Labeled Diagram of Dandelion Parts
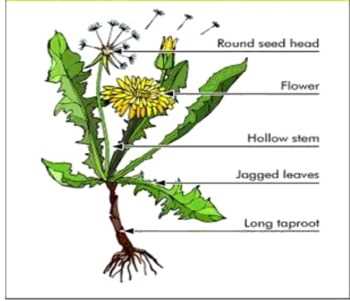
Exploring the intricate design of familiar flora reveals the beauty and complexity of nature. Each element plays a crucial role in the overall function, contributing to the plant’s life cycle and survival. Recognizing these components enhances our appreciation for the diversity of plant life.
By examining the various segments of this particular species, we can uncover how they interact and support each other. The significance of each feature becomes evident, showcasing a remarkable synergy that enables the plant to thrive in its environment. This examination offers insights not only into the anatomy but also into the ecological importance of these botanical specimens.
Through a detailed study of its features, we can foster a deeper connection with the natural world. Understanding these attributes allows enthusiasts and scholars alike to engage more meaningfully with the ecosystems that surround us, highlighting the essential role these organisms play in our environment.
Understanding the Dandelion Structure

Exploring the intricate design of this common flowering plant reveals a fascinating interplay of elements that contribute to its resilience and adaptability. Each component plays a vital role in its lifecycle and ecological significance.
Key Components

- Roots: Anchoring the organism to the soil, these structures absorb essential nutrients and water.
- Stem: The stalk supports the flower head and transports nutrients throughout the plant.
- Leaves: Broad and often jagged, these facilitate photosynthesis, capturing sunlight to fuel growth.
- Flower Head: A cluster of tiny florets that attract pollinators and aid in reproduction.
Ecological Roles
- Providing food for various insects, contributing to biodiversity.
- Enhancing soil quality through root systems that prevent erosion.
- Offering medicinal properties, used in traditional remedies.
Understanding the structure of this plant not only enhances appreciation for its beauty but also highlights its importance in various ecosystems.
Parts of a Dandelion Explained
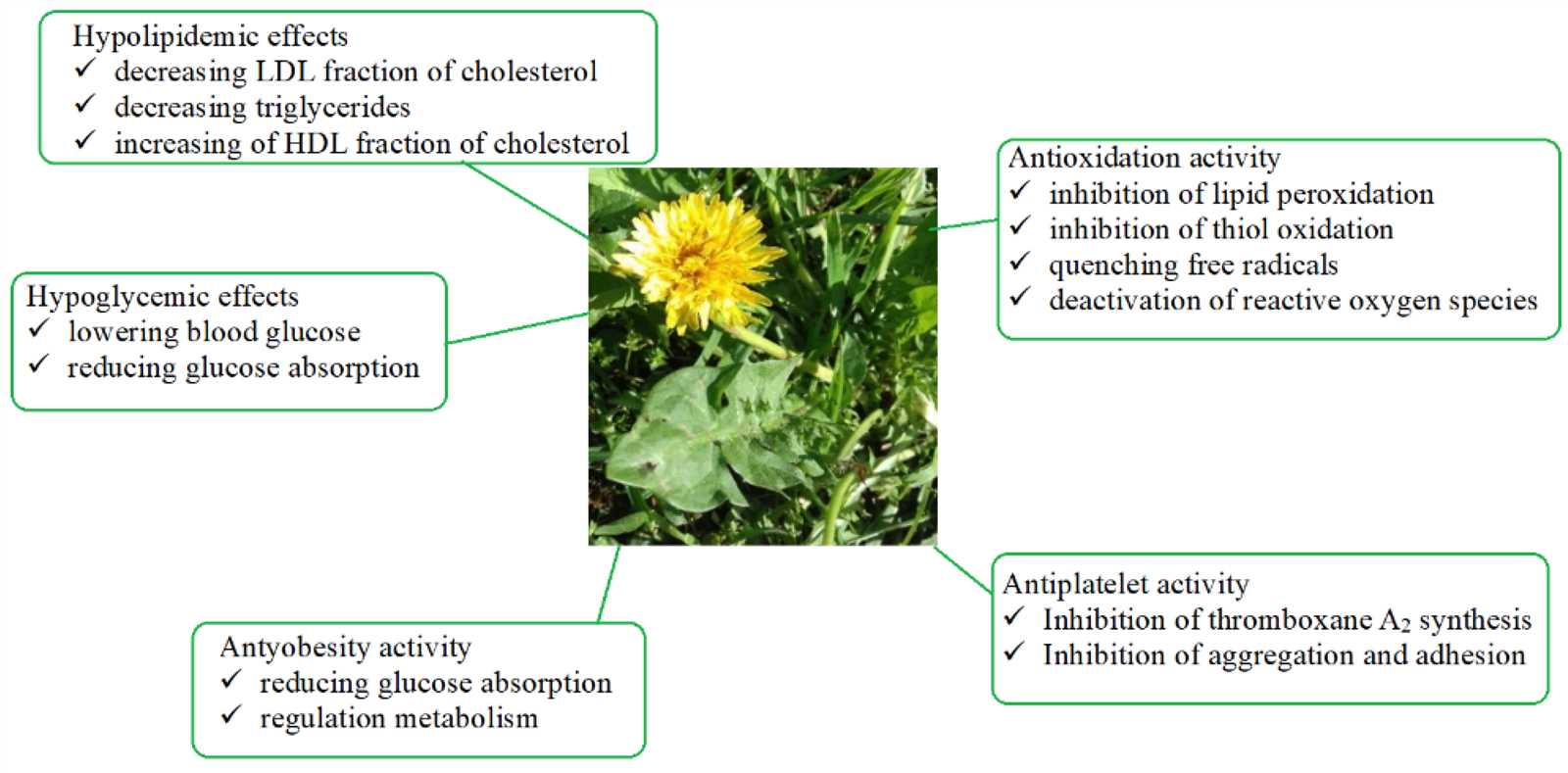
This section provides an overview of the various components found in this common flowering plant. Each element plays a crucial role in its life cycle and ecological interactions. Understanding these features can enhance appreciation for its biology and environmental significance.
- Root: The underground structure anchors the plant, absorbing nutrients and water essential for growth.
- Stem: A sturdy stalk that supports the flower head, allowing it to reach toward sunlight.
- Leaves: Arranged in a rosette at the base, these green structures perform photosynthesis, converting sunlight into energy.
- Flower Head: The bright yellow cluster consists of numerous tiny florets, attracting pollinators and producing seeds.
- Seeds: Each seed is equipped with a fluffy pappus that aids in wind dispersal, promoting propagation.
By examining these distinct elements, one gains insights into how they collectively contribute to the survival and reproduction of this resilient species.
Role of Leaves in Photosynthesis

