Understanding the Components of a Fuel Dispenser Through Diagrams
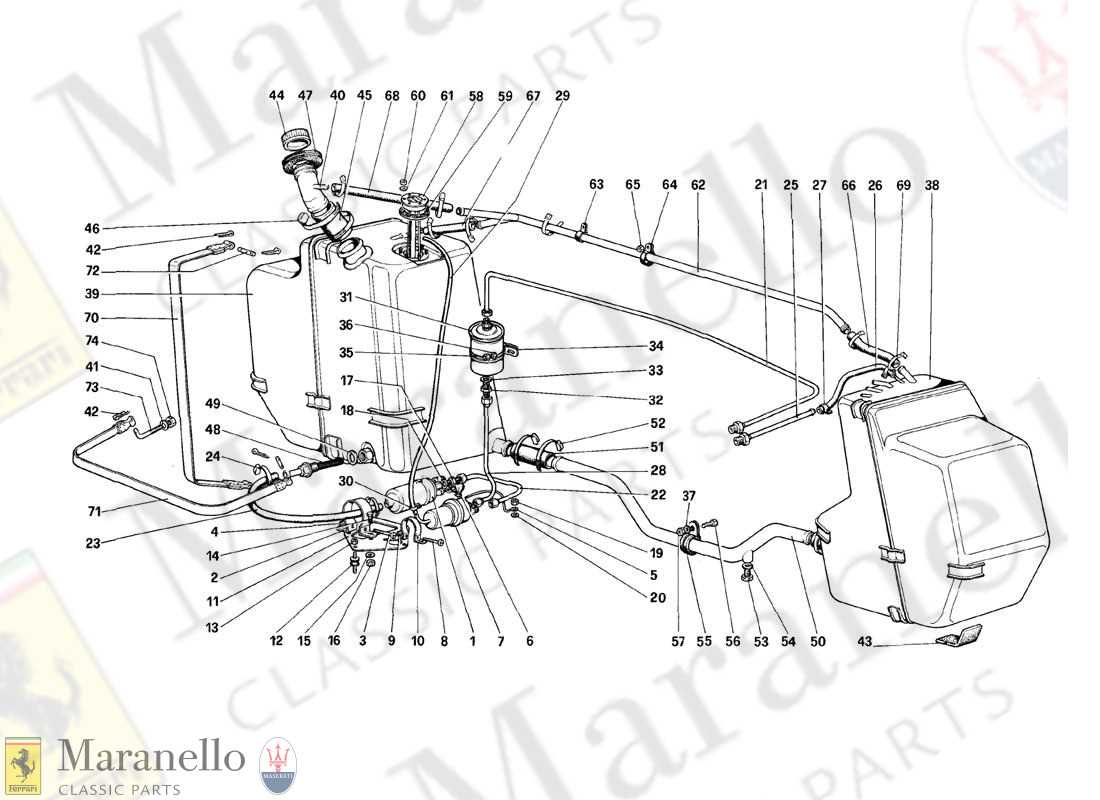
The intricate machinery behind refueling systems plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient operation and safety. This section aims to explore the essential elements that contribute to the functionality of these systems, providing insights into their structure and importance.
By examining the various components, readers can gain a clearer understanding of how each element interacts within the overall system. From the mechanisms that facilitate fluid movement to the technology ensuring precise measurements, every piece is vital for optimal performance.
Ultimately, a comprehensive overview of these mechanisms not only enhances operational knowledge but also fosters appreciation for the engineering that supports modern refueling processes. Join us as we delve into the intricate details that define this essential equipment.
