Understanding the Components of an Air Impact Wrench
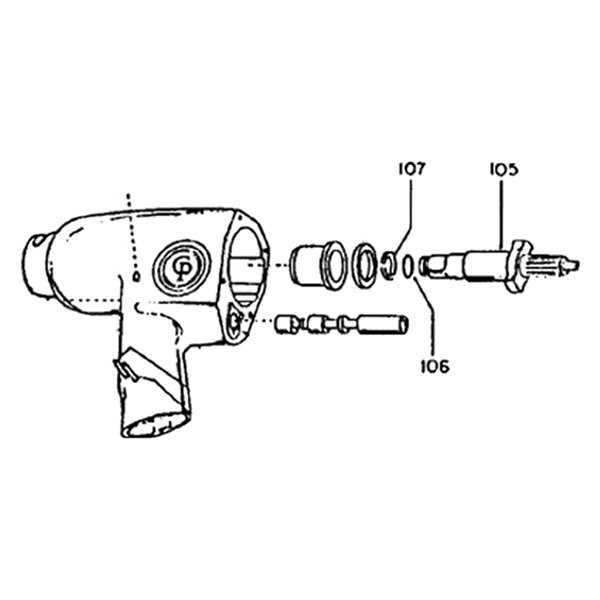
In the realm of power tools, a thorough grasp of individual components is essential for effective operation and maintenance. Each segment plays a crucial role in enhancing performance and ensuring longevity, making it vital to familiarize oneself with their functions and interconnections.
Visual representations serve as an ultimate resource for those looking to deepen their knowledge. By examining these illustrations, users can identify how various elements interact and contribute to overall efficiency.
Moreover, recognizing the significance of each component not only aids in troubleshooting but also empowers users to make informed decisions when selecting replacements or upgrades. This foundational understanding is key to maximizing the utility of these indispensable tools.
Understanding Air Impact Wrench Functionality
This section explores the essential mechanisms behind a powerful tool that delivers high torque output, often utilized in various industrial and automotive applications. Understanding its operation can enhance efficiency and effectiveness during tasks that require significant force.
Core Components
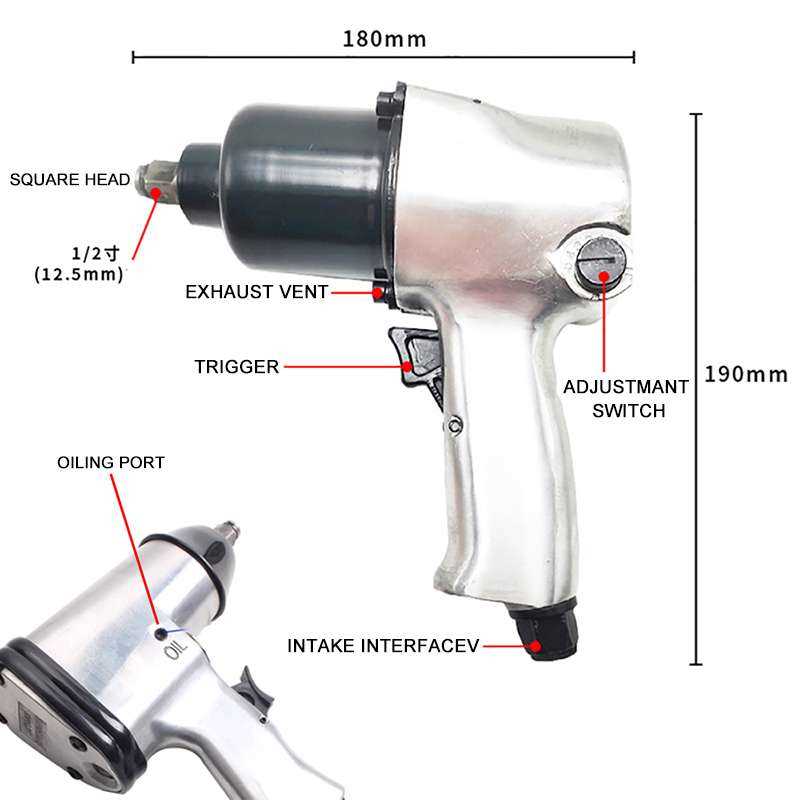

- Motor: Drives the internal mechanisms.
