Comprehensive Guide to Motorcycle Part Names with Diagrams
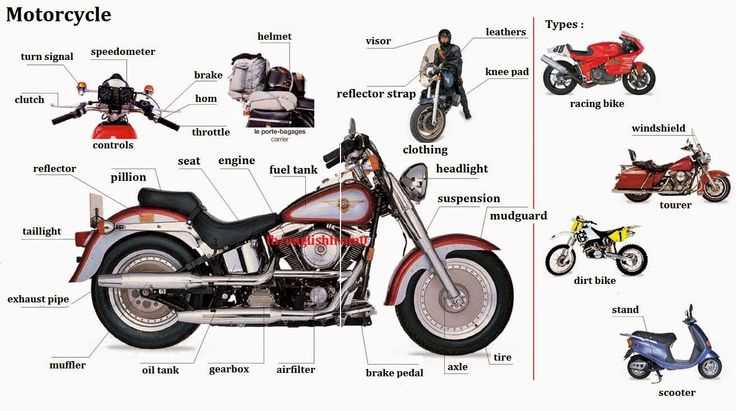
Exploring the intricate elements that contribute to the functionality of two-wheeled vehicles reveals a fascinating world of mechanics and design. Each segment plays a pivotal role, working in harmony to ensure smooth operation and rider safety. By grasping these essentials, enthusiasts and newcomers alike can enhance their appreciation for the engineering behind these machines.
Delving into the various components, one can uncover the significance of each piece, from the engine to the frame, and everything in between. Understanding these features not only aids in maintenance but also empowers riders to make informed choices about upgrades and repairs. As we embark on this journey, we aim to clarify the ultimate structure of these vehicles, shedding light on their functionality.
By examining the specific elements and their interconnections, we can appreciate the complexity that lies within. This knowledge is not just for mechanics; it enriches the experience of anyone passionate about the open road. Join us as we explore the essential building blocks that define the essence of two-wheeled adventures.
Understanding Motorcycle Components
Exploring the various elements of a two-wheeled vehicle reveals the intricate design and engineering that contribute to its performance and functionality. Each segment plays a crucial role in ensuring safety, efficiency, and an enjoyable riding experience. By familiarizing ourselves with these components, we can better appreciate how they work together to create a cohesive machine.
Key Elements and Their Functions

The core of this vehicle consists of several essential features, each serving a distinct purpose. The engine powers the machine, transforming fuel into motion, while the frame provides structural integrity and supports various attachments. The suspension system absorbs shocks from the road, enhancing rider comfort and control. Understanding how these features interact helps in maintenance and improving overall performance.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Essential Parts of a Motorcycle
Understanding the key components of two-wheeled vehicles is crucial for any enthusiast or owner. Each section plays a significant role in ensuring optimal performance, safety, and comfort. Below is an overview of the fundamental elements that make up these machines.
- Engine: The heart of the vehicle, responsible for generating power and torque.
- Transmission: This mechanism transfers power from the engine to the wheels, allowing for speed adjustments.
- Chassis: The frame that supports all other components and provides structural integrity.
- Suspension: This system absorbs shocks from the road, ensuring a smooth ride and stability.
- Brakes: Essential for safety, these components slow down or stop the vehicle effectively.
- Fuel Tank: Stores the necessary fuel for the engine to operate efficiently.
- Wheels and Tires: Critical for traction and stability, they enable movement and control on various surfaces.
- Electrical System: Powers lights, indicators, and ignition, essential for visibility and starting the engine.
Each of these elements works in harmony to deliver a seamless riding experience. Proper maintenance and understanding of their functions can enhance both safety and performance.
Visual Guide to Motorcycle Elements
This section provides an insightful exploration into the various components that contribute to the functionality and aesthetics of two-wheeled vehicles. Understanding these elements enhances the overall experience for enthusiasts and riders alike.
- Frame: The structure that supports all other components.
- Engine: The powerhouse that propels the vehicle forward.
- Wheels: Essential for movement and stability.