Understanding Fuel Dispenser Components
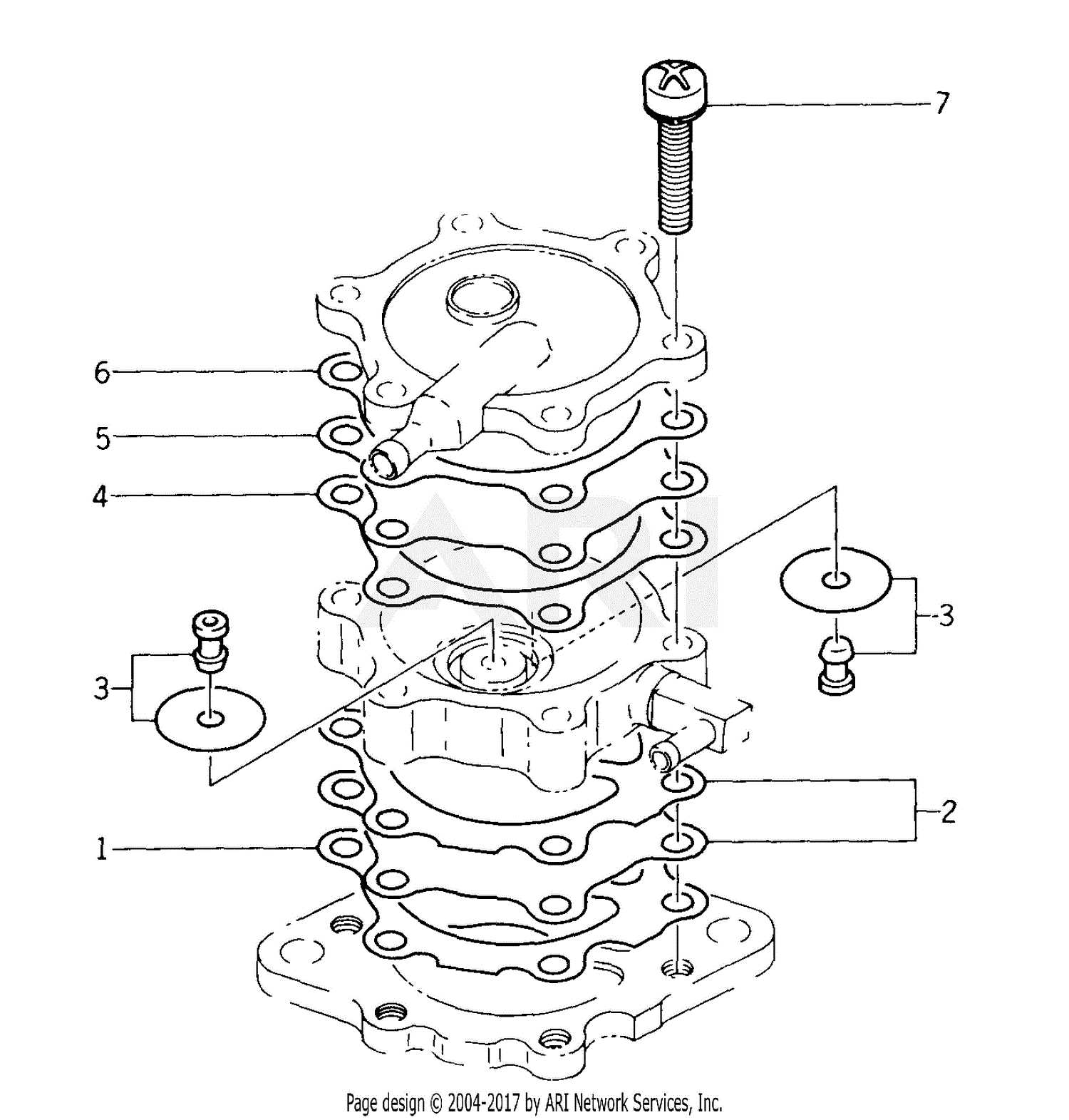
In any refueling setup, the various elements work in harmony to ensure a seamless experience. Each component plays a crucial role in the overall functionality, contributing to efficiency and safety. Familiarity with these elements allows for better maintenance and troubleshooting, enhancing operational reliability.