- Hammer Mechanism: Generates the impact force.
- Drive Socket: Connects to fasteners.
- Exhaust System: Releases air after use.
Operational Principles
- Compressed air powers the motor.
- The hammer mechanism rapidly strikes the drive socket.
- This creates a high-torque output that loosens or tightens fasteners efficiently.
- Exhaust air is expelled, keeping the tool cool.
Key Components of Air Impact Wrenches
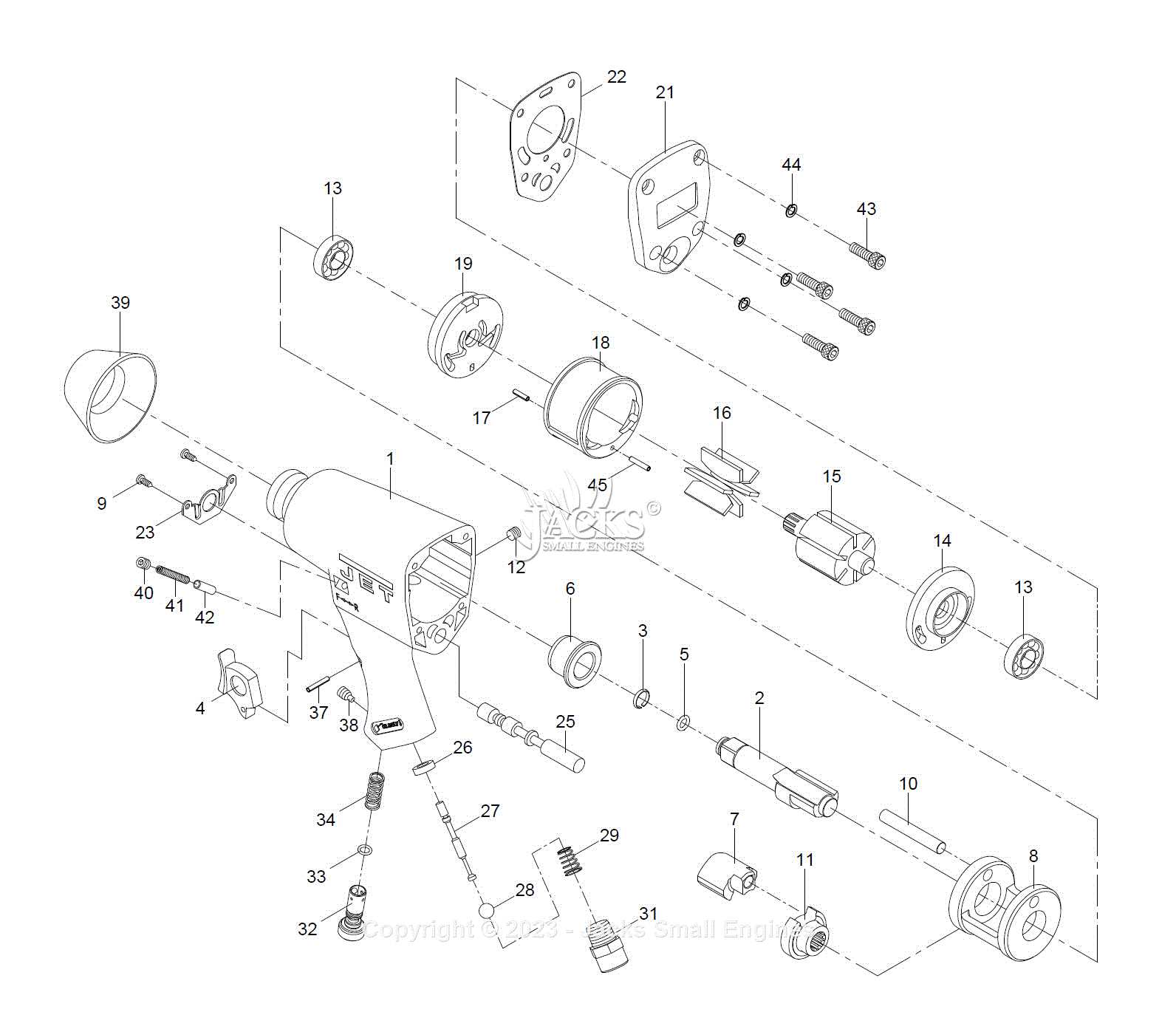
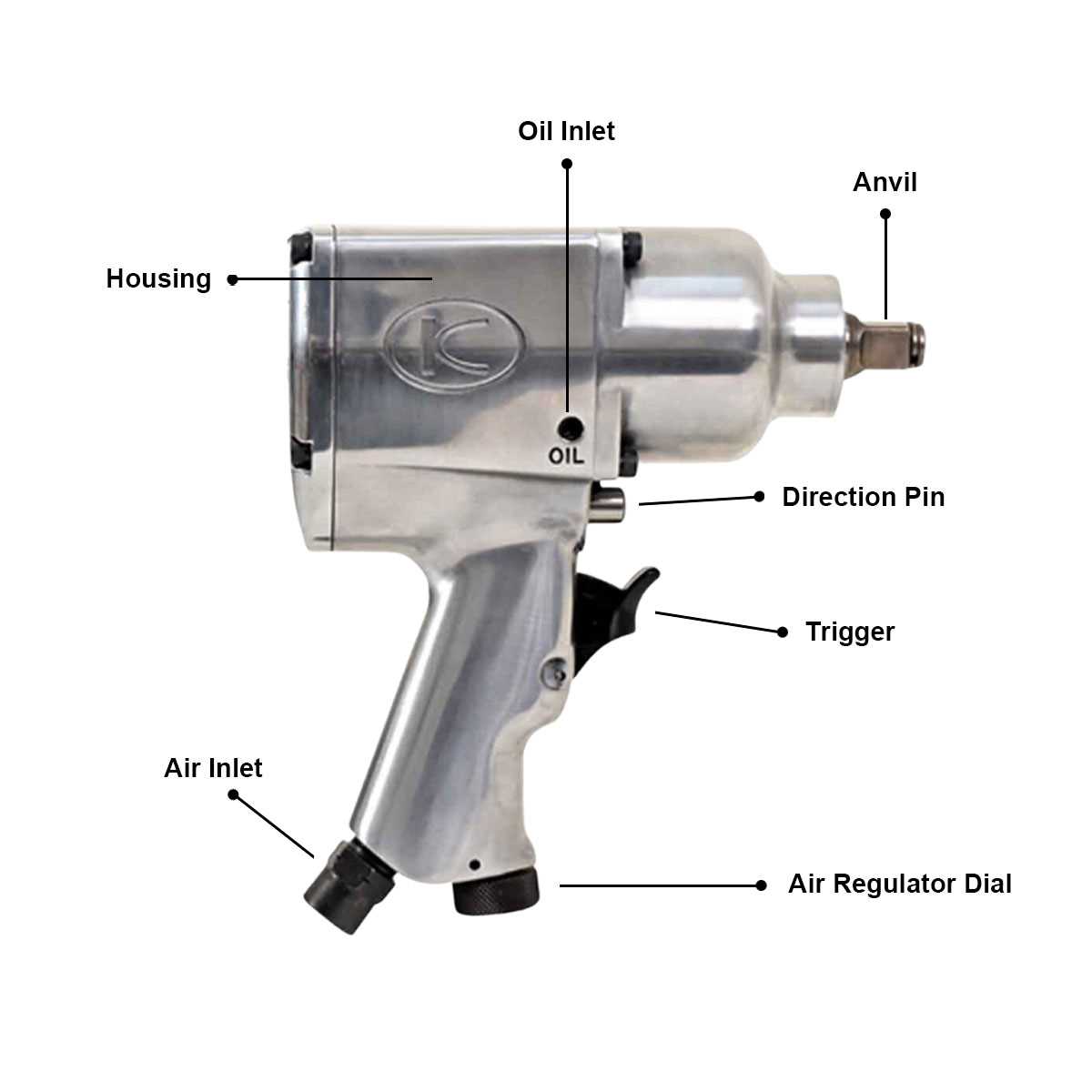
