Exploring the Essential Parts of a Flower with Diagram
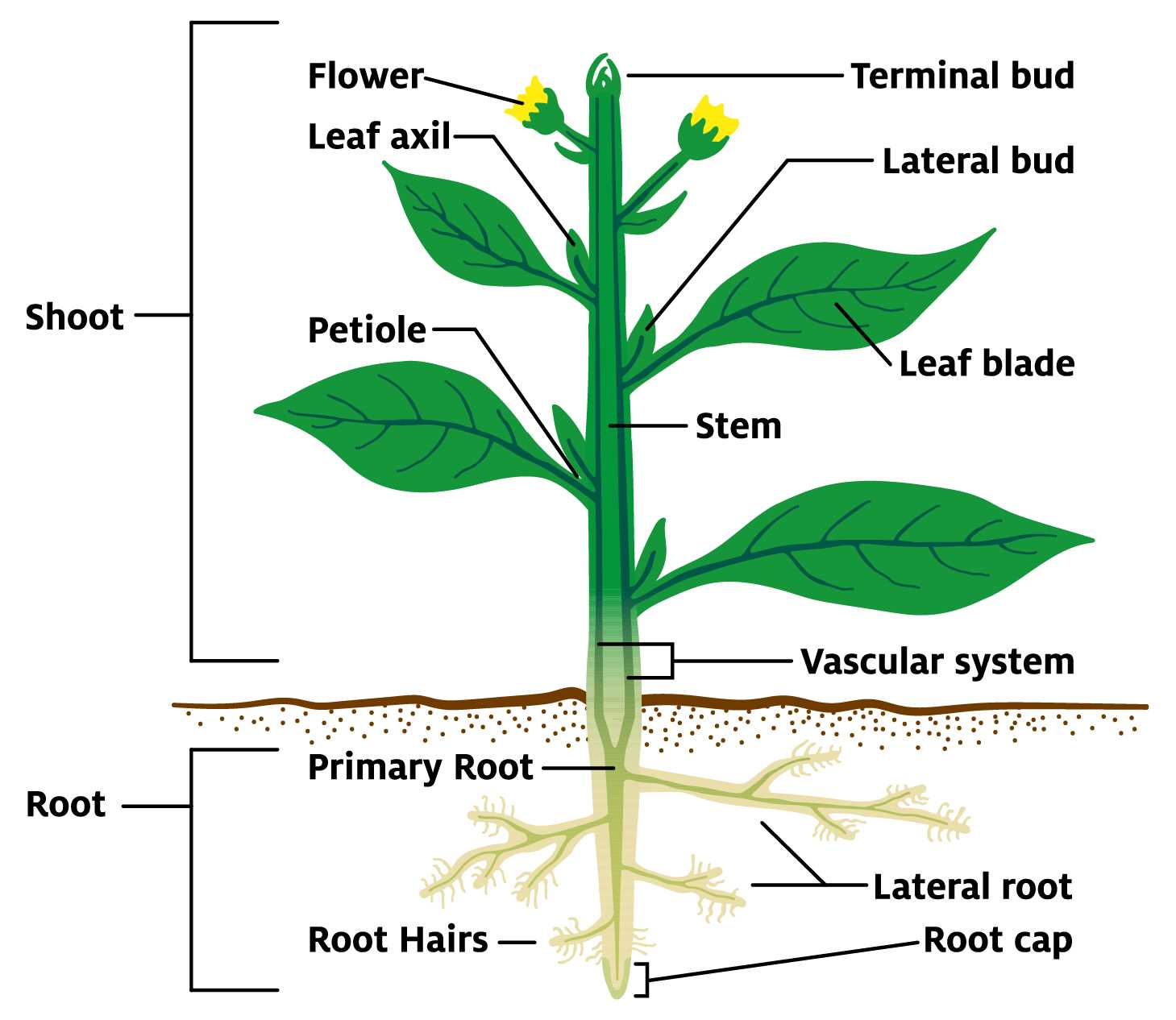
Exploring the intricate world of botanical anatomy reveals a stunning array of components that contribute to reproduction and beauty. Each element plays a vital role in the lifecycle of plants, showcasing nature’s incredible design.
Delving into these features offers insights into their functions and interactions. From attracting pollinators to ensuring successful fertilization, each structure is essential for thriving ecosystems.
In this guide, we’ll break down the fundamental characteristics of these components, providing a comprehensive overview alongside a visual representation for enhanced clarity. Get ready to uncover the ultimate secrets behind plant morphology!
