Comprehensive Guide to 2016 GMC Acadia Parts Diagram
When exploring the internal structure of a vehicle, it becomes crucial to understand the interconnected systems that make it run efficiently. Every component, from mechanical to electrical, plays a vital role in the overall performance. This section aims to offer a clear perspective on the essential elements found within a modern SUV, ensuring you have the knowledge to navigate through its intricate framework.
By delving into the various elements of this popular model, we will break down how each individual system contributes to the vehicle’s operation. Whether it’s the engine, transmission, or electrical layout, having a detailed understanding of these core areas can be a game-changer for troubleshooting and maintenance.
Through this overview, you will be better equipped to identify, examine, and replace key units
2016 GMC Acadia Parts Overview
Understanding the key mechanical and electrical elements of this vehicle helps in maintaining and repairing it effectively. These components ensure smooth performance and reliability on the road, covering everything from the engine to interior controls.
Engine and Drivetrain Components
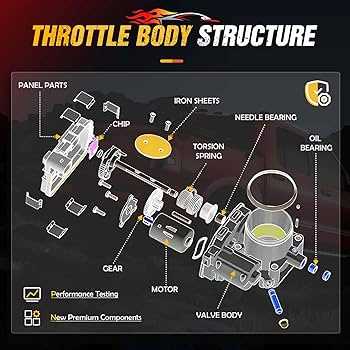
The core of this vehicle’s functionality revolves around the powertrain, including several crucial systems that ensure efficient power distribution and fuel management. The assembly includes various interconnected systems that require regular maintenance to prevent breakdowns.
- Transmission assembly for power transfer
- Fuel injection system for optimal combustion
- Exhaust system to manage emissions
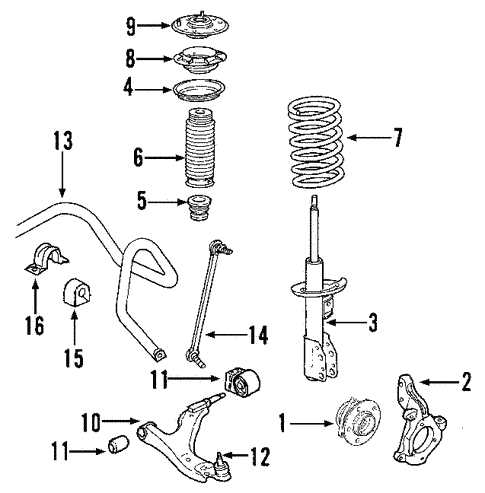
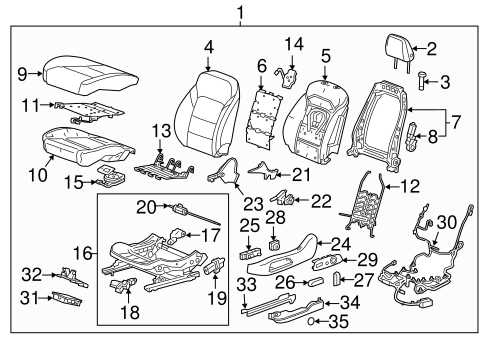
- Control Arms: These pivotal components connect the wheels to the frame, allowing for up-and-down movement while keeping the wheels aligned during turns.
- Shock Absorbers: Responsible for dampening the energy generated by road bumps, these elements prevent excessive bouncing and improve overall ride quality.
- Springs: Coil or leaf springs support the vehicle’s weight and help absorb shocks from uneven road surfaces.
- Stabilizer Bar: Also known as the sway bar, this part reduces body roll during cornering by distributing
Braking Mechanism Overview
The braking system plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and control of the vehicle during motion. It operates by converting kinetic energy into heat, allowing the vehicle to slow down or come to a complete stop. A well-maintained braking setup is essential for optimal performance and reliability in all driving conditions.
Main Components of the System
Several interconnected elements make up the system responsible for halting the vehicle. Each part works in unison to ensure efficient braking response and stability:
- Brake Pedal – The starting point of the process, the driver applies pressure to engage the system.
