growth. |
| Bulb | A storage organ that nourishes the plant during dormant periods and supports new growth. |
Essential Components of a Tulip
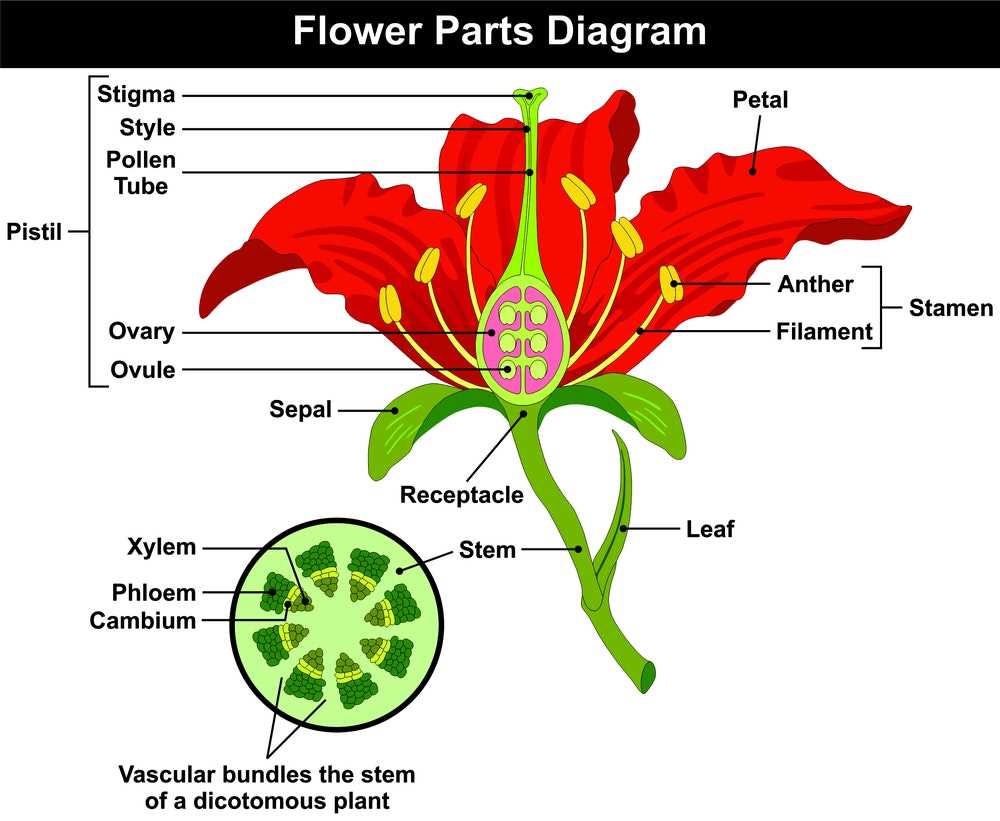
The anatomy of a particular bloom reveals a fascinating structure, each element playing a vital role in its overall beauty and reproductive success. Understanding these integral components can enhance appreciation for this vibrant specimen.
At the base lies the bulb, a storage organ that provides the necessary nutrients for growth. This underground structure is crucial for survival during unfavorable conditions and serves as the starting point for new life each season.
The stem serves as a support system, elevating the blossom towards the sun and allowing it to reach for light. Its sturdy composition ensures that the blossom stands tall and can withstand environmental challenges.
At the top, the vivid petals captivate the eye with their rich colors and shapes. These modified leaves are not only striking but also play a key role in attracting pollinators, which are essential for reproduction.
The center contains reproductive structures, including the stamens and pistil. The stamens produce pollen, while the pistil houses the ovary, where seeds are formed after fertilization. This collaboration is fundamental to the life cycle of the plant.
By exploring these essential elements, one gains a deeper understanding of how each contributes to the vitality and splendor of this remarkable specimen.
Functions of Each Flower Part
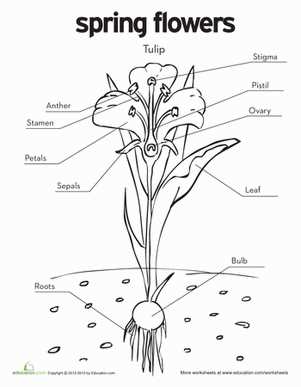
The intricate structures within a bloom play vital roles in reproduction and overall health. Each component contributes uniquely to the lifecycle, ensuring successful pollination and seed development. Understanding these functions enhances appreciation for botanical complexity.