Leaves are essential components of plants, serving as the primary sites for the conversion of light energy into chemical energy. Through intricate structures and processes, they capture sunlight and facilitate the transformation of carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. This remarkable ability not only sustains the plant itself but also plays a critical role in supporting life on Earth.
The surface of leaves is equipped with specialized cells that contain chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for absorbing light. This absorption triggers a series of biochemical reactions, enabling the plant to harness solar energy. Additionally, the leaf’s structure optimizes gas exchange, allowing carbon dioxide to enter and oxygen to exit efficiently, thus maintaining the delicate balance of atmospheric gases.
Furthermore, leaves are designed to maximize light capture through their broad, flat surfaces, which increase the area available for photosynthesis. The arrangement of leaves on a stem, known as phyllotaxis, also ensures that each leaf receives adequate light without overshadowing others. Through these adaptations, leaves play a vital role in the energy cycle of ecosystems, supporting various forms of life.
Flower Anatomy and Pollination

Understanding the structure of flowering plants is essential to grasp the intricate processes of reproduction in nature. Each bloom is a complex arrangement of various components that play specific roles in attracting pollinators and facilitating reproduction. By examining these components, we can appreciate how plants ensure their survival and genetic diversity through reproduction.
Key Components of a Flower
A typical blossom consists of several key structures, each with its distinct function. The colorful petals serve to attract insects and other animals, while the sepals provide protection for the developing bud. Within the bloom, the male reproductive organs, known as stamens, produce pollen, while the female reproductive part, called the pistil, contains the ovary where seeds develop. This intricate design maximizes the chances of successful fertilization.
The Role of Pollination
Pollination is a vital process that occurs when pollen is transferred from the male to the female reproductive structures. Various agents, such as bees, butterflies, and wind, assist in this transfer, promoting genetic exchange and enabling the formation of seeds. Successful pollination leads to the development of fruits and seeds, ensuring the continuation of plant species. Understanding these processes highlights the critical interdependence between plants and their pollinators in ecosystems.
Reproductive Functions of Dandelion Seeds

