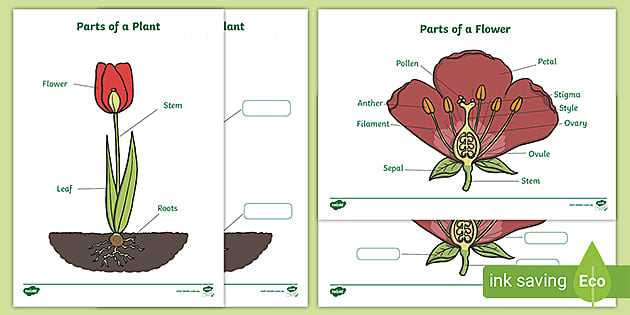
Understanding the Labeled Diagram of Flower Parts
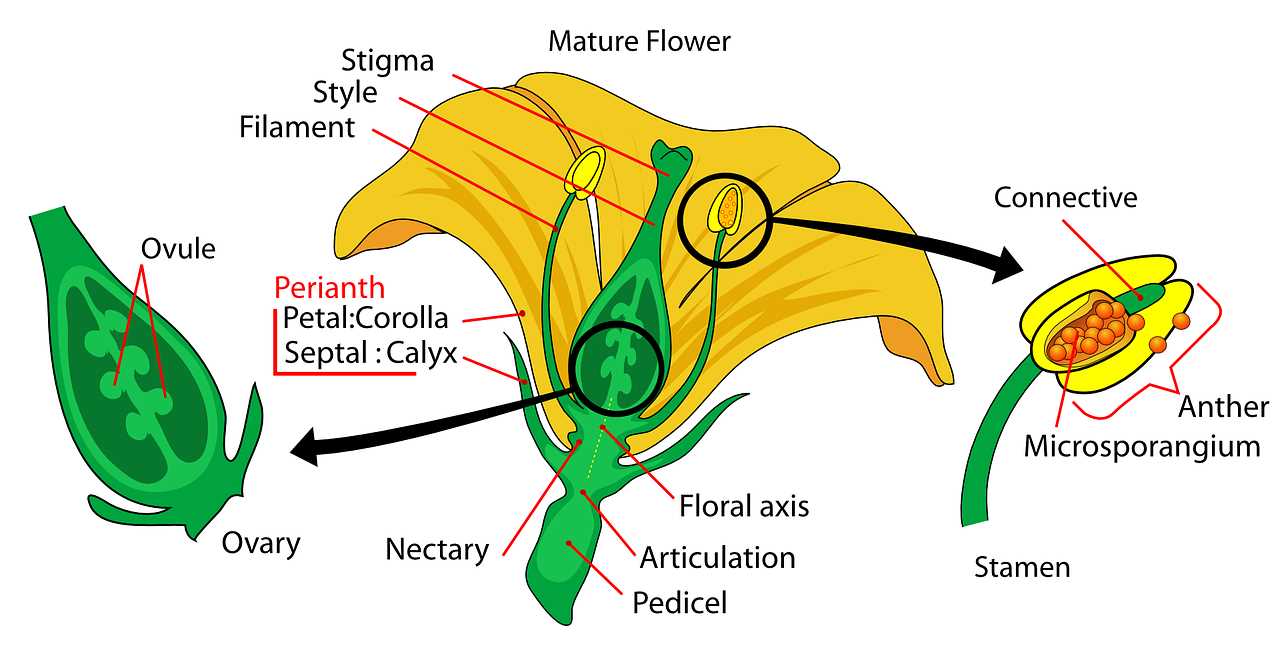
Exploring the intricate structure of flowering plants reveals a fascinating world of biological design. Each component plays a crucial role in the plant’s life cycle, contributing to reproduction, growth, and overall health. By examining these individual elements, one can gain insight into the complex processes that sustain these beautiful organisms.
The essential structures found in blossoms are not only vital for their survival but also showcase a remarkable array of forms and functions. From the vibrant outer layers that attract pollinators to the inner parts that facilitate reproduction, every feature is intricately linked. This interplay between structure and function is a testament to the elegance of nature’s design.
To fully appreciate the wonders of these botanical marvels, it is important to delve deeper into each segment’s role and significance. By doing so, one can unlock a greater understanding of how these elements interact and contribute to the plant’s reproductive success and ecological balance.
Understanding Flower Anatomy
This section explores the intricate structures that contribute to the beauty and functionality of blooming plants. Each element plays a vital role in reproduction and overall health.
