International 1086 Parts Diagram Overview
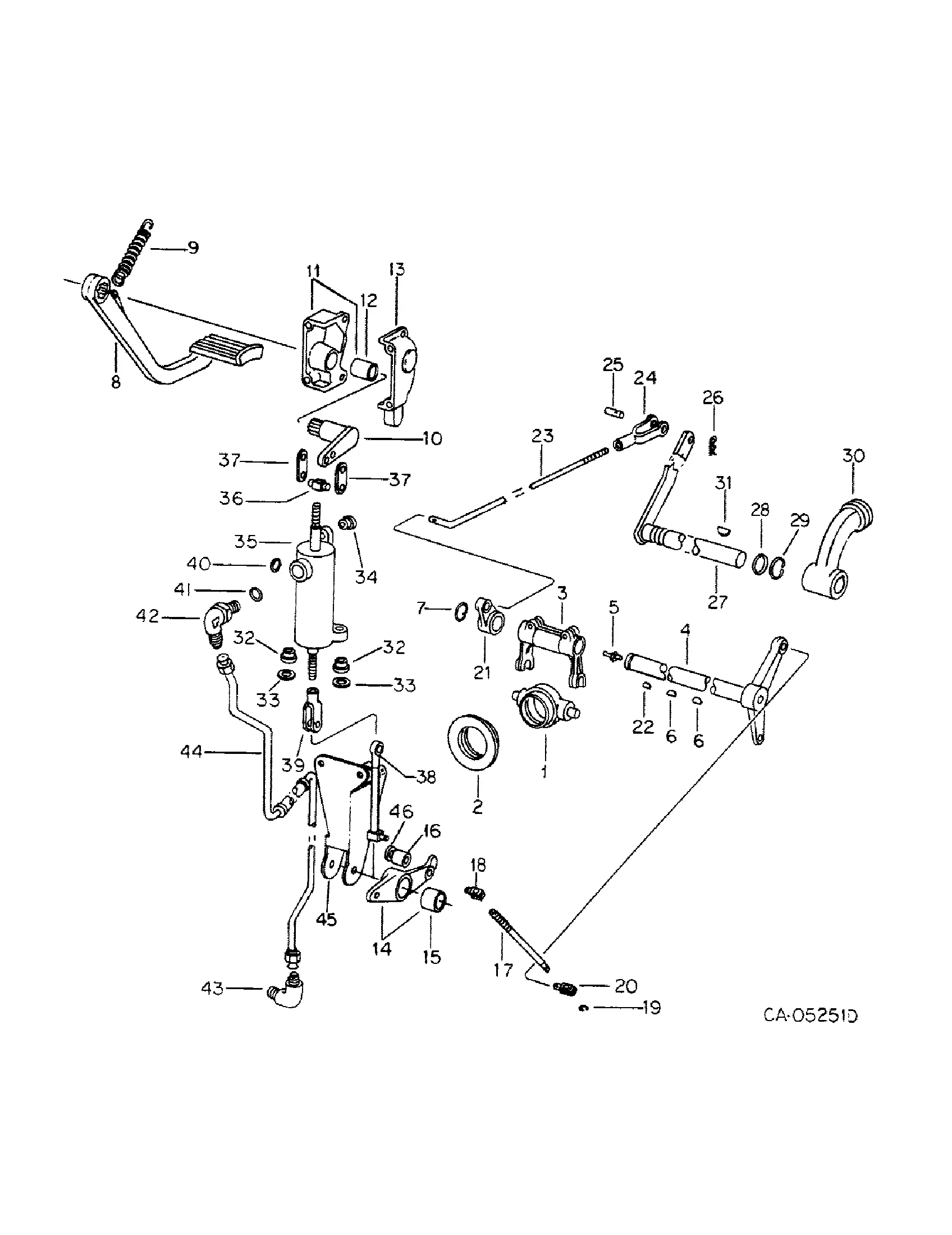
In the realm of heavy machinery used in agriculture, a comprehensive understanding of the various components is essential for effective maintenance and operation. The intricacies of these machines often require detailed illustrations to aid in identifying and replacing specific elements. Familiarity with these components not only enhances performance but also extends the lifespan of the equipment.