Understanding Flower Structure
Grasping the anatomy of blooming plants reveals the intricate design that supports their reproduction and survival. Each component plays a crucial role, contributing to the overall functionality and beauty of these organisms. This exploration highlights how various elements interact and support the plant’s life cycle.
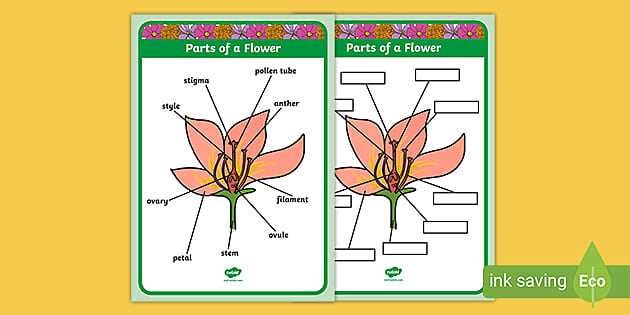
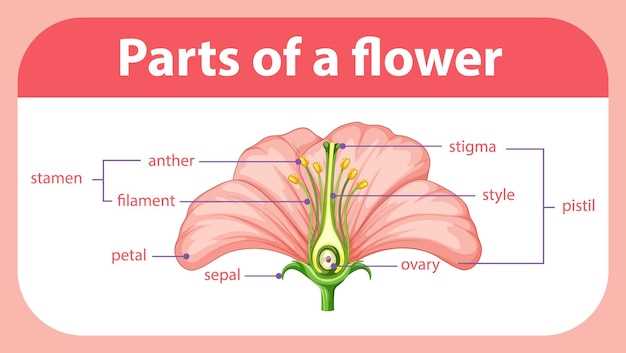
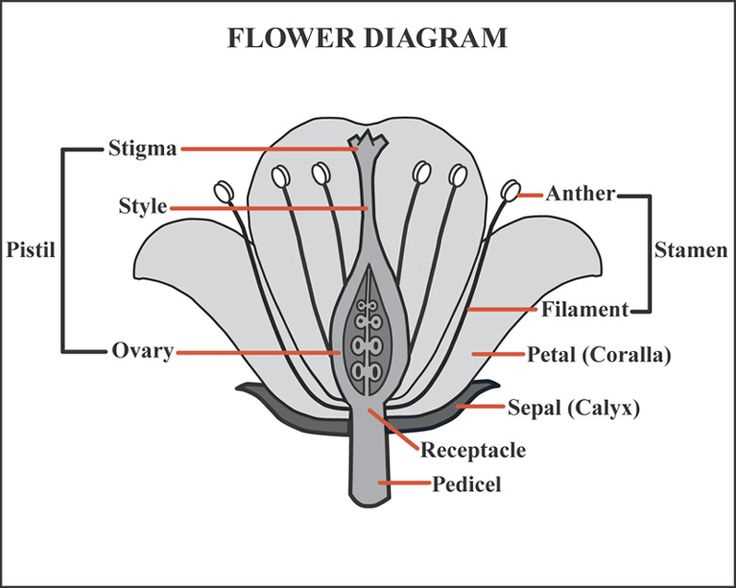
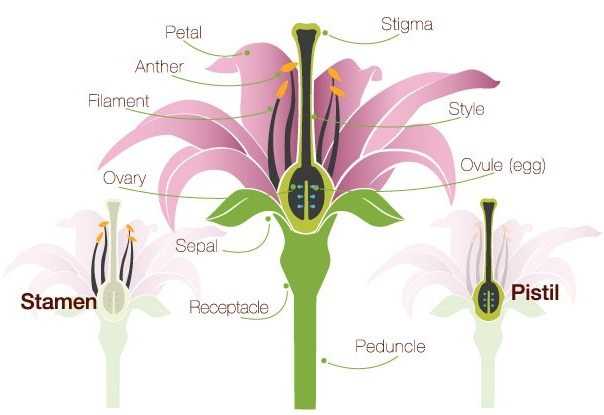
Stamens serve as the male reproductive units, producing pollen necessary for fertilization. Their structure is optimized for effective pollen dispersal. In contrast, pistils represent the female counterpart, designed to capture pollen and facilitate seed development. These reproductive features are often surrounded by colorful petals, which attract pollinators through their vibrant hues and enticing fragrances.
Additionally, the sepal protects the budding reproductive structures, ensuring their safety during development. The receptacle, or base, holds everything together, acting as the foundation for these vital components. Together, these elements create a harmonious system essential for the continuation of many plant species.
