Understanding the Components of a Heating Radiator

In any efficient thermal system, the intricate interplay of various elements ensures optimal performance and comfort. Each component plays a crucial role in the overall functionality, contributing to effective temperature management within a space. Grasping the arrangement and significance of these elements is essential for both maintenance and enhancement of efficiency.
Recognizing how each element interacts is key to understanding the broader mechanism. From circulation channels to control units, the synergy between these parts allows for the seamless transfer of warmth. This connection not only dictates the system’s effectiveness but also influences energy consumption and user experience.
In this exploration, we will delve into the fundamental aspects of these components, highlighting their design and interrelations. By appreciating the intricacies of the system, individuals can make informed decisions about repairs, upgrades, or modifications to achieve desired results.
Understanding Heating Radiator Components
In the realm of thermal systems, various elements work in unison to facilitate efficient temperature regulation. Each component plays a critical role in ensuring optimal performance and reliability. Gaining insight into these elements can enhance understanding of how these systems function and improve maintenance practices.
Core Elements
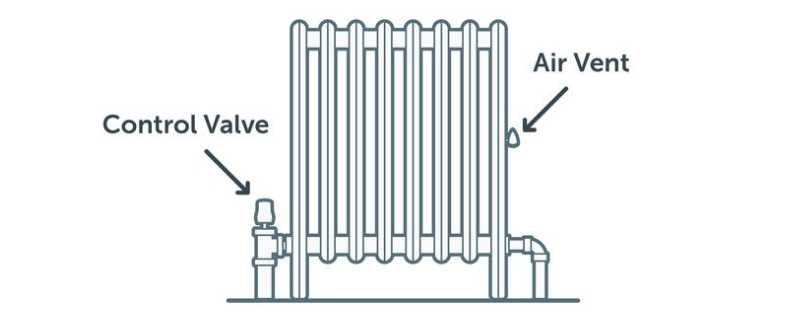
The primary components include the structure designed to contain the fluid, the mechanisms responsible for heat transfer, and the attachments that support flow management. Together, these elements create a pathway for warmth to circulate, ensuring even distribution throughout a space.
Functionality and Maintenance
Regular upkeep of these components is essential for longevity. Cleaning and inspecting each section can prevent inefficiencies and prolong the lifespan of the entire assembly. Familiarity with each part’s role not only aids in troubleshooting issues but also empowers users to optimize their thermal experience.
Key Parts of a Heating Radiator
Understanding the essential components of a thermal unit is crucial for ensuring efficient performance and effective warmth distribution. Each element plays a significant role in the overall functionality, contributing to the system’s ability to maintain a comfortable environment. Below, we explore the primary constituents that make up this vital equipment.
Core Components
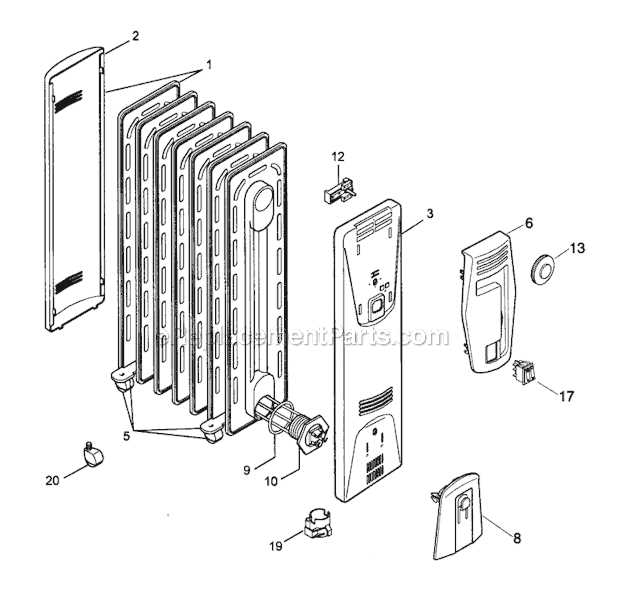
The main structure is typically constructed from metal, which facilitates rapid heat transfer. This core is responsible for absorbing heat from the fluid circulating within and radiating it into the surrounding space. Its design can vary, affecting the efficiency and style of heat delivery.
Supporting Elements
In addition to the core, there are several auxiliary mechanisms that enhance performance. Valves control the flow of hot fluid, allowing for adjustments based on desired temperature. Mounting brackets secure the unit in place, ensuring stability and proper alignment. Finally, thermostatic devices monitor temperature, providing feedback to optimize energy usage.
