Brain Structure and Functions of Each Part
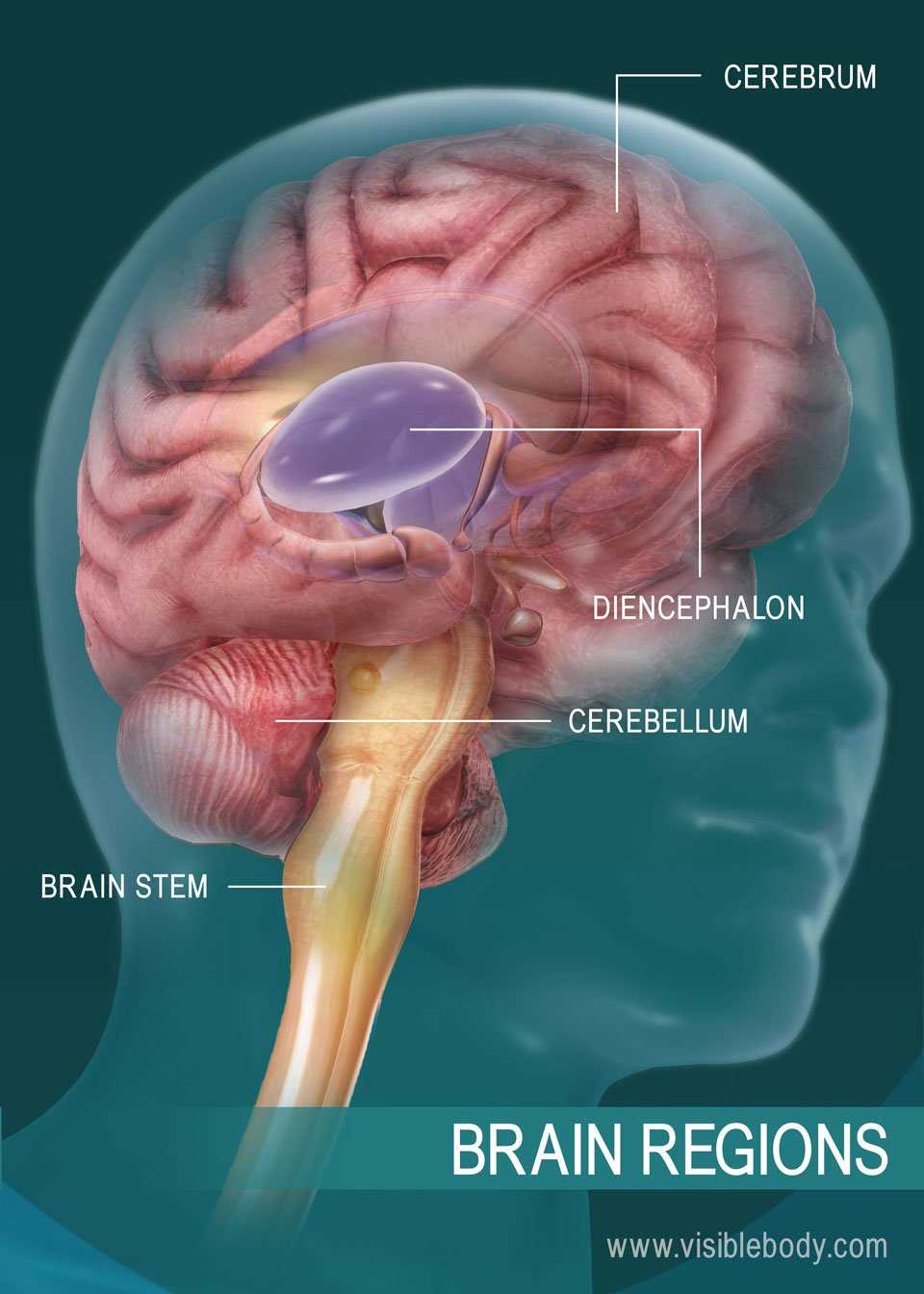
The structure within the skull is a marvel of nature, governing countless bodily functions and cognitive abilities. From the regulation of basic survival mechanisms to the complexity of higher thought processes, this remarkable system is at the core of human life. Understanding its different sections reveals how it controls everything from movement to emotions and decision-making.