Key Components of a Flower

Understanding the essential elements of a bloom reveals its intricate design and vital roles in reproduction. Each segment contributes uniquely to the overall functionality, ensuring the continuation of plant species and enhancing their beauty. These constituents work together harmoniously, facilitating processes like pollination and seed formation.
Reproductive Structures
At the core of a bloom are structures dedicated to reproduction. These include the stamens, which produce pollen, and the carpels, which house ovules. This combination plays a pivotal role in the fertilization process, enabling the development of seeds and fruits.
Supportive Features
Alongside reproductive elements, supportive features such as petals and sepals enhance both protection and attraction. Petals, often brightly colored, draw in pollinators, while sepals provide a protective layer during bud formation. Together, they create a welcoming environment for various pollinators, aiding in successful fertilization.
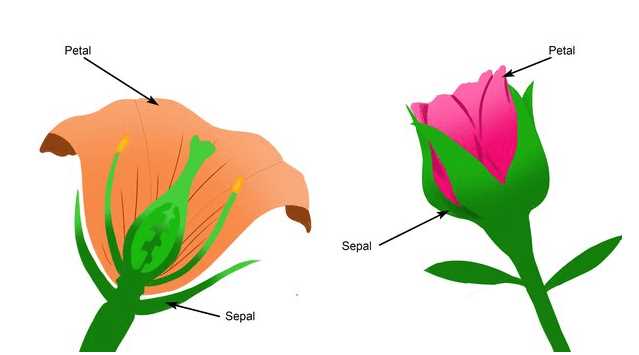
The Role of Petals
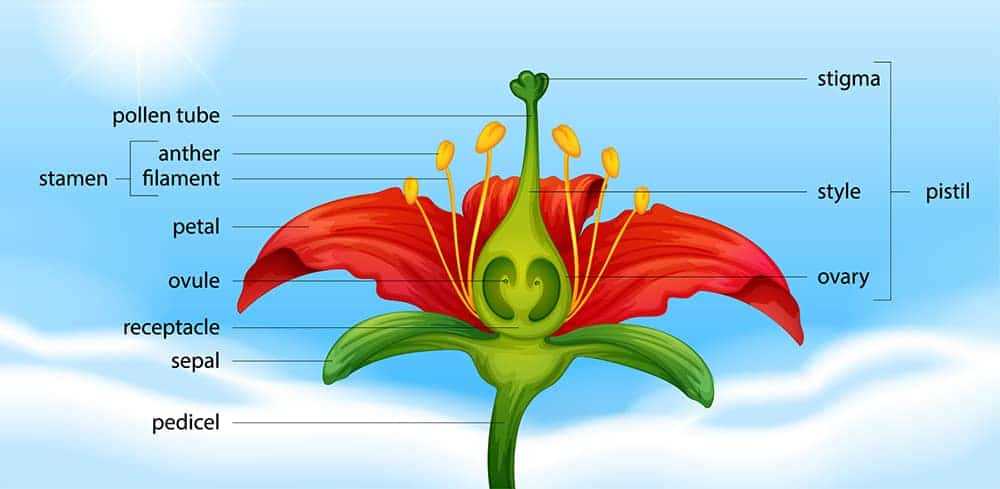

Petals serve as an essential component in the reproductive process of many plants, captivating both pollinators and human observers alike. Their vibrant hues and intricate shapes play a crucial part in attracting various species, ensuring successful pollen transfer and reproduction.
Functionality is paramount, as these structures provide a visual cue for insects and birds, guiding them toward nectar sources. Additionally, the arrangement and texture of petals can influence the efficiency of pollination, creating a delicate balance between plant and pollinator interactions.
Moreover, petals contribute to the overall health of the reproductive system by protecting the more delicate organs hidden within. In essence, their beauty is not merely aesthetic; it holds profound ecological significance.
Functions of Sepals
Sepals play a crucial role in the development and protection of reproductive structures. These elements serve multiple functions that contribute to the overall health and success of plant species.