How Radiators Distribute Heat
The process of warmth dissemination in a living space involves several interconnected elements working in harmony. This system is designed to ensure an even distribution of warmth, creating a comfortable environment for inhabitants. Understanding this process can enhance the effectiveness of the system and improve energy efficiency.
At the core of this mechanism are various components that play specific roles:
- Fluid Circulation: A heated liquid is circulated through a network, transferring energy as it moves.
- Surface Area: The exterior surfaces of the units maximize contact with the air, facilitating heat exchange.
- Convection and Radiation: Warm air rises while cooler air descends, creating a natural flow that distributes warmth throughout the room.
To optimize the effectiveness of this system, consider the following strategies:
- Ensure there are no obstructions around the units to allow for proper airflow.
- Regularly check for air pockets within the circulating fluid, as these can hinder performance.
- Maintain consistent temperatures to enhance comfort levels and reduce energy consumption.
By understanding how warmth is managed and distributed, individuals can make informed decisions to improve comfort and efficiency in their spaces.
Types of Heating Radiators Explained

Understanding the various models available can help homeowners choose the best option for their needs. Each type comes with unique features, advantages, and applications, making it essential to evaluate them based on efficiency, aesthetic appeal, and installation requirements.
Common Variants
- Convectors: Known for their efficiency, these devices utilize air movement to distribute warmth quickly throughout a space.
- Panel Units: Featuring a sleek design, they blend seamlessly into modern interiors while providing consistent warmth.
- Baseboard Models: Ideal for tight spaces, these units run along the base of walls and are often less intrusive in room design.
- Cast Iron: Renowned for their durability and heat retention, these traditional options add a vintage charm to any room.
Specialty Options
- Towel Warmers: Perfect for bathrooms, these models offer both functionality and luxury, keeping towels warm and dry.
- Electric Units: These provide flexibility, as they can be installed in areas without central heating, perfect for supplemental warmth.
- Hydronic Systems: Utilizing hot water, these systems deliver efficient and comfortable heating throughout larger spaces.
Common Issues in Radiator Systems
In any heating network, various complications can arise, affecting efficiency and comfort. Understanding these problems is essential for maintaining optimal performance and ensuring longevity. This section explores typical challenges that users may encounter and their potential solutions.
Leaks and Drips
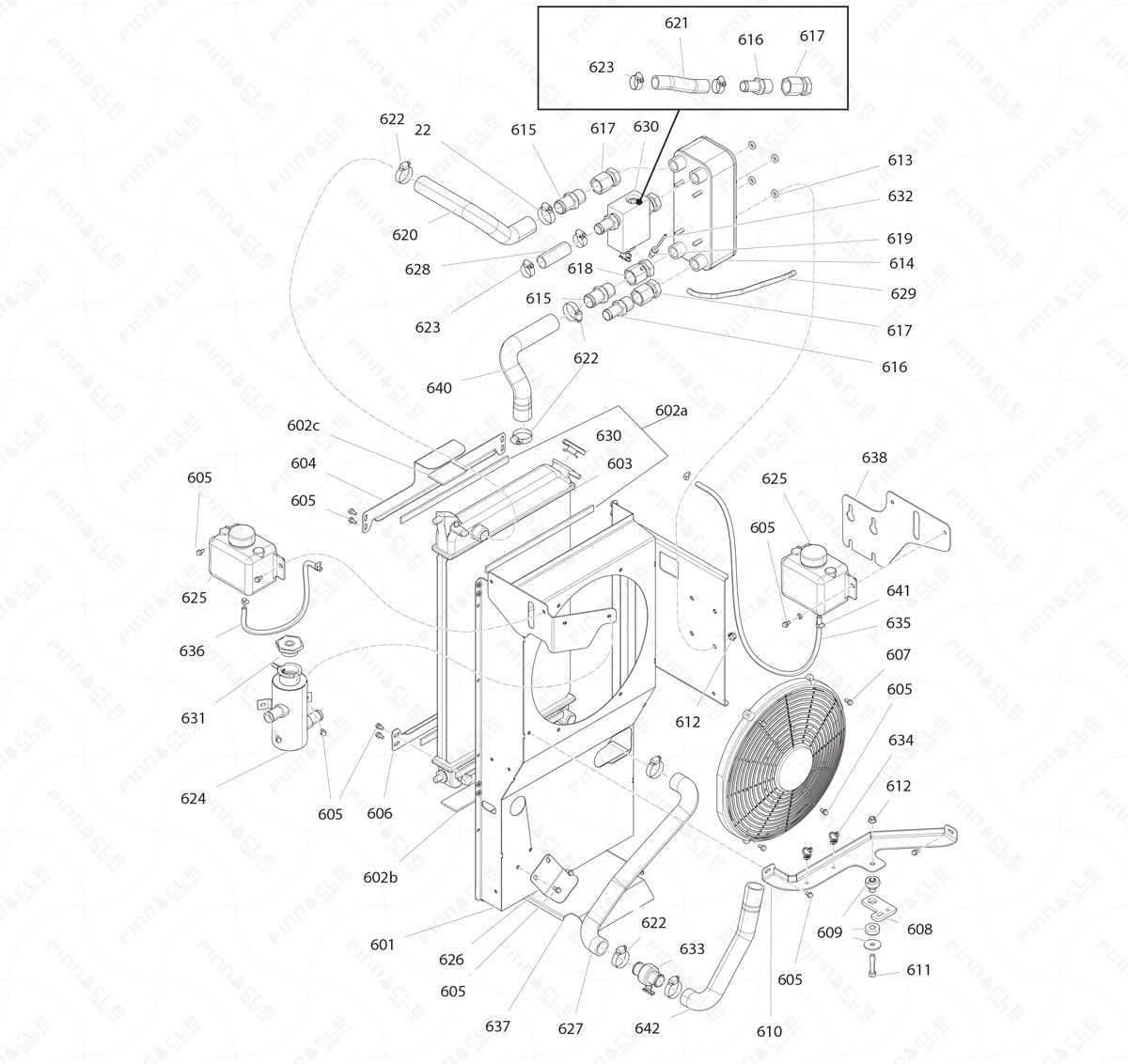
