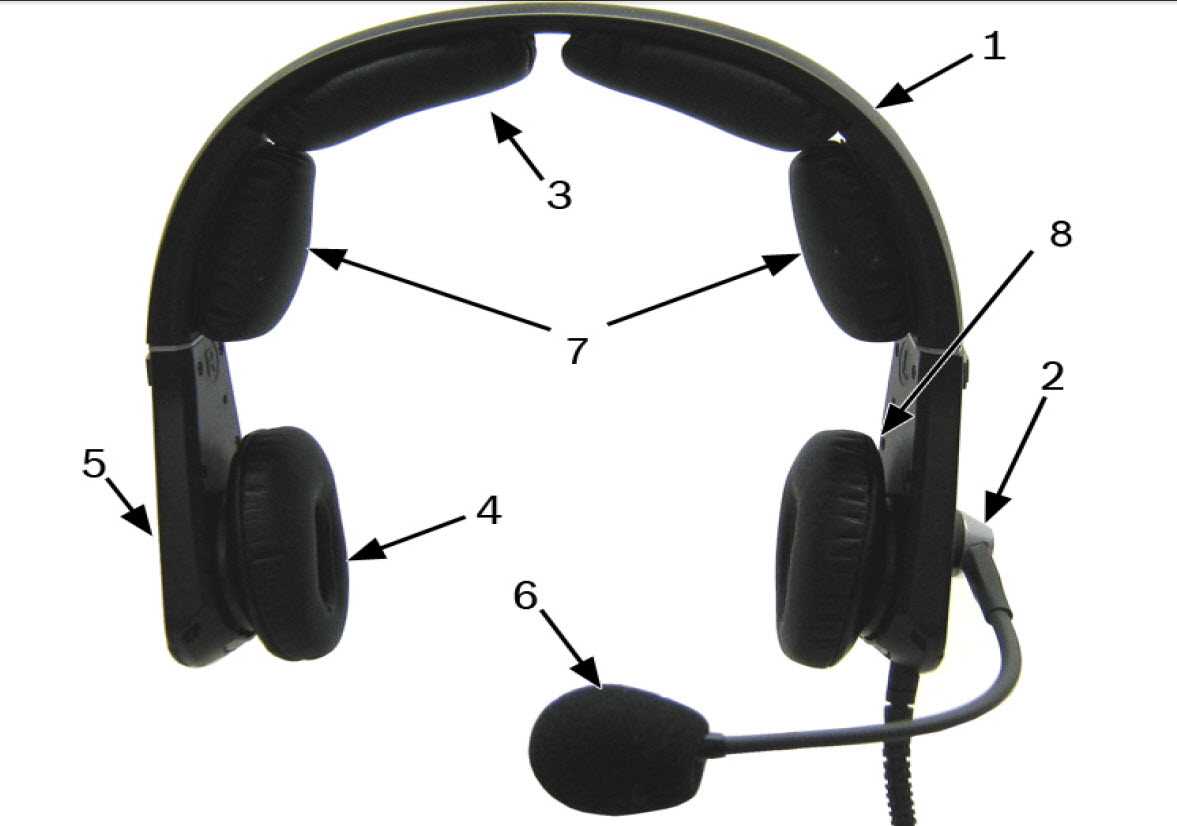
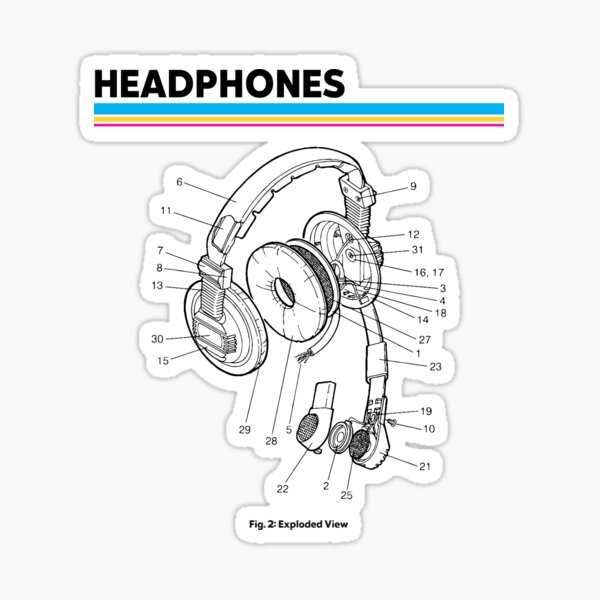
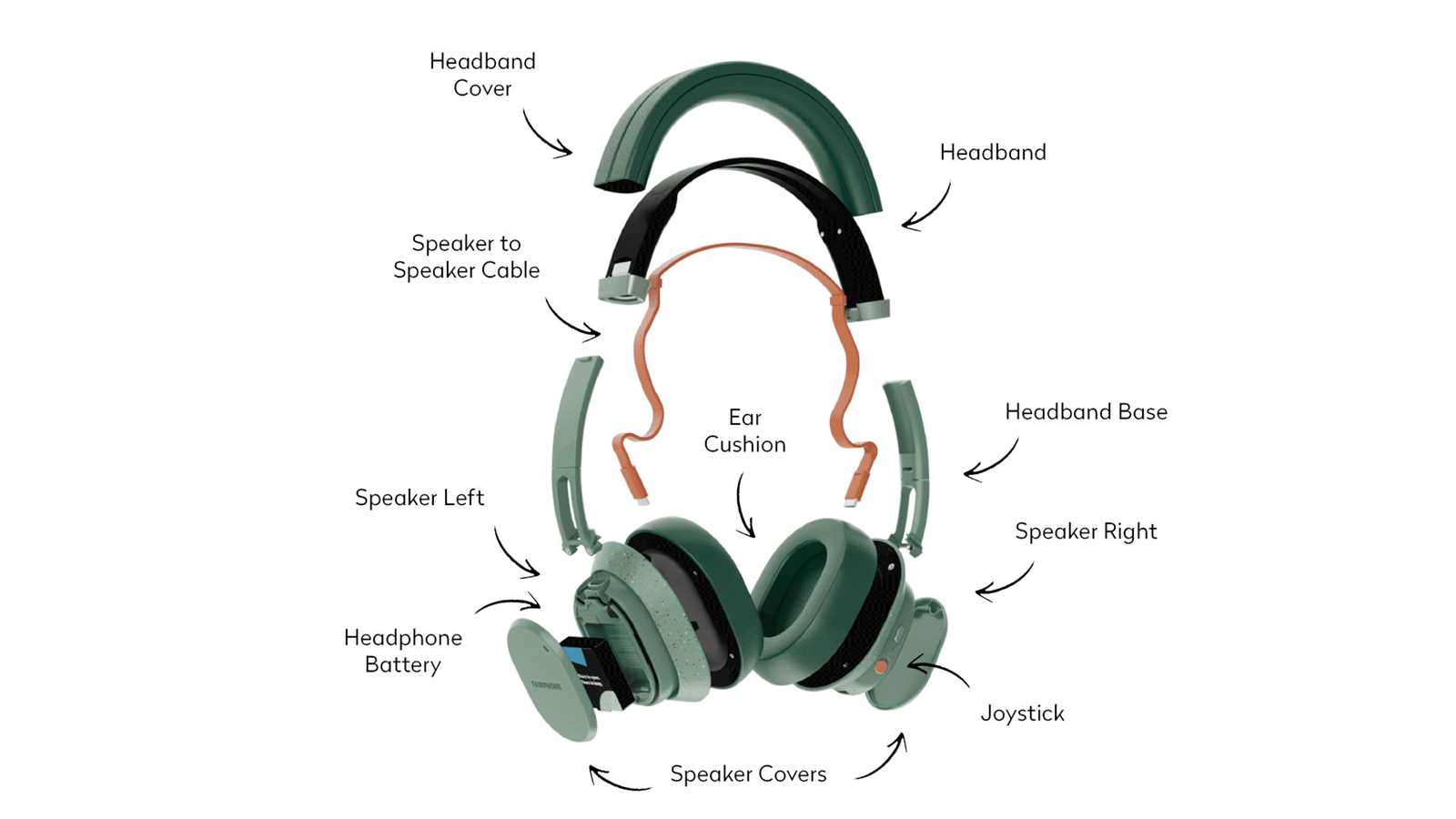
Headphones Parts Diagram Overview
In the realm of audio technology, the functionality and experience of listening depend greatly on the intricate elements that comprise these devices. Each component plays a significant role in delivering sound quality and user comfort. By exploring these elements, one can gain a deeper appreciation for how audio equipment operates and the craftsmanship involved in its design.