Each region plays a specialized role, ensuring that the body’s physiological functions remain in harmony. Some zones are dedicated to sensory processing, while others manage our abilities to think, plan, and interact with the world. Exploring these regions provides insight into the intricate relationship between structure and function.
By examining this organization, we can better appreciate how these various regions work together to form a unified system. Whether involved in motor skills, emotional responses, or complex cognitive tasks, these divisions are essential to our daily existence and overall well-being.
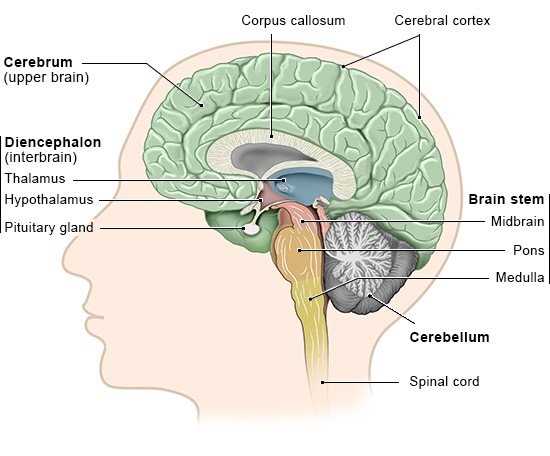
Brain Diagram and Functions
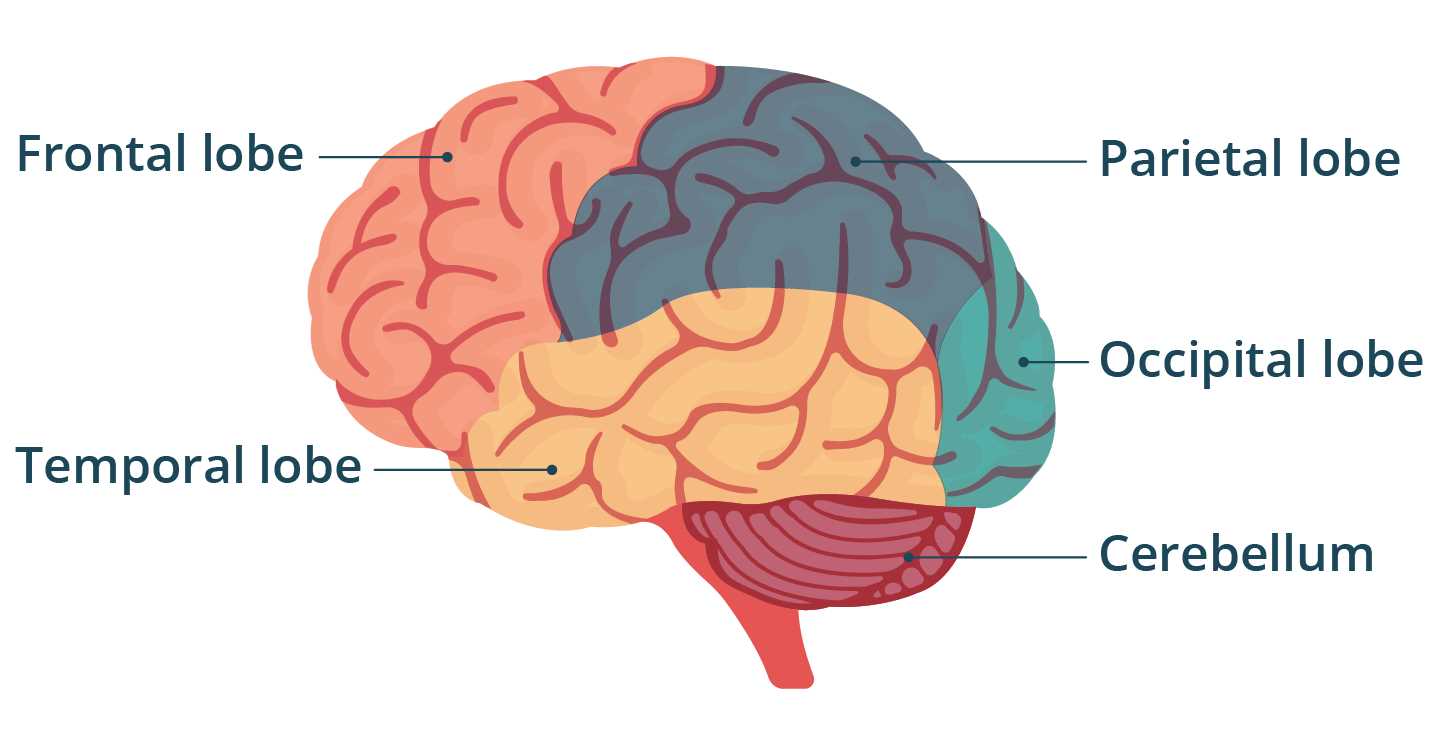
The structure of the human mind is an intricate network that manages countless processes vital for survival and interaction with the environment. Each component is specialized for particular tasks, collaborating seamlessly to regulate everything from motor skills to complex cognitive abilities. Understanding how these sections work together can shed light on behaviors, emotions, and body functions.