- Reproductive Systems:
- Stamens – male reproductive organs
- Carpels – female reproductive structures
- Support Structures:
- Peduncle – stem supporting the bloom
- Receptacle – base where other parts connect
- Attractive Features:
- Petals – colorful components that attract pollinators
- Sepals – protective leaves encasing the bud
Understanding these components allows us to appreciate the complexity of plant life and their ecological significance.
Key Components of a Flower
The intricate structure of a bloom plays a vital role in the reproductive process of plants. Understanding the essential elements within this botanical marvel provides insight into how nature perpetuates life. Each component contributes uniquely, ensuring successful pollination and seed production.
Essential Elements
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Stamen | The male reproductive part, responsible for producing pollen. |
| Pistil | The female reproductive structure, where fertilization occurs. |
| Petals | Colorful structures that attract pollinators. |
| Sepals | Leaf-like structures that protect the bud before blooming. |
Functions and Importance
Each element not only serves its specific function but also interacts with others to create a cohesive system that supports the plant’s lifecycle. Understanding these components enhances appreciation for the complexity of nature and the interconnectedness of life forms.
The Role of Petals in Attraction
The vibrant structures surrounding reproductive organs play a crucial role in drawing attention from potential pollinators. Their colors, shapes, and patterns are finely tuned to attract specific species, ensuring successful reproduction and genetic diversity. This visual allure not only enhances the plant’s appeal but also facilitates vital ecological interactions.
| Color | Pollinator Attraction |
|---|---|
| Red | Hummingbirds |
| Yellow | Bees |
| Blue | Butterflies |
| White | Nights Pollinators |
The intricate designs and fragrances emitted by these structures further enhance their ability to entice. Ultimately, the interplay between visual signals and sensory cues ensures that these organisms thrive in their environments.
Function of Stamen in Pollination
The stamen plays a crucial role in the reproductive process of certain plants, facilitating the transfer of genetic material between individuals. This essential component ensures the continuation of species and promotes biodiversity.
Comprising two main structures, the anther and filament, the stamen is designed for maximum efficiency in pollen production and distribution. The anther produces tiny grains containing male gametes, while the filament supports the anther, positioning it optimally for interaction with pollinators.
During the process of pollination, when insects, birds, or wind come into contact with the stamen, pollen grains are transferred to other reproductive structures, often leading to fertilization. This relationship between the stamen and various pollinators underscores the ultimate significance of these structures in sustaining ecosystems and ensuring plant propagation.
Understanding the function of the stamen not only highlights its role in reproduction but also emphasizes the delicate balance of nature, where each component contributes to the greater whole.
Exploring the Pistil’s Structure
The central component of reproduction in many plants is a fascinating structure that plays a crucial role in the fertilization process. This intricate design not only facilitates the union of gametes but also supports the development of seeds. Understanding its elements can provide insights into the complexities of plant biology.
Components of the Pistil
This essential structure typically consists of three main sections: the stigma, style, and ovary. Each part has a distinct function, working harmoniously to ensure successful reproduction. The stigma captures pollen, the style serves as a conduit, and the ovary houses ovules, which will transform into seeds upon fertilization.
Significance in Plant Reproduction
The role of this central unit extends beyond mere reproduction; it influences genetic diversity and adaptation in plant species. By studying its anatomy and functionality, one can delve into the ultimate mechanisms that underpin plant life and survival strategies in various environments.
Importance of Sepals for Protection
Sepals play a crucial role in safeguarding reproductive structures during their early development. These outermost layers not only provide physical defense but also contribute to the overall health of the organism.
The protective functions of these green leaf-like structures include:
- Shielding delicate buds from environmental threats
- Preventing damage from pests and diseases
- Maintaining moisture levels around reproductive organs
Moreover, their presence can enhance the visual appeal of the reproductive phase, attracting pollinators and aiding in the ultimate goal of reproduction.
