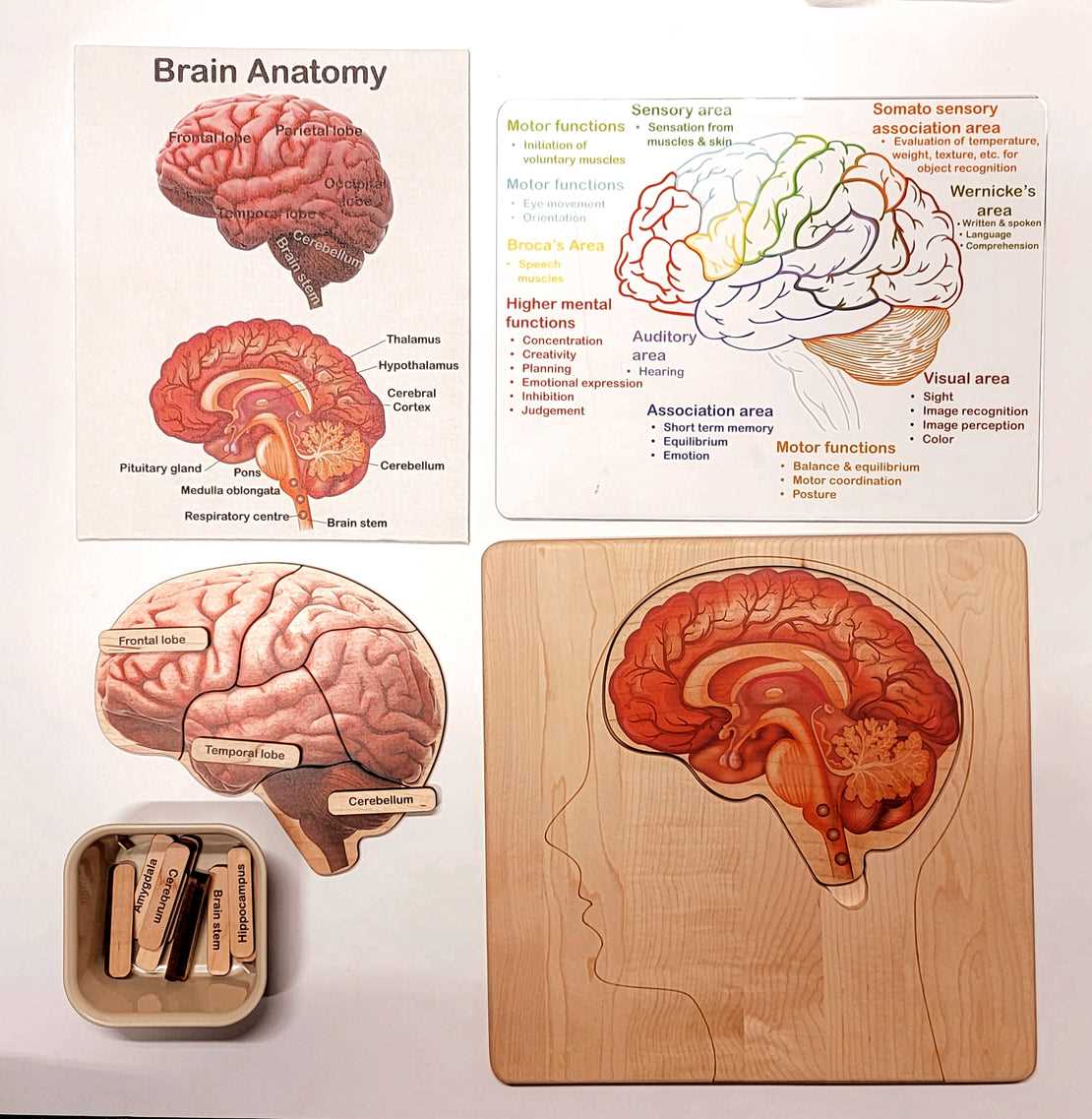
Understanding the Parts and Functions of the Brain Diagram
The human mind is an incredibly complex organ that orchestrates a multitude of processes essential to daily life. It serves as the central hub for all cognitive activities, controlling everything from movement to emotions. Understanding the intricate structure of this vital organ can provide insights into how we perceive, think, and react to the world around us.
Various regions within this organ are responsible for distinct roles, contributing to our ability to perform a wide range of activities. Each section has a specialized role, from managing sensory input to regulating vital bodily functions. Together, they create a seamless system that allows humans to interact with their environment efficiently.