Illustrative guides serve as invaluable resources, providing clear representations of each segment within the machinery. These guides facilitate troubleshooting and repair processes, enabling operators and technicians to locate issues quickly and efficiently. A thorough grasp of the configurations within the system allows for informed decisions when it comes to repairs and replacements.
Moreover, having access to well-organized representations empowers users to comprehend the interconnections between various components. This knowledge is crucial for optimizing the functionality of the equipment and ensuring that all parts work harmoniously together. By delving into the details of these illustrations, one can significantly enhance operational efficacy and reduce downtime.
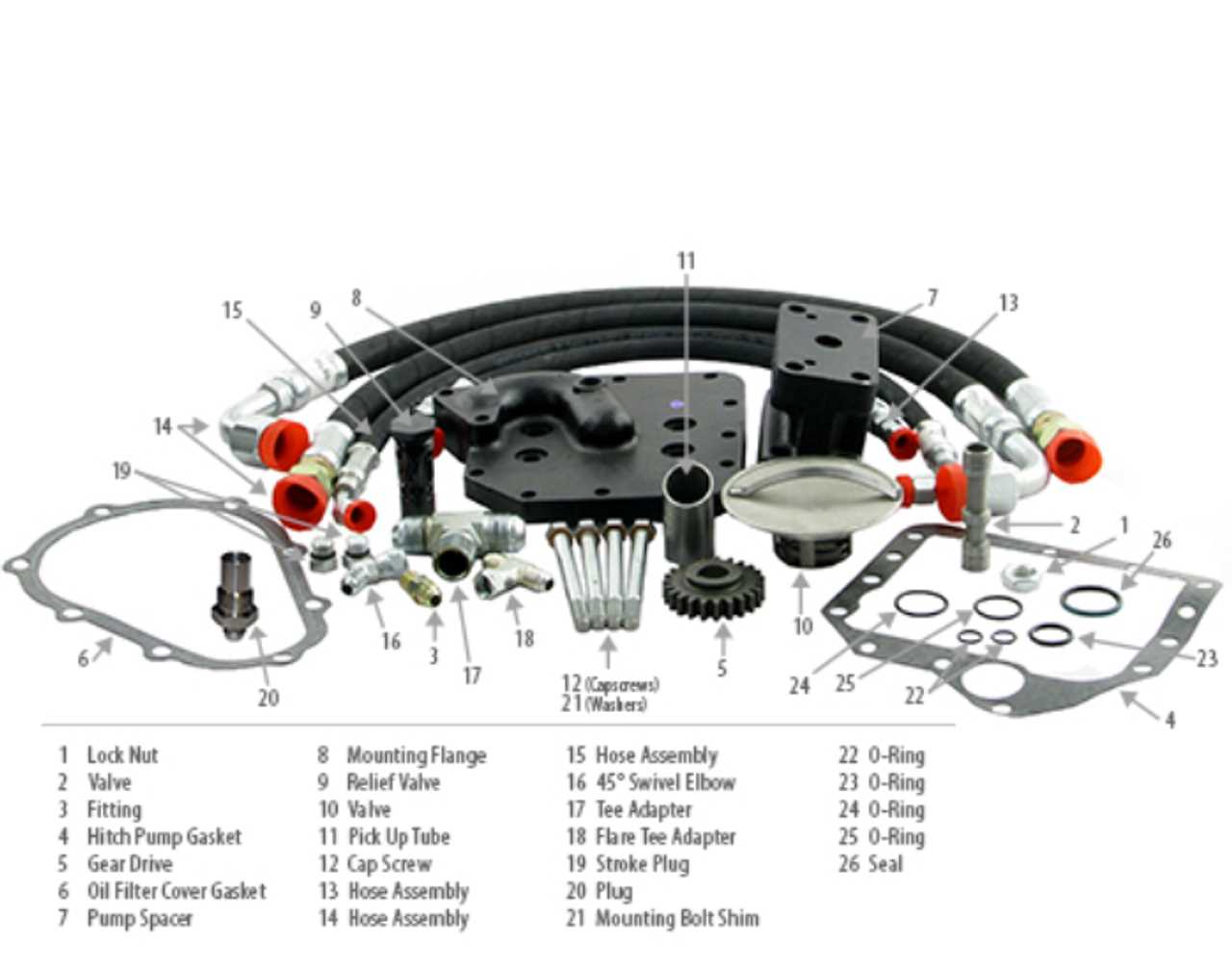
The arrangement of fluid power systems plays a crucial role in the functionality and efficiency of machinery. A well-structured hydraulic configuration ensures optimal performance and reliability, enabling the effective transfer of power through fluids. Understanding the layout of such systems can aid in maintenance and troubleshooting, ultimately extending the lifespan of the equipment.