Reproductive Functions
The primary aim of many structures is to facilitate reproduction. The stamen, comprising anther and filament, produces pollen, while the pistil, with stigma, style, and ovary, captures pollen for fertilization. This symbiotic relationship between the male and female elements is crucial for the generation of new life.
Support and Attraction
Other structures serve essential support and attraction roles. The sepals encase and protect the developing components, while vibrant petals draw in pollinators with their colors and scents. This interplay not only aids in reproduction but also ensures the survival of various species through effective pollination.
Diagram Overview: Key Features
This section delves into the essential components and characteristics that define the structure of a blooming specimen. Understanding these attributes is crucial for both enthusiasts and scholars alike, as they provide insights into the growth and reproductive processes of the organism.
Essential Components
Each element plays a distinct role in the life cycle and functionality of the organism. Here are some of the key features that contribute to its overall beauty and complexity:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Petals | Often vibrant and colorful, these structures attract pollinators. |
| Sepals | Green leaf-like structures that protect the budding specimen. |
| Stamens | The male reproductive organs, responsible for pollen production. |
| Pistils | The female reproductive component, facilitating fertilization. |
Functional Roles
Understanding how these components interact with one another enhances appreciation for their intricate relationships. Each element not only serves its purpose but also contributes to the overall harmony and functionality of the specimen in its environment.
Life Cycle of Tulip Flowers
The journey of these stunning blooms begins with a remarkable transformation that takes place in several distinct stages. Each phase plays a crucial role in ensuring the vibrant display that captivates many admirers in gardens and parks around the world.
Stages of Development
- Seed Stage: The life begins with seeds, which are dispersed by various means, such as wind or animals.
- Germination: Under favorable conditions, seeds absorb moisture and nutrients, leading to sprouting.
- Bulb Formation: As the plant matures, it develops a bulb underground, storing energy for future growth.
- Growth Phase: With the arrival of spring, shoots emerge from the soil, reaching for sunlight and air.
- Blooming: The final stage occurs when buds open, revealing their colorful petals and attracting pollinators.
Factors Influencing Growth
- Climate: Temperature and weather patterns significantly affect the timing of each stage.
- Soil Quality: Nutrient-rich soil promotes healthy bulb development and flowering.
- Water Supply: Adequate moisture is essential for sprouting and sustaining growth.
- Sunlight: Exposure to sunlight influences blooming and the overall vigor of the plant.
Pollination Process in Tulips
The reproductive mechanism of these vibrant blooms involves a fascinating interplay between various elements of nature. This process is crucial for the continuation of species and relies heavily on the transfer of pollen from one structure to another, ensuring fertilization and the production of seeds.
The timing of this interaction is essential, as the readiness of the reproductive organs plays a significant role in successful fertilization. Environmental factors, such as temperature and humidity, also influence the overall efficiency of this process, highlighting the delicate balance necessary for nature’s cycles.
Ultimately, understanding this intricate process not only sheds light on the beauty of these plants but also emphasizes the importance of biodiversity and the role of pollinators in maintaining ecological health.
Importance of Petals in Tulips
Petals play a crucial role in the allure and functionality of certain blooms. They serve not only as a visual attraction but also contribute to various ecological interactions, enhancing the overall reproductive success of these plants.
Aesthetic Appeal
The vibrant hues and unique shapes of petals significantly attract pollinators. This visual beauty is essential for:
- Encouraging visits from bees and butterflies.
- Enhancing the overall marketability of cultivated varieties.
- Creating diverse landscapes and gardens.
Ecological Functions
Beyond their beauty, petals also serve important ecological functions:
- Providing a landing platform for insects.
- Contributing to the overall health of ecosystems.
- Facilitating cross-pollination among various species.
Role of Stamens and Pollen
The reproductive structures in many plants play a crucial role in the process of reproduction, facilitating the transfer of genetic material and the formation of new life. Among these structures, specific elements are responsible for producing and distributing the grains essential for fertilization.
Stamens serve as the male reproductive organs, playing a vital role in sexual reproduction. Their main functions include:
- Producing pollen grains that contain sperm cells.
- Facilitating the transfer of pollen to receptive surfaces, enabling fertilization.
- Contributing to the overall reproductive success of the plant by ensuring genetic diversity.
Pollen, the fine powder produced by these reproductive organs, is fundamental in the life cycle of many plant species. Key aspects of pollen include:
- Being transported by wind, insects, or water to reach the stigma of compatible structures.
- Containing the genetic material required for the fertilization process.
- Serving as a vital food source for various pollinators, thus promoting ecological relationships.