In this section, we will explore the key regions that make up this remarkable structure, detailing their individual responsibilities. With a clearer understanding of its components, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and sophistication of the human mind.
Overview of Brain Anatomy
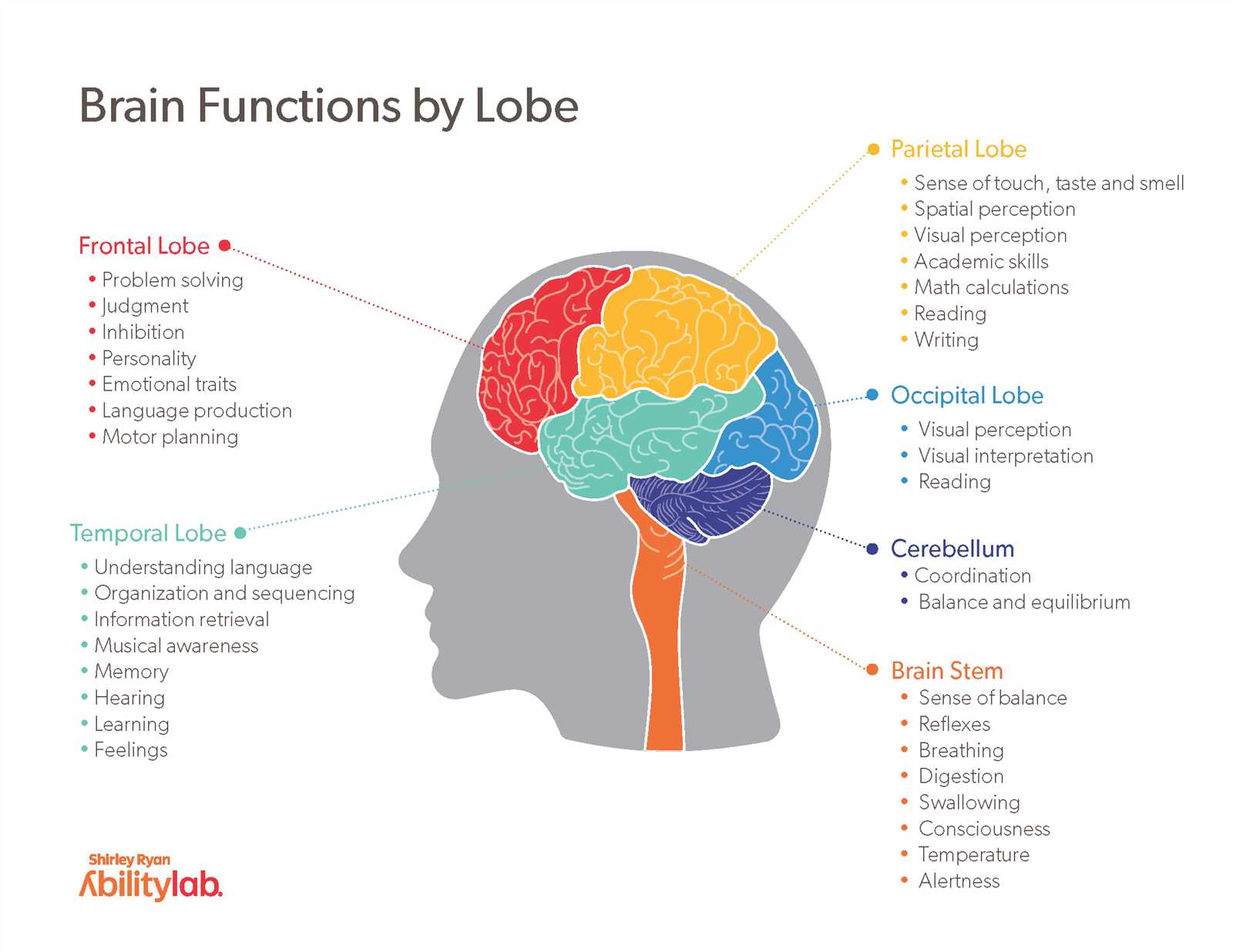
The central organ governing the body’s vital processes consists of interconnected structures that coordinate physical and cognitive activities. It serves as the core control center, processing sensory information, managing movement, and regulating behavior and thought. These regions collaborate to ensure the smooth operation of essential functions such as breathing, digestion, memory, and decision-making.
| Region | Primary Role |
|---|---|
| Cerebral Cortex | Responsible for higher-level thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making. |
| Cerebellum | Coordinates motor control, balance, and muscle coordination. |
| Limbic System | Handles emotions, motivation, and memory formation. |
| Brainstem | Controls basic life-supporting functions such as heart rate and breathing. |
Major Brain Regions Explained
The central nervous system is a highly organized and intricate structure, responsible for various essential processes that sustain life and regulate behaviors. Different regions of this complex system manage everything from vital bodily functions to higher-level cognitive tasks.