Every segment within these sound-producing devices is engineered to perform specific tasks, contributing to the overall acoustic performance. From the transducers that convert electrical signals into sound waves to the cushioned elements designed for comfort during prolonged use, each piece works in harmony to enhance the listening experience. Understanding these individual elements not only informs users about their equipment but also aids in troubleshooting and maintenance.
In this discussion, we will delve into the various components, highlighting their functions and importance. By examining these elements, readers will become more knowledgeable about the inner workings of their audio devices, leading to more informed choices when selecting or using them.
This section explores the various elements that contribute to the functionality and experience of audio devices worn on the ears. Understanding these components is essential for anyone interested in the technology behind sound transmission and audio quality. Each element plays a significant role in delivering a seamless auditory experience.
Key Elements of Audio Devices
- Driver Unit: The core component responsible for converting electrical signals into sound waves.
- Casing: The outer shell that protects internal parts and influences sound quality.
- Headband: The part that connects the two speakers, providing comfort and stability during use.
- Pads: Cushions that rest against the ears, enhancing comfort and noise isolation.
- Cables: Wires that transmit audio signals from the source to the drivers.
Understanding Each Component

- Driver Unit: This component is crucial for sound production, with different types offering varying sound profiles.
- Casing: Materials used in the casing can affect sound resonance and overall durability.
- Headband: Adjustable and padded headbands provide personalized comfort for extended listening sessions.
- Pads: Different materials for ear cushions impact noise cancellation and comfort levels.
- Cables: Quality of cables can influence signal integrity and durability.
Outer Shell Materials and Design
The outer casing of audio devices plays a crucial role in both aesthetics and functionality. Various materials contribute to the overall structure, influencing factors such as durability, weight, and acoustic performance. The choice of design also significantly impacts user experience, as it affects comfort and usability.
Common Materials: Manufacturers often use materials like plastic, metal, and wood to construct the exterior. Each material offers distinct advantages; for instance, plastic is lightweight and cost-effective, while metal provides enhanced durability. Wood, on the other hand, can deliver unique acoustic properties, enriching sound quality.
Design Considerations: Ergonomic design is essential for ensuring comfort during extended use. Curved shapes and padded surfaces are commonly integrated to enhance fit and reduce pressure on the ears. Additionally, the aesthetic aspect cannot be overlooked, as consumers are drawn to visually appealing designs that reflect their personal style.
Ultimately, the materials and design of the outer casing are integral to the performance and appeal of audio devices, influencing both how they look and how they sound.
Drivers: Types and Functions
The core components responsible for sound reproduction play a crucial role in audio devices. These elements convert electrical signals into audible sound waves, influencing both the quality and clarity of the audio experience. Understanding the various types and their functions can enhance one’s appreciation of the technology behind sound delivery.
Dynamic Drivers
Dynamic drivers are among the most commonly used types in audio equipment. They utilize a diaphragm, voice coil, and magnet to produce sound. When electrical signals pass through the voice coil, it creates a magnetic field that moves the diaphragm, generating sound waves. This design is known for its efficiency and ability to produce deep bass and clear highs.
Balanced Armature Drivers
Balanced armature drivers offer a different approach to sound production. These components use a small armature that pivots between magnets, creating sound. This design allows for precise control over frequency response, making them ideal for delivering detailed audio. They are often found in high-fidelity devices and in-ear monitors, where size constraints demand compact yet powerful solutions.