One of the most prevalent issues involves the occurrence of leaks. These can result from corrosion, worn seals, or loose fittings, leading to a loss of fluid and reduced efficacy. Regular inspection can help identify leaks early, allowing for timely repairs and preventing more significant damage.
Air Traps
Air pockets can hinder the proper circulation of fluid within the system, causing cold spots and inefficient heating. Purging the system to remove trapped air can significantly improve performance. This maintenance step is often overlooked but is crucial for ensuring uniform temperature distribution.
| Issue | Symptoms | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Leaks | Visible drips, reduced fluid level | Tighten fittings, replace seals |
| Air Traps | Cold spots, noise in the system | Bleed the system |
| Blockages | Poor heating performance | Flush the system |
Importance of Radiator Maintenance
Regular upkeep of essential home components ensures optimal performance and longevity. Neglecting these vital elements can lead to inefficiencies, increased energy costs, and even costly repairs. By understanding the significance of proper care, homeowners can maintain a comfortable living environment while preventing future issues.
Benefits of Routine Upkeep
Routine maintenance offers several advantages that enhance both functionality and safety. By addressing minor concerns before they escalate, homeowners can enjoy a more reliable system. Additionally, regular checks contribute to energy efficiency, reducing overall utility expenses.
Common Maintenance Practices
Implementing simple care strategies can make a significant difference. These practices not only extend the life of components but also improve performance. Below is a summary of common maintenance tasks:
| Task | Frequency | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Monthly | Identify leaks and damage |
| Bleeding | Seasonally | Remove trapped air, enhance efficiency |
| Cleaning | Annually | Prevent dust buildup, improve airflow |
| Professional Checkup | Every 2 years | Thorough assessment, early issue detection |
Energy Efficiency in Heating Radiators
Optimizing thermal performance is essential for reducing energy consumption and costs. Various elements play a crucial role in enhancing the effectiveness of these systems, ensuring that they deliver warmth efficiently while minimizing waste. By focusing on innovative designs and materials, significant advancements can be made in energy conservation.
Proper Insulation is fundamental. Ensuring that the surrounding environment retains heat will greatly enhance overall efficiency. Well-insulated spaces reduce the demand for additional energy input, resulting in lower utility bills and a reduced carbon footprint.
Smart Technology has transformed the way we manage temperature control. Programmable thermostats and intelligent systems allow for precise adjustments based on usage patterns, thereby preventing unnecessary energy expenditure. By integrating these technologies, users can significantly improve their thermal management while enjoying enhanced comfort.