- Master Cylinder – Transforms the pedal’s motion into hydraulic pressure,
Transmission Parts and Functions
The transmission system plays a vital role in ensuring smooth and efficient power delivery from the engine to the wheels. It is composed of numerous interconnected elements, each designed to manage torque and regulate speed. Understanding these components is key to appreciating how the mechanism operates and maintains vehicle performance.
Key Components

Among the main elements, gears, shafts, and clutches work together to modify the output speed and force. Gears adjust the engine’s power to match driving conditions, while shafts transmit this adjusted power to different parts of the system. Clutches engage and disengage the engine, allowing for seamless transitions between different speed levels.
Functionality
Each part contributes to
Electrical System Diagram
The electrical layout of a vehicle is essential for understanding how different components interact and function together. This section provides an overview of the various elements involved in the electrical infrastructure, including power distribution, circuit pathways, and key connections that ensure the system operates efficiently.
Key Components
Understanding the vital elements that comprise the electrical framework is crucial for troubleshooting and maintenance. The following table outlines some of the primary components and their respective functions:
Component Function Battery Supplies electrical energy to start the engine and power accessories. Alternator Recharges the battery and powers the electrical system while the engine is running. Fuses Protects circuits by breaking the connection in case of overload. Relays Acts as a switch to control high-current devices with a low-current signal. Understanding the Circuit Flow
The flow of electricity throughout the system is guided by various circuits that connect each component. Recognizing how these circuits are structured is vital for effective diagnostics and repairs. Following the pathways will help in identifying issues and ensuring all elements function harmoniously.
Exhaust System Assembly
The assembly of the exhaust system plays a crucial role in the overall performance and efficiency of a vehicle. This component is responsible for directing harmful gases away from the engine and reducing emissions, ensuring that the vehicle operates smoothly and meets environmental standards. Understanding the structure and function of this system is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting, enabling owners to keep their vehicles in optimal condition.
Key Components of the Exhaust System
Several key elements comprise the exhaust assembly, each serving a distinct purpose. The exhaust manifold collects gases from the engine cylinders and directs them into the exhaust pipes. Following this is the catalytic converter, which plays a vital role in minimizing harmful emissions by converting toxic substances into less harmful gases. Finally, the muffler reduces noise produced by the exhaust gases, ensuring a quieter operation.
Importance of Proper Assembly
Correct assembly of the exhaust components is vital for the system’s efficiency and the vehicle’s overall performance. Any misalignment or improper installation can lead to leaks, increased emissions, and reduced engine power. Regular inspections and maintenance of the exhaust assembly can prevent potential issues, ensuring that the vehicle remains compliant with emission regulations and operates at its best.
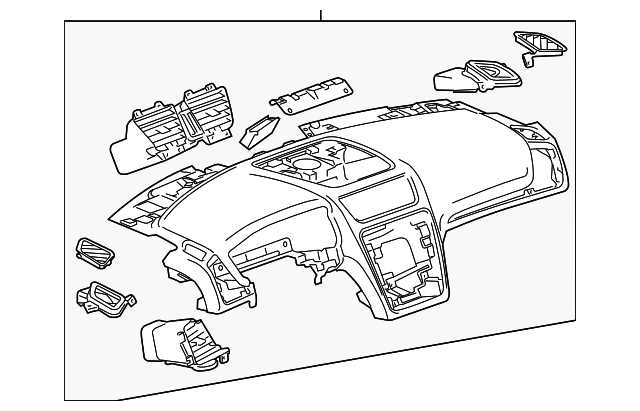
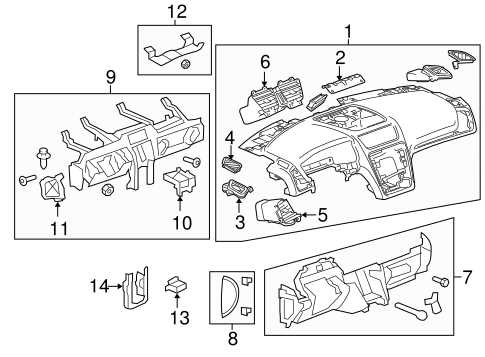
Interior Features and Controls
The cabin of modern vehicles is designed to offer comfort and convenience, integrating a variety of functionalities that enhance the driving experience. These features encompass both aesthetic and practical elements, providing users with an engaging environment while on the road.
