2007 Mazda 6 Parts Overview
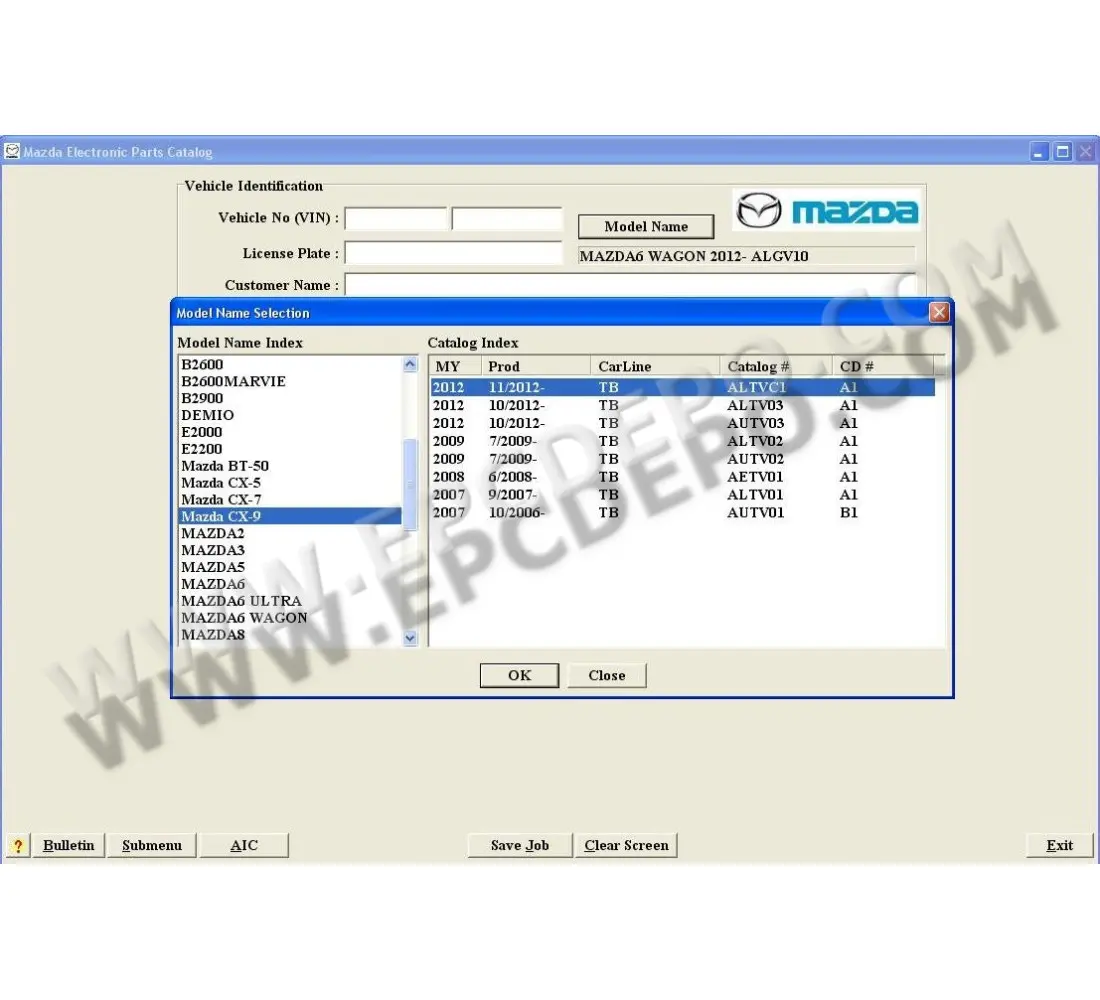
When exploring the intricacies of automotive design, it’s essential to have a clear visualization of how various elements within a vehicle interact and connect. A comprehensive illustration of the arrangement and functionality of these components can significantly aid in understanding maintenance and repair processes.