This section provides insight into the various components typically found within a hydraulic setup, illustrating their interconnections and functions. Familiarity with these elements will facilitate a better grasp of how they work together to achieve desired outcomes.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Pump | Generates hydraulic pressure by moving fluid |
| Reservoir | Stores hydraulic fluid and allows for heat dissipation |
| Valves | Control the flow and direction of fluid within the system |
| Actuators | Convert hydraulic energy into mechanical movement |
| Filters | Remove contaminants from hydraulic fluid to ensure system cleanliness |
Engine Specifications and Components
This section delves into the crucial aspects of engine design, emphasizing the various elements that contribute to its performance and efficiency. Understanding the specifications and components is essential for maintaining optimal functionality and ensuring longevity.
Key Specifications

Several critical specifications define the capabilities and features of the engine. These include:
- Displacement: The total volume of all cylinders, typically measured in liters or cubic inches.
- Horsepower: A measure of the engine’s power output, indicating its ability to perform work.
- Torque: The rotational force produced by the engine, which influences acceleration and pulling power.
- Compression Ratio: The ratio of the cylinder’s volume at its largest to its smallest, impacting efficiency and performance.
Essential Components
The engine comprises various components, each playing a vital role in its operation. Key components include:
- Cylinders: The chambers where fuel and air mix for combustion.
- Pistons: Movable elements within the cylinders that compress the air-fuel mixture and convert energy into mechanical power.
- Crankshaft: The component that transforms the linear motion of pistons into rotational motion.
- Fuel System: Comprising the fuel tank, pump, and injectors, this system ensures a proper supply of fuel for combustion.
- Cooling System: Essential for maintaining optimal operating temperatures, preventing overheating, and ensuring efficient performance.
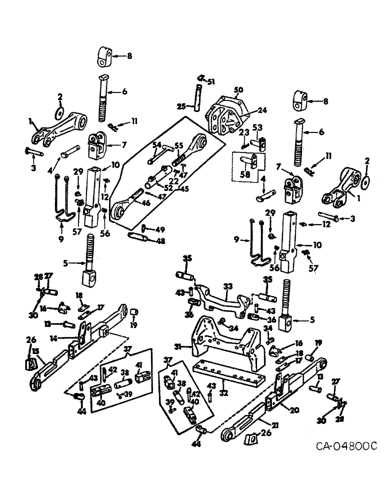
Transmission and Gear Configuration
This section focuses on the intricate systems that facilitate the transfer of power within heavy machinery. Understanding the arrangements and functions of these components is crucial for optimal performance and efficiency. Proper configuration ensures smooth operation and longevity of the equipment.