Key Components
- Infotainment System
- Climate Control
- Instrument Cluster
- Seating Arrangements
Each of these elements plays a significant role in ensuring a seamless interaction between the driver and the vehicle. The infotainment system typically serves as the central hub for navigation, entertainment, and connectivity.
User Controls
- Touchscreen Interface
- Steering Wheel Controls
- Physical Buttons and Knobs
Control mechanisms are designed for ease of access and functionality, allowing drivers to adjust settings without distraction. Understanding these controls can enhance the overall driving experience and improve safety on the road.
Cooling and Heating System
The climate control system plays a crucial role in ensuring comfort within a vehicle’s cabin. It operates by regulating the temperature and airflow, providing a pleasant environment for occupants, regardless of external weather conditions.
This system consists of several key components that work together to maintain optimal temperatures:
- Compressor: This component compresses refrigerant gas, allowing it to flow through the system.
- Condenser: Located in front of the radiator, it cools and converts the refrigerant from gas to liquid.
- Evaporator: This unit absorbs heat from the cabin air, providing a cooling effect when the refrigerant evaporates.
- Heater Core: Similar to a small radiator, it warms the air using engine coolant, contributing to the heating process.
- Blower Motor: This fan circulates air through the system, directing it to various vents within the vehicle.
Maintenance of the climate control system is vital for its efficient operation. Here are some important practices to consider:
- Regularly check and replace the cabin air filter to ensure proper airflow.
- Inspect refrigerant levels and recharge if necessary to maintain cooling efficiency.
- Examine hoses and connections for leaks or damage that could affect system performance.
- Test the heater and air conditioning functions periodically to confirm they are operating correctly.
