Fuse
Transmission Breakdown and Key Elements
The transmission system is a crucial component in vehicles, responsible for transferring power from the engine to the wheels. Understanding its structure and function is essential for effective maintenance and repair. This section explores the various elements that make up the transmission, highlighting their roles and interconnections.
At the heart of the transmission lies the gearbox, which adjusts the vehicle’s speed and torque. It consists of multiple gears that engage and disengage as needed, allowing for smooth acceleration and deceleration. Additionally, the clutch plays a vital role by enabling the driver to change gears seamlessly. This mechanism temporarily disconnects the engine from the transmission, facilitating gear shifts without damaging the system.
Another key component is the torque converter, which transfers engine power to the transmission while allowing for some slippage. This function is particularly important during stops, as it prevents stalling by maintaining engine speed. Furthermore, the transmission fluid serves as both a lubricant and a coolant, ensuring that the system operates efficiently and at optimal temperatures.
Overall, recognizing the critical parts of the transmission system can aid in diagnosing issues and enhancing the longevity of the vehicle. Proper care and understanding of these elements are essential for any car owner.
Exhaust System Diagram and Components
The exhaust system plays a crucial role in managing emissions and ensuring the efficient operation of the engine. This intricate assembly is designed to channel exhaust gases away from the engine, reducing harmful pollutants and noise levels. Understanding the various components of this system is essential for maintaining optimal vehicle performance and compliance with environmental standards.
Key Elements of the Exhaust Assembly
At the heart of the exhaust system are several critical components that work together seamlessly. The catalytic converter serves to transform harmful gases into less toxic substances before they are expelled into the atmosphere. Following this is the muffler, which minimizes noise produced by the exhaust gases. Additionally, the exhaust manifold collects gases from multiple cylinders and directs them into the system.
Functionality and Maintenance Tips
Regular inspection and maintenance of the exhaust components are vital for ensuring their longevity and efficiency. Signs of wear, such as unusual noises or decreased fuel efficiency, may indicate the need for servicing. Addressing these issues promptly can prevent more extensive damage and costly repairs down the line.
Cooling System Parts Explanation
The cooling system is essential for maintaining optimal engine temperature and preventing overheating. Understanding the various components involved can help ensure proper functioning and longevity of the vehicle’s engine.
Key elements of the cooling system include:
- Radiator: This component dissipates heat from the coolant, allowing it to cool before re-entering the engine.
- Water Pump: Responsible for circulating coolant throughout the engine and radiator, maintaining a consistent flow.
- Thermostat: Regulates the temperature of the coolant, opening and closing to maintain the desired engine temperature.
- Coolant Reservoir: Stores excess coolant and allows for expansion and contraction as temperatures fluctuate.
- Hoses: Flexible tubes that transport coolant between the engine, radiator, and other components.
Each of these components plays a crucial role in ensuring the cooling system operates efficiently. Regular maintenance and checks can prevent potential issues and promote overall vehicle reliability.
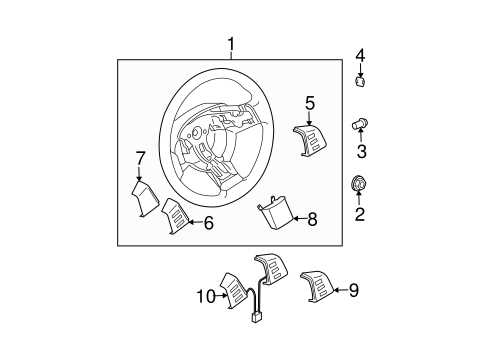
Steering Mechanism Layout
The layout of the steering mechanism is essential for ensuring smooth handling and control of the vehicle. It comprises various components that work together to facilitate precise navigation and maneuverability. Understanding the arrangement and function of these elements can enhance the overall driving experience.
Key Components
- Steering Wheel: The primary interface for the driver, allowing for directional control.
- Steering Column: Connects the steering wheel to the steering gear, transmitting the driver’s input.
- Steering Gear: Converts the rotational motion of the steering wheel into lateral movement of the wheels.
