Ktm 50 Parts Diagram Guide
Exploring the structure of a small off-road motorbike can provide valuable insights for both new and experienced riders. These vehicles are designed with a compact framework that supports various essential elements, each playing a crucial role in delivering power and agility on rough terrains.
Comprehending the arrangement of these elements not only helps in regular maintenance but also in understanding how different sections work together. When each component is recognized and understood, troubleshooting and replacements become much easier, which is especially beneficial for those passionate about keeping their vehicle in top shape.
Whether you are upgrading or simply performing routine upkeep, knowing the specific layout can make all the difference. A clear visualization of the arrangement aids in identifying areas that may need attention, ensuring smoother and more enjoyable rides on any trail.
In this section, we’ll explore an overview of the components comprising the KTM 50, detailing its various elements and their functions.
1. Essential Components
- Key elements
- Crucial parts
2. Functional Aspects
Exploring how each part contributes to the operation of the KTM 50.
3. Structural Breakdown
- Detailed structure
- Comprehensive breakdown
4. Key Mechanisms
Examining the primary mechanisms integral to the KTM 50’s performance.
5. Interconnections
- Linkages
- Connections
6. Comparative Analysis
Contrasting different parts and their functionalities within the KTM 50.
7. Visual Representation
- Diagrammatic portrayal
- Visual guide
8. Maintenance Insights
Tips on maintaining and caring for the parts of the KTM 50.
9. Performance Impact
- Effect on performance
- Impact analysis
10. Compatibility Factors
Factors affecting part compatibility within the KTM 50.
11. Upgrades and Modifications
- Enhancements
- Customizations
12. Future Developments
Potential advancements in KTM 50 parts technology.
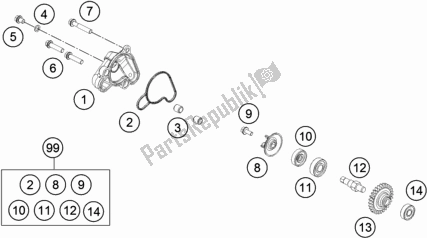
Engine Components and Layout
The engine comprises multiple elements that work together to deliver power efficiently. Understanding the structure of these components helps to grasp how they contribute to the overall functionality and performance.
- Cylinder: The primary location where fuel combustion occurs, driving the piston up and down to generate motion.
- Piston: Moves within the cylinder, creating the necessary compression for fuel ignition and translating energy into movement.
- Crankshaft: Connected to the piston, this part converts the linear motion into rotational force, which then powers the vehicle.
- Carburetor: Responsible for mixing air and fuel in precise ratios to ensure optimal combustion and engine performance.
- Exhaust System: Channels gases produced during combustion out of the engine, aiding in ventilation and maintaining engine efficiency.
These components are arranged systematically, each playing a critical role in ensuring smooth and consistent operation. Together, they form the essential structure that drives the engine’s performance and reliability.
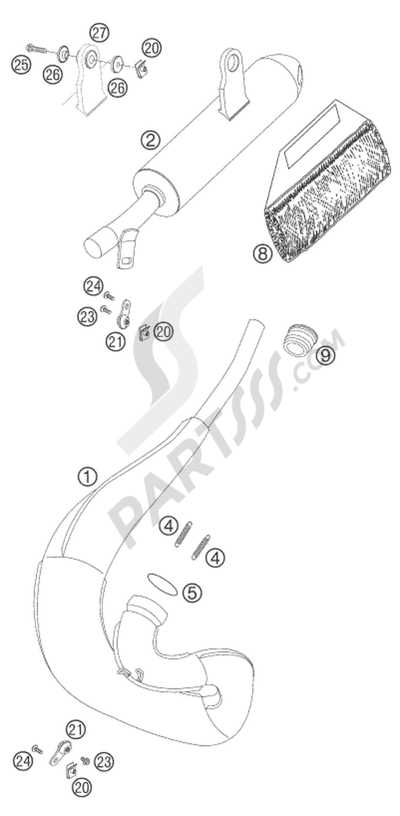
Exhaust System Design
The design of the exhaust system plays a crucial role in enhancing the overall performance and efficiency of a motorbike. By carefully engineering the exhaust components, it is possible to improve airflow, reduce emissions, and optimize engine output. A well-designed exhaust system balances sound control and power delivery, ultimately impacting the vehicle’s riding experience and responsiveness.
Key elements like the pipe layout, muffler construction, and exhaust outlet design are tailored to achieve specific performance characteristics. These components are crafted to enhance torque and horsepower while minimizing weight, ensuring both efficiency and durability. The materials used in the construction also affect heat management and corrosion resistance, adding to the system’s longevity.
Fuel System Configuration
The fuel system plays a crucial role in delivering the right amount of fuel to the engine, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. By regulating the flow and pressure, this system allows the engine to operate smoothly, adapting to various driving conditions. A well-designed setup enhances both power output and fuel economy, directly impacting the overall riding experience.