The transmission plays a vital role in adjusting the engine’s output to match the demands of the task at hand. Gear ratios are carefully designed to provide the necessary torque and speed for various operational scenarios. Below is a table illustrating the key components and their functions in the transmission and gear setup.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Transmission Unit | Regulates power flow from the engine to the wheels. |
| Gear Selector | Allows the operator to change gear ratios based on speed requirements. |
| Clutch Assembly | Enables smooth engagement and disengagement of gears. |
| Drive Shaft | Transmits power from the transmission to the drive wheels. |
| Gear Set | Determines the ratio of speed and torque delivered to the wheels. |
Electrical System and Wiring Guide
This section provides an overview of the electrical framework and wiring methodologies essential for optimal functionality in agricultural machinery. Understanding the intricacies of these systems is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
The electrical configuration comprises various components, each serving a specific purpose. Here are the primary elements to consider:
- Power Supply Unit: Delivers electricity to the system.
- Wiring Harness: Connects different electrical parts and ensures proper communication.
- Fuses and Relays: Protect circuits from overload and control power flow.
- Control Switches: Manage the operation of various systems and features.
- Lighting Systems: Provide visibility and safety during operation.
Proper wiring techniques are vital for preventing faults and enhancing performance. Follow these guidelines for effective installation and maintenance:
- Use high-quality, insulated wires to prevent short circuits.
- Secure connections to avoid loose contacts, which can lead to malfunctions.
- Label wires and connectors for easier identification during repairs.
- Regularly inspect the electrical system for signs of wear and tear.
By adhering to these practices, users can ensure the longevity and reliability of the electrical system, minimizing downtime and enhancing operational efficiency.
Fuel System and Tank Details
The fuel system is a vital component that ensures the efficient operation of heavy machinery. It is designed to store, filter, and deliver the necessary fuel to the engine for optimal performance. Understanding the specifics of this system, including its components and configurations, is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Fuel Tank | A large reservoir that stores the fuel required for operation. |
| Fuel Pump | Transports fuel from the tank to the engine. |
| Fuel Filter | Removes impurities and contaminants from the fuel before it reaches the engine. |
| Fuel Lines | Pipes that connect the tank, pump, filter, and engine, ensuring proper fuel flow. |
| Injector | Sprays the fuel into the engine’s combustion chamber for ignition. |
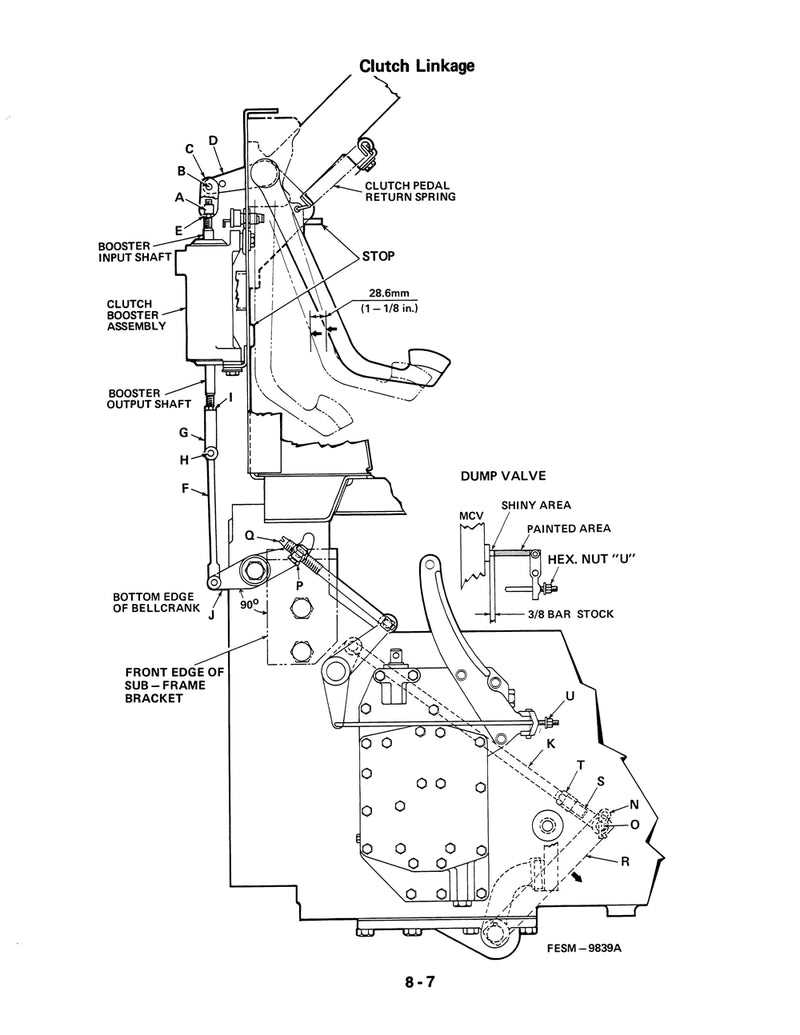
Brake and Steering Mechanisms Explained
The effectiveness and safety of a vehicle largely depend on its braking and steering systems. These essential components work in tandem to ensure that operators can maintain control and stop efficiently when necessary. Understanding how these systems function is crucial for both operators and technicians, as it aids in troubleshooting and maintenance.