How Flowers Reproduce: An Overview
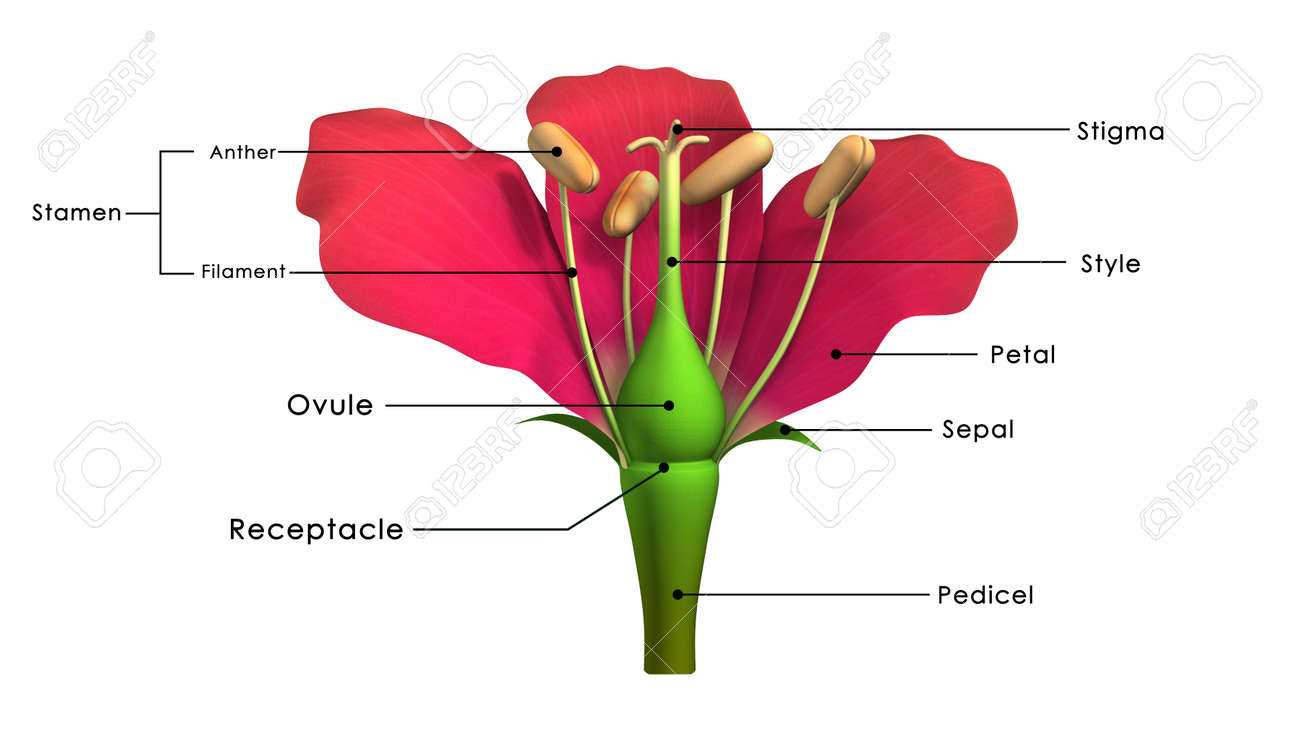
The intricate process of reproduction in these vibrant botanical structures involves a fascinating interplay of various components. Understanding this phenomenon is essential to appreciate the beauty and diversity of plant life. Through specialized mechanisms, these organisms ensure the continuation of their species and the creation of new generations.
At the heart of reproduction lies the union of male and female gametes, which often occurs through a process known as pollination. This event can take place via various agents, such as wind, insects, or water, each playing a crucial role in facilitating genetic exchange. Once fertilization occurs, it leads to the development of seeds, which contain the next generation of plants.
Moreover, the structures involved in this reproductive cycle exhibit remarkable adaptations that enhance their chances of successful mating. For instance, some species have evolved vivid colors and enticing scents to attract pollinators, while others rely on specific environmental conditions to ensure effective reproduction.
In summary, the reproductive processes of these living entities highlight the complexity and elegance of nature’s design, showcasing how life perpetuates itself through a combination of attraction, interaction, and adaptation.
Types of Pollinators and Their Impact
Pollinators play a crucial role in the ecosystem, facilitating the transfer of pollen from one organism to another, thereby promoting reproduction and biodiversity. Their actions not only support the growth of various species but also have significant implications for agriculture and food production. Understanding the diversity of these agents and their contributions helps underscore their importance in maintaining healthy environments.
Main Categories of Pollinators
Various creatures contribute to the pollination process, each with unique characteristics and methods of interaction with plants. The primary groups include insects, birds, and mammals, each displaying distinct behaviors that enhance floral fertilization.
| Type of Pollinator | Examples | Impact on Ecosystem |
|---|---|---|
| Insects | Bees, butterflies, moths | Essential for the reproduction of many flowering species, crucial for food supply. |
| Birds | Hummingbirds, sunbirds | Help in the pollination of plants that produce tubular flowers, enhancing biodiversity. |
| Mammals | Bats, some rodents | Pollinate nocturnal blooms, contributing to the diversity of plant life. |
Significance of Pollinators
The presence of these organisms not only supports the ecological balance but also significantly impacts agricultural practices. By aiding in the production of fruits, vegetables, and nuts, pollinators enhance food security and economic stability. Their decline poses serious threats to both natural ecosystems and human livelihoods, highlighting the need for conservation efforts and awareness.