In summary, the interplay between stamens and pollen not only facilitates reproduction but also supports the intricate web of life, ensuring the continuation of various plant species and their interactions within ecosystems.
Significance of Tulip Bulbs
These underground structures serve as a crucial component in the life cycle of certain plants, providing essential nutrients and energy for growth. Their importance extends beyond mere survival, influencing both ecological dynamics and human culture.
Ecological Role
- Support for local ecosystems by attracting pollinators.
- Contribute to soil health through their growth and decay.
- Provide food sources for various organisms.
Cultural and Economic Importance
- Symbol of beauty and elegance in various cultures.
- Key elements in horticulture and landscaping.
- Major contributors to the economy through trade and tourism.
Impact of Sepals on Growth
The outermost structures play a crucial role in the development and vitality of plants. They serve as protective layers, shielding the inner components from environmental stressors and pests. Their health directly influences overall growth and reproductive success.
| Function | Impact on Growth |
|---|---|
| Protection | Prevents damage from external factors, ensuring healthy development. |
| Support | Provides structural integrity, allowing for optimal light exposure. |
| Water Retention | Helps maintain moisture levels, crucial for cellular function. |
| Pollinator Attraction | Enhances reproductive chances by guiding pollinators effectively. |
Identifying Tulip Varieties by Structure
Understanding the diverse forms of these beautiful blooms can greatly enhance one’s appreciation for their unique characteristics. By examining the various structural features, enthusiasts can distinguish between different cultivars and make informed choices for gardens or arrangements.
Key structural elements to consider include:
- Petal Shape: The outline and curvature can vary significantly.
- Height: Some varieties grow tall and slender, while others remain compact.
- Leaf Structure: Leaf width and color can provide clues to the specific type.
- Stamen Arrangement: The position and number of stamens can differ between groups.
To further aid in identification, consider the following classifications based on structural traits:
- Early Bloomers: Generally shorter with broad leaves.
- Late Bloomers: Typically taller with elongated petals.
- Fringed Varieties: Notable for their jagged petal edges.
- Double-Flowered Types: Characterized by densely packed petals.
By paying attention to these attributes, one can become adept at recognizing and categorizing the many exciting variations available in the marketplace.
Common Diseases Affecting Tulip Parts
Various ailments can significantly impact the health of these beautiful plants, often manifesting in different ways across their structures. Understanding these conditions is crucial for maintaining vibrant growth and preventing extensive damage.
Fungal infections are among the most prevalent issues, often leading to symptoms such as wilting and discoloration. Botrytis blight is a notable example, causing a gray mold to form, especially in humid conditions. Regular inspection and proper air circulation can help mitigate this threat.
Bacterial infections also pose a serious risk, with soft rot being particularly destructive. This condition can cause tissues to become mushy and emit foul odors, leading to plant decay. Ensuring that the soil is well-drained and avoiding overcrowding can reduce susceptibility.
Additionally, viral diseases can affect the overall vigor of the plants. The tobacco mosaic virus can result in mottled leaves and stunted growth, impacting aesthetic appeal and flowering potential. Maintaining clean gardening practices and using virus-free bulbs are essential preventive measures.
In conclusion, vigilance against these ailments is key to fostering healthy specimens. By recognizing symptoms early and implementing sound cultural practices, one can ensure robust development and prolonged beauty.
Tips for Drawing Tulip Diagrams
Creating a visual representation of botanical elements can be an enjoyable and educational experience. To effectively illustrate these elements, it is essential to focus on various techniques and approaches that enhance clarity and detail. Below are some valuable suggestions to elevate your artistic interpretation.
1. Start with Basic Shapes: Begin by sketching simple forms to outline the structure. Use circles and ovals to represent the overall shape, allowing for adjustments as you refine your drawing.
2. Pay Attention to Proportions: Maintaining accurate proportions is crucial. Observe real-life examples to ensure your rendition accurately reflects the dimensions and relationships of the different components.
3. Use Layering Techniques: Build your illustration in layers, starting with the foundational elements and gradually adding details. This method allows for better organization and more control over the final composition.
4. Incorporate Textures: Experiment with various shading techniques to depict the surface details. Using cross-hatching or stippling can add depth and realism to your artwork.
5. Color Wisely: When adding color, choose a palette that mirrors nature. Observe how light affects colors and use gradients to enhance the three-dimensional effect.
6. Study and Reference: Utilize reference images and real specimens to inform your drawing. Understanding the anatomy and characteristics of each component will improve accuracy and authenticity.
7. Practice Regularly: Like any skill, consistent practice is vital for improvement. Dedicate time to sketching different variations and styles to develop your unique artistic voice.