Understanding Braking Systems
The braking system is designed to slow down or stop the vehicle by converting kinetic energy into thermal energy through friction. Various types of brakes are used, including disc and drum systems, each with unique characteristics and applications. Regular inspection and maintenance are vital for optimal performance and safety.
Overview of Steering Mechanisms
Steering mechanisms enable precise control of vehicle direction. These systems can vary significantly, with options such as manual and power steering. The choice of system affects handling, ease of use, and overall driving experience. Proper care and understanding of these systems enhance vehicle responsiveness and safety.
| Component | Function | Maintenance Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Brakes | Slow down or stop the vehicle | Check pads, fluid levels, and inspect for wear |
| Steering Wheel | Controls the direction of the vehicle | Ensure proper alignment and check for play |
| Brake Lines | Transmits hydraulic fluid to the brakes | Inspect for leaks and wear |
| Power Steering Pump | Provides hydraulic pressure for steering | Check fluid levels and listen for unusual noises |
Common Maintenance Practices for Longevity

Ensuring the durability and optimal performance of heavy machinery requires a strategic approach to upkeep. Regular maintenance not only extends the lifespan of equipment but also enhances its efficiency. Implementing systematic procedures can prevent costly breakdowns and ensure that machinery operates smoothly under various conditions.
Routine Inspections
Conducting frequent examinations of machinery is vital for identifying potential issues before they escalate. These inspections should encompass checking fluid levels, examining belts and hoses, and assessing the overall condition of the components. By maintaining a checklist, operators can ensure that all critical areas are reviewed consistently.
Lubrication and Cleaning
Proper lubrication reduces friction between moving parts, preventing wear and tear. Regularly applying appropriate lubricants to designated areas is essential. Additionally, keeping the equipment clean helps prevent dirt and debris buildup, which can lead to mechanical failures.
| Maintenance Activity | Frequency | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Daily | Check for leaks, cracks, and loose components. |
| Fluid Level Check | Weekly | Ensure oil and coolant levels are within recommended limits. |
| Filter Replacement | Monthly | Replace air and oil filters to maintain performance. |
| Lubrication | Biweekly | Apply lubricants to moving parts as per manufacturer guidelines. |
| Deep Cleaning | Quarterly | Thoroughly clean all surfaces to remove dirt and grime. |
Finding Replacement Parts and Resources
Locating suitable components for machinery can often be a daunting task. However, with the right approach and resources, individuals can effectively navigate the process of acquiring the necessary items. This section aims to provide guidance on how to identify and obtain reliable replacements for various equipment.
Utilizing Online Resources
One of the most efficient ways to search for replacements is through online platforms. Many websites specialize in offering a wide range of components, allowing users to easily filter options based on specific criteria. Utilizing these tools can save time and ensure that you find quality replacements.
Connecting with Local Suppliers
In addition to online searches, reaching out to local vendors can be beneficial. These suppliers often have extensive knowledge of the equipment and may offer personalized assistance. Establishing a relationship with a trusted local provider can lead to valuable insights and better access to the components needed.