Main Elements
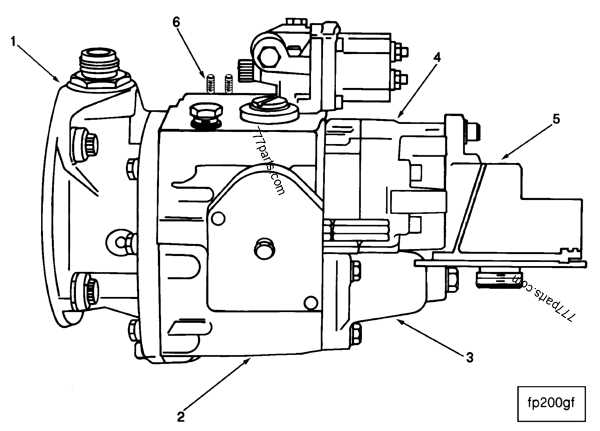
The essential components include a variety of mechanical and electronic devices. These parts manage the transfer of liquid, regulate flow, and ensure accurate measurement. Additionally, safety mechanisms are integrated to prevent leaks and malfunctions, protecting both users and the environment.
Modern systems often feature advanced control technologies that facilitate user interaction and enhance performance monitoring. Digital displays and interfaces provide real-time data, enabling quick adjustments and improving user experience. Understanding these control systems is vital for efficient operation and timely maintenance.
Overview of Fuel Dispenser Functionality
This section explores the essential components and their interactions within a refueling apparatus. Understanding these mechanisms provides insights into how these systems operate efficiently and safely to meet user needs.
The operation of these systems can be broken down into several key functions:
- Measurement: Accurate tracking of the volume being transferred is crucial for both the user and provider.
- Control: User inputs dictate the flow and stop mechanisms, ensuring the process is both user-friendly and safe.
- Flow Regulation: Maintaining consistent delivery rates is essential for efficiency and preventing spills.
- Dispensing Mechanism: This includes the nozzle and hose system, designed for easy handling and secure connections.
- Safety Features: Emergency shut-off valves and leak detection systems help mitigate risks during operation.
In summary, these systems integrate various elements to create a seamless experience, prioritizing both functionality and safety for users.
Main Parts of Fuel Dispensers
Understanding the key components of a refueling device is essential for both operators and users. These elements work in harmony to ensure efficient and safe transfer of liquids. Each section plays a critical role in the overall functionality and reliability of the system.
1. Nozzle: The interface through which the liquid is dispensed. This element is designed to provide precise control over the flow and to minimize spills.
2. Hose: A flexible conduit that connects the nozzle to the storage tank. It allows for easy movement while ensuring the integrity of the flow during operation.
3. Pump: The mechanism responsible for moving the liquid from the storage tank to the nozzle. This component is vital for maintaining the desired pressure and flow rate.
4. Meter: An instrument that measures the quantity of liquid being dispensed. This ensures accurate transactions and helps maintain customer trust.
5. Control System: The electronic or mechanical unit that manages the operation of the device. It regulates flow, monitors transactions, and can provide diagnostic information for maintenance.
6. Safety Features: Includes emergency shut-off valves and spill containment systems. These are crucial for preventing accidents and ensuring compliance with safety regulations.
Each of these elements is integral to the successful operation of the refueling device, contributing to efficiency, safety, and user satisfaction.
Importance of Each Component
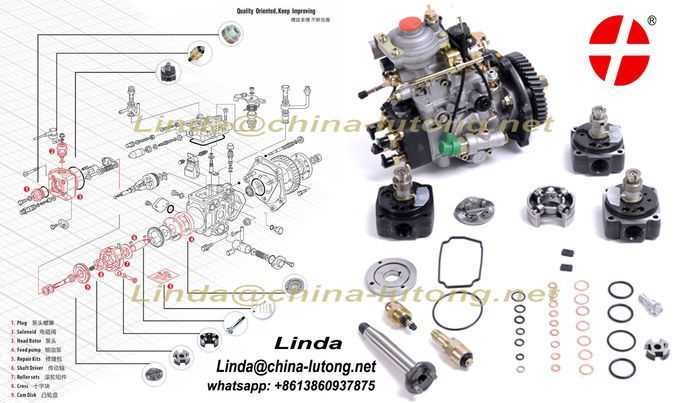

Understanding the significance of every element within a refueling system is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and safety. Each component plays a specific role, contributing to the overall efficiency and reliability of the entire mechanism.