Understanding the workings of this system and adhering to maintenance guidelines can enhance comfort and prolong the lifespan of the vehicle’s climate control features.
Fuel System Components
The fuel system in a vehicle is crucial for delivering the right amount of fuel to the engine, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. Understanding the various elements involved in this system helps in diagnosing issues and performing maintenance effectively.
- Fuel Tank: This is the storage unit for gasoline or diesel, designed to keep fuel safe and secure.
- Fuel Pump: An essential component that transfers fuel from the tank to the engine, typically electric or mechanical in nature.
- Fuel Filter: Responsible for removing impurities from the fuel before it reaches the engine, thus protecting vital components.
- Fuel Injectors: These devices atomize the fuel, spraying it into the combustion chamber for efficient mixing with air.
- Fuel Lines: Tubes that transport fuel between the tank, pump, filter, and injectors, designed to withstand pressure and prevent leaks.
Each of these components plays a significant role in the functionality of the fuel delivery system, impacting overall engine performance and reliability.
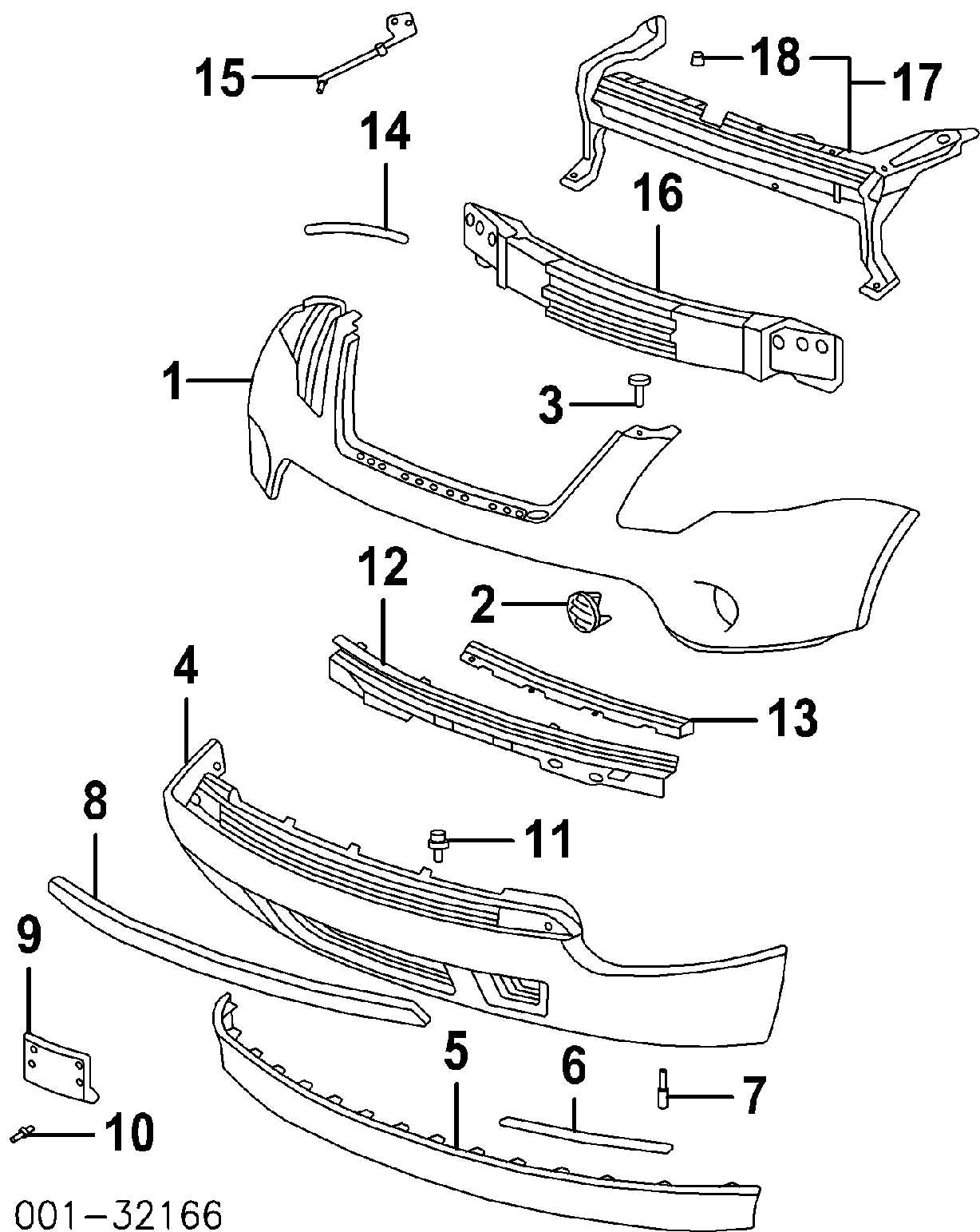
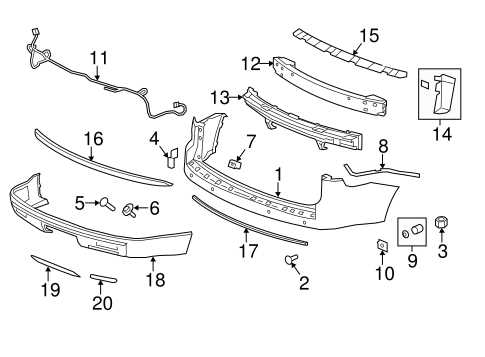
Body Frame and Exterior Parts
The structure of a vehicle is essential for its performance, safety, and aesthetic appeal. This section delves into the various components that make up the outer shell and framework, emphasizing their roles and interactions. Understanding these elements is crucial for maintenance and repairs, ensuring longevity and optimal functionality.
Framework Structure
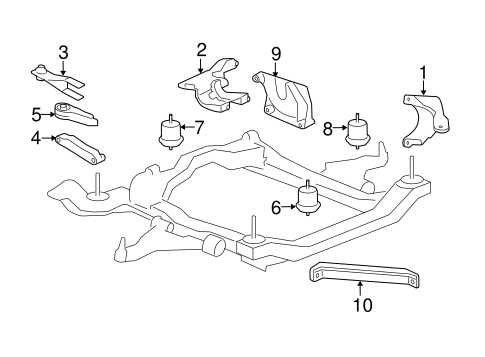
The framework serves as the backbone of the vehicle, providing strength and stability. It consists of several key sections that contribute to the overall integrity. These include crossmembers, rails, and pillars, each engineered to absorb impacts and distribute forces. Regular inspections of these components can help identify wear and tear, allowing for timely interventions to enhance safety.