Cables: Importance and Specifications
The significance of connections in audio devices cannot be understated, as they play a crucial role in delivering high-quality sound. The type and quality of these connections greatly influence the overall listening experience, making it essential to understand their characteristics and specifications.
Cable construction often determines durability and performance. Common materials include copper and oxygen-free copper, which ensure minimal signal loss and enhance sound clarity. Additionally, shielding is vital for preventing interference from external sources, thus preserving audio integrity.
Another critical aspect is the length of the connection. Longer cables may introduce resistance, affecting sound quality. Conversely, very short connections can limit mobility. Therefore, choosing the appropriate length is essential for both convenience and performance.
When considering connectors, options such as 3.5mm, 6.3mm, and XLR are common. Each type has its specific use cases and advantages, catering to different audio setups and preferences. Understanding these specifications aids in selecting the right connection for optimal sound delivery.
Ear Pads: Comfort and Styles
The cushioning elements that come into contact with the ears play a vital role in enhancing the overall experience of using audio devices. These components not only provide necessary comfort during extended listening sessions but also contribute significantly to the acoustic performance by ensuring a snug fit. Various materials and designs are available, catering to diverse preferences and needs.
Comfort is paramount when selecting the right cushioning. Soft materials like memory foam and plush fabrics offer a luxurious feel, reducing pressure on the ears. For those who prioritize breathability, options featuring mesh or perforated surfaces can help prevent overheating, making them ideal for long-term use.
In addition to comfort, styles vary widely. Some users may prefer sleek, minimalist designs that blend seamlessly with modern aesthetics, while others might opt for bold colors and patterns that express personal style. The choice of cushioning can also affect the overall look of the audio device, adding an element of customization.
Ultimately, selecting the right cushioning involves balancing comfort and style. By understanding the available options and considering individual preferences, users can enhance their audio experiences significantly.
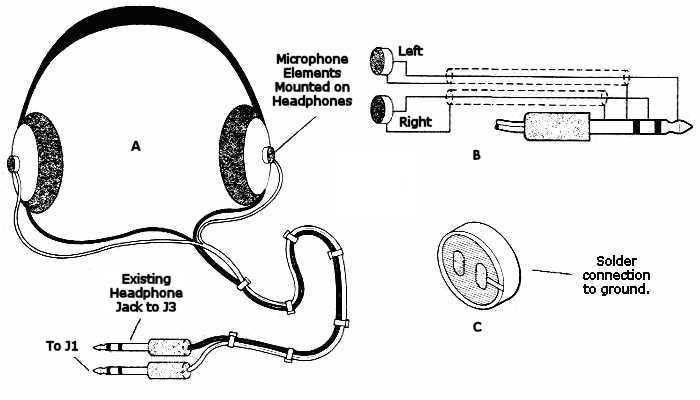
Microphones: Placement and Types
Microphones play a crucial role in audio equipment, capturing sound for various applications. Their effectiveness depends not only on their design but also on their positioning and the type used. Understanding the different styles and optimal placements can significantly enhance audio quality and clarity.
There are several types of microphones, each suited for specific scenarios. Common categories include dynamic, condenser, and ribbon microphones. Below is a table summarizing their characteristics and ideal usage contexts:
| Type | Characteristics | Best Used For |
|---|---|---|
| Dynamic | Durable, handles high sound pressure levels | Live performances, loud sound sources |
| Condenser | Sensitive, captures detailed sound | Studio recordings, vocals, acoustic instruments |
| Ribbon | Warm sound, good transient response | Strings, brass, and certain vocal applications |
Placement is equally important in maximizing sound capture. Proper positioning ensures that the microphone picks up the intended sound source while minimizing background noise. Factors such as distance, angle, and environment should be considered when setting up microphones.
Headband Mechanisms Explained
The headband is a crucial component that contributes to the overall functionality and comfort of audio devices. Its design and structure play a significant role in ensuring a secure fit while allowing for adjustments to accommodate different head sizes. Understanding the various mechanisms at work can enhance the user experience and provide insights into the product’s durability and usability.