Protective Role
One primary function involves safeguarding the delicate parts located within. This protection is vital during various growth stages:
- Shielding buds from environmental factors
- Preventing damage from pests
- Maintaining moisture levels
Supportive Role
Additionally, sepals provide structural support, aiding in the stability of surrounding elements. Their supportive function includes:
- Anchoring petals
- Contributing to overall shape and form
- Facilitating pollinator access by positioning floral components
Exploring Stamens and Anthers
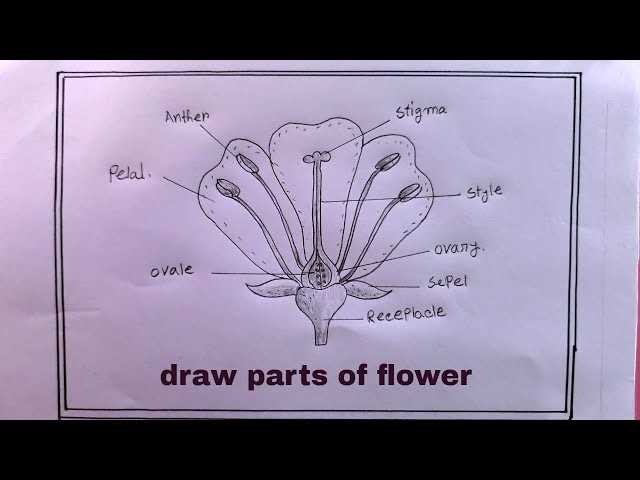
Delving into the components responsible for reproduction reveals fascinating structures that play a crucial role in pollination. These elements are vital for the continuation of many plant species, showcasing nature’s ultimate design in ensuring genetic diversity.
Structure and Function
Stamens, comprising two main sections, contribute significantly to reproductive processes. The filament supports the anther, where pollen grains are produced. This arrangement facilitates efficient transfer of pollen to pollinators, enhancing the chances of successful fertilization.
Importance in Pollination
The anther’s role cannot be overstated; it is instrumental in the release of pollen during the flowering phase. As pollinators visit, they inadvertently carry this vital genetic material to other blossoms, promoting cross-pollination and enriching the plant’s gene pool. The connection between stamens and successful reproduction is a prime example of ecological interdependence.
The Importance of Pistils
Pistils play a crucial role in the reproductive process of angiosperms, serving as essential components for successful fertilization. These structures are not only responsible for producing ovules but also for receiving pollen, which is vital for seed development. Understanding their significance provides insight into the complexities of plant reproduction and biodiversity.
Functions of Pistils
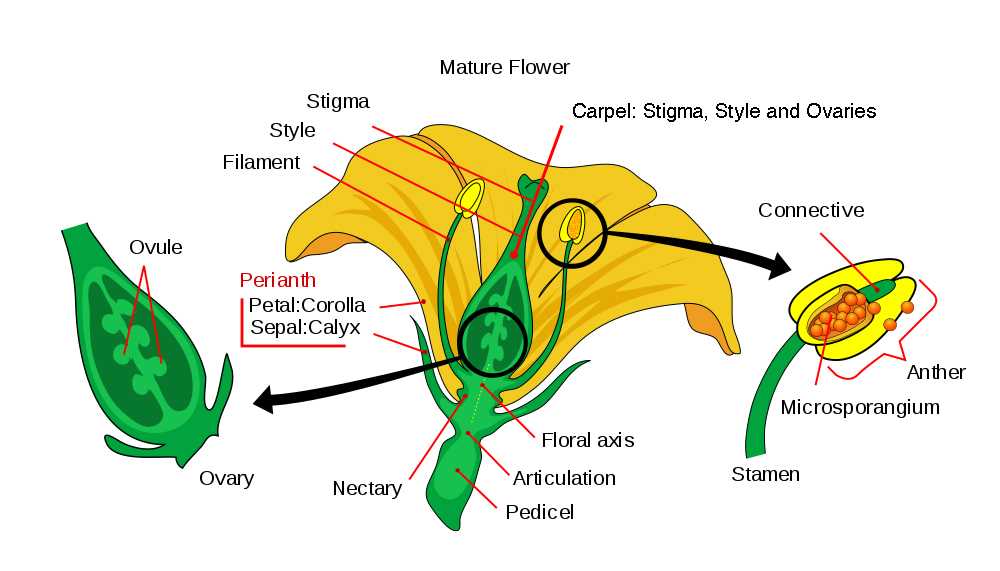
The primary functions of pistils encompass several key processes that facilitate reproduction. Below are some of the most important roles they fulfill:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Pollination | Pistils attract pollinators, allowing for the transfer of pollen from male structures. |
| Fertilization | Once pollen lands on the stigma, it germinates and travels down to fertilize ovules. |
| Seed Development | After fertilization, pistils contribute to the formation and nourishment of seeds. |
| Genetic Diversity | Pistils promote genetic variation through cross-pollination, enhancing resilience in ecosystems. |
Significance in Ecosystems
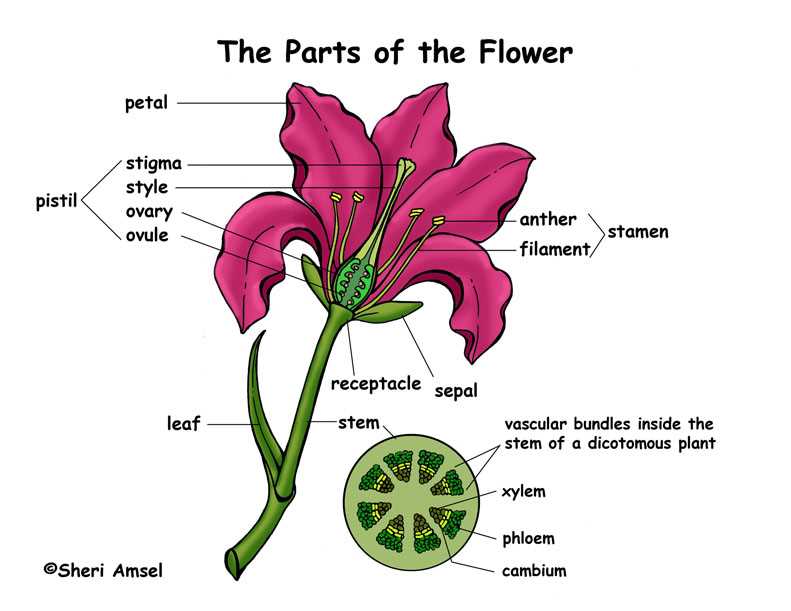
Pistils are integral to maintaining ecological balance. By supporting pollination, they help sustain food webs and contribute to the survival of various species. The interdependence between plants and pollinators emphasizes the importance of protecting these relationships, as the decline of one can adversely affect the other.