Detailed schematics provide insights into the structure and organization of different assemblies, allowing enthusiasts and professionals alike to approach mechanical tasks with greater confidence. By familiarizing oneself with these representations, one can enhance their knowledge of the overall system, promoting effective troubleshooting and efficient repairs.
Moreover, these visuals serve as valuable resources for anyone looking to customize or upgrade their vehicle. Recognizing the placement and relationship of individual components ensures that modifications are implemented safely and effectively, contributing to the overall performance and longevity of the automobile.
This section aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of a specific vehicle model, outlining its essential components and their arrangement. The focus will be on the various systems and parts that contribute to the overall functionality and performance, offering valuable insights for enthusiasts and owners alike.
Key Features and Specifications
Understanding the fundamental characteristics and specifications of the vehicle is crucial. This includes details such as engine types, transmission options, and performance metrics, which play a significant role in how the vehicle operates.
Component Classification
Identifying and categorizing the different elements of the vehicle helps in better comprehension of its structure. Components can be classified into several categories, including:
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Engine System | Includes all parts related to the engine, such as the block, pistons, and valves. |
| Transmission System | Encompasses elements that facilitate gear shifting and power transfer. |
| Suspension System | Consists of components that support the vehicle’s weight and enhance ride quality. |
| Braking System | Involves parts that ensure effective stopping and safety measures. |
Key Features of the 2007 Model
This model is recognized for its blend of performance, comfort, and advanced technology. It offers a variety of features designed to enhance the driving experience while ensuring safety and reliability.
Performance and Handling
- Smooth and responsive steering for a more engaging drive.
- Available powerful engine options to suit different driving preferences.
- Efficient fuel consumption for a balance of power and economy.
Interior Comfort and Technology
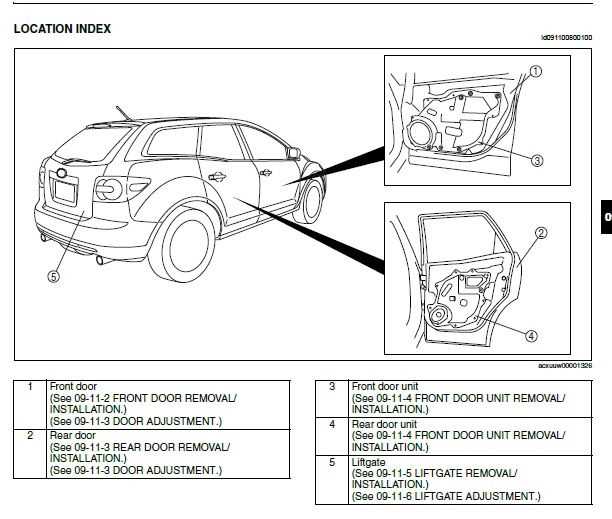
- Spacious cabin with quality materials for a refined atmosphere.
- Advanced audio system providing superior sound quality.
- Intuitive dashboard layout with easy-to-navigate controls.
Engine Components and Layout
This section explores the essential elements and configuration of the power unit found in the vehicle, emphasizing its critical role in overall performance and functionality.
Understanding the primary components is vital for comprehending how they work together to drive the automobile efficiently. Key parts include:
- Block: The main structure housing various components.
- Cylinder Head: Contains the combustion chambers and facilitates air and fuel intake.
- Pistons: Move up and down within the cylinders to generate power.
- Crankshaft: Converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion.
- Camshaft: Controls the opening and closing of the valves.
The arrangement of these components is meticulously designed to maximize efficiency and performance. Each part plays a distinct role in the combustion process and the engine’s operation, contributing to the vehicle’s overall capability.
Regular maintenance and understanding of these elements are crucial for ensuring longevity and reliability. Familiarity with these components empowers owners to make informed decisions regarding care and repairs.
Transmission System Parts Explained
The transmission system is a crucial component of any vehicle, responsible for transferring power from the engine to the wheels. Understanding the various elements of this system can enhance maintenance and performance. Each part plays a significant role in ensuring smooth operation and responsiveness during driving.