Typically, the headband consists of a flexible frame that connects the two ear cups. This frame is engineered to distribute weight evenly, minimizing pressure on the ears during extended use. Many models feature adjustable sections that can be lengthened or shortened, allowing users to customize the fit according to their preferences.
Some headbands incorporate cushioning to enhance comfort, providing a soft barrier between the device and the user’s head. This padding can vary in thickness and material, contributing to a more enjoyable experience, especially during prolonged listening sessions. Additionally, certain designs may include swiveling or rotating mechanisms, allowing the ear cups to pivot for better alignment with the ears.
Innovative headband designs also integrate foldable features, making storage and portability more convenient. These models can collapse into a compact form, making them ideal for travel. Understanding these mechanisms not only highlights the engineering behind audio devices but also assists users in selecting models that best meet their needs.
Connectors: Variants and Uses
Connectors play a crucial role in enabling audio devices to interface with various equipment. Understanding the different types available and their applications can greatly enhance the user experience. This section explores the various connector types commonly found in audio equipment and their specific purposes.
Types of Connectors
- 3.5mm Jack: Widely used for personal audio devices, this compact connector offers compatibility with numerous devices.
- 6.35mm (1/4 inch) Jack: Often found in professional audio equipment, this larger connector provides a secure connection and enhanced durability.
- USB: Used for digital audio connections, USB connectors allow for high-quality sound transmission and device charging.
- XLR: Common in professional settings, XLR connectors are known for their secure locking mechanism and balanced audio transmission.
- Lightning: Designed for Apple devices, this connector offers a reversible design for user convenience.
Common Applications
- Connecting personal devices to smartphones and laptops.
- Integrating with professional audio interfaces and mixers.
- Enabling seamless connectivity in live sound environments.
- Facilitating charging and data transfer between devices.
Each type of connector serves a specific function, ensuring compatibility and optimal performance across various applications. Choosing the right connector is essential for achieving the desired audio quality and convenience in usage.
Noise Cancellation Technology Overview
This technology is designed to minimize unwanted ambient sounds, allowing users to enjoy audio content more fully. It utilizes a combination of electronic and acoustic methods to achieve a quieter listening environment. The primary goal is to enhance the overall auditory experience by reducing interference from external noises.
Active noise control employs microphones that pick up surrounding sounds and generate opposing sound waves to cancel them out. This process requires sophisticated algorithms to ensure effective performance across various sound frequencies. By continuously adjusting to the environment, this method provides a more immersive experience.
In contrast, passive noise isolation relies on the physical structure of the device to block external sounds. This is achieved through materials and design that create a seal around the ears, effectively reducing noise penetration. While less dynamic than active methods, passive isolation can be very effective, especially in high-noise environments.
Both techniques can be used separately or in combination to optimize sound quality. Users benefit from a tailored auditory experience that enhances focus and enjoyment in diverse settings, whether commuting, traveling, or simply relaxing.
Acoustic Tuning and Sound Quality
Achieving optimal auditory performance involves a delicate balance of various components and their interactions. This section explores how adjustments and refinements in design can significantly impact the auditory experience.
Several key factors contribute to the overall sound quality:
- Driver Design: The configuration and materials used in the drivers play a crucial role in producing sound waves. Different designs can enhance specific frequencies, resulting in a clearer and more immersive listening experience.
- Casing Material: The choice of materials for the housing can influence sound resonance. Rigid and lightweight materials often reduce unwanted vibrations, allowing for a more accurate sound reproduction.
- Sealing and Fit: Proper sealing and an ergonomic fit can create an effective barrier against external noise, which helps to improve the clarity and depth of the audio.
- Equalization: Adjusting the frequency response through equalization techniques can tailor the sound signature to personal preferences or specific genres, enhancing the overall listening experience.
Incorporating these elements into the design process can lead to significant improvements in sound quality. Each adjustment not only refines the auditory output but also creates a more engaging and enjoyable experience for the listener.