Understanding the essential elements of these powerful tools is crucial for effective usage and maintenance. Each component plays a significant role in the overall functionality and performance, contributing to the efficiency and power of the tool. Familiarity with these key parts enables users to troubleshoot issues and optimize their operation.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Motor | Generates rotational force, driving the tool’s output. |
| Anvil | The part that holds and transmits torque to the fastener. |
| Housing | Encases the internal mechanisms, providing protection and durability. |
| Trigger | Controls the activation and speed of the tool’s operation. |
| Air Inlet | Where compressed air enters the tool, powering its functions. |
| Exhaust Port | Releases air after use, often designed to direct exhaust away from the user. |
| Clutch | Regulates torque output, allowing for precise fastening and loosening. |
Types of Air Impact Wrench Designs
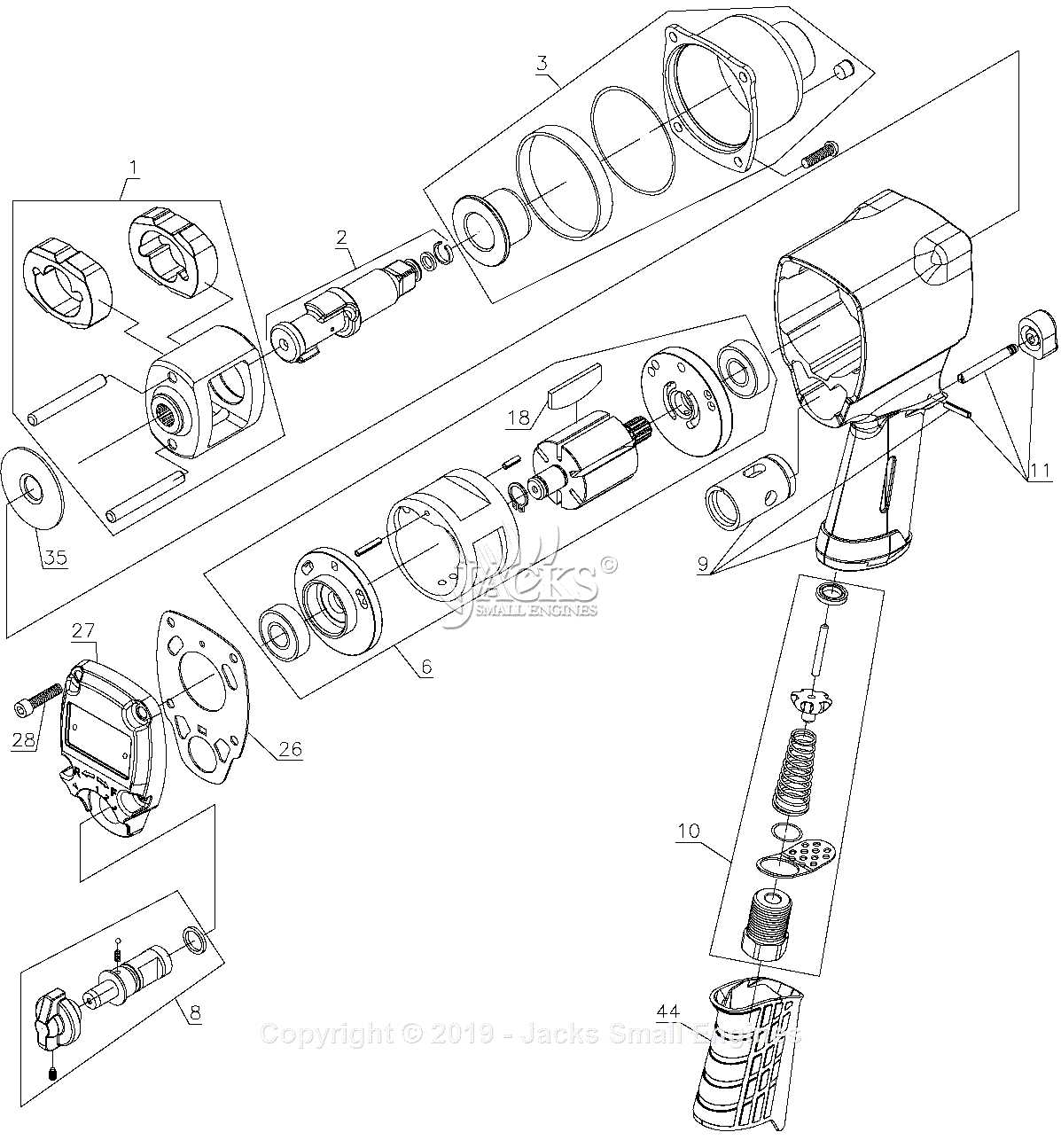
This section explores various designs commonly found in pneumatic tools used for fastening tasks. Each design offers distinct advantages and applications, catering to different user needs and environments.