- Linkage System: Connects the steering gear to the wheels, facilitating movement.
Functionality Overview
The steering mechanism operates through a series of interactions among its components. When the driver turns the steering wheel, the motion is transmitted through the column to the steering gear, which then pivots the linkage system. This action adjusts the angle of the wheels, allowing the vehicle to change direction effectively.
Proper maintenance and understanding of the steering assembly are crucial for safety and performance. Regular inspections can help identify potential issues, ensuring reliable operation on the road.
Fuel System Parts Mapping
The fuel delivery network in a vehicle is crucial for optimal performance, ensuring that the engine receives the necessary fuel for combustion. This section provides an overview of the various components involved in this intricate system, highlighting their functions and relationships without delving into specific identifiers.
Fuel Tank: This reservoir holds the fuel, providing a stable supply to the engine. Its design varies based on the vehicle model, influencing fuel capacity and placement.
Fuel Pump: Located within or near the fuel tank, this component is responsible for transferring fuel from the tank to the engine at the required pressure. Its efficiency directly impacts engine performance.
Fuel Filter: Acting as a barrier against contaminants, this filter ensures that only clean fuel reaches the engine. Regular maintenance is essential to prevent clogs that can hinder performance.
Fuel Injector: This device atomizes fuel and injects it into the combustion chamber, playing a vital role in the efficiency of the fuel-air mixture. Proper functioning is critical for effective combustion and power output.
Fuel Lines: These conduits transport fuel between the tank, pump, filter, and injector. Their integrity is crucial to prevent leaks and ensure a consistent flow of fuel.
Regulator: This component maintains optimal fuel pressure within the system, adjusting flow based on engine demand. Its reliability is essential for balanced engine operation.
Understanding these components and their roles in the fuel delivery system is fundamental for diagnosing issues and ensuring smooth vehicle operation.
Air Conditioning System Breakdown