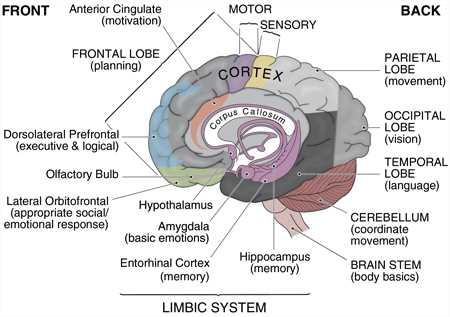
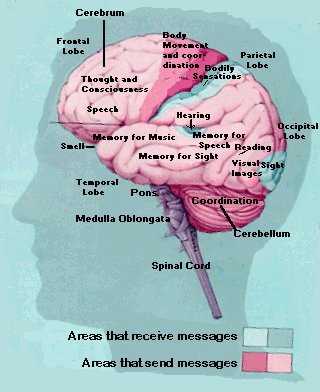
Cognitive Centers
Several regions are responsible for higher-level thinking, memory, and decision-making. These areas process information from sensory inputs and play a critical role in forming thoughts, learning new skills, and making judgments. Additionally, these areas manage language and speech, facilitating communication with others.
Movement Control
Physical coordination, balance, and voluntary movements rely on specific sections that handle motor functions. These regions coordinate muscle activity, enabling precise movements and reactions. Coordination of tasks like walking, writing, or running is highly dependent on these functional areas.
| Region | Main Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
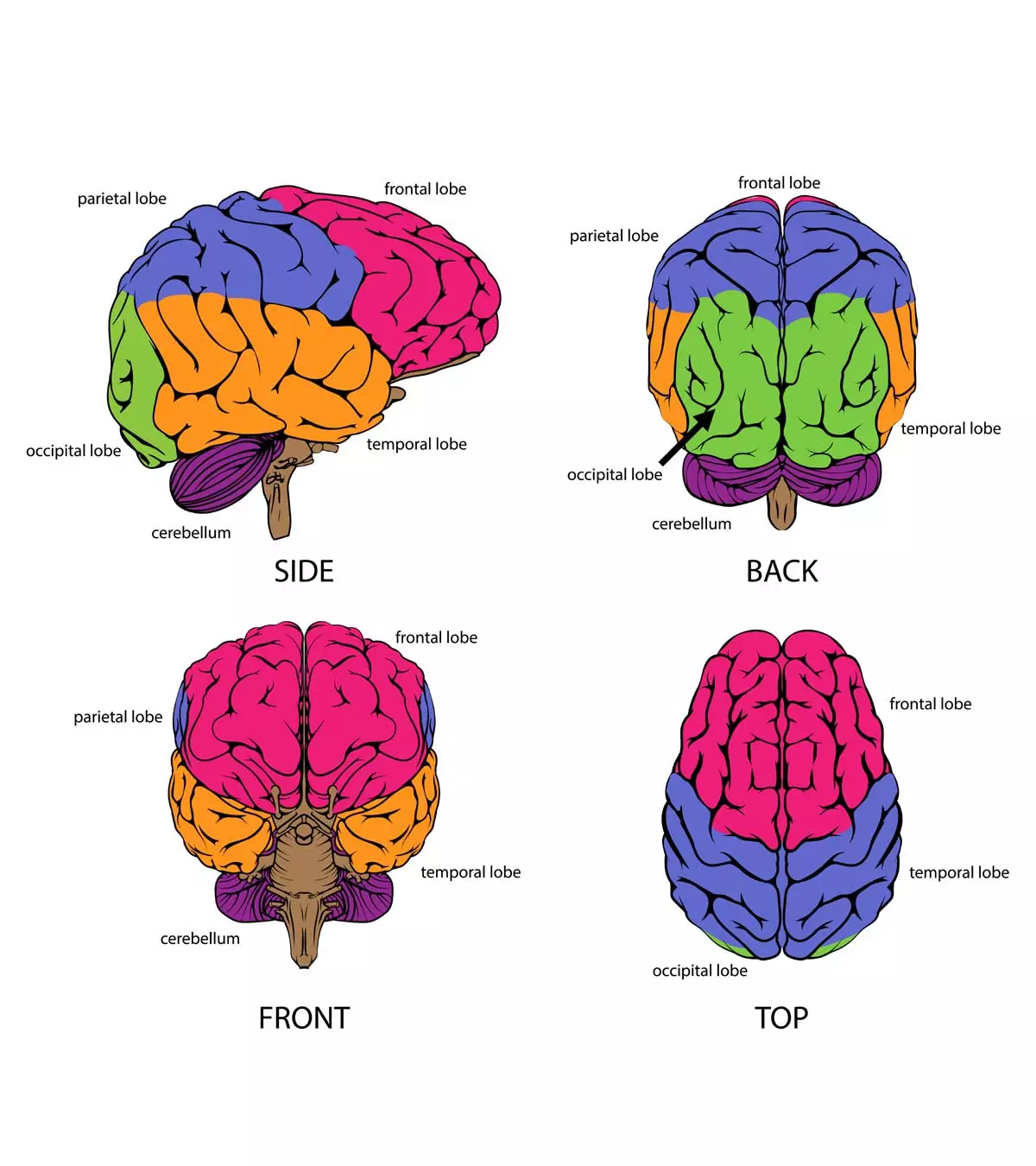
| Frontal Lobe | Decision Making, Problem Solving, Voluntary Movement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Temporal Lobe