Exterior Components
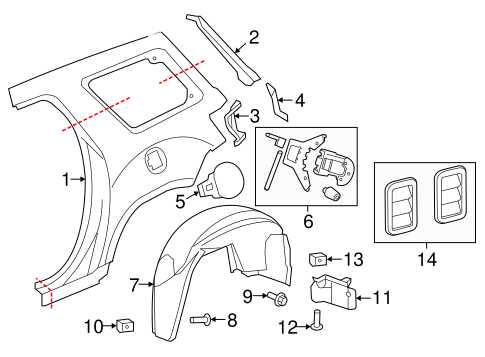
The outer components not only define the vehicle’s appearance but also contribute to its aerodynamics and functionality. This includes panels, bumpers, and fenders, which are designed to protect internal mechanisms while also enhancing visual appeal. Proper alignment and maintenance of these elements are vital to prevent damage and ensure a smooth driving experience.
Steering System Diagram
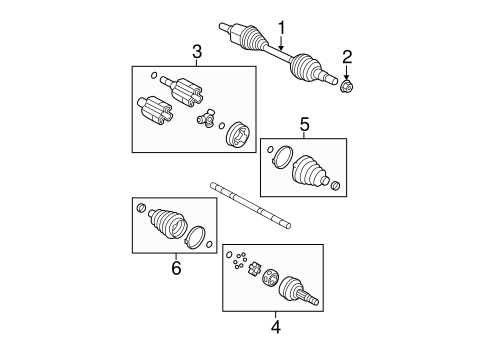
The steering assembly is a crucial component that enables drivers to maneuver their vehicle effectively. Understanding the layout and functionality of this system can enhance maintenance and troubleshooting efforts. A comprehensive overview of the steering structure reveals various interconnected elements that work in unison to ensure precise handling and responsiveness.
Key Components
Among the essential parts of the steering mechanism are the steering wheel, column, rack and pinion, and tie rods. The steering wheel serves as the primary interface for the driver, translating rotational movement into steering action. The column connects the wheel to the rack and pinion, facilitating the transfer of force. The rack and pinion assembly converts the rotational motion into linear movement, while the tie rods link the assembly to the wheels, ensuring directional control.
Functionality Overview
This assembly operates through a series of mechanical interactions that allow for smooth and responsive steering. When the driver turns the steering wheel, the motion is transmitted down the column to the rack and pinion. This mechanism then shifts the tie rods, which in turn pivot the wheels. The entire system is designed to provide a balance between comfort and control, making it vital for safe driving experiences.
Lighting and Signal System
The lighting and signaling framework of a vehicle plays a crucial role in ensuring safety and communication on the road. This system encompasses various components designed to provide visibility in low-light conditions and convey the driver’s intentions to other road users.
Headlights are essential for illuminating the path ahead, allowing the driver to navigate safely during nighttime or adverse weather conditions. They come in different styles, including halogen, LED, and xenon, each offering distinct advantages in brightness and energy efficiency.
Taillights serve as a vital signaling mechanism, alerting following vehicles to the presence of a vehicle and its actions. The incorporation of brake lights enhances safety by indicating deceleration, while turn signals provide critical information about directional changes.
In addition, fog lights are specifically designed to improve visibility in foggy or rainy conditions, minimizing the risk of accidents. The configuration of the lighting and signaling components contributes to the overall effectiveness of the vehicle’s safety measures.
Regular maintenance of the lighting and signaling system is essential to ensure proper functionality. Drivers should routinely check all bulbs and connections to avoid any failures that could compromise road safety.