- Cerebral Cortex: The outer layer, responsible for higher thought processes such as reasoning, problem-solving, and decision-making.
- Cerebellum: Controls coordination, balance, and fine motor skills, ensuring smooth and precise movements.
- Limbic System: Involved in emotion regulation, memory formation, and motivation, playing a key role in behavioral responses.
- Thalamus: Acts as a relay center, directing sensory information to appropriate areas for processing.
- Hypothalamus: Regulates homeostasis, including body temperature, hunger, and hormonal activity.
- Brainstem: Manages basic life functions like heart rate, breathing, and sleeping patterns, serving as the connection between the spinal cord and higher regions.
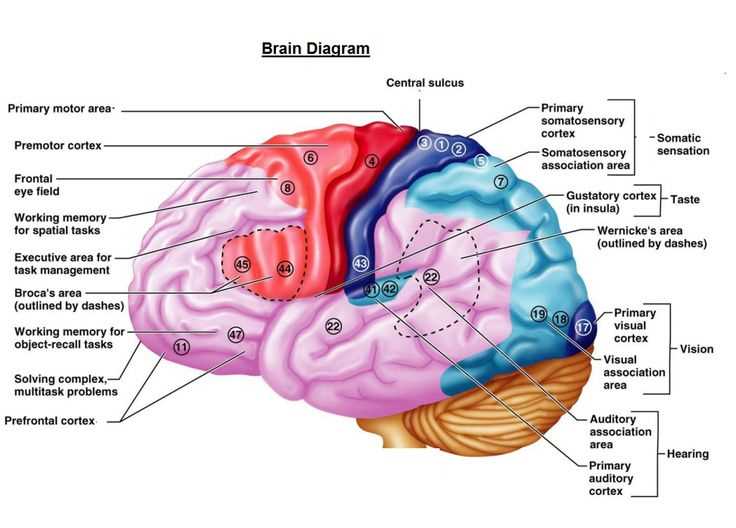
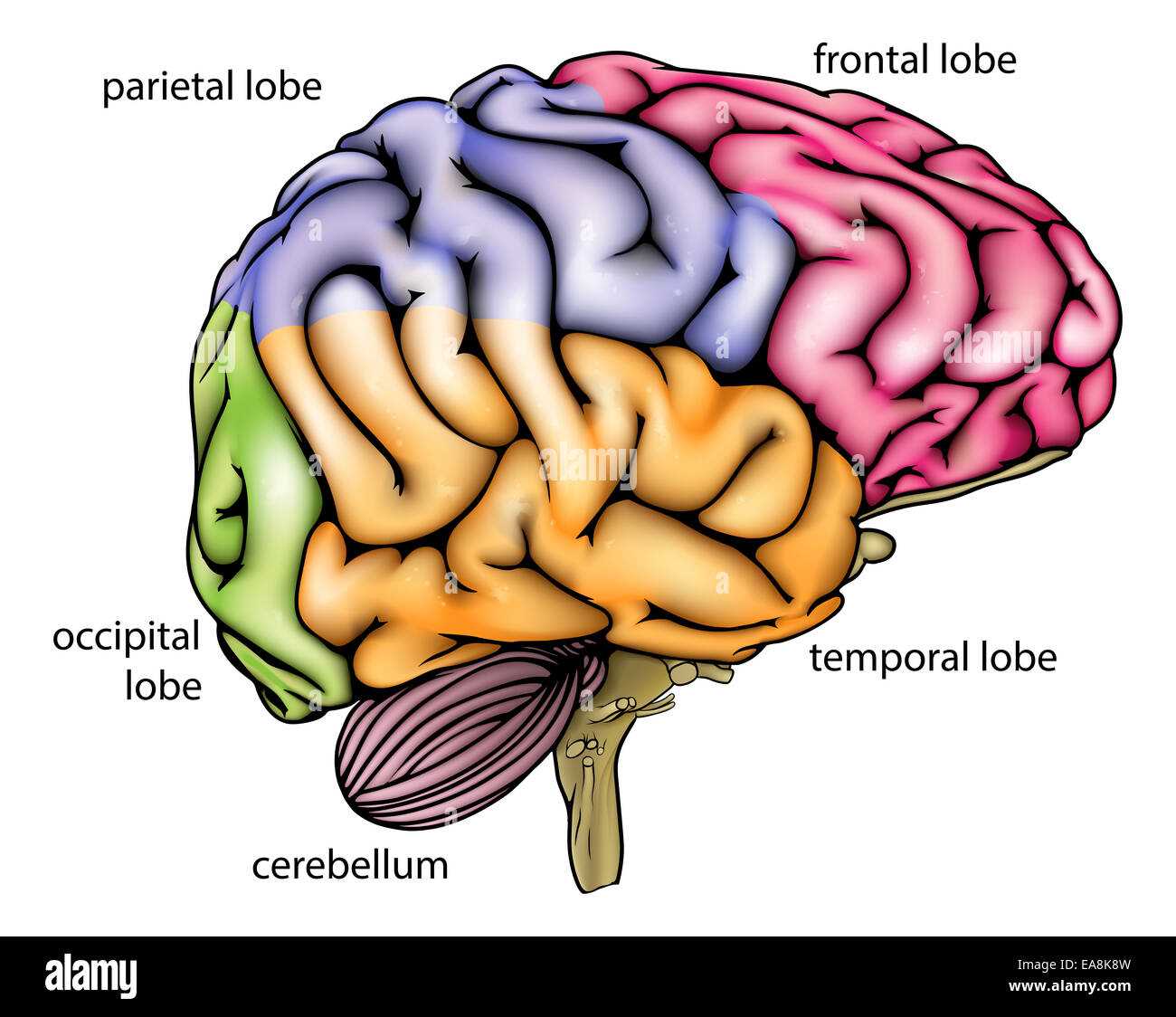
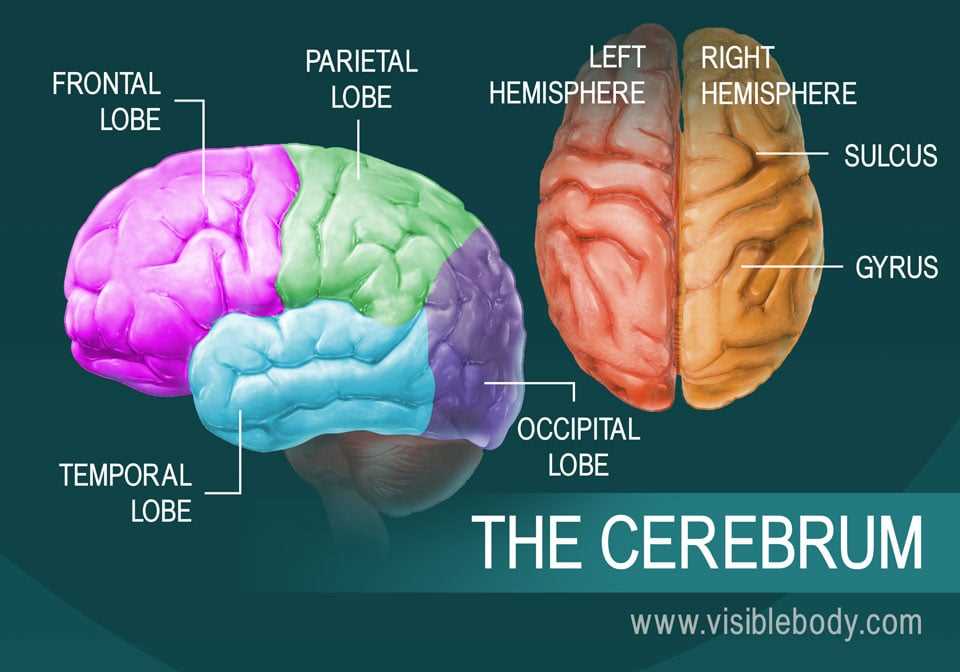
Function of the Cerebral Cortex
The cerebral cortex plays a critical role in various high-level processes that are essential for human cognition and interaction. It is responsible for handling complex tasks such as thought, perception, and decision-making. This region is also involved in managing sensory inputs, allowing for interpretation and response to external stimuli.