- Brakes: Crucial for safety, allowing the rider to slow down or stop.
- Suspension: Provides comfort and handles road irregularities.
Each element plays a vital role, and together they create an ultimate riding experience. Familiarity with these components aids in maintenance and enhances appreciation for engineering.
- Familiarize yourself with each element.
- Understand their functions and interconnections.
- Explore modifications for personalization.
By delving into these aspects, riders can deepen their knowledge and improve their overall enjoyment of their machines.
Key Functions of Each Component
Understanding the essential roles of various elements within a two-wheeled vehicle is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and safety. Each component plays a specific part in the overall functionality, contributing to the seamless operation and handling of the machine. Recognizing these functions allows riders and enthusiasts to appreciate the intricate engineering behind their vehicles.
Engine: The heart of the vehicle, responsible for converting fuel into motion. It generates the power needed to propel the machine forward, while also influencing acceleration and speed.
Transmission: This system transfers the power produced by the engine to the wheels. It allows for gear changes, enabling the rider to adapt to different speeds and terrains.
Brakes: Vital for safety, these mechanisms slow down or stop the vehicle. Effective braking systems are essential for maintaining control and preventing accidents.
Suspension: This component ensures a smooth ride by absorbing shocks from the road. It enhances stability and comfort, allowing the rider to maintain control even on uneven surfaces.
Wheels: Integral for movement, they provide traction and stability. The design and materials used can significantly affect handling and performance, influencing how the vehicle interacts with the road.
Fuel System: Responsible for delivering fuel to the engine, this system ensures optimal combustion and efficiency. Proper functioning of the fuel system is key to performance and economy.
Electrical System: This includes all components related to lighting, ignition, and electronics. It plays a critical role in starting the vehicle and ensuring visibility during rides.
Frame: The structure that supports all other components, providing rigidity and stability. It also contributes to the overall design and aesthetics of the vehicle.
Common Names and Terminology
Understanding the terminology associated with two-wheeled vehicles is essential for enthusiasts and newcomers alike. This section aims to illuminate the various terms used within the community, providing clarity and enhancing communication among riders and mechanics.
Essential Components
Familiarity with key components helps riders appreciate their machines better. Terms like engine, chassis, and wheels represent the foundational elements that contribute to overall performance. Each of these parts plays a vital role in the vehicle’s functionality and safety.
Operational Terms
In addition to components, certain operational terms are crucial. Throttle, brake, and clutch are essential for controlling speed and maneuverability. Mastering these terms aids riders in discussing techniques and improvements effectively.
Motorcycle Engine Parts Explained
Understanding the components that drive a two-wheeled vehicle is essential for enthusiasts and mechanics alike. Each element plays a crucial role in the overall functionality and performance of the machine. By delving into the intricacies of these mechanisms, one can appreciate how they work in harmony to deliver a seamless riding experience.
At the heart of any vehicle is the power unit, which converts fuel into motion. This process involves various systems, including combustion chambers where air and fuel mix, ignite, and produce energy. The resulting force drives pistons that translate linear motion into rotational energy.
Connected to the pistons is the crankshaft, a vital component that transforms this linear movement into a rotational force, ultimately powering the wheels. Meanwhile, the camshaft regulates the opening and closing of valves, ensuring the right mixture of air and fuel enters the combustion area at the appropriate times.
The cooling system is equally important, preventing overheating and maintaining optimal operating temperatures. Coolant circulates through channels, absorbing heat and dissipating it through radiators or fins. Additionally, the lubrication system reduces friction between moving elements, extending their lifespan and enhancing efficiency.
Electrical systems are also key players, providing the spark necessary for ignition and powering essential accessories. This network includes batteries, alternators, and ignition coils, working together to ensure smooth operation.
By exploring these critical elements, one can gain a deeper understanding of what makes a two-wheeled vehicle tick, leading to improved maintenance practices and a more rewarding riding experience.