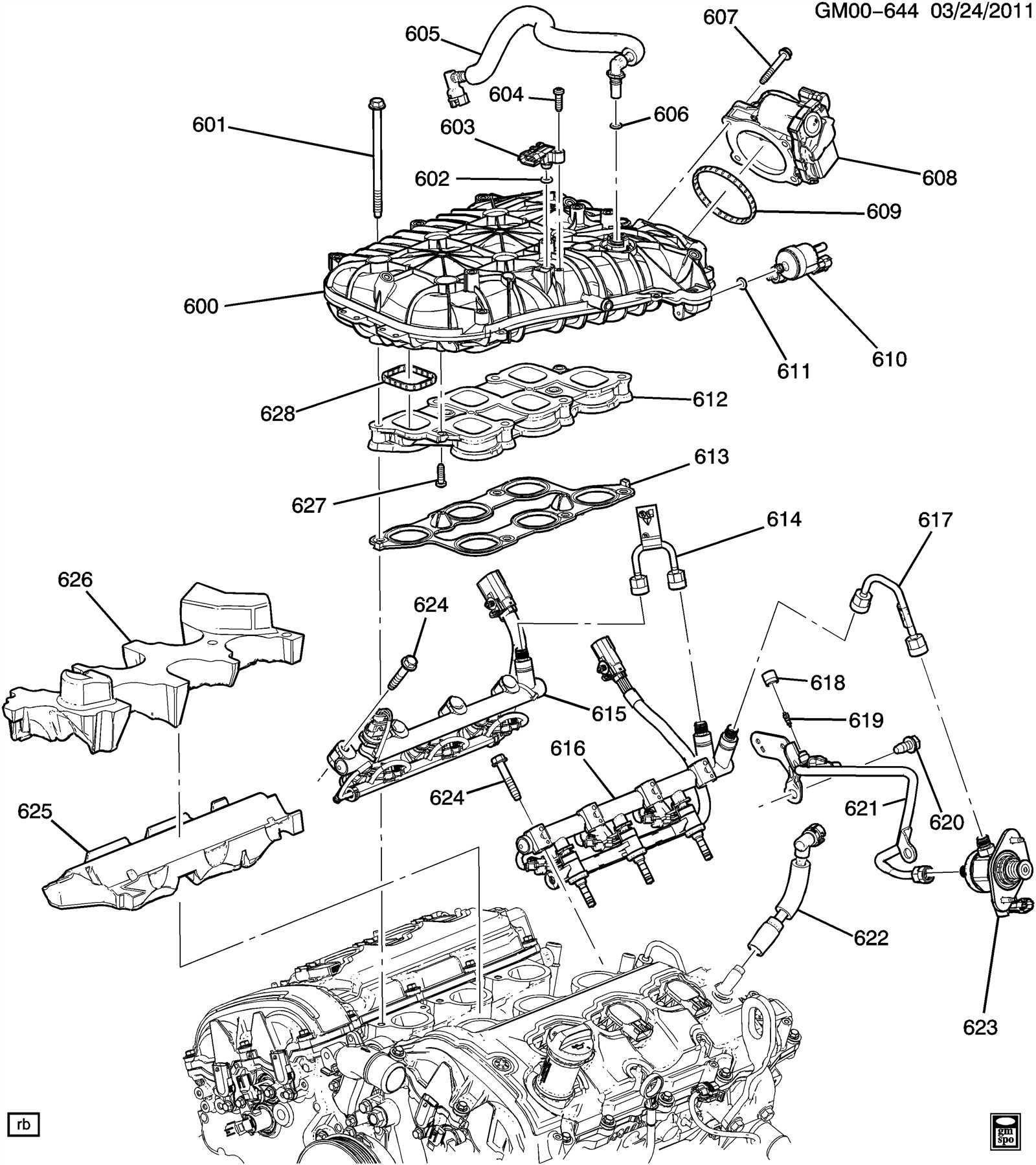
Engine Components Breakdown
The engine is a complex system composed of various interconnected elements that work together to ensure optimal performance. Understanding how each of these components functions within the larger mechanical structure can provide valuable insights into how the entire system operates and what is required to keep it running smoothly.
Key Sections of the Engine

At the heart of the engine is the cylinder block, which houses essential parts like pistons and the crankshaft. The block serves as the foundation for many other critical components and is designed to endure significant levels of pressure and heat. Additionally, the cylinder head sits atop the block, sealing the combustion chamber and controlling airflow with valves that open and close at precise intervals.
Supporting Systems
Beyond the primary structure, several auxiliary systems contribute to the engine’s performance. These include the fuel
Suspension System Layout
The suspension system is a critical component of vehicle functionality, ensuring a smooth and controlled ride by absorbing shocks and maintaining proper tire contact with the road. This section explores the key elements that work together to provide stability, handling, and comfort for both drivers and passengers.