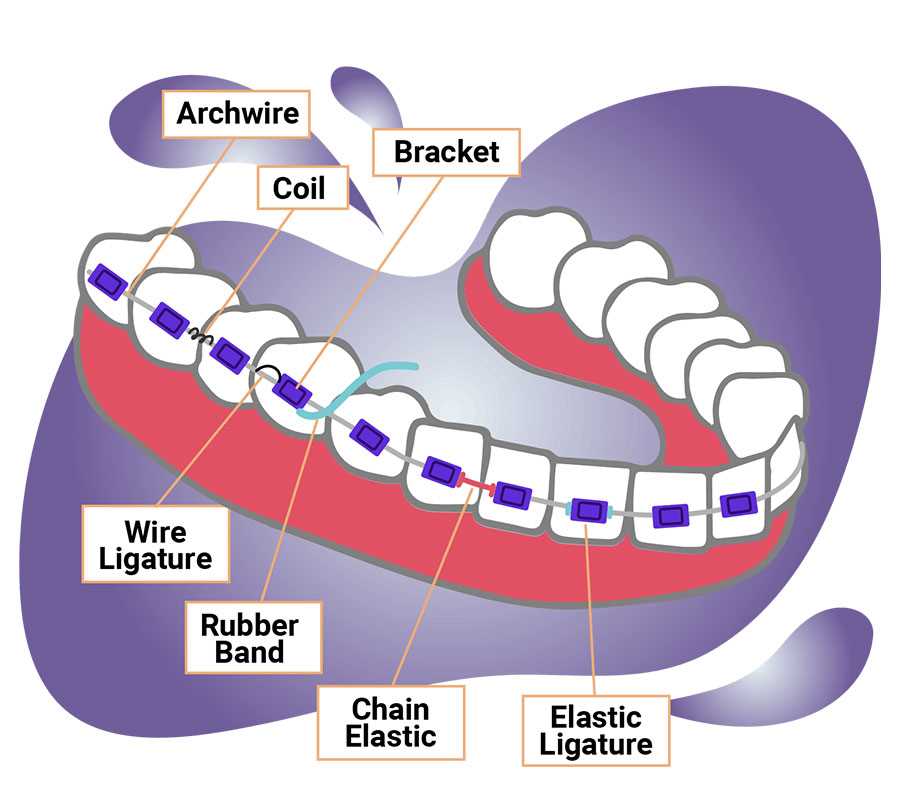
Understanding the Parts of Braces Diagram
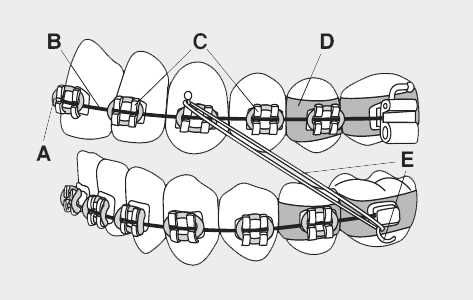
When undergoing treatment to correct dental alignment, it’s essential to be aware of the various elements involved. These devices consist of multiple intricate pieces, each serving a distinct role in guiding the teeth into their optimal position. Recognizing how these components work together helps to demystify the process and can provide insight into how they achieve lasting results.
Each piece of the dental appliance plays a crucial part in adjusting the teeth. Some elements are designed to apply gentle pressure, while others help maintain the structure or provide support for neighboring pieces. Together, they create a system that steadily transforms the smile, ensuring proper alignment over time.
Understanding these details can empower those undergoing treatment, making the journey smoother and more predictable. Knowing how these mechanisms interact offers a clearer view of the overall strategy used to achieve a healthy, well-aligned dental structure.
Understanding the Key Components of Braces
Orthodontic devices consist of several crucial elements that work together to help align teeth and improve oral health. Each of these elements plays a unique role in guiding the process, making it important to understand how they interact to achieve the desired results.
Main Elements and Their Functions
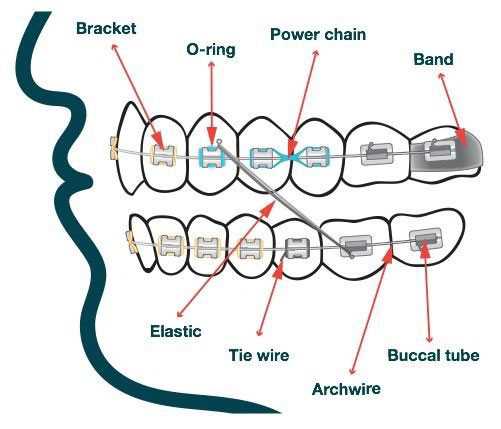
- Fasteners: These are small attachments that are bonded directly to each tooth, providing a secure base for other components to connect.