- Pinless Design: This configuration utilizes a unique mechanism that enhances durability and reduces maintenance.
- Twin Hammer Design: Known for its efficiency, this model features two hammers that deliver a powerful force, making it ideal for heavy-duty operations.
- Single Hammer Design: A simpler mechanism that provides adequate torque for lighter applications, offering ease of use.
- Composite Design: Constructed with lightweight materials, this design reduces fatigue and increases maneuverability for prolonged use.
Understanding these variations allows users to select the most suitable option for their specific requirements, ultimately enhancing performance and productivity.
Importance of Torque Specifications
Understanding the significance of torque specifications is crucial in ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of any fastening tool. Proper torque settings prevent damage to components and enhance the safety and reliability of mechanical assemblies.
Precision in Applications
In various applications, adhering to the correct torque values guarantees that connections are neither too loose nor excessively tight. This precision is vital for maintaining structural integrity and avoiding premature wear or failure.
Impact on Performance
Moreover, following recommended torque specifications improves overall performance. It minimizes the risk of slippage or loosening over time, thereby ensuring that machinery operates smoothly and efficiently. Neglecting these guidelines can lead to costly repairs and safety hazards.
Diagram Overview of Air Impact Wrenches
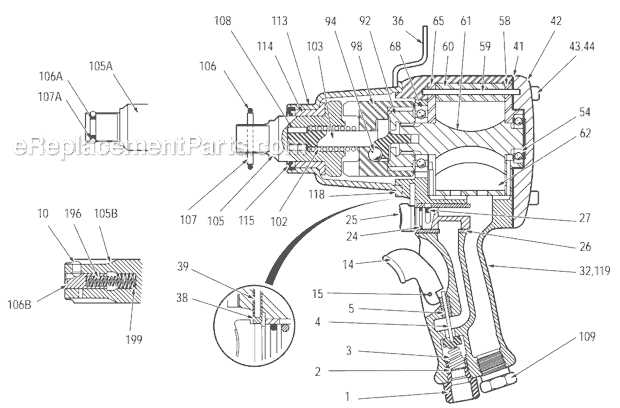
This section explores the essential components and their functions within a pneumatic tool designed for high-torque applications. Understanding these elements is crucial for effective usage and maintenance, enabling users to achieve optimal performance.
Key Components
Each tool consists of a motor, a casing, and an output mechanism. The motor generates power, while the casing houses the internal mechanisms. The output mechanism translates the motor’s energy into rotational force, making it indispensable for various tasks.
Functionality and Maintenance
Grasping how these components interact enhances user experience and efficiency. Regular upkeep of each part ensures longevity and reliability, ultimately leading to better results in demanding environments.