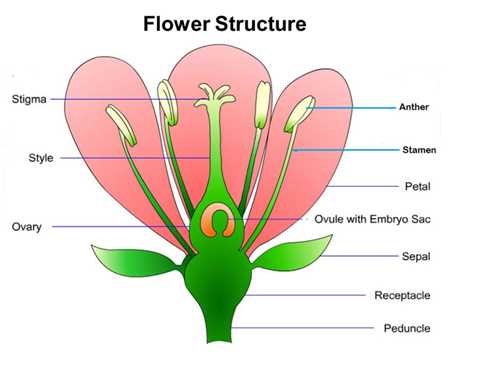
Diagram of Flower Parts Explained
This section offers a comprehensive overview of the various components found in a blooming specimen. Each element plays a crucial role in the life cycle and reproduction, contributing to the overall beauty and function of the organism.
Key Elements and Their Functions
Stamens serve as the male reproductive organs, producing pollen that is essential for fertilization. Meanwhile, the pistil, which is the female counterpart, receives this pollen to facilitate the formation of seeds.
Supportive Structures
Common Flower Types and Their Features
Exploring the diversity of botanical blooms reveals an astonishing variety of forms, colors, and structures. Each type exhibits unique characteristics that contribute to its beauty and ecological roles. Understanding these distinctions can enhance appreciation and aid in identification, whether for gardening, conservation, or simply enjoyment.
Popular Varieties
Some common species are frequently admired for their aesthetic qualities and adaptability in different environments. Below is a summary of several widely recognized types and their notable traits.
| Type | Color | Size | Blooming Season |
|---|---|---|---|
| Roses | Red, Pink, Yellow | Medium to Large | Spring to Fall |
| Tulips | Various | Small to Medium | Spring |
| Daisies | White, Yellow | Small | Spring to Summer |
| Sunflowers | Yellow, Brown | Large | Summer |
Ecological Importance
The varieties mentioned not only provide visual delight but also play significant roles in their ecosystems. They attract pollinators, support local wildlife, and contribute to soil health. Recognizing their features helps cultivate a deeper understanding of their place in nature and the importance of conservation efforts.
The Lifecycle of a Flowering Plant
The journey of a blooming organism is a fascinating process that showcases nature’s intricate design. This cycle involves various stages, each playing a crucial role in the continuation of the species. Understanding these phases helps appreciate the beauty and complexity of botanical life.
The lifecycle can be divided into several key stages:
- Seed Germination: The initial phase begins when a dormant seed absorbs moisture and swells, leading to the emergence of a new plant.
- Seedling Development: As the young plant grows, it develops roots and leaves, establishing a foundation for further growth.
- Mature Growth: The organism reaches full size, becoming capable of reproduction. During this phase, it may produce foliage and branches that support photosynthesis.
- Reproductive Phase: This stage involves the formation of structures responsible for creating seeds, ensuring the survival of the next generation.
- Seed Dispersal: Once matured, seeds are dispersed through various means, including wind, water, or animal activity, allowing them to find suitable environments to grow.
Each of these stages is interconnected, contributing to the sustainability and diversity of plant life. By recognizing the significance of each phase, we gain a deeper appreciation for the natural world and its cycles.
Environmental Factors Affecting Flowers
The growth and development of blooming plants are significantly influenced by various external conditions. These elements play a crucial role in determining how these organisms thrive, reproduce, and adapt to their surroundings. Understanding these influences can enhance cultivation practices and promote healthier ecosystems.
Light Conditions
Illumination is vital for the photosynthetic processes that sustain these organisms. Different species have unique requirements regarding the amount and quality of light they need. Insufficient sunlight can lead to stunted growth and poor flowering, while excessive light can cause damage to the delicate structures. Therefore, finding the right balance is essential for optimal development.
Soil Composition and Moisture
The substrate in which these plants are rooted affects their nutrient uptake and overall health. Soil pH, texture, and organic matter content determine the availability of essential minerals. Additionally, moisture levels are critical; both overwatering and drought conditions can adversely impact their vitality. Managing these factors ensures robust and vibrant growth, ultimately enhancing reproductive success.
Applications of Flower Knowledge in Botany
Understanding the structure and functions of reproductive organs is essential in the field of botany. This knowledge aids in identifying species, enhancing cultivation techniques, and contributing to biodiversity conservation efforts. Insights into the life cycles and reproductive strategies of plants facilitate advancements in agriculture and horticulture.
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Species Identification | Recognizing different species through reproductive traits. |
| Crop Improvement | Enhancing yield and disease resistance through breeding. |
| Biodiversity Conservation | Protecting endangered species by understanding their reproduction. |
| Ecological Research | Studying interactions between plants and pollinators. |