- Connecting Wires: Thin, flexible lines that run through the fasteners, applying the necessary pressure to gradually shift tooth positions.
- Elastic Bands: These small rings provide additional force, helping to adjust bite and ensure proper alignment over time.
Additional Support Components

- Hooks: Often found near the molars, these allow for extra elastic bands to be attached, providing more precise adjustments.
- Arch Anchors: These provide stability at the ends of the connecting wires, ensuring the structure remains secure during the adjustment process.
Archwires: The Backbone of Braces
Archwires play a critical role in guiding the alignment process during orthodontic treatment. These metal wires are responsible for applying the necessary pressure to shift teeth into their desired positions over time. Their flexibility and shape memory allow them to maintain consistent tension, gradually adjusting dental structures as they are secured to the other components of the appliance.
Different types of archwires are used throughout treatment, each with specific characteristics tailored to various stages of correction. These wires vary in materials, thickness, and strength, impacting the overall effectiveness and comfort of the procedure.
| Type | Material | Stage of Use | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nickel-Titanium | Flexible alloy | Initial phase | ||||||||||||||||||
| Stainless Steel | Strong metal | Intermediate phase | ||||||||||||||||||
| Beta-Titanium | Moderately stiff | Final adjustments |
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Metal Slot | Holds the guiding wire in place, directing tooth movement. |
| Base Pad | Adheres to the tooth surface, ensuring secure attachment. |
| Hooks | Provide anchor points for additional supporting elements, enhancing stability. |