The main components of the fuel system work together to maintain a balanced mixture of air and fuel. The carburetor or fuel injector is responsible for adjusting the fuel ratio, while the fuel pump ensures steady pressure for efficient delivery. Each component’s role is interconnected, making proper maintenance essential for reliable performance.
Understanding the configuration of this system helps in diagnosing potential issues and optimizing the engine’s response. Regular inspection of elements such as the fuel filter, lines, and valves helps prevent clogs and ensures consistent flow, which is vital for sustained power and control.
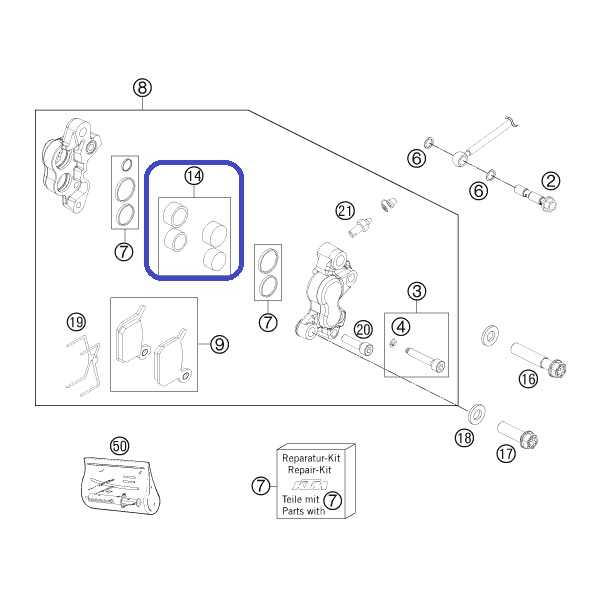
Brake System Components
The brake system is essential for safe and effective stopping performance, comprising multiple elements that work together to control and reduce speed. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring that the braking process is both responsive and reliable.
Main Elements of the Brake System
- Brake Lever: The lever initiates the braking process, allowing the rider to apply pressure and engage the system smoothly.
- Brake Caliper: The caliper houses the brake pads and applies pressure to create friction against the wheel, slowing down the vehicle.
- Brake Pads: These pads create the necessary friction when pressed against the disc, providing the stopping power required.
Supporting Components
- Master Cylinder: Converts lever action into hydraulic pressure, ensuring efficient force transmission to the caliper.
- Brake Lines: These tubes carry hydraulic fluid, which transmits the force generated by the master cylinder to the brake caliper.
- Brake Rotor: Attached to the wheel, this disc provides the surface against which the brake pads apply pressure, creating the necessary friction.
Suspension Assembly Breakdown
In this section, we delve into the details of the suspension assembly, offering a comprehensive look at each component’s role in enhancing ride stability and performance. Understanding the structure of the suspension helps in assessing wear and optimizing maintenance routines for improved handling and durability.
Key Components of the Suspension System
- Front Forks: These parts absorb shocks from the terrain, providing a smooth and balanced ride. Adjustable settings allow for customization based on riding conditions.
- Shock Absorbers: Located at the rear, these components reduce vibrations and maintain tire contact with the ground for better control.
- Linkage System: This system connects the shocks and helps in distributing force, enhancing stability, especially on uneven surfaces.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
- Regular Inspections: Check for signs of leaks or wear, especially around seals and bolts, to prevent unexpected breakdowns.
- Cleaning and Lubrication: Keep the suspension components clean and lubricated to avoid rust and ensure smooth operation.
- Proper Adjustments: Fine-tune settings based on your riding preferences to maximize comfort and control.
Transmission Parts Layout
In this section, we explore the arrangement and components of the transmission system, focusing on the detailed configuration and organization of its elements. We delve into the structure that governs the transfer of power within the mechanism, elucidating the intricate interplay of interconnected parts that facilitate seamless functionality.
Understanding the layout of these crucial components provides a comprehensive view of how energy is transmitted throughout the system. This examination highlights the integration of various mechanisms that harmoniously operate to ensure optimal performance, utilizing synonyms to enrich the discourse on mechanical intricacies.
Electrical System Components
Understanding the various elements of an electrical system is essential for proper maintenance and efficient operation. The system is made up of components that work together to power and manage the essential functions of the vehicle, from starting the engine to controlling lighting and sensors. Each element plays a specific role, ensuring the overall functionality of the machine.
Ignition System
The ignition system is crucial as it provides the initial spark needed to start the engine. It consists of multiple interconnected parts, including the spark plug, ignition coil, and stator. Together, they generate the spark necessary for combustion, allowing the engine to run smoothly and consistently. Regular checks on these components can prevent common starting issues and ensure reliable performance.