Key Components of the Transmission System

- Transmission Case: The housing that contains the internal components and protects them from external elements.
- Clutch: Engages and disengages the engine from the transmission, allowing for smooth gear changes.
- Gear Sets: Different gears that adjust the vehicle’s speed and torque.
- Shift Forks: Mechanisms that move the gears into position during shifting.
- Torque Converter: Transfers power from the engine to the transmission and allows for a smooth start without stalling.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Routine inspections and maintenance of the transmission components can prevent major failures and extend the lifespan of the system. Regular fluid checks and timely replacements of worn-out parts are essential for optimal performance.
Electrical System and Wiring Diagrams
The electrical framework of a vehicle plays a crucial role in its functionality, encompassing various components that ensure efficient operation. Understanding the wiring schematics and the relationships between different elements can aid in troubleshooting and maintenance.
These illustrations provide insight into the connections and pathways that facilitate power distribution throughout the vehicle. They help identify components such as the battery, alternator, fuses, and various sensors.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Battery | Stores electrical energy for starting the engine and powering accessories. |
| Alternator | Generates electrical power while the engine runs, charging the battery. |
| Fuses | Protects electrical circuits by breaking the connection in case of overload. |
| Sensors | Monitor various parameters and send data to the engine control unit. |
Suspension System Parts Overview
The suspension system plays a critical role in ensuring a smooth and stable ride by absorbing shocks and maintaining tire contact with the road. This intricate assembly comprises several key components, each contributing to the overall performance and comfort of the vehicle.
Components of the Suspension Assembly: The primary elements include springs, dampers, control arms, and bushings. Each component works in harmony to support the weight of the vehicle while minimizing road vibrations.
Functionality and Importance: Springs are responsible for absorbing energy from road irregularities, while dampers help control the oscillations caused by the springs. Control arms connect the chassis to the wheels, allowing for movement and flexibility. Bushings reduce friction and wear between moving parts, enhancing durability.
Understanding the suspension system is essential for maintaining optimal handling and ride quality. Regular inspection and maintenance of these components can significantly improve vehicle performance and safety.
Braking System Components Breakdown
The braking system is a critical element of any vehicle, responsible for ensuring safe and controlled deceleration. Understanding its various components is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. Each part plays a unique role in the overall functionality, contributing to the performance and reliability of the entire system.
Brake Pads: These are the components that press against the brake rotors, generating the necessary friction to slow down or stop the vehicle. High-quality brake pads enhance performance and reduce noise during operation.
Brake Rotors: Also known as discs, these circular components provide a surface for the brake pads to clamp onto. Their material and design affect heat dissipation and overall braking efficiency.
Calipers: This part houses the brake pads and is responsible for applying pressure to them. The caliper’s hydraulic system enables effective force transfer from the brake pedal to the pads.
Brake Lines: These tubes transport brake fluid from the master cylinder to the calipers. The integrity of these lines is crucial, as any leaks can lead to a loss of braking power.
Master Cylinder: This component converts the force from the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure, facilitating the movement of brake fluid throughout the system. Its reliability is vital for consistent braking performance.
Brake Fluid: A specially formulated liquid that transfers force and helps prevent corrosion within the braking system. Regular checks and changes are necessary to ensure optimal functionality.
By familiarizing yourself with these essential components, you can better appreciate the complexity and importance of the braking system in any vehicle. Proper care and timely replacements of these parts contribute to enhanced safety and performance on the road.
Cooling System Components Explained
The cooling system in a vehicle plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal engine temperature. This system ensures that the engine does not overheat, allowing it to function efficiently and reliably. Understanding the various components involved can help in recognizing their significance in overall vehicle performance.
One of the primary elements of the cooling system is the radiator, which dissipates heat from the coolant before it circulates back to the engine. This component is designed to maximize air exposure, facilitating effective heat transfer. Additionally, the water pump is responsible for circulating coolant throughout the engine and radiator, ensuring a continuous flow that regulates temperature.