Key Elements and Their Roles
Every section is engineered to work harmoniously, ensuring a seamless operation. The following table outlines the main elements and their respective functions:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Pump | Delivers liquid at the required pressure. |
| Meter | Measures the quantity dispensed accurately. |
| Nozzle | Controls the flow and facilitates easy handling. |
| Hoses | Connect various parts and transport the liquid. |
Ensuring Efficiency
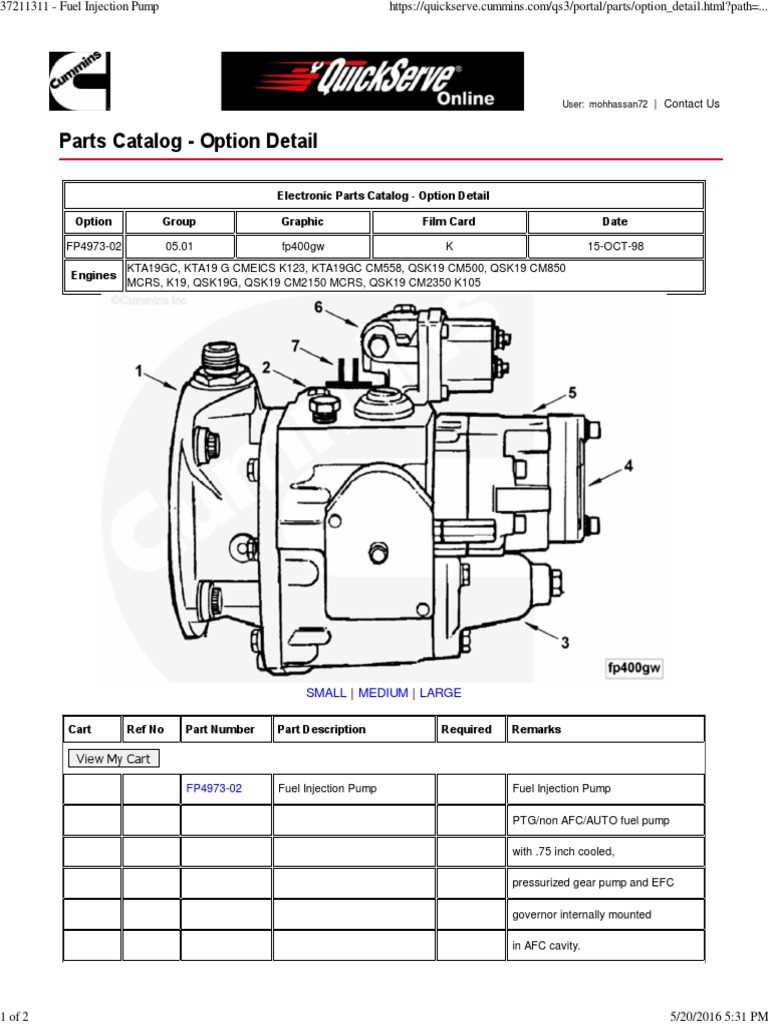
Maintaining and understanding these components enhances the longevity and functionality of the entire system. Each plays an integral role in achieving the ultimate performance of the operation.
Fuel Pump: Key Role Explained
The central component responsible for transferring essential liquids plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient operation. Its function goes beyond mere movement, influencing performance and reliability in various applications. Understanding this element is vital for grasping the overall mechanics involved.