| Area of the Cortex | Primary Role |
|---|---|
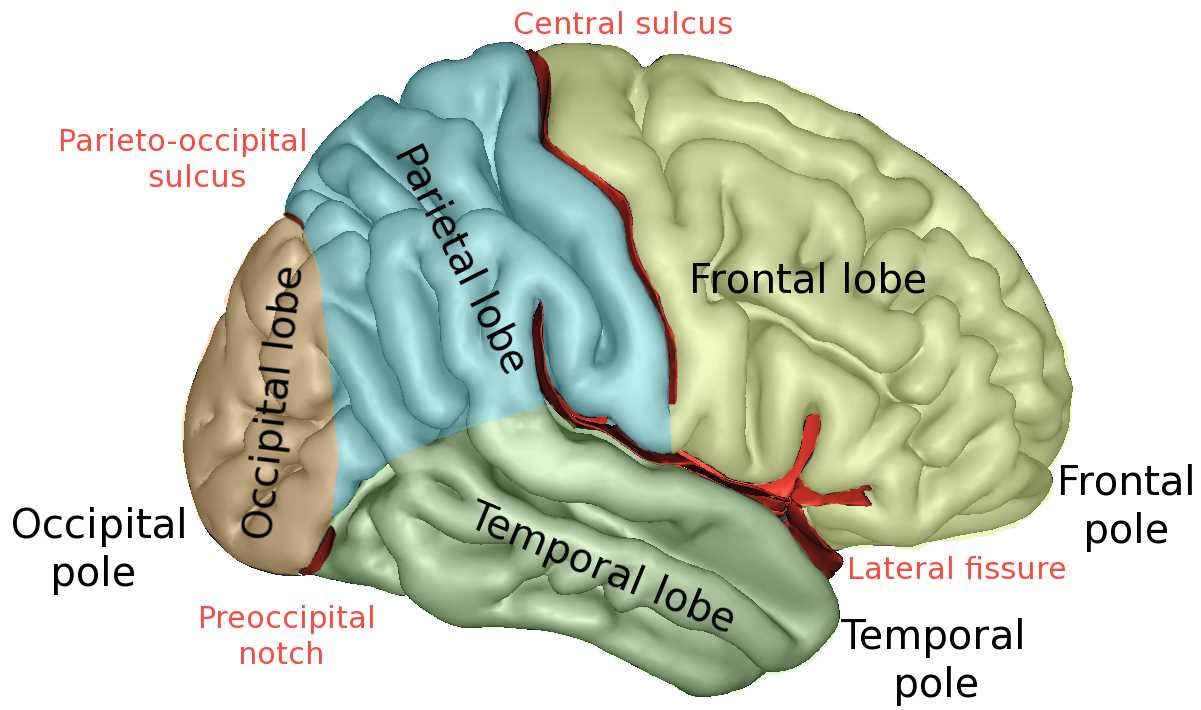
| Frontal Lobe | Involved in reasoning, problem-solving, and planning. |
| Parietal Lobe | Processes sensory information such as touch and spatial awareness. |
| Temporal Lobe | Handles auditory processing and memory retention. |
| Occipital Lobe | Responsible for visual processing. |
Role of the Cerebellum
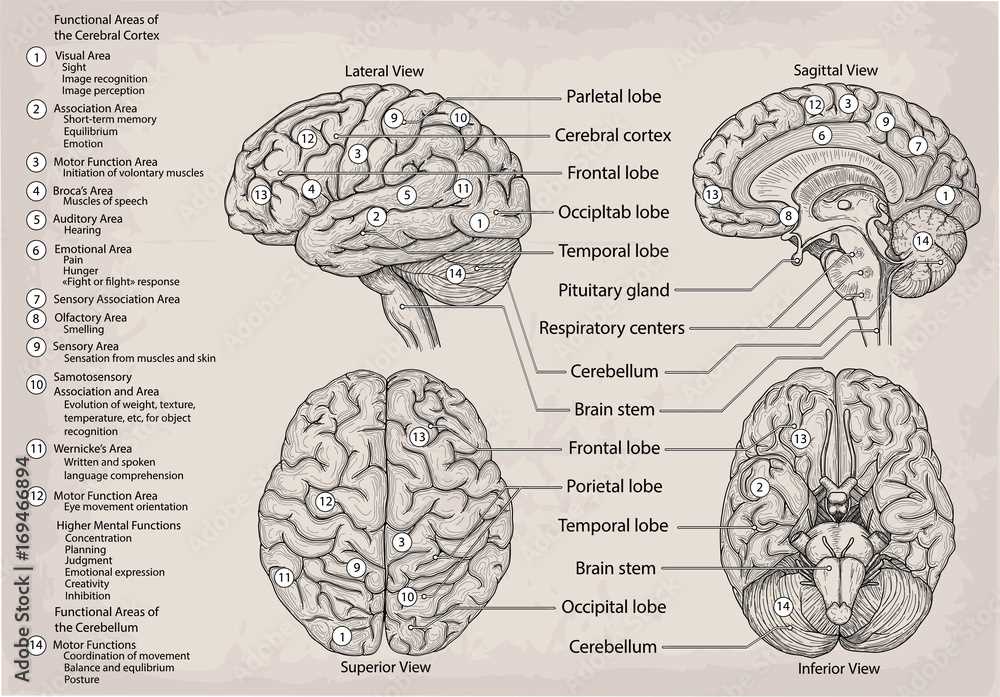
The cerebellum plays a crucial role in coordinating various physical activities and ensuring smooth, balanced movements. Its primary function revolves around managing motor control, enabling individuals to perform everyday actions with precision and fluidity.