Transmission System Overview
The transmission system plays a crucial role in the functionality and performance of two-wheeled vehicles. This complex assembly facilitates the transfer of power from the engine to the wheels, allowing for effective control of speed and torque. Understanding its components and how they interact is essential for both enthusiasts and those involved in maintenance and repair.
Key Components
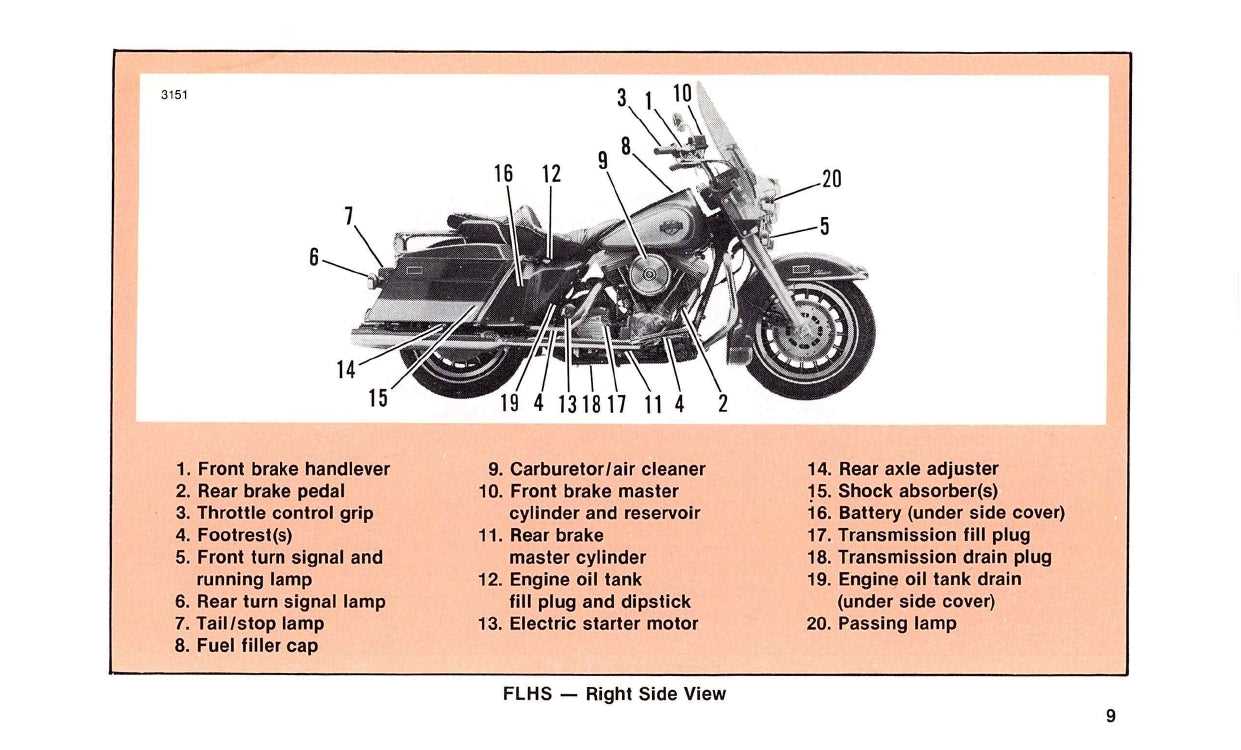
Several key elements work together within the transmission system to ensure smooth operation. Each component has a specific function that contributes to the overall efficiency and responsiveness of the vehicle.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Clutch | Engages and disengages the engine from the transmission, allowing for smooth gear shifts. |
| Gearbox | Houses various gears that control the ratio of engine speed to wheel speed, enabling acceleration and deceleration. |
| Chain/Belt | Transfers power from the gearbox to the wheels, ensuring effective motion. |
| Shifter | Allows the rider to change gears manually or automatically, providing control over power delivery. |
Operating Principles
At its core, the transmission system operates by modifying the engine’s output to match the desired speed and power requirements. By selecting different gears, the rider can optimize performance for various conditions, whether navigating through city traffic or cruising on highways. This adaptability is what makes the system vital for both performance and safety.