This mechanism is designed to maintain consistent pressure and flow, ensuring that the necessary substances reach their intended destinations. Without it, the entire system could face significant inefficiencies or failures. Let’s delve into its key characteristics and functions.
| Characteristic | Importance |
|---|---|
| Pressure Regulation | Ensures optimal delivery for performance |
| Flow Consistency | Maintains stable operation throughout |
| Durability | Resists wear and prolongs lifespan |
| Efficiency | Minimizes energy consumption during operation |
Dispensing Nozzle: Design and Use
The dispensing nozzle is a crucial component designed for the controlled transfer of liquids. Its innovative construction facilitates the safe and efficient release of various substances, ensuring user convenience and minimizing the risk of spills or accidents. Understanding its design and functionality is essential for optimal performance and maintenance.
Design Features
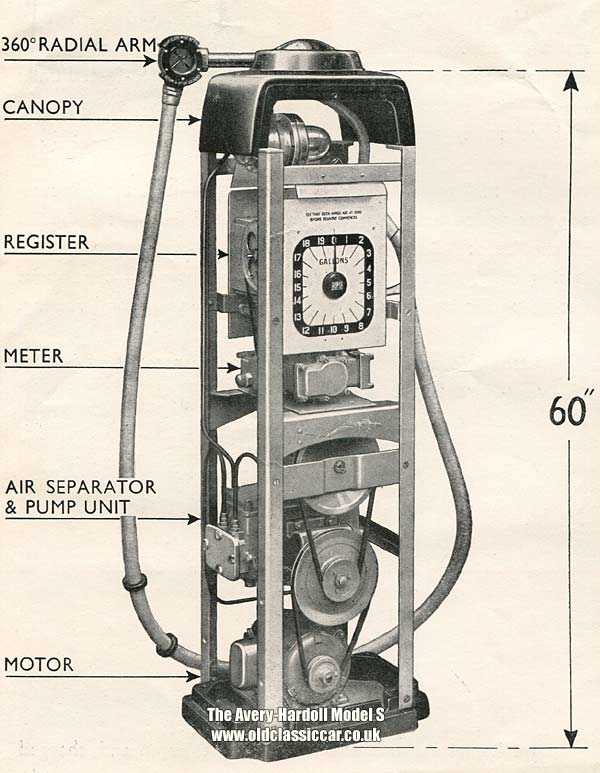
These nozzles are typically engineered with precision to allow for smooth operation. They often include a trigger mechanism that regulates the flow, providing users with complete control. Materials used in their manufacture are selected for durability and resistance to corrosion, enabling them to withstand harsh conditions. Ergonomic designs enhance user comfort, while advanced sealing systems prevent leakage, contributing to safety and efficiency.
Applications and Benefits
The versatility of dispensing nozzles makes them suitable for a variety of environments, from industrial settings to retail applications. Their ease of use allows for quick and efficient transfers, which is particularly advantageous in busy operations. Furthermore, the incorporation of safety features reduces the likelihood of mishaps, making them a reliable choice for professionals handling various liquids.
Meter Mechanism: How It Works
The meter mechanism is a critical component in measuring liquid flow accurately. Its design ensures precise readings and reliability in various applications.
Key elements of the meter mechanism include:
- Sensor: Detects the flow rate of the liquid.
- Gear System: Translates movement into readable measurements.
- Display Unit: Presents the data in an understandable format.
Understanding how these components interact is essential for effective operation:
- The sensor activates when liquid starts to flow.
- The gear system adjusts based on flow speed.
- The display unit updates in real-time, providing accurate information.
This synergy allows for the ultimate accuracy in monitoring liquid distribution, ensuring efficient processes across various industries.
Hoses: Types and Specifications

In the world of fluid transfer, hoses play a crucial role in ensuring efficient and safe operation. Their design and material composition are essential factors that influence performance and longevity. Understanding the various types available, along with their specifications, is vital for selecting the right option for specific applications.
Types of Hoses
- Rubber Hoses: Known for their flexibility and durability, these are commonly used in various environments.
- Polyurethane Hoses: Lightweight and resistant to abrasion, making them suitable for demanding conditions.
- Stainless Steel Hoses: Ideal for high-pressure applications, offering excellent corrosion resistance.
- Silicone Hoses: Highly flexible and heat-resistant, often utilized in high-temperature applications.