How Ovules Contribute to Reproduction
Ovules play a crucial role in the reproductive process of many plants, serving as the sites where fertilization occurs and seeds develop. These structures are essential for the continuation of plant species, providing a means for genetic exchange and variation.
Formation and Development
Located within the ovary, ovules begin as small, undeveloped structures. As the reproductive cycle progresses, they undergo maturation, ultimately leading to the formation of seeds upon successful fertilization. This development is vital for ensuring that the genetic material is passed on to the next generation.
Fertilization Process
During fertilization, pollen grains reach the ovule, initiating a series of events that result in the fusion of gametes. This union not only triggers the formation of a zygote but also influences the traits of the resulting offspring. Thus, ovules are instrumental in shaping the diversity and adaptability of plant life.
Pollination Process Explained

This essential biological process plays a vital role in the reproduction of numerous plant species. It involves the transfer of male gametes to female structures, facilitating fertilization and subsequent seed development. Understanding this intricate mechanism unveils the relationship between flora and various pollinators, highlighting its importance in ecosystems and agriculture.
Types of Pollination
Several methods exist for transferring pollen, each with unique characteristics:
- Self-pollination: Occurs within the same plant, where pollen from the male anther fertilizes the female stigma.
- Cross-pollination: Involves pollen transfer between different plants, promoting genetic diversity.
- Wind pollination: Relies on air currents to carry lightweight pollen grains to receptive stigmas.
- Animal pollination: Involves insects, birds, and other animals that facilitate pollen transfer while seeking nectar or food.
Steps in the Pollination Process
- Pollen production: Male reproductive structures generate pollen grains, containing sperm cells.
- Pollen transfer: Various agents, such as wind or animals, transport pollen to the female stigma.
- Pollen germination: Upon landing on a compatible stigma, the pollen grain germinates and forms a pollen tube.
- Fertilization: The pollen tube grows down to the ovule, allowing sperm cells to fertilize the egg cell.
- Seed development: Following fertilization, seeds form within the ovule, eventually leading to the creation of new plants.
Flower Symmetry Types
Understanding floral symmetry unveils fascinating aspects of nature’s design. These arrangements can significantly influence pollination and plant reproduction, showcasing a variety of structural forms.
Types of Symmetry
- Radial Symmetry: Flowers exhibit uniformity around a central axis, allowing multiple lines of symmetry.
- Bilateral Symmetry: Floral structures display a mirror-like quality, offering only one line of symmetry, which can enhance specific pollination strategies.
Examples
- Radial: Daisies and sunflowers.
- Bilateral: Orchids and sweet peas.