Braking Mechanisms in Detail
Understanding the intricacies of stopping systems is crucial for ensuring safety and control in two-wheeled vehicles. These mechanisms play a pivotal role in performance, affecting both responsiveness and stability during operation. A deep dive into their components reveals how various technologies work together to achieve optimal deceleration.
Types of Braking Systems
Braking systems can generally be classified into two main categories: hydraulic and mechanical. Hydraulic systems utilize fluid pressure to activate the brakes, providing smoother and more efficient stopping power. In contrast, mechanical systems rely on physical linkages and cables, offering a simpler design but often less effective performance under extreme conditions.
Key Components
Each braking system consists of several essential components. The brake pads create friction against the rotor, while the caliper houses the pistons that apply pressure. Additionally, the master cylinder is vital for generating hydraulic pressure, while the brake lines transport this pressure to the calipers. Understanding these elements allows for a deeper appreciation of how effective stopping power is achieved.
Suspension System and Its Importance
The suspension mechanism plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth and stable ride. It absorbs shocks from uneven surfaces, maintaining contact between the wheels and the ground. This function enhances comfort and control, allowing for a more enjoyable experience for the rider.
Key Functions of the Suspension Mechanism
- Shock Absorption: It mitigates impacts from bumps and potholes, reducing the jarring effect on the rider.
- Stability: A well-designed system enhances stability during turns and maneuvers, promoting safety.
- Traction: By keeping the wheels in contact with the terrain, it improves grip and handling.
Types of Suspension Systems
- Conventional: Utilizes springs and dampers to absorb shocks, commonly found in various vehicles.
- Progressive: Features variable spring rates, providing a balance between comfort and performance.
- Adjustable: Allows riders to modify settings for different conditions, enhancing versatility.
In summary, the suspension mechanism is vital for ensuring a safe and pleasant journey. Its ability to absorb shocks, maintain stability, and enhance traction underscores its significance in the overall design and functionality of two-wheeled vehicles.
Electrical Components and Their Roles
The intricate network of electrical elements within a two-wheeled vehicle plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and safety. Each component works in harmony to manage power distribution, control systems, and enhance the overall riding experience. Understanding these components is essential for both enthusiasts and technicians alike.
Key Elements and Functions
Among the fundamental elements are the battery, which stores energy, and the alternator, responsible for generating electricity while the engine runs. These components provide the necessary power for various systems, including lighting and ignition.
Importance of Wiring and Control Units
Wiring serves as the backbone of the electrical system, facilitating communication between components. Control units, such as the ECU, process signals and ensure that each part operates efficiently, ultimately contributing to the vehicle’s reliability and performance.
Accessories and Upgrades Explained
Enhancing your ride often involves selecting additional elements that can improve performance, comfort, and aesthetics. Understanding these enhancements is essential for achieving the ultimate experience on the road.
Types of Enhancements
Upgrades can range from functional modifications, like improved suspension systems, to aesthetic additions, such as custom seats. Each choice serves a distinct purpose, allowing riders to tailor their experience to their preferences.
Benefits of Customization
Investing in enhancements not only boosts the overall functionality but also personalizes the ride. Improved safety features and increased ergonomics contribute significantly to a rider’s enjoyment and confidence on longer journeys.
Maintaining Your Motorcycle Parts
Proper upkeep of your two-wheeled machine is crucial for longevity and performance. Regular attention to various components ensures safety and enhances your riding experience. By adopting a systematic approach, you can prevent wear and tear while optimizing functionality.
Essential Maintenance Tasks
Key activities include routine inspections, lubrication, and timely replacements. Understanding the vital functions of each element allows for targeted care, prolonging the life of your vehicle.
Maintenance Schedule
| Component | Maintenance Frequency | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| Chain | Every 500 miles | Lubricate and adjust tension |
| Tires | Monthly | Check pressure and tread |
| Brakes | Every 1,000 miles | Inspect and replace pads if necessary |
| Oil | Every 3,000 miles | Change oil and filter |