Milling Machine Diagram and Parts Overview
The realm of precision engineering offers a fascinating insight into the intricate designs and functionalities that drive modern production. An exploration of the essential elements that comprise these sophisticated instruments reveals not only their purpose but also the artistry involved in their construction.
In this section, we will uncover the key features that contribute to the effective operation of these essential tools. By examining each component closely, one can appreciate how they interconnect to achieve the ultimate goal of efficiency and accuracy in crafting various materials.
Delving into the specifics allows enthusiasts and professionals alike to gain a deeper understanding of how these devices are assembled and function as a cohesive unit. Whether for educational purposes or practical applications, recognizing the significance of each element enhances one’s appreciation of this remarkable field.
Milling Machine Overview
This section offers a comprehensive insight into a vital tool in various industries, focusing on its essential components and functionalities. Understanding this equipment is crucial for those involved in manufacturing and engineering processes, as it plays a key role in shaping materials with precision.
Key Features
The principal characteristics of this equipment include its versatility and precision. It is capable of executing a wide range of tasks, from simple cuts to complex shapes, making it indispensable in workshops and production facilities.
Components
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Table | Supports the workpiece and provides a stable surface for operations. |
| Spindle | Drives the cutting tool, enabling various operations. |
| Tool Holder | Secures the cutting tool in place during use. |
| Feed Mechanism | Controls the movement of the workpiece relative to the tool. |
| Motor | Powers the spindle and other moving parts for operation. |
Key Components of Milling Machines
Understanding the fundamental elements of these tools is essential for both novices and experts in manufacturing. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring precision and efficiency during various operations. Here, we explore the primary features that contribute to their functionality.
- Base: The sturdy foundation that supports the entire setup, ensuring stability during use.
- Column: A vertical structure that houses critical elements and provides support for other components.
- Table: The horizontal platform where workpieces are secured, allowing for accurate positioning and movement.
- Spindle: The rotating element that holds cutting tools and drives them during operation, crucial for achieving desired shapes.
- Feed Mechanism: This system controls the movement of the table and the workpiece, ensuring precise adjustments.
- Cutter: The tool responsible for removing material from the workpiece, available in various shapes and sizes to suit different tasks.
- Coolant System: A vital feature that reduces heat during cutting, prolonging tool life and enhancing performance.
Each of these components is designed to work in harmony, allowing for a wide range of machining processes, from simple to complex operations.
Understanding the Milling Process
This section explores the intricate procedure used to shape materials, focusing on how various tools interact with surfaces to achieve precise dimensions and finishes. The process is essential in manufacturing, allowing for versatility in production and the creation of complex geometries.
Key Concepts
- Material removal techniques
- Tool movement and feed direction
- Surface finish requirements
Steps Involved
- Select the appropriate tool based on material and desired outcome.
- Secure the workpiece to ensure stability during operation.
- Adjust the speed and feed rates for optimal efficiency.
- Monitor the process for precision and quality control.
Types of Milling Machines Explained
Various categories of these tools cater to specific tasks in the realm of fabrication. Understanding their unique features and capabilities can significantly enhance efficiency in manufacturing processes. Each type serves distinct functions, allowing users to select the optimal option based on their requirements.
Vertical Variants
Vertical types are characterized by their spindle orientation. This setup allows for precise cutting operations, making them ideal for intricate designs and detailed work. Additionally, they often come equipped with adjustable tables, providing versatility in handling different materials.
Horizontal Variants
Horizontal options excel in handling large workpieces and performing heavy-duty tasks. Their design facilitates effective chip removal, ensuring smoother operations. This type is particularly favored in industrial settings where durability and strength are paramount.
Common Parts and Their Functions
This section focuses on the essential components found in a typical apparatus, highlighting their roles and importance in the overall operation. Understanding these elements is crucial for anyone looking to grasp the fundamentals of the equipment’s functionality.