The fascinating life cycle of these plants showcases their remarkable ability to reproduce and spread across diverse environments. Their seeds play a crucial role in ensuring the survival and proliferation of the species, utilizing innovative mechanisms to enhance their dispersal and establishment in new locations.
Seed Structure and Adaptations
The seeds are equipped with a lightweight structure that facilitates wind dispersal. This adaptation allows them to travel great distances, enabling the species to colonize various habitats effectively. The feathery appendages, often compared to parachutes, aid in catching the wind and extending the reach of each seed.
Reproductive Strategies
These organisms employ both sexual and asexual reproduction methods. Sexual reproduction occurs when pollen from one flower fertilizes another, leading to genetic diversity. Conversely, asexual reproduction allows for rapid population growth, as a single plant can produce numerous seeds without the need for cross-pollination.
The role of environmental conditions also plays a vital part in seed development and viability. Factors such as temperature, moisture, and soil quality influence the germination rates and overall success of seedlings. This adaptability to varying conditions enhances their chances of thriving in new environments.
In conclusion, the seeds serve as essential tools for propagation and ecological resilience. Their unique features and reproductive strategies ensure the continuation of this resilient species in ever-changing landscapes.
Life Cycle Stages of Dandelions
The journey of this resilient plant unfolds through several distinct phases, each contributing to its remarkable adaptability and survival. Understanding these stages provides insight into the life process that ensures its continuity in diverse environments.
-
Germination:
The initial phase begins with the sprouting of seeds, often triggered by favorable soil conditions and moisture. This marks the start of a new life cycle.
-
Seedling:
Once the seeds germinate, small seedlings emerge, characterized by tender leaves. During this stage, the young plant focuses on establishing its root system.
-
Vegetative Growth:
In this stage, the plant grows vigorously, producing rosettes of leaves. This phase is crucial for energy absorption through photosynthesis.
-
Flowering:
The emergence of vibrant yellow blooms signals the transition to reproductive maturity. These flowers attract pollinators, facilitating the next stage of reproduction.
-
Seed Production:
Post-pollination, the flowers develop into seed heads, releasing numerous seeds that can disperse over great distances, ensuring the plant’s propagation.
-
Dormancy:
As environmental conditions change, the plant may enter a dormant state, conserving energy until the next growing season arrives.
Each phase plays a vital role in maintaining the plant’s lifecycle, showcasing its remarkable ability to thrive in various conditions.
Importance of Taproot in Growth
The foundational structure of many plants plays a crucial role in their overall development and stability. This primary root system not only anchors the plant securely in the soil but also facilitates essential processes that promote healthy growth. Understanding the significance of this root type reveals its influence on the plant’s ability to thrive in various environments.
Nutrient Absorption
Effective nutrient uptake is one of the key benefits offered by a robust root system. The primary root extends deep into the ground, reaching layers of soil that may contain vital minerals and moisture. This allows the plant to access nutrients that are often unavailable to shallower root systems, thereby enhancing its growth potential.
Resilience to Stress
A well-developed root structure contributes to the plant’s resilience against environmental stresses. By securing itself firmly in the soil, it can better withstand adverse conditions such as drought or heavy winds. This stability not only supports the plant during challenging times but also encourages a more vigorous and sustained growth pattern.
Identifying Dandelion Varieties
Understanding the various types of this resilient plant can enhance your appreciation for their unique characteristics. Each variety showcases distinct features, making identification an intriguing endeavor. By observing leaf shape, flower structure, and growth habits, one can learn to differentiate between them effectively.
Leaf Characteristics: The foliage is a crucial element in identification. Some varieties display deeply lobed leaves, while others feature smooth edges. The color and texture can also vary significantly, offering additional clues to their identity.
Flower Structure: The blooms, often bright yellow, can differ in size and arrangement. Observing the number of petals and the arrangement of flowers on the stem can provide insights into which variety you are encountering.
Growth Habits: Consider how these plants grow in their environment. Some may thrive in open fields, while others prefer shaded areas. Noting the height and overall form of the plant can also aid in distinguishing between types.
By focusing on these attributes, anyone can become adept at recognizing the various forms of this common yet fascinating botanical wonder.
Common Misconceptions About Dandelions
Many people hold incorrect beliefs about this ubiquitous yellow flower that often appears in gardens and lawns. Misunderstandings can lead to negative perceptions, overshadowing its true value and potential benefits. Here, we will explore some prevalent myths surrounding this plant.
- They are just weeds: A common notion is that these flowers serve no purpose. In reality, they offer numerous ecological benefits, including attracting pollinators and providing food for various insects.
- All parts are inedible: Many assume that this plant is entirely unsuitable for consumption. However, various sections–like the leaves, roots, and blossoms–are not only edible but also nutritious and can be used in salads, teas, and more.
- They ruin lawns: The belief that these flowers destroy beautiful green spaces is widespread. In fact, their presence can indicate healthy soil and biodiversity, contributing positively to the ecosystem.
- They spread quickly and uncontrollably: While they do have the ability to proliferate, they are not as invasive as some believe. With proper management, their growth can be easily controlled.
By addressing these misconceptions, we can appreciate the true significance of this flower in our environment and culinary practices.
Dandelion Uses in Traditional Medicine
The versatile plant has long been recognized for its medicinal properties across various cultures. Historically, its numerous applications have made it a staple in herbal remedies, offering a range of health benefits. This section explores its traditional uses and the wisdom behind them.
Common Applications
- Digestive Health: Known for its ability to stimulate appetite and aid digestion, this herb has been utilized to alleviate bloating and improve overall gastrointestinal function.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Its anti-inflammatory properties have made it popular for treating conditions like arthritis, helping to reduce swelling and pain.
- Detoxification: Many cultures have employed this plant to support liver function and promote detoxification, enhancing the body’s natural cleansing processes.
Preparation Methods