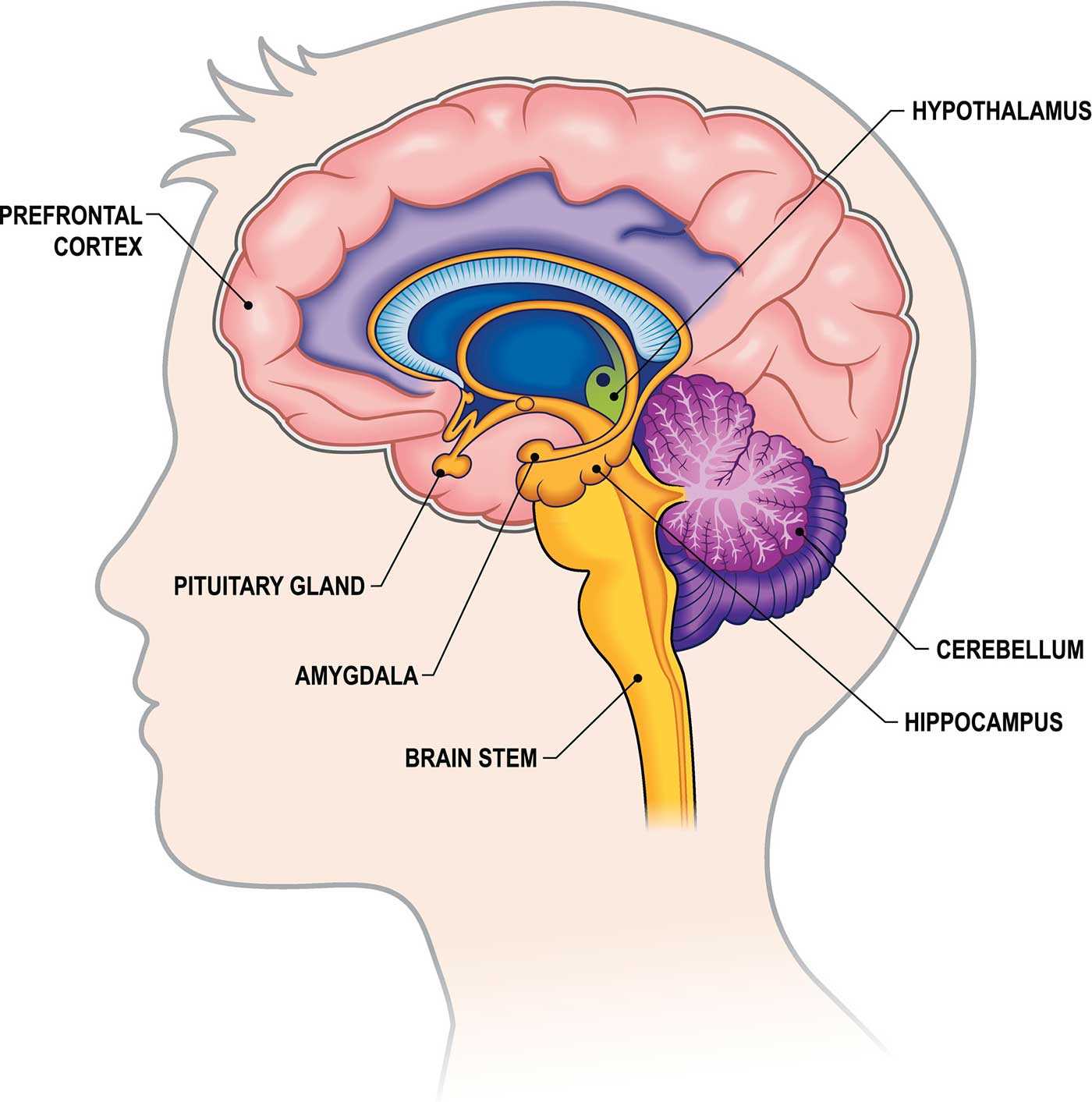
The Role of the Cerebral Cortex
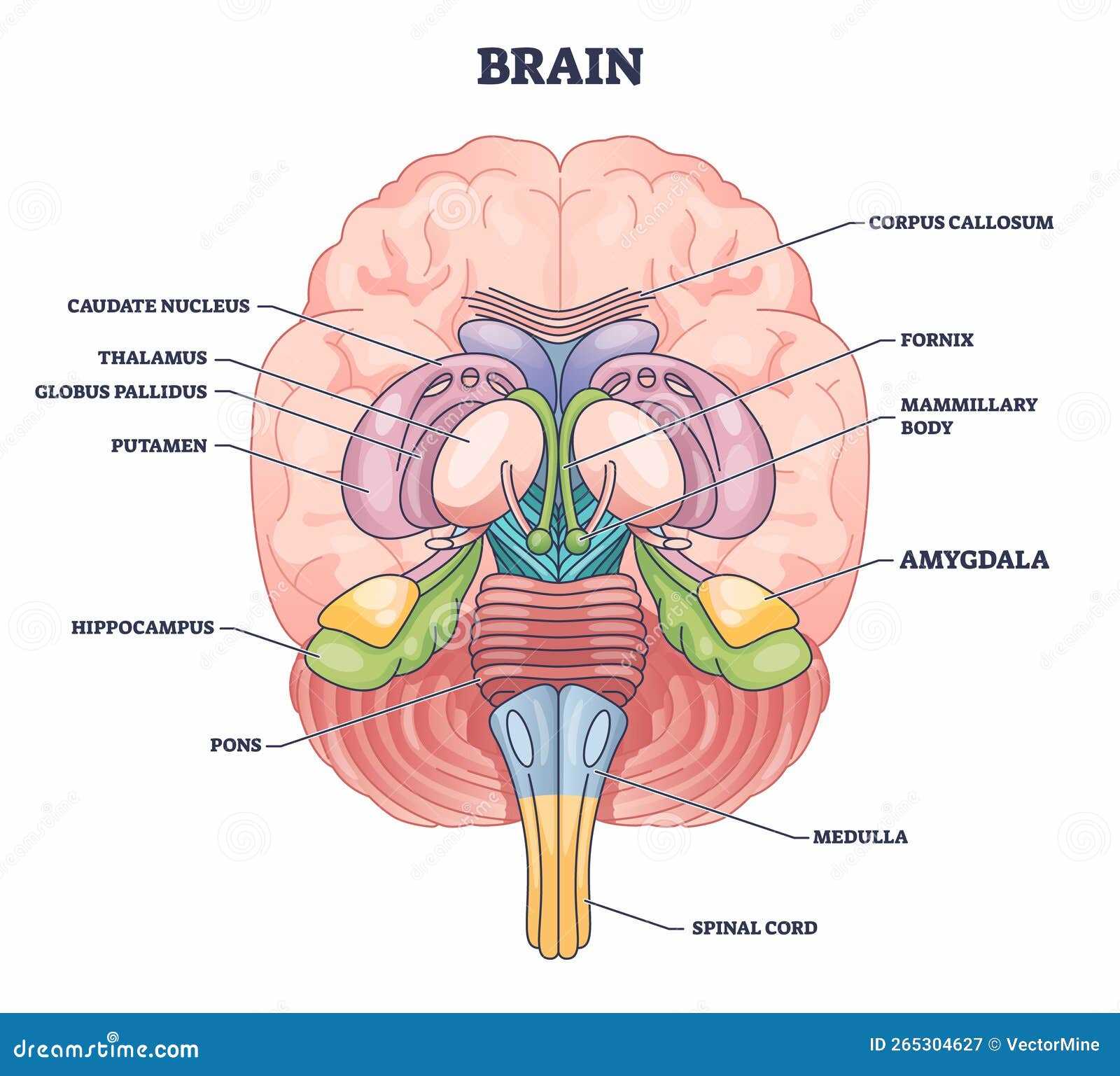
The cerebral cortex plays a central role in managing complex tasks essential for everyday functioning. It oversees various higher-order processes that allow individuals to engage with their environment thoughtfully and purposefully. This region is critical for coordinating actions, analyzing sensory input, and influencing decisions based on learned experiences. Decision-making is a fundamental responsibility of this area, where signals are processed and assessed to guide behavior. Additionally, it enables critical thinking and problem-solving, fostering creativity and adaptability. Another vital function of the cerebral cortex involves handling information from the senses. It helps decode visual, auditory, and tactile stimuli, ensuring that the surroundings are understood clearly. Through this