Main Components
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Table | Supports the workpiece and provides stability during processing. |
| Spindle | Holds and rotates the cutting tool, allowing for precise material removal. |
| Tool Holder | Secures the cutting tool in place, ensuring accurate machining. |
| Feed Mechanism | Controls the movement of the workpiece relative to the tool, facilitating various operations. |
Additional Features
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Column | Provides vertical support and houses essential components for stability. |
| Motor | Powers the spindle and other moving parts, ensuring efficient operation. |
| Control Panel | Allows the operator to adjust settings and monitor performance during use. |
| Cooling System | Maintains optimal temperatures, preventing overheating of tools and materials. |
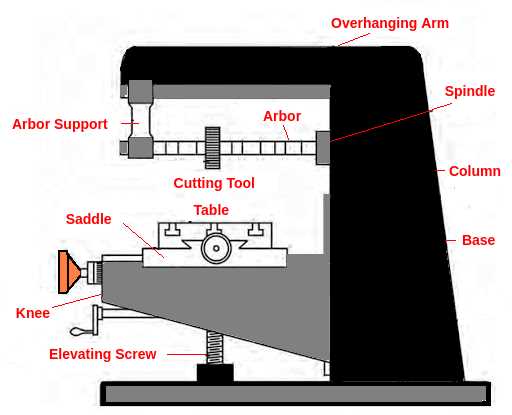
Diagram of a Standard Milling Machine
This section presents a visual representation of a typical equipment used in manufacturing processes, highlighting its various components and their functionalities. Understanding these elements is crucial for grasping how the overall system operates efficiently.
Main Components
- Base
- Column
- Table
- Spindle
- Tool Holder
Functionality Overview
- The base provides stability and support.
- The column houses essential drive mechanisms.
- The table allows for material placement and movement.
- The spindle drives the cutting tools.
- The tool holder secures the tools during operation.
Importance of Tool Holders
Tool holders play a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of various operations in manufacturing. They serve as the essential link between the cutting tool and the equipment, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
- Precision: They provide a stable and precise fit for tools, minimizing vibration and enhancing cutting accuracy.
- Tool Change: Quick-change options enable faster transitions between tasks, increasing overall productivity.
- Durability: High-quality holders can withstand significant wear, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
- Versatility: Various types accommodate different tools, making them adaptable for multiple applications.
- Safety: Properly secured tools minimize risks of accidents and ensure a safer working environment.
Ultimately, investing in quality tool holders contributes to improved performance and cost-effectiveness in any production setting.
Exploring Milling Machine Attachments
Attachments play a crucial role in enhancing the versatility and functionality of cutting tools. By providing various capabilities, they enable operators to perform a wide range of tasks with precision and efficiency. Understanding these additions can significantly improve productivity and expand the range of possible applications.
Types of Attachments
Several types of enhancements are commonly utilized, each serving distinct purposes:
- Vises: Essential for securely holding workpieces in place.
- Cutting Tools: Various shapes and sizes tailored for specific tasks, such as drilling or contouring.
- Power Feed Units: Allow for automatic movement of the workpiece, enhancing precision and reducing manual effort.
- Tool Holders: Facilitate quick changes between different cutting tools, improving workflow.
- Rotary Tables: Enable 360-degree rotation, allowing for complex geometries to be machined accurately.
Benefits of Utilizing Attachments

Incorporating these additions offers numerous advantages:
- Increased Precision: Specialized attachments improve the accuracy of cuts and shapes.
- Enhanced Productivity: Streamlining tasks leads to faster completion times.
- Versatile Operations: The ability to perform multiple functions makes it easier to adapt to different projects.
- Cost Efficiency: Maximizing the capabilities of existing tools reduces the need for additional equipment.
Understanding and effectively utilizing these enhancements can lead to greater efficiency and superior results in various applications.
Maintenance Tips for Milling Machines
Regular upkeep is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of any machining equipment. By following specific guidelines, users can enhance reliability, reduce wear, and prevent costly breakdowns. This section provides practical advice on how to maintain your device effectively.
Daily Checks
Start each day with a thorough inspection. Lubrication of moving components is crucial; ensure that all bearings and gears are properly greased. Additionally, examine coolant levels and check for any leaks or signs of wear. Keeping a clean workspace also helps in preventing debris from interfering with operations.
Periodic Maintenance
Incorporate regular service intervals into your schedule. Replace worn-out filters and check the alignment of the spindle to maintain accuracy. Inspect electrical connections and clean any dust or grime buildup. Consistent maintenance not only enhances performance but also extends the lifespan of your equipment.
Future Trends in Milling Technology
The evolution of cutting tools and fabrication techniques is poised to redefine precision and efficiency in the industry. As advancements emerge, professionals are increasingly focusing on automation, digital integration, and enhanced material performance to streamline processes and improve outcomes.
Automation and Smart Technology
Automation stands at the forefront of this transformation, utilizing smart systems to enhance productivity and reduce human error. Robotics and artificial intelligence are being integrated to monitor operations, ensuring optimal performance and adaptive processes that respond to real-time data.
Materials and Sustainability
Innovations in materials are also crucial, with an emphasis on sustainability and recyclability. Future developments aim to create advanced alloys and composites that not only enhance durability but also minimize environmental impact, aligning with global sustainability goals.