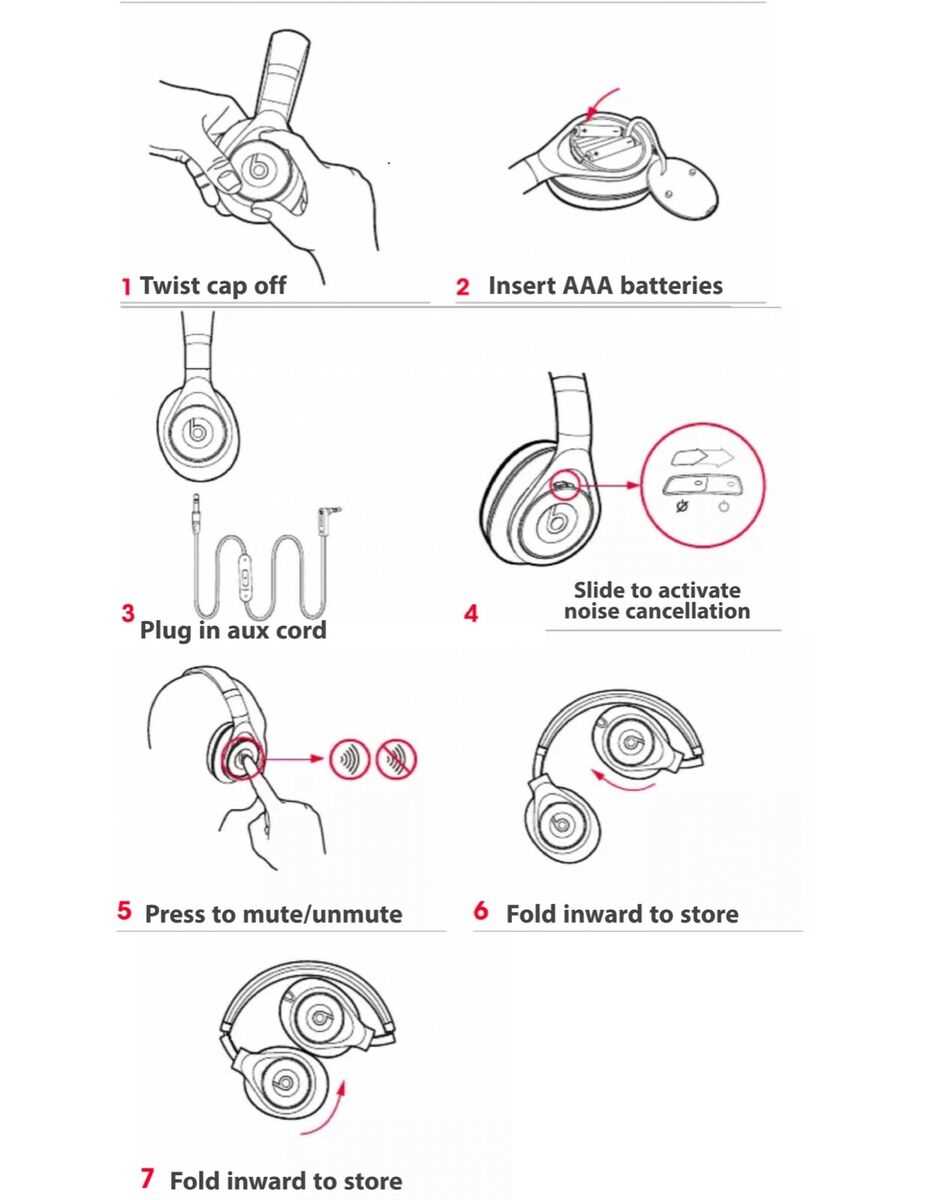
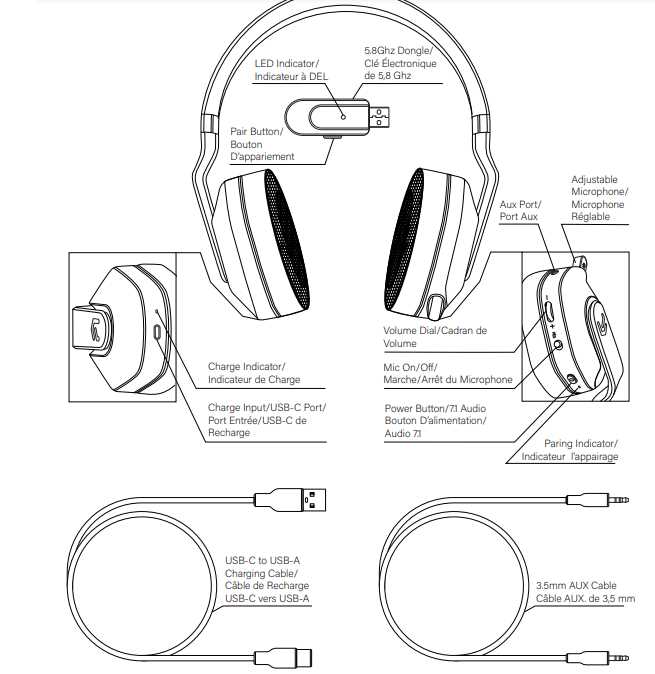
Control Buttons: Features and Locations
The control interface of audio devices plays a crucial role in user experience, allowing for seamless interaction with various functionalities. Understanding the layout and features of these controls enhances usability and ensures an enjoyable listening experience.
Common Functions
Most devices are equipped with buttons that serve essential functions such as adjusting volume, skipping tracks, and activating voice assistants. These controls are strategically placed for easy access, enabling users to make adjustments without disrupting their enjoyment.
Button Placement

The positioning of control elements varies by model, with some offering side-mounted buttons while others feature a central control scheme. Familiarizing oneself with these locations is vital for efficient use. For instance, volume controls are typically located on the right side, while playback buttons may be centralized for quick access during use.
In summary, understanding the functionality and positioning of control elements can significantly improve the interaction and overall experience with audio devices. A well-designed layout contributes to user satisfaction and convenience.
Bluetooth Connectivity and Components
The advent of wireless technology has transformed how audio devices connect and interact with various devices. This section delves into the essential elements and functionalities that facilitate seamless wireless communication, ensuring high-quality sound and user convenience.
Key Elements of Wireless Connectivity
Several critical components work together to establish a reliable connection:
- Bluetooth Chipset: The core element that enables wireless communication by transmitting and receiving signals.
- Antenna: Responsible for sending and receiving radio waves, significantly affecting the range and quality of the connection.