Common Flower Types and Examples
Diverse varieties of blooming plants showcase remarkable characteristics, captivating enthusiasts and nature lovers alike. Each category possesses unique features, colors, and forms that contribute to the beauty of gardens and landscapes. Understanding these classifications enhances appreciation for their ecological roles and aesthetic contributions.
Roses exemplify classic elegance, celebrated for their layered petals and enchanting fragrances. Commonly found in shades of red, pink, and white, these blossoms symbolize love and passion. Their cultivation spans centuries, resulting in numerous hybrids and varieties.
Daisies, with their cheerful appearance, embody simplicity and resilience. Typically characterized by white petals surrounding a bright yellow center, these plants thrive in various environments. They often represent purity and innocence in cultural contexts.
Tulips display vibrant colors and distinct shapes, making them popular in springtime gardens. Originating from Central Asia, these bulbs offer a striking visual display and come in an array of hues, symbolizing renewal and new beginnings.
Orchids stand out for their intricate structures and exotic allure. With thousands of species, these blooms exhibit unique patterns and colors, often associated with beauty and luxury. Their adaptability allows them to flourish in diverse habitats around the globe.
Sunflowers, known for their towering height and bright yellow faces, follow the sun’s path throughout the day. These cheerful plants are not only visually stunning but also serve as a vital source of food for pollinators, illustrating the connection between beauty and ecology.
Flowering Plants in Ecosystems
These vibrant organisms play a crucial role in sustaining diverse habitats. Their interactions with various elements in nature create a balanced environment, fostering both flora and fauna. Through their life cycles, they contribute significantly to ecological dynamics, influencing nutrient cycles and energy flow.
Importance of Pollination
Pollinators rely on these organisms for sustenance, establishing essential relationships that drive biodiversity. The process of reproduction not only ensures survival but also enhances genetic variation, allowing ecosystems to adapt to changing conditions.
Habitat and Shelter
These organisms provide shelter and food for numerous species, forming the backbone of many ecosystems. Their presence promotes stability, enabling a wide range of organisms to thrive within various environmental contexts.
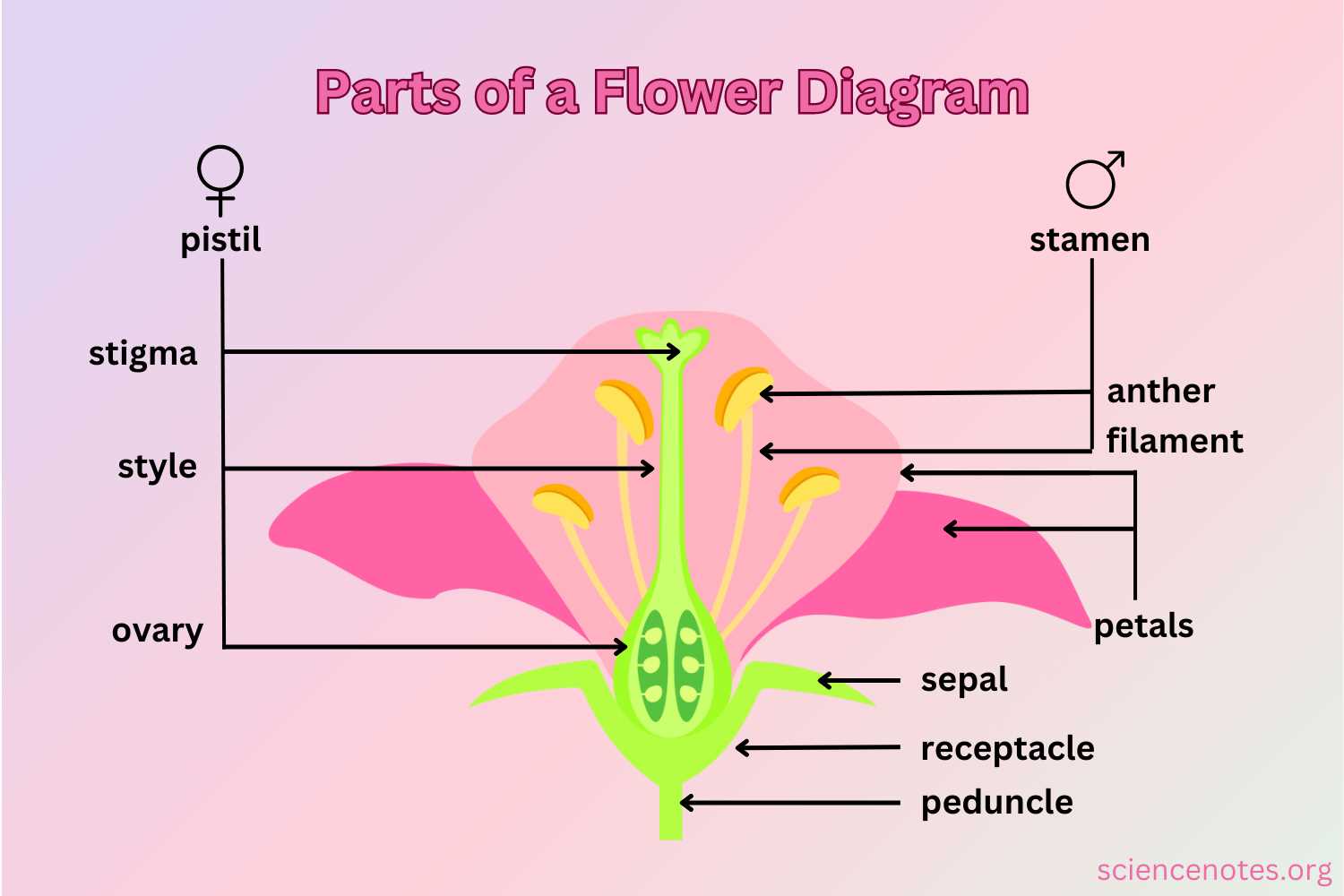
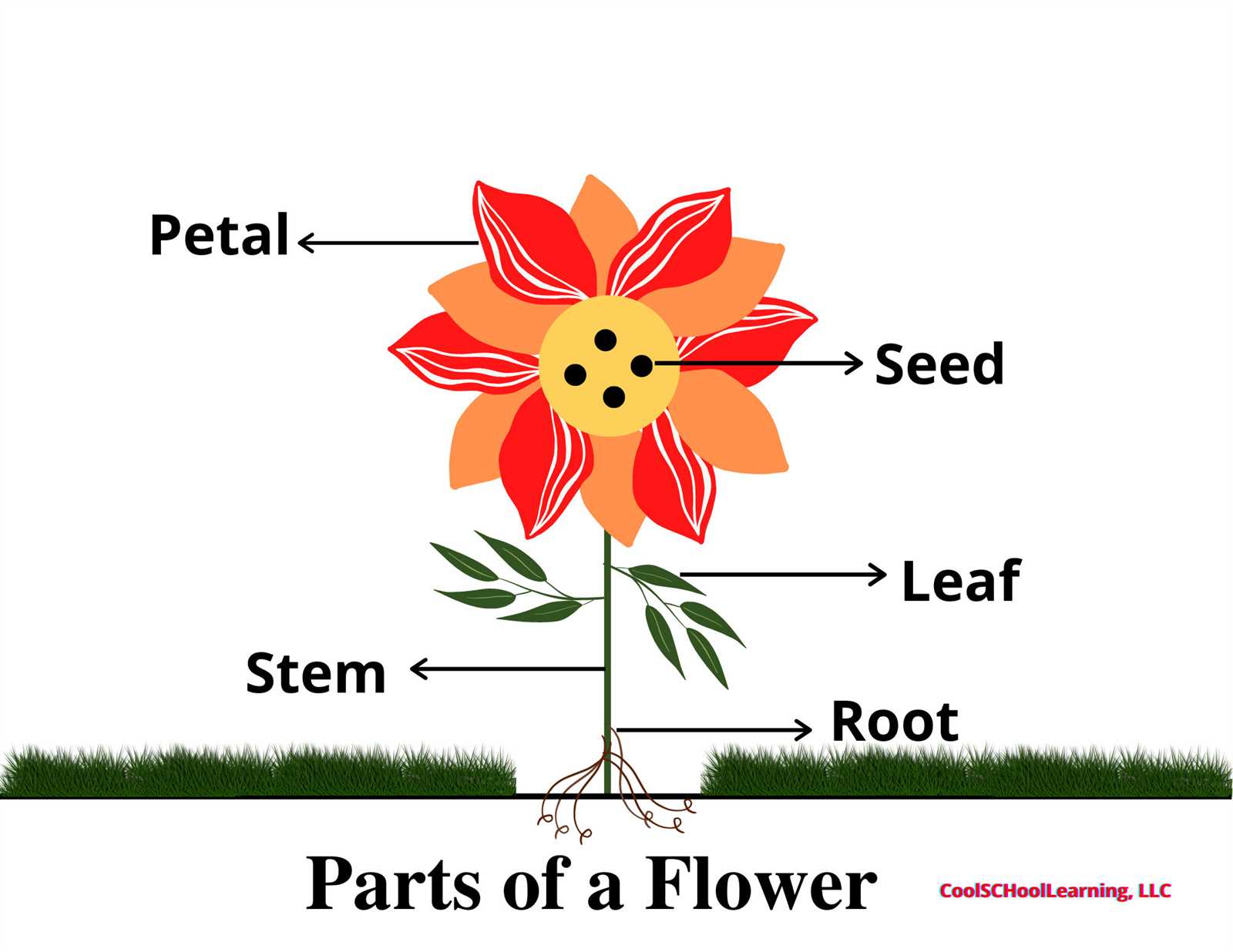
Understanding Flower Anatomy Diagram
An exploration of the intricate structure of blooms reveals a fascinating world of components, each playing a crucial role in reproduction and beauty. This section delves into the essential elements that contribute to the functionality and allure of these botanical marvels.