The air conditioning system in a vehicle plays a crucial role in ensuring passenger comfort by regulating temperature and humidity levels. Understanding its components and their functions can enhance maintenance and troubleshooting efforts.
Compressor: This vital component pressurizes the refrigerant and circulates it through the system. It acts as the heart of the air conditioning setup, enabling the cooling process to commence.
Condenser: Located in front of the radiator, the condenser cools and condenses the refrigerant vapor into a liquid. This step is essential for heat exchange, allowing the system to effectively lower cabin temperatures.
Evaporator: Situated inside the cabin, the evaporator absorbs heat from the air, leading to a drop in temperature. As air passes over the evaporator, it cools down before being circulated back into the vehicle.
Expansion Valve: This component regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator. It ensures the right amount of refrigerant is delivered, optimizing the cooling efficiency and preventing system overload.
By familiarizing oneself with these key elements, vehicle owners can better appreciate their air conditioning system’s functionality and identify potential issues that may arise.
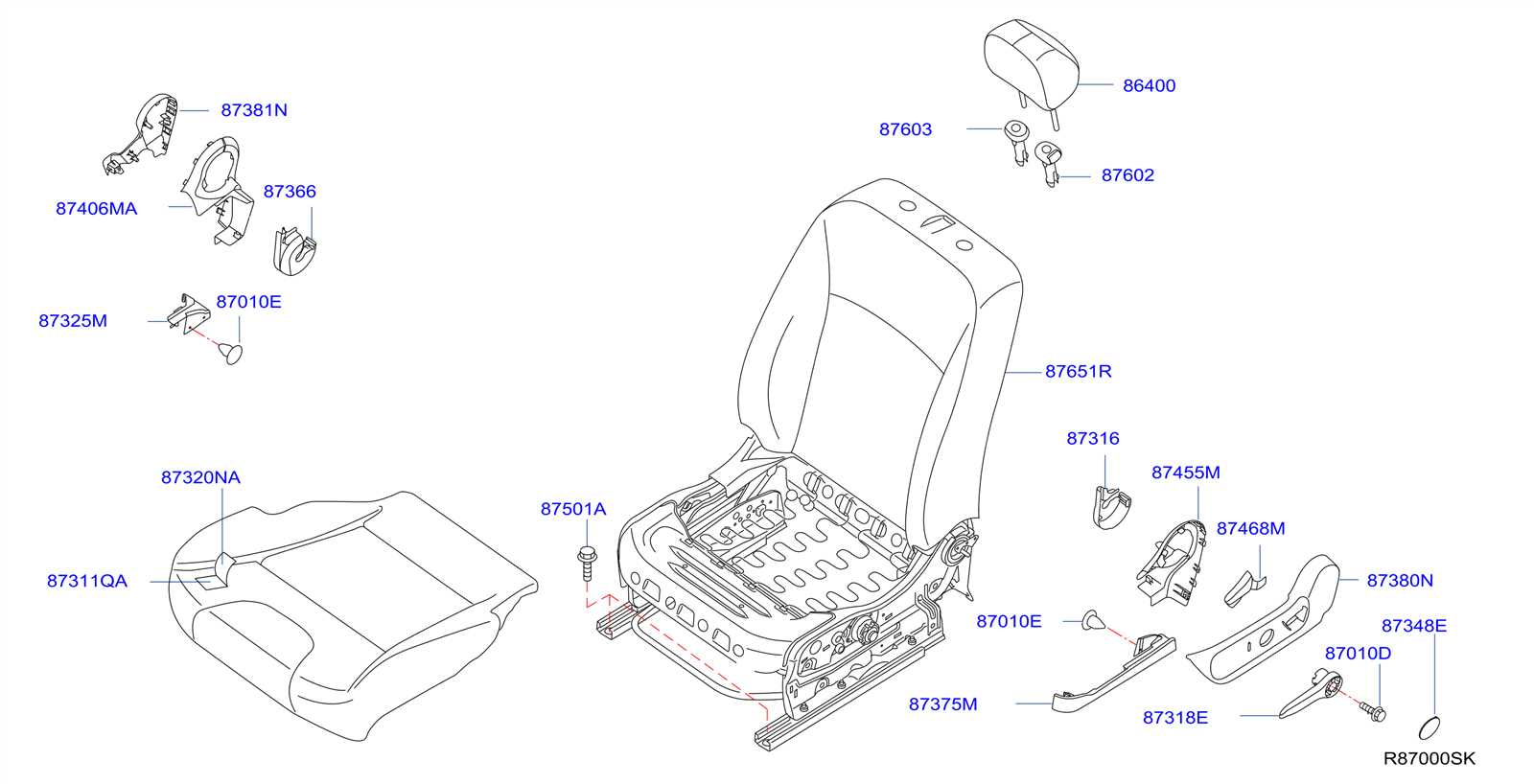
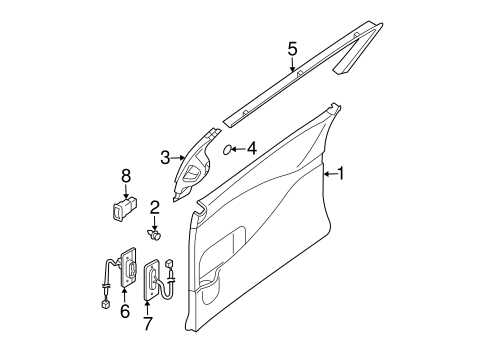
Body Frame Parts Distribution
The distribution of structural components in vehicles plays a crucial role in ensuring overall integrity and safety. This section delves into how various elements are arranged within the frame, contributing to both strength and functionality. Understanding the positioning and interaction of these components is essential for effective maintenance and repair.
Typically, the frame is composed of several key elements, each serving a specific purpose. The primary supports provide the foundation for the vehicle’s structure, while additional reinforcements enhance durability and resistance to external forces. The arrangement of these components is strategically designed to optimize weight distribution, thereby improving handling and stability.
Moreover, the integration of various subassemblies within the frame adds to the complexity of the structure. For instance, attachment points for other systems, such as suspension and drivetrain, are meticulously planned to facilitate seamless operation. Proper understanding of this distribution is vital for mechanics and technicians, as it aids in diagnosing issues and implementing effective solutions.
|