Incorporating high-performance materials also contributes to better energy retention. Utilizing advanced alloys and coatings can maximize heat transfer capabilities, ensuring that warmth is distributed evenly throughout the environment. This not only enhances comfort but also supports energy conservation efforts.
Lastly, regular maintenance is vital for sustaining efficiency. Periodic checks and cleaning ensure that systems operate optimally, preventing blockages and other issues that could hinder performance. By committing to maintenance, users can prolong the lifespan of their equipment while maintaining high levels of efficiency.
Choosing the Right Radiator Size
Selecting the appropriate dimensions for a heating unit is crucial for ensuring optimal comfort in any space. The right size not only enhances efficiency but also contributes to energy savings and consistent temperature control.
To determine the best fit for your area, consider the following factors:
- Room Size: Measure the square footage of the space. Larger rooms typically require more substantial units.
- Insulation: Assess the level of insulation in your home. Well-insulated spaces retain heat better and may need smaller units.
- Window Size and Type: Larger or single-pane windows can lead to heat loss, necessitating more powerful units.
- Ceiling Height: Higher ceilings may require additional capacity to maintain even warmth.
- Local Climate: In colder regions, a more robust unit is essential to cope with lower temperatures.
By evaluating these elements, you can achieve a perfect balance between size and efficiency, leading to a comfortable environment throughout the colder months.
Installation Process for Radiators
Setting up a heating unit in your space is crucial for ensuring a cozy environment. This guide provides a step-by-step approach to effectively installing such systems, ensuring they function optimally and safely. Proper installation is key to enhancing efficiency and longevity.
Preparation Steps
Before starting the installation, gather all necessary tools and materials. Ensure you have a clear understanding of the layout and positioning of the unit to maximize heat distribution. Proper preparation can save time and reduce complications during the installation process.
| Tool/Material | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Wrench Set | To tighten connections securely |
| Pipe Cutter | For adjusting pipe lengths |
| Level | To ensure unit is mounted evenly |
| Sealant Tape | To prevent leaks in connections |
Installation Procedure

Begin by selecting the appropriate location on the wall, ideally beneath a window. Mark the spots for brackets, ensuring they are level. Next, secure the brackets to the wall. Once the brackets are in place, mount the unit and connect the necessary piping. Finally, check all connections for tightness and any potential leaks before testing the system.
Innovations in Radiator Design
Recent advancements in thermal systems have led to the development of more efficient and aesthetically pleasing models. These innovations focus on improving energy transfer, enhancing user comfort, and integrating smart technologies that adapt to changing environments. The result is a new generation of heating solutions that blend functionality with modern design elements.
One significant trend is the incorporation of eco-friendly materials and manufacturing processes. By using sustainable resources, manufacturers are reducing their carbon footprint while maintaining high performance. Additionally, new surface treatments enhance thermal conductivity, allowing for quicker heat distribution and improved overall efficiency.
Smart technology has also revolutionized this field, with devices that can be controlled remotely or programmed to adjust settings based on occupancy or weather conditions. This not only maximizes comfort but also minimizes energy consumption, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
Moreover, innovative designs now prioritize space efficiency and aesthetic appeal, offering sleek, compact solutions that fit seamlessly into modern interiors. With customizable options and finishes, these contemporary systems serve as both functional appliances and stylish decor elements, elevating the overall ambiance of living spaces.
Radiator Safety and Regulations

Ensuring the well-being of individuals and the integrity of structures is paramount when dealing with any form of heat distribution system. Adhering to established guidelines and standards not only enhances efficiency but also minimizes risks associated with improper installations and maintenance. This section explores essential safety protocols and regulatory frameworks that govern the operation and management of thermal systems.
| Aspect | Description | Regulatory Body |
|---|---|---|
| Installation Standards | Requirements for proper setup to prevent hazards. | International Organization for Standardization (ISO) |
| Maintenance Guidelines | Protocols to ensure safe operation and longevity. | Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) |
| Inspections | Regular checks to identify potential issues before they escalate. | Local Building Authorities |
| Emergency Procedures | Steps to follow in case of a malfunction or hazard. | National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) |
Compliance with these standards is crucial for the safety of users and the efficiency of the system. Regular training and awareness initiatives can significantly contribute to a safer environment in both residential and commercial settings.