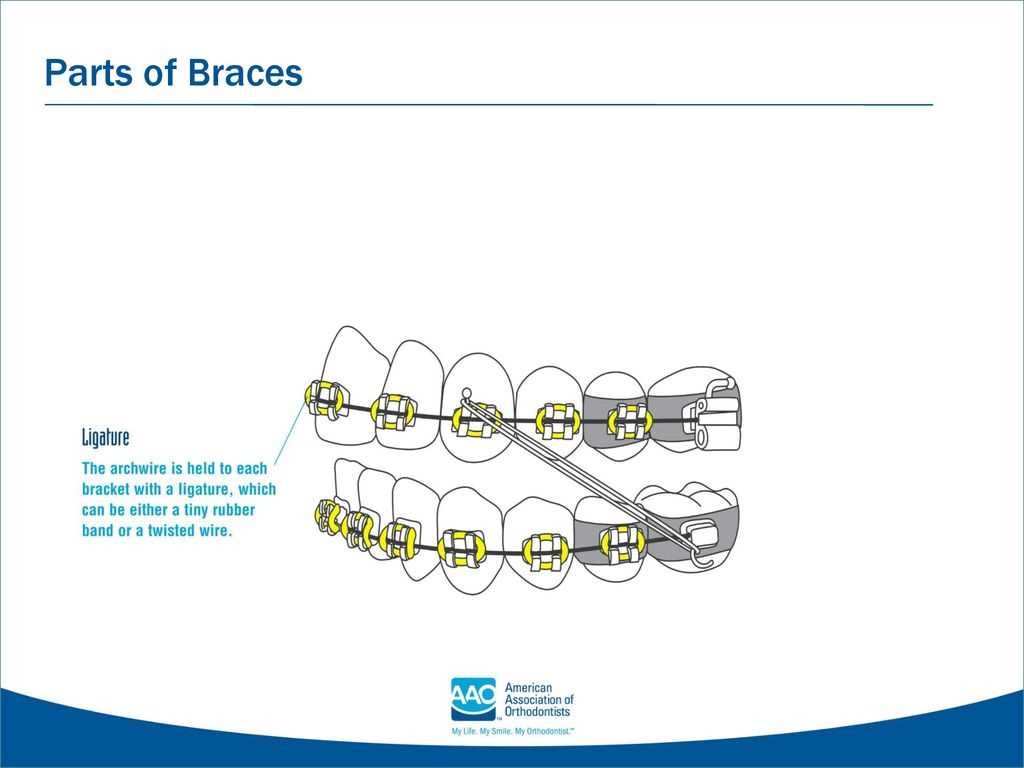
Elastic Ligatures: Securing the Archwire
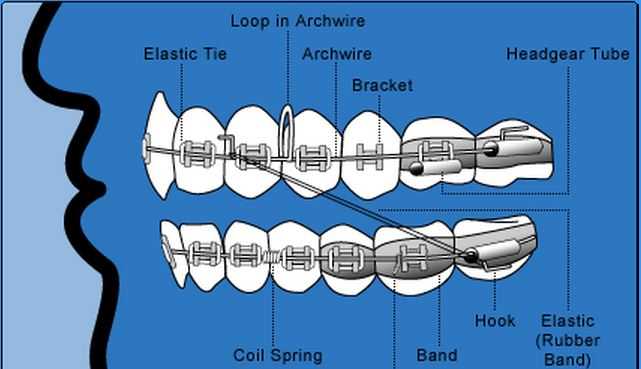
Elastic ligatures play a crucial role in maintaining the positioning of the wire, ensuring that it remains firmly attached to the support structure. These small, flexible loops are essential for holding everything in place, allowing for gradual alignment over time. By using elastic ties, the wire can be adjusted to apply gentle pressure where needed, aiding in the overall process of reshaping.
How Elastic Ligatures Work
- They are placed around individual points, ensuring the wire stays aligned.
- The elasticity helps distribute tension evenly across the structure.
- They can be replaced easily during routine adjustments.
Materials and Durability
Elastic ties are usually made of medical-grade rubber or synthetic materials, designed for durability and flexibility. While they are strong, regular checkups ensure they are functioning properly and can be changed if needed to maintain effectiveness.
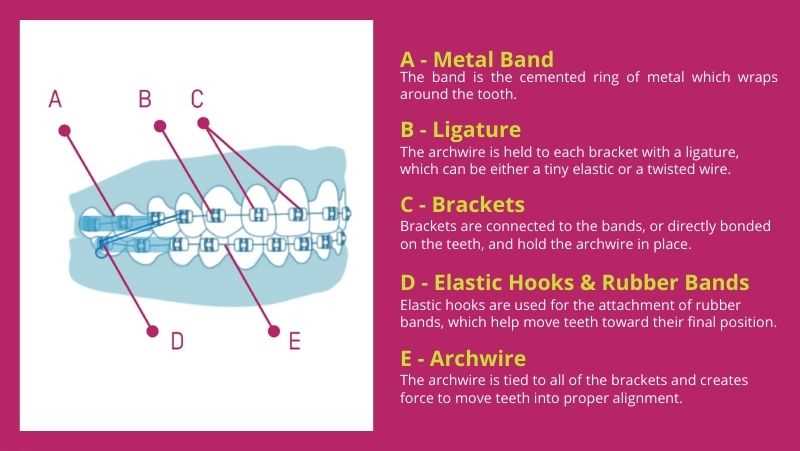
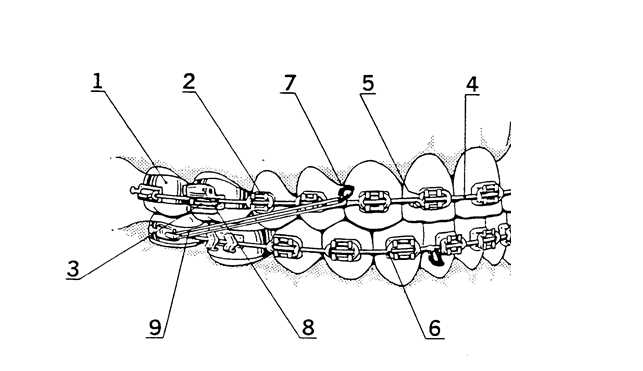
Metal Bands: Anchoring Molar Brackets
Metal bands play a crucial role in supporting key components placed around molar teeth. These small, sturdy rings are designed to encircle the back teeth, providing a strong foundation for further attachments. This secure framework ensures that any adjustments made to the alignment process are stable and effective.
Strength and Stability
The primary function of metal bands is to offer firm anchorage. By fitting tightly around the molars, they act as a base for elements needed in the correction of dental alignment. This reinforcement helps distribute force evenly, which is essential for guiding proper adjustments over time.