- Battery: Provides the necessary power for the wireless features, influencing usage time and efficiency.
- Audio Codec: Converts audio signals into a format suitable for transmission, ensuring sound quality during playback.
Functionality and Performance
The effective operation of these components is crucial for achieving optimal performance:
- Pairing Process: Initial setup where devices are connected via Bluetooth, allowing for a streamlined experience.
- Signal Stability: Affected by factors such as distance, interference, and obstacles, which can impact audio quality.
- Audio Quality: Influenced by the codec used and the capabilities of the devices involved, ensuring clarity and richness in sound.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
To ensure the durability and optimal performance of your audio devices, regular care and proper usage are essential. By following a few straightforward practices, you can extend the lifespan of these gadgets significantly.
1. Keep Them Clean: Regularly wipe down surfaces with a soft, dry cloth to remove dust and grime. Avoid using harsh chemicals that could damage the finish.
2. Store Properly: When not in use, store your devices in a protective case to prevent damage from external factors. This also helps avoid tangling of cables.
3. Avoid Extreme Temperatures: Keep your gadgets away from direct sunlight or extreme cold, as these conditions can affect their performance and battery life.
4. Be Gentle with Cables: Avoid pulling on cables forcefully or wrapping them too tightly. Proper handling helps prevent fraying and other forms of wear.
5. Monitor Volume Levels: Listening at high volumes for extended periods can lead to damage. Keep the volume at a reasonable level to preserve sound quality.
Implementing these strategies will help maintain functionality and ensure that your audio devices serve you well for years to come.