process, individuals can interact, communicate, and navigate efficiently. Understanding the Limbic SystemThe limbic system plays a crucial role in regulating various emotional, behavioral, and physiological processes. This network is responsible for the integration of complex functions that influence mood, memory, and instinctual actions. Its components work in harmony to shape responses to external stimuli and internal drives, making it essential for maintaining balance in both mental and physical states. Key Functions and RegulationThis system governs emotional reactions, helping individuals process feelings such as fear, pleasure, and anger. It also assists in forming long-term memories by connecting experiences with emotions. Additionally, it plays a role in regulating certain automatic bodily functions, such as heart rate and arousal, which are closely tied to emotional states. Coordination with Other RegionsThe limbic network interacts with various regions responsible for decision-making, sensory processing, and motor functions. This collaboration allows for the formation of adaptive behaviors and reactions to environmental changes. The communication within this system ensures that emotions and memories are processed efficiently, influencing learning and survival mechanisms. The Significance of the Brainstem
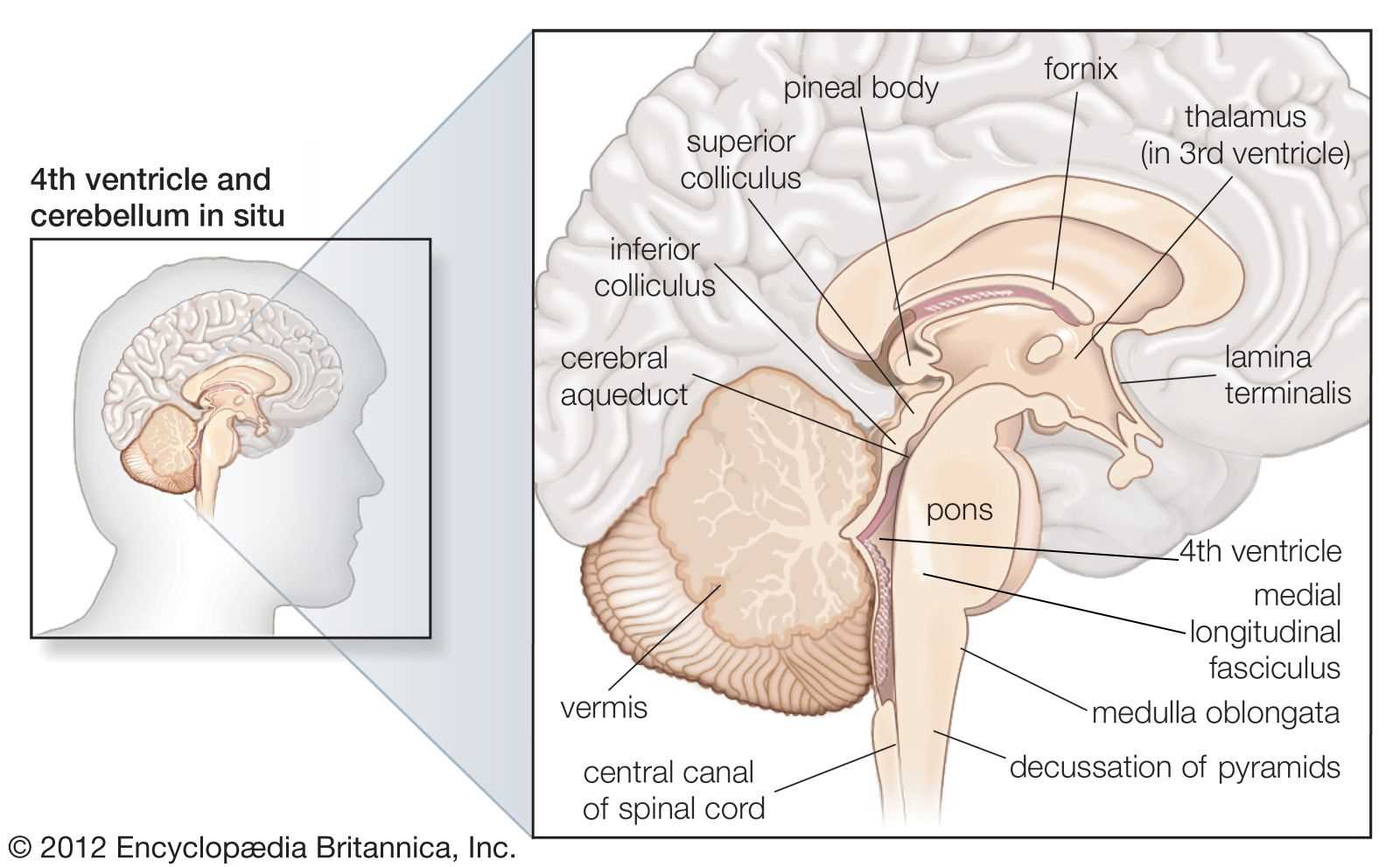
The importance of this central structure in the nervous system cannot be overstated. It serves as a vital hub, connecting major pathways that are essential for fundamental processes required to sustain life. This area is responsible for various automatic functions that occur without conscious thought.
These functions are critical to everyday survival, acting as the body’s control center for involuntary actions, ensuring the body operates smoothly even in the absence of conscious control. Functions of the Cerebellum
The cerebellum plays a crucial role in managing the coordination and precision of physical actions. While it doesn’t directly initiate movements, its responsibility lies in fine-tuning and ensuring smooth execution of motor tasks. This part of the nervous system ensures that actions are carried out with balance and accuracy, seamlessly integrating sensory information. Coordination and Balance
The cerebellum ensures that all physical actions are coordinated effectively, maintaining proper timing and accuracy. It helps in balancing the body by receiving input from various sensory systems, such as the inner ear, to ensure stability during movement. Motor LearningAnother critical role of the cerebellum is aiding in motor learning. This involves improving movements through practice, allowing for faster and more accurate responses during repetitive tasks. It adapts motor activity based on experiences, ensuring long-term refinement of physical skills.