Durability and Comfort
Made from durable materials, metal bands are designed to withstand constant pressure. They are carefully placed to minimize discomfort while offering the necessary strength for long-term treatment. Their robust design ensures they remain effective throughout the duration of the process.
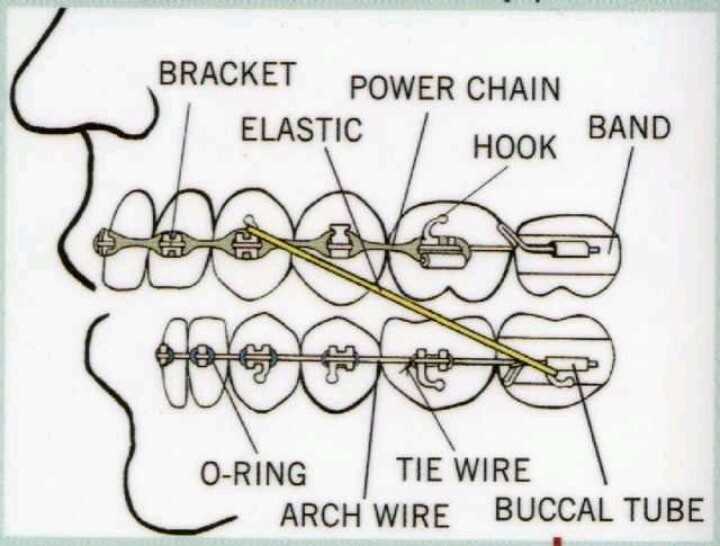
Power Chains: Enhancing Tooth Movement
Power chains are essential components utilized in orthodontic treatment to facilitate the movement of teeth. They consist of a series of connected elastic links that apply consistent pressure, aiding in the alignment and positioning of dental structures. By leveraging the unique properties of these elastic materials, orthodontists can achieve more efficient and effective results throughout the treatment process.
These innovative tools play a crucial role in various orthodontic applications, such as closing gaps between teeth and correcting alignment issues. The interconnected design allows for uniform force distribution across multiple teeth, enhancing the overall effectiveness of the treatment. Additionally, power chains can be adjusted to provide varying levels of tension, ensuring that the pressure applied is tailored to the specific needs of each patient.
In summary, power chains serve as vital aids in orthodontic care, streamlining the movement of teeth and contributing to successful treatment outcomes. Their ability to apply consistent pressure over time makes them an invaluable resource for achieving desired dental alignment.
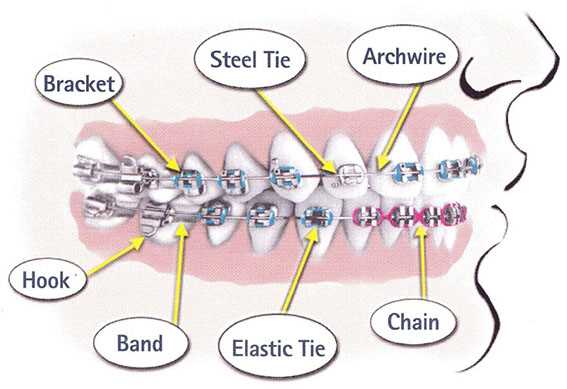
Buccal Tubes: Connecting Molars to Archwire
Buccal tubes serve as crucial components in the alignment and adjustment process of teeth. They provide a stable connection point that links specific teeth to the main wire, facilitating efficient movement and proper positioning. Understanding their role is essential for comprehending the overall mechanics of dental adjustment systems.
Functionality and Importance
The primary purpose of buccal tubes is to secure the archwire to the molars, enabling effective force distribution throughout the dental structure. Here are some key aspects of their functionality:
- Enhance the stability of the molars.
- Allow for precise adjustments during treatment.
- Support the overall framework for tooth alignment.
Types and Variations
Buccal tubes come in different styles and sizes to cater to various dental needs. Some common variations include:
- Standard buccal tubes: Typically used for most patients.
- Custom buccal tubes: Tailored for individual treatment requirements.
- Functional buccal tubes: Designed for specific orthodontic procedures.