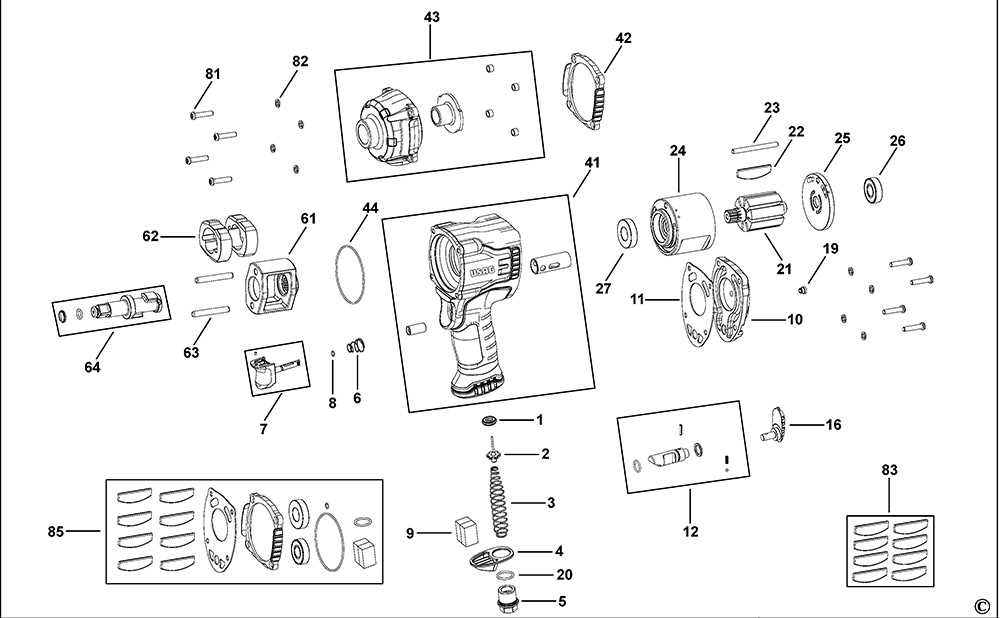
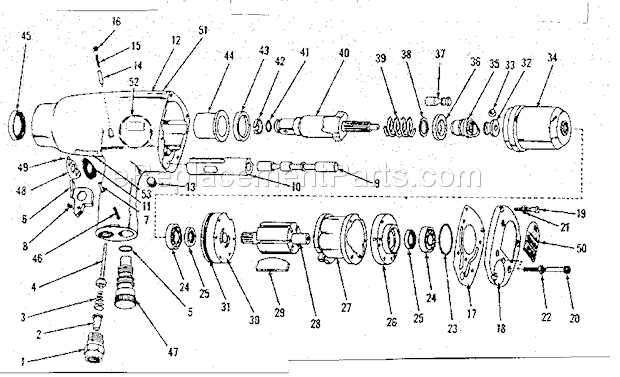
How to Read the Parts Diagram
Understanding the layout of a tool’s components is essential for effective maintenance and repairs. By familiarizing yourself with the visual representation, you can easily identify each element and its function, ensuring a smoother workflow when servicing the device.
Key Elements to Identify
When examining the illustration, focus on the numbered sections that correspond to individual components. This will help you grasp the relationships between various elements and their specific roles in the overall mechanism.
Using the Legend
The accompanying legend serves as a crucial reference. It typically lists the components along with their part numbers and descriptions, enabling you to locate replacements or understand the assembly better.
| Component Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Housing |
| 2 | Motor |
| 3 | Trigger |
| 4 | Gear Set |
Common Wear and Tear Issues
Tools subjected to high torque and repetitive motion often experience degradation over time. Understanding these issues is crucial for maintaining efficiency and extending the lifespan of your equipment.
- Seals and Gaskets: These components can become brittle, leading to leaks and reduced performance.
- Bearings: Over time, bearings may wear out, resulting in increased friction and noise during operation.
- Drive Mechanism: The internal drive system can experience wear, affecting torque delivery and consistency.
- Housing: Cracks and dents in the outer casing can compromise structural integrity and safety.
- Fasteners: Loose or stripped fasteners can cause components to misalign, leading to malfunction.
Regular inspection and timely replacement of these elements are vital for optimal performance.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Proper upkeep of your tools is essential for ensuring their durability and optimal performance. By following a few straightforward practices, you can significantly extend the lifespan of your equipment and maintain its effectiveness over time.
Regular Cleaning
- Remove dust and debris after each use.
- Use compressed air to clear out any internal components.