| Key Functions | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coordination | Helps integrate different movements into harmonious actions, allowing for smooth execution of complex tasks. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance | Maintains stability by processing signals from sensory systems and ensuring proper posture and movement. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fine Motor Skills | Regulates precise, controlled actions needed for tasks such as writing or manipulating small objects. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Motor Learning | Assists in acquiring new motor skills through practice and repetition, improving efficiency over time. |
| Structure | Role | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amygdala | Regulates emotional responses such as fear and pleasure. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hippocampus | Crucial for forming new memories and spatial navigation. |
| Hippocampus Role | Description | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Memory Processing | Transfers short-term memories into long-term storage. | ||||||||||||||||
| Neurotransmitter | Primary Role | Associated Disorders |
|---|---|---|
| Dopamine | Reward and pleasure, motor control | Parkinson’s disease, schizophrenia |
| Serotonin | Mood regulation, sleep, appetite | Depression, anxiety disorders |
| GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid) | Inhibition of neuronal activity | Anxiety disorders, epilepsy |
| Norepinephrine | Attention, response to stress | ADHD, depression |
| Acetylcholine | Memory, muscle contraction | Alzheimer’s disease, myasthenia gravis |
Understanding the diverse roles of these neurotransmitters is essential for developing targeted therapies for various neurological and psychological conditions. Ongoing research continues to uncover the complexities of these substances and their profound impact on human behavior and health.
Brain’s Role in Homeostasis
The central nervous system plays a crucial role in maintaining balance within the body, ensuring that various physiological processes operate optimally. This system continuously monitors internal conditions, allowing for adjustments that promote stability despite external changes.
Homeostasis is the state of equilibrium that the body strives to achieve. It involves complex interactions between different systems, where regulatory mechanisms activate to respond to fluctuations. The control center is essential for interpreting sensory information and coordinating appropriate responses to maintain this balance.
One significant aspect of this regulatory role is the management of temperature, hydration, and energy levels. By processing information from sensory receptors, the central command can trigger actions such as sweating, shivering, or altering thirst and hunger sensations. These actions are vital in helping organisms adapt to their environments and maintain an internal steady state.
Furthermore, the intricate network facilitates communication among various organs, enhancing their ability to work together harmoniously. This synchronization ensures that all bodily functions align with the overall goal of sustaining a stable internal environment, which is fundamental for survival.
Impact of the Brain on Behavior
The central organ of the nervous system plays a crucial role in determining how individuals interact with their environment. Its complex network facilitates communication between various regions, influencing actions, emotions, and cognitive processes. Understanding this influence is essential for comprehending human behavior and mental states.
Numerous factors contribute to the effects of this organ on behavior:
- Neurotransmitters: Chemical messengers that transmit signals between neurons, impacting mood and responses.
- Structure: The organization of different regions affects functions like memory, decision-making, and social interactions.
- Plasticity: The ability to adapt and change in response to experiences, shaping habits and learning processes.
- Genetics: Inherited traits can influence predispositions to certain behaviors and mental health conditions.
- Environment: External factors, such as social interactions and cultural influences, can modify behavior through neural mechanisms.
Research in neuroscience continually uncovers new insights into how the organ affects individual actions and societal norms. By exploring these connections, we can better understand the intricacies of human behavior.