Springs: Adjusting Tooth Pressure
In orthodontic treatment, the effective application of force is essential for guiding teeth into their desired positions. The components that provide this force play a crucial role in achieving optimal alignment. By fine-tuning these elements, practitioners can influence the level of pressure exerted on individual teeth, ensuring that movement occurs at a controlled and gradual pace.
Understanding the Functionality
The primary role of these components is to create tension that impacts the dental structure. Adjustments can be made to increase or decrease the pressure as needed, which is vital for accommodating the varying needs of each patient. Such modifications can promote comfort and enhance the overall effectiveness of the treatment process.
Adjustment Techniques
Practitioners typically utilize specific techniques to alter the tension applied. This can involve changing the spring’s position, using different sizes, or employing various tension settings. Each method aims to achieve the right balance, promoting effective movement while minimizing discomfort.
Monitoring Progress
Regular check-ups are crucial for assessing the effectiveness of the adjustments made. By closely monitoring the patient’s response, orthodontists can make informed decisions about further modifications, ensuring that each step is conducive to achieving the desired results.
Elastics: Correcting Bite and Jaw Position
In orthodontic treatment, specific accessories play a vital role in enhancing dental alignment and improving the overall functionality of the mouth. Among these, elastics are essential components that assist in repositioning the teeth and aligning the jaw for optimal occlusion. Their strategic application can significantly influence the treatment outcomes, allowing for precise adjustments in dental positioning.
Elastics are designed to create a force that gently guides the teeth into their desired locations. They are typically connected between different brackets or anchors, providing the necessary tension to correct misalignments. The consistent application of this force helps in achieving a harmonious relationship between the upper and lower dental arches, facilitating better biting and chewing mechanics.
| Type of Elastic | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Class I Elastics | Corrects minor discrepancies between the upper and lower teeth. |
| Class II Elastics | Shifts the upper teeth back and the lower teeth forward to improve bite. |
| Class III Elastics | Moves the upper teeth forward while retracting the lower teeth. |
| Vertical Elastics | Adjusts vertical relationships between the dental arches. |
By adhering to the prescribed use of elastics, patients can experience more efficient treatment, leading to improved comfort and satisfaction with their dental alignment process. Regular follow-ups with the orthodontist ensure that the progress is monitored and any necessary adjustments can be made to the elastic configurations.
Hooks: Aiding Elastic Band Placement
In orthodontic treatment, specific components are utilized to facilitate the adjustment and alignment of teeth. One such element is the hook, which plays a vital role in enhancing the effectiveness of elastic bands. These bands are essential for correcting bite issues and ensuring proper dental positioning.
Hooks serve several important functions in the application of elastic bands:
- Stability: They provide a secure anchor point, allowing the elastic bands to exert consistent pressure on the teeth.
- Versatility: Hooks can be positioned in various locations, accommodating different treatment plans and individual needs.
- Ease of Use: Their design enables efficient placement and adjustment of elastic bands, streamlining the overall process.
Proper positioning of the hooks is crucial for achieving the desired outcomes. Orthodontists carefully consider the placement of these components to optimize the effectiveness of the elastic bands:
- Assess the alignment and spacing of the teeth.
- Determine the appropriate hook placement based on the treatment objectives.
- Ensure that the elastic bands are correctly attached to the hooks for maximum efficiency.
By integrating hooks into the treatment process, orthodontists can enhance the overall effectiveness of elastic bands, contributing to a successful outcome in dental alignment and positioning.
Retainers: Maintaining Results After Treatment
After the completion of orthodontic procedures, ensuring the longevity of the achieved results becomes essential. The use of specific devices plays a crucial role in stabilizing the positioning of teeth and preventing any potential movement. These supportive tools serve to maintain the alignment established during the treatment phase, fostering lasting changes in oral health and aesthetics.
Importance of Consistent Use
Regular and consistent application of these devices is vital for preserving the desired outcomes. Neglecting to use them as recommended can lead to undesired shifts, ultimately requiring further adjustments. Following the prescribed guidelines not only supports optimal results but also enhances the overall effectiveness of the initial corrective measures.
Care and Maintenance Tips
Proper care of these devices is essential for their effectiveness and durability. Regular cleaning with gentle solutions helps prevent the buildup of plaque and bacteria. It’s advisable to avoid exposure to extreme temperatures, which could compromise their structure. By ensuring the longevity of these tools, individuals can significantly enhance the likelihood of maintaining their improved smiles over time.