Key Components of Bloom Structure
Recognizing the various elements allows for a deeper appreciation of their interconnected functions. Each component contributes uniquely to the overall reproductive success of plants, enhancing their appeal to pollinators and facilitating growth.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Petals | Attract pollinators with vibrant colors and scents. |
| Sepals | Protect the developing bud before blooming. |
| Stamens | Produce pollen, essential for fertilization. |
| Pistils | Receive pollen and facilitate seed development. |
Importance of Bloom Architecture
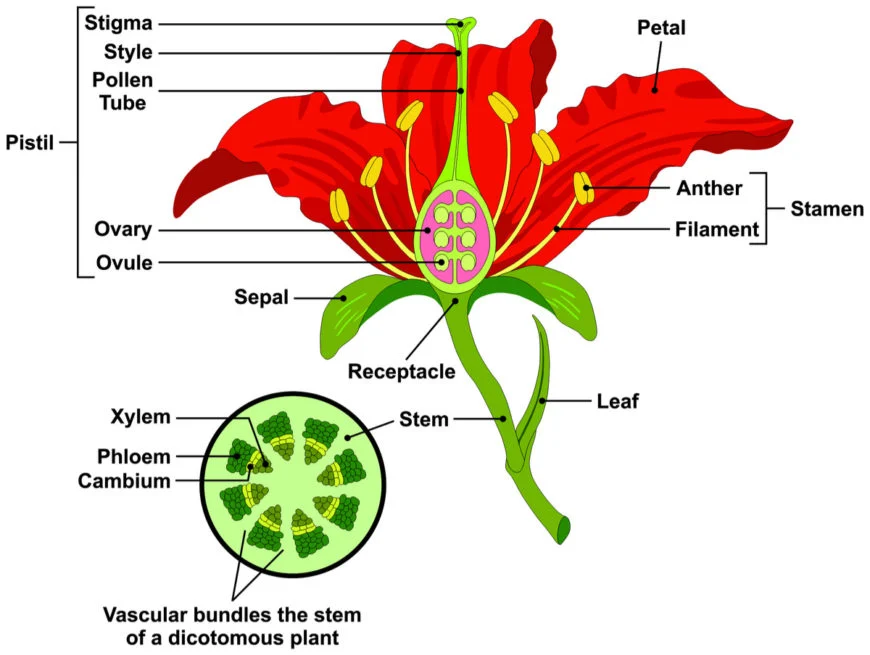
Understanding the architecture of blossoms offers insight into their ecological roles and evolutionary adaptations. Each structure not only serves a distinct purpose but also interacts harmoniously with the environment, ensuring the survival of various species.
Uses of Flowers in Culture
Throughout history, blooms have played a significant role in human traditions and societies, serving various symbolic and practical purposes. They often embody emotions, convey messages, and enhance celebrations.
In many cultures, the beauty and fragrance of these natural creations are deeply intertwined with rituals and customs. Their presence can transform ordinary moments into meaningful experiences.
- Symbolism: Different species carry unique meanings, representing concepts such as love, friendship, and mourning.
- Celebrations: Events like weddings, birthdays, and festivals often feature arrangements, creating an atmosphere of joy and festivity.
- Medicinal Uses: Many cultures utilize blooms in traditional medicine, believing in their healing properties.
- Art and Literature: Artists and writers frequently draw inspiration from these natural wonders, reflecting their beauty and significance in various forms of expression.
These examples illustrate the diverse roles that blossoms play, enriching human experiences and cultural practices around the globe.