- Teas: Infusing the leaves or roots in hot water creates a soothing drink that may support various bodily functions.
- Tinctures: Alcohol-based extracts are made to capture the beneficial compounds for concentrated use.
- Salves: Topical applications can provide relief for skin irritations and wounds.
These traditional applications highlight the enduring significance of this remarkable herb in the realm of natural healing, illustrating its continued relevance in contemporary practices.
Ecological Role of Dandelions
This remarkable flowering plant plays a crucial role in various ecosystems. Its presence contributes significantly to soil health, biodiversity, and the overall functionality of habitats. The influence of this species extends beyond its striking appearance, impacting numerous organisms and environmental processes.
Soil Enrichment

The root system of this plant is known for its ability to penetrate deeply into the ground, which helps to aerate the soil. Additionally, as it grows, it brings essential nutrients to the surface, enhancing soil fertility. The following aspects illustrate its contribution:
- Breaks compacted soil layers.
- Facilitates nutrient cycling through organic matter decomposition.
- Promotes beneficial microbial activity.
Support for Wildlife

This plant serves as a vital resource for various species within the ecosystem. Its flowers and leaves provide sustenance for numerous insects and animals. Key benefits include:
- Attracts pollinators, such as bees and butterflies.
- Offers food for herbivores like rabbits and deer.
- Provides habitat and shelter for small organisms.
In summary, this remarkable flowering plant is integral to maintaining ecological balance. Its diverse contributions to soil health and support for wildlife underscore its importance in natural environments.
Cultivation and Care Tips
Understanding the essential aspects of nurturing these resilient plants can lead to a flourishing garden. Proper attention to their growth requirements ensures vibrant development and healthy yield. This section outlines key strategies to promote optimal conditions for growth.
First and foremost, selecting an appropriate location is crucial. These plants thrive in well-drained soil with ample sunlight, ideally receiving at least six hours of direct light each day. Incorporating organic matter can enhance soil quality, providing essential nutrients for robust growth.
Watering is another vital component. While these plants are drought-resistant, consistent moisture during dry spells supports better development. It’s advisable to water deeply and infrequently to encourage strong root systems.
Pest management should also be considered. Regular monitoring for common pests helps in early identification and treatment, ensuring the health of the plants. Natural remedies or organic pesticides can be effective in keeping harmful insects at bay.
Lastly, regular harvesting promotes continuous growth and prevents overcrowding. By periodically removing mature specimens, you allow for new growth and maintain a tidy appearance in your garden. Following these guidelines will lead to a thriving and vibrant display.
Impact of Dandelions on Soil Health
The presence of certain flowering plants can significantly influence the condition and fertility of the ground in which they grow. These resilient organisms not only adapt well to diverse environments but also contribute positively to the ecosystem. Their unique characteristics make them beneficial for maintaining and enhancing soil quality.
Nutrient Cycling
One of the primary benefits of these plants is their role in nutrient cycling. Their deep taproots penetrate the soil, bringing up essential minerals from lower layers. When these roots decompose, they release valuable nutrients, enriching the upper soil layer. This process fosters a more nutrient-rich environment that supports various forms of plant life.
Soil Structure Improvement
Moreover, the growth habits of these flowering plants can improve soil structure. Their extensive root systems create channels in the earth, promoting better aeration and drainage. This enhanced porosity allows water to infiltrate more effectively, reducing erosion and compaction. As a result, the overall health of the soil is significantly improved, supporting sustainable agriculture and natural ecosystems.
In summary, the impact of these flowering plants on soil health is profound. They play a crucial role in enriching the nutrient profile and enhancing the physical properties of the earth, leading to healthier and more productive environments.