- Wipe down external surfaces with a soft cloth.
Lubrication
- Apply the recommended lubricant to moving parts regularly.
- Check for any signs of wear and replace lubricant as necessary.
- Avoid over-lubricating, which can attract dirt and grime.
Comparing Pneumatic and Electric Tools
This section explores the differences between two popular categories of tools used for heavy-duty tasks. Each type brings unique advantages and disadvantages, impacting performance, efficiency, and usability in various settings.
Performance and Efficiency
Pneumatic devices are known for their high torque output and faster operation, making them ideal for intensive applications. Conversely, electric tools provide ease of use and portability, although they may not match the sheer power of their pneumatic counterparts.
Maintenance and Cost
When considering maintenance, pneumatic tools generally require more upkeep due to the necessity of an air compressor and regular lubrication. Electric options tend to be simpler and less costly over time, as they don’t rely on additional equipment.
| Feature | Pneumatic Tools | Electric Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Power Output | High torque | Moderate torque |
| Portability | Requires compressor | Easy to transport |
| Maintenance | More frequent | Less frequent |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower initial investment |
Safety Precautions When Using Tools

Ensuring safety during tool operation is crucial for preventing accidents and injuries. Proper precautions help create a secure environment, enabling users to work effectively while minimizing risks associated with equipment handling. Awareness of potential hazards and adherence to safety guidelines play a vital role in promoting a safe workspace.
Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as safety goggles, gloves, and hearing protection. This gear acts as a barrier against debris, noise, and other harmful elements that can cause injury. Additionally, maintain a clean and organized workspace to reduce the likelihood of slips and falls.
Before starting any task, familiarize yourself with the tool’s manual and operational procedures. Understanding how to properly operate and maintain the equipment is essential for safe usage. Regularly inspect tools for any signs of wear or damage, and do not use faulty equipment; instead, report and repair it immediately.
It’s important to maintain focus while working. Avoid distractions and never rush through tasks. If you feel fatigued or unwell, take a break or postpone the work until you are in a suitable condition to continue. Lastly, ensure that all safety features of the equipment are functional before use, as these mechanisms are designed to protect the user.
Troubleshooting Common Problems

When working with powerful tools, encountering issues can be a frustrating experience. Understanding typical challenges and their solutions is essential for maintaining efficiency and extending the lifespan of your equipment. Below are some common issues you may face and practical steps to resolve them.
Low Performance
If you notice that the tool is not delivering the expected power, consider the following factors:
- Check the air supply for adequate pressure.
- Inspect hoses for any kinks or blockages.
- Examine the fittings for leaks, which can reduce performance.
Unusual Noises
Strange sounds can indicate internal problems. Take these actions to diagnose the issue:
- Listen for grinding noises, which may suggest worn bearings.
- Identify rattling sounds that could point to loose components.
- Ensure all fasteners are tightened and secure.
Addressing these issues promptly will help you maintain optimal performance and prevent further complications.
Choosing the Right Impact Wrench
Selecting the ideal tool for heavy-duty fastening tasks can significantly enhance efficiency and productivity. Understanding the key features and specifications will guide you toward the ultimate choice that meets your specific needs.
Understanding Specifications
When exploring options, consider factors like torque, speed, and size. Torque determines the tool’s power, while speed affects how quickly you can complete a task. Make sure to choose a size that feels comfortable and manageable for prolonged use.
Assessing Your Needs
Evaluate the types of projects you typically undertake. If you often work on vehicles or construction, a model with higher torque capabilities is essential. For lighter tasks, a more compact version may suffice, allowing for greater maneuverability and ease of use.
Advancements in Impact Wrench Technology
Recent innovations have transformed the landscape of high-torque tools, enhancing efficiency and performance across various industries. These developments focus on improving power delivery, reducing weight, and increasing user comfort.
- Brushless motors for longer life and better energy efficiency
- Smart technology integration for precision control
- Ergonomic designs to minimize user fatigue
- Enhanced durability through advanced materials
Ultimately, these advancements contribute to increased productivity and safety in demanding environments, allowing users to tackle tough tasks with greater ease.