Specifications to Consider
- Diameter: The inner diameter affects flow rate and pressure.
- Pressure Rating: Indicates the maximum pressure the hose can withstand safely.
- Temperature Range: Determines the operating temperatures suitable for the material.
- Material Composition: Influences resistance to chemicals, abrasion, and environmental factors.
By understanding the types and specifications of hoses, users can make informed decisions to ensure optimal performance in their specific settings.
Filtration Systems in Dispensers

Effective filtration mechanisms play a crucial role in ensuring the quality and integrity of the liquid being transferred. These systems are designed to remove impurities and contaminants, safeguarding both equipment and the end product.
Importance of Filtration
- Enhances the purity of the liquid.
- Prevents damage to internal components.
- Promotes efficient operation and longevity.
Types of Filtration Systems
- Strainer Filters: Remove larger particles from the liquid.
- Carbon Filters: Eliminate odors and chemical impurities.
- Microfiltration: Captures small particles and microorganisms.
Control Systems: Electronic Functions
The electronic functions within control systems play a pivotal role in managing operations and ensuring optimal performance. These systems utilize a variety of sensors, actuators, and control algorithms to maintain desired parameters and enhance efficiency. By integrating advanced technology, they facilitate real-time monitoring and automation, significantly reducing human error and improving overall functionality.
Key Components of Electronic Control Systems
Essential elements include microcontrollers, which process input signals and execute commands, and sensors that gather data on environmental conditions. Actuators respond to the control signals by making necessary adjustments, thereby maintaining stability and performance standards. This seamless interaction between components creates a robust framework for effective management.
Benefits of Advanced Electronic Functions
Implementing sophisticated electronic functions leads to numerous advantages, such as increased accuracy, enhanced safety, and reduced operational costs. Furthermore, these systems are designed to adapt to varying conditions, ensuring reliability across diverse applications. Ultimately, they represent a significant advancement in the evolution of automation and control technologies.
Safety Features in Fuel Dispensers
Ensuring safety in the transfer of liquids is paramount. Various mechanisms and technologies are integrated to minimize risks and protect users. These measures not only enhance operational reliability but also promote a secure environment for all involved.
Emergency Shut-off Systems are crucial; they allow for immediate cessation of flow in case of an incident, effectively mitigating potential hazards. Similarly, Leak Detection Technologies are implemented to identify and respond to any unwanted spills swiftly, reducing environmental impact.
Another essential aspect is the inclusion of Anti-siphoning Devices, which prevent unauthorized access and potential misuse, while Security Locks safeguard against tampering. Regular maintenance and adherence to safety protocols further ensure these features operate effectively, underscoring the commitment to user protection.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
In the operation of refueling systems, various challenges may arise that can affect efficiency and functionality. Understanding these common obstacles and their solutions is crucial for maintaining optimal performance.
Inconsistent Flow: One prevalent issue is irregular delivery. This may stem from blockages in the supply lines or malfunctioning valves. Regular maintenance and inspection can help identify and resolve these obstructions.
Leakage: Another significant concern is the occurrence of leaks. These can lead to safety hazards and financial losses. Inspecting seals and joints regularly ensures they remain intact and effective.
Electrical Failures: Electrical components may experience malfunctions, causing system interruptions. Checking connections and replacing faulty parts promptly can mitigate this risk.
Calibration Issues: Accurate measurement is essential for proper operation. If discrepancies arise, recalibration of the measuring systems is necessary to ensure precise delivery.
By addressing these common issues proactively, operators can enhance reliability and longevity of their equipment.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Ensuring the durability of your equipment involves regular upkeep and attention to detail. By following certain practices, you can significantly extend its operational life and enhance performance.
Regular Inspections
- Conduct monthly checks for wear and tear.
- Look for signs of corrosion or damage.
- Ensure all connections are secure and leak-free.
Cleaning and Lubrication
- Clean components regularly to prevent buildup.
- Apply appropriate lubricants to moving parts.
- Use non-corrosive cleaning agents for safety.