Another essential part is the thermostat, which acts as a temperature regulator. It opens and closes based on the coolant temperature, allowing for optimal engine warmth while preventing overheating. Furthermore, coolant hoses connect various components, enabling the efficient transport of coolant. These hoses must be durable and leak-free to maintain system integrity.
Finally, cooling fans assist in airflow through the radiator, particularly when the vehicle is stationary or moving slowly. These fans help maintain adequate cooling, especially during high-demand situations. Each component of the cooling system works synergistically to ensure that the engine operates within a safe temperature range.
Fuel System and Related Parts

The fuel system is a crucial component of any vehicle, responsible for delivering the necessary fuel to the engine for optimal performance. This intricate assembly includes various elements that work in harmony to ensure efficient operation, from storage to combustion.
Understanding the different components involved in the fuel delivery process can aid in effective maintenance and troubleshooting. Below is a table detailing the key elements and their functions within the fuel system.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Fuel Tank | Stores fuel until it is needed by the engine. |
| Fuel Pump | Moves fuel from the tank to the engine. |
| Fuel Filter | Removes impurities from the fuel before it reaches the engine. |
| Fuel Injector | Sprays fuel into the engine’s combustion chamber at precise intervals. |
| Fuel Rail | Distributes fuel to the injectors. |
Interior Components and Accessories
The interior of a vehicle is designed to provide comfort and functionality for both the driver and passengers. Understanding the various elements that make up the cabin can enhance the overall driving experience. This section explores essential components and accessories that contribute to the vehicle’s interior design.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Dashboard | Houses essential instruments and controls for the driver, offering a clear layout for ease of access. |
| Seats | Designed for comfort and support, often featuring adjustable settings and various materials. |
| Center Console | Acts as a storage and control hub, typically including cup holders, armrest storage, and multimedia controls. |
| Door Panels | Enclose the sides of the cabin, incorporating armrests, handles, and speaker placements. |
| Headliner | Provides insulation and aesthetic appeal, covering the roof of the interior space. |
| Floor Mats | Protect the flooring from dirt and wear, available in various styles and materials for customization. |
| Sun Visors | Block sunlight and glare, often equipped with mirrors for added convenience. |
Exterior Parts and Body Diagram
The exterior components of a vehicle play a crucial role in both aesthetics and functionality. Understanding the various elements that comprise the outer shell can enhance maintenance and repair efforts. This section explores the key features that contribute to the overall design and structure.
Fenders are essential for protecting the wheels and maintaining aerodynamic efficiency. They come in various shapes and sizes, tailored to the specific model.
Bumpers serve not only as protective elements but also as integral parts of the vehicle’s styling. Their design can influence impact absorption and pedestrian safety.
Hoods provide access to the engine compartment while also playing a significant role in the vehicle’s exterior appearance. Their contours and materials can vary widely, reflecting both form and function.
Doors are vital for accessibility, offering both security and insulation. They often incorporate features like windows and locks, which are essential for convenience and safety.
Finally, mirrors and lights not only enhance visibility but also contribute to the overall aesthetic appeal. Each of these components works in harmony to ensure the vehicle is not only functional but also visually appealing.
Replacement and Maintenance Tips

Ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of your vehicle requires regular upkeep and timely component replacement. Adopting a proactive approach can help you identify potential issues before they escalate, thus saving time and expenses.
Here are some essential tips to consider:
| Task | Frequency | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Change | Every 5,000 miles | Use quality oil and filter for best results. |
| Tire Rotation | Every 6,000 miles | Helps ensure even wear and prolongs tire life. |
| Brake Inspection | Every 10,000 miles | Check pads, rotors, and fluid levels regularly. |
| Coolant Flush | Every 30,000 miles | Prevents overheating and corrosion. |
Always refer to your vehicle’s service manual for specific recommendations and consult with professionals when necessary. Regular attention to these tasks will enhance reliability and efficiency.