Understanding the hypothalamus reveals its intricate role in orchestrating many aspects of daily life. Its influence extends beyond basic functions, affecting mood, behavior, and overall health, making it a critical area of study in neuroscience. The Role of the Thalamus in Sensory ProcessingThe thalamus serves as a crucial hub in the network responsible for processing sensory information. It acts as a relay station, channeling signals from various sensory modalities to appropriate regions of the cerebral cortex for further interpretation. This intricate function ensures that sensory inputs are not only received but also correctly integrated for perception and response. Located near the center of the central nervous system, the thalamus is involved in numerous functions related to sensory modalities. It plays a pivotal role in filtering and prioritizing sensory data, allowing the most relevant stimuli to reach conscious awareness while diminishing distractions from less important information. Through its connections with different cortical areas, it facilitates communication between sensory inputs and higher cognitive processes. In addition to its role in sensory processing, the thalamus contributes to regulating sleep, alertness, and consciousness. Its influence extends beyond mere relay; it actively participates in shaping how sensory experiences are perceived, interpreted, and acted upon. Understanding the thalamus’s contributions provides valuable insights into the complexity of sensory integration and overall neural functioning. How the Amygdala Regulates Emotions
The amygdala plays a pivotal role in emotional responses, influencing how individuals react to various stimuli. This small, almond-shaped structure is integral to processing feelings such as fear, pleasure, and anger. Understanding its function provides insights into how emotions are generated and managed in daily life. When faced with a threat or significant event, the amygdala quickly activates, triggering a cascade of responses throughout the body. This mechanism enables rapid reactions, often referred to as the “fight or flight” response. Additionally, it interacts with other regions to shape emotional experiences and decision-making processes.
Through these functions, the amygdala contributes significantly to emotional regulation, affecting both personal well-being and interpersonal relationships. A deeper understanding of its role can enhance approaches to emotional health and therapeutic interventions. The Importance of the Hippocampus in Memory
The hippocampus plays a crucial role in the formation and retrieval of memories, serving as a vital component of the memory system. This region is essential for converting short-term experiences into long-lasting recollections, allowing individuals to learn from their surroundings and retain valuable information throughout their lives. Functions of the HippocampusThis structure is primarily involved in the consolidation of new memories. It aids in organizing and integrating information from various sensory inputs, enabling a coherent representation of experiences. Furthermore, the hippocampus is significant for spatial memory, helping individuals navigate their environment and remember locations. Impact on Learning and Emotion
In addition to its memory-related functions, the hippocampus interacts closely with emotional processes. It helps regulate emotional responses tied to specific memories, enhancing the learning experience by associating feelings with events. This connection underscores its role not only in memory retention but also in understanding the emotional context of experiences. Basal Ganglia and Motor ControlThe basal ganglia are a group of nuclei that play a crucial role in the regulation of movement and coordination. This complex system is responsible for refining motor commands, ensuring smooth and purposeful actions. By integrating signals from various regions, it facilitates the execution of voluntary movements while inhibiting unwanted actions, contributing significantly to motor planning and control. Functionality OverviewThis system is instrumental in various functions related to motor activity. It participates in habit formation, procedural learning, and the regulation of muscle tone. Its intricate connections allow it to modulate motor commands, thereby influencing how movements are initiated, sustained, and adjusted. Dysfunction in this area can lead to various movement disorders, highlighting its importance in maintaining motor equilibrium. Key Components and Their Roles
The Pituitary Gland’s Influence on Hormones
The pituitary gland plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes through its production and secretion of hormones. This small but mighty organ orchestrates a complex network of hormonal signals, influencing multiple systems within the body. Its actions extend to growth, metabolism, and reproductive functions, highlighting its significance in maintaining overall health and balance. Regulatory FunctionsThis gland serves as a command center, controlling other glands in the endocrine system. By releasing specific hormones, it regulates vital activities such as growth and energy usage. The influence it exerts can determine how the body responds to stress, reproductive health, and even water retention, showcasing its vast impact on bodily functions. Hormonal InteractionsThe interplay between the pituitary gland and various hormones demonstrates its pivotal role in homeostasis. For instance, it releases growth hormone (GH) to stimulate growth and development while producing adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) to manage stress responses. Additionally, its interaction with the thyroid and adrenal glands illustrates the intricate balance necessary for optimal health. |