Charging System
The charging system is responsible for maintaining the battery’s charge and supplying power to other electrical components. This system typically includes the battery, alternator, and voltage regulator. While the battery stores electrical energy, the alternator replenishes it, and the voltage regulator ensures that the electrical output is steady and sufficient. A well-functioning charging
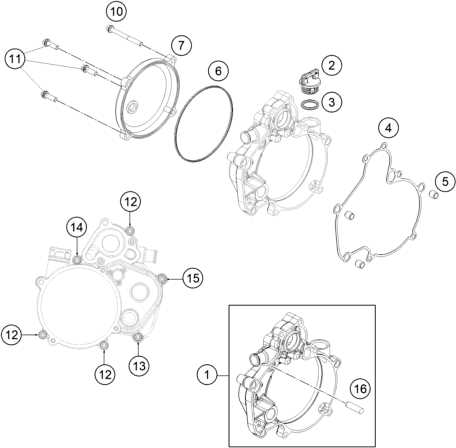
Cooling System Structure
The cooling system is a crucial component designed to maintain optimal engine temperature during operation. It circulates coolant fluid to prevent overheating, ensuring reliable performance. This system typically includes various elements that work together to regulate temperature and protect the engine from excessive heat.
Components within the cooling system vary but commonly feature a radiator, hoses, and a water pump. These elements collaborate to direct coolant through specific pathways, allowing efficient heat dissipation. By transporting heat away from the engine, the cooling system contributes to the overall efficiency and longevity of the machinery.
Frame and Chassis Elements
The structure and bodywork are integral to ensuring stability and balance during a ride. These components form the foundation of the vehicle, providing support for the engine and other systems, while also playing a key role in overall maneuverability and control. A well-designed frame contributes to both durability and performance, allowing riders to handle various terrains with confidence.
The frame, typically crafted from durable materials, is engineered to absorb impacts and resist deformation. The chassis components connect seamlessly with other elements, forming a cohesive system that enhances handling and provides a stable platform for all mechanical functions. Each element of the frame and chassis works in harmony to create a balanced and responsive ride experience.
Critical connections between the frame and other elements are carefully designed to optimize load distribution and maintain rigidity. By focusing on these aspects, manufacturers aim to deliver an enduring and reliable experience, regardless of the terrain or riding conditions.
Handlebar and Control Setup
The proper arrangement of the handlebars and controls is crucial for an optimal riding experience. This section delves into the components involved in achieving an effective setup that enhances comfort, safety, and performance.
Essential Components
- Handlebar
- Throttle Control
- Clutch Lever
- Brake Lever
- Switch Gear
Adjusting the Handlebar Position
To ensure maximum comfort and control, adjusting the handlebar position is essential. Consider the following steps:
- Loosen the handlebar clamp bolts.
- Position the handlebars at a comfortable height and angle.
- Retighten the clamp bolts securely.
Regular checks of the handlebar and control setup will not only enhance your riding experience but also contribute to the longevity of the components.
Wheel Assembly and Components

The wheel assembly plays a crucial role in the overall functionality and performance of a vehicle. It encompasses various elements that work together to ensure stability, traction, and maneuverability. Understanding the components involved in this assembly is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key Elements of the Wheel Assembly
Each wheel consists of several critical components, including the rim, spokes, hub, and tire. The rim provides the structure to hold the tire in place, while the spokes connect the rim to the hub, distributing weight and enhancing durability. The hub is the central part that connects the wheel to the axle, allowing for smooth rotation.
Importance of Proper Maintenance
Regular inspection and maintenance of the wheel assembly are vital for optimal performance. Ensuring that all components are in good condition helps prevent issues such as wobbling or uneven wear. Proper alignment and tire pressure also contribute to improved handling and safety on the road.
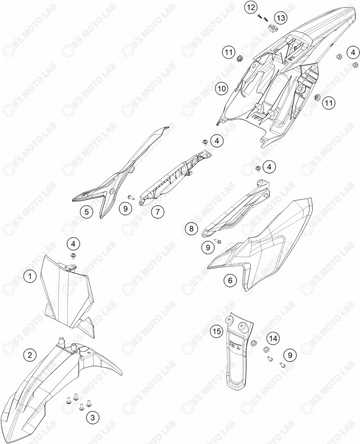
Bodywork and Protective Elements

The structure and safety components of a lightweight vehicle play a crucial role in its overall performance and rider safety. These elements not only enhance the aesthetic appeal but also contribute to the durability and functionality of the machine. Understanding the various components that make up the bodywork and protective features is essential for maintaining optimal performance and ensuring longevity.
Body panels are designed to reduce aerodynamic drag while providing structural integrity. These components are often made from lightweight materials, which help in maintaining the balance and handling of the vehicle. Protective elements, such as guards and shields, are strategically placed to minimize damage during falls or collisions, safeguarding vital mechanical parts and the rider.
Regular inspection and maintenance of these components are vital to ensure that they remain in good condition. Upgrading to high-quality materials can also improve performance and protection, making it a worthwhile investment for enthusiasts seeking to enhance their riding experience.