Understanding Lab Equipment Through Diagrams and Crosswords
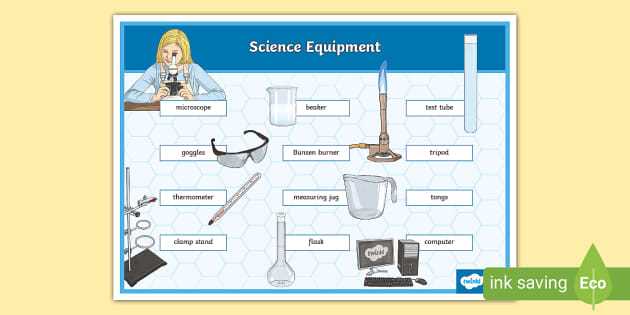
In the realm of scientific discovery, a diverse array of instruments plays a crucial role in facilitating experiments and observations. These tools, essential for researchers and students alike, provide the foundation for a deeper understanding of various phenomena. By recognizing the significance of each item, one can truly appreciate the intricate world of scientific inquiry.
Through this section, we will embark on an exciting journey to uncover the names and functions of these vital instruments. By engaging with interactive puzzles and challenges, readers will have the opportunity to enhance their knowledge while enjoying the learning process. This immersive approach not only reinforces familiarity but also encourages a lasting connection to the field.
As we delve into the fascinating details, the ultimate goal is to equip readers with a comprehensive understanding of these fundamental tools. Whether you are a seasoned professional or a curious novice, this exploration promises to enrich your appreciation for the scientific method and its indispensable resources.
Understanding Lab Equipment Basics
This section aims to explore the fundamental tools and instruments used in scientific research, emphasizing their significance in various experiments. By familiarizing oneself with these essentials, one can better appreciate the role they play in obtaining accurate results and fostering innovation.
Key Instruments and Their Functions
Among the primary tools are beakers, flasks, and pipettes, each serving a distinct purpose in handling liquids. Beakers are typically used for mixing, while flasks allow for easier storage and swirling of substances. Pipettes are essential for precise measurements, ensuring that the correct volume is transferred during experiments.
Safety and Best Practices
Understanding how to handle these instruments safely is crucial. Proper training and adherence to protocols help prevent accidents and ensure reliable outcomes. Familiarity with the correct usage of personal protective gear also plays a vital role in maintaining a safe working environment.
Essential Tools for Scientific Research
In the realm of scientific inquiry, the right instruments are pivotal for obtaining accurate results and advancing knowledge. These tools facilitate exploration and experimentation, enabling researchers to push boundaries in various fields.
- Measurement Devices:
- Thermometers
- Balances
- Calipers
- Sample Preparation:
- Beakers
- Pipettes
- Test tubes
- Observation Tools:
- Microscopes
- Telescopes
- Spectrophotometers
- Safety Gear:
- Gloves
- Goggles
- Lab coats
These instruments, among others, form the backbone of rigorous research practices, ensuring that findings are reliable and significant.
Types of Laboratory Glassware Explained
Understanding various types of glass containers is essential for anyone working in scientific environments. Each piece serves specific purposes, enhancing accuracy and efficiency during experiments.
Common Types

- Beakers: Versatile vessels used for mixing, heating, and pouring liquids.
- Flasks: Often used for storing and boiling solutions, available in various shapes.
- Test Tubes: Ideal for small-scale reactions and observations.
- Pipettes: Essential for measuring and transferring precise volumes of liquid.
Specialized Glassware
- Burettes: Used for titration, allowing precise addition of reactants.
- Volumetric Flasks: Designed for accurate dilutions and preparation of standard solutions.
- Separatory Funnels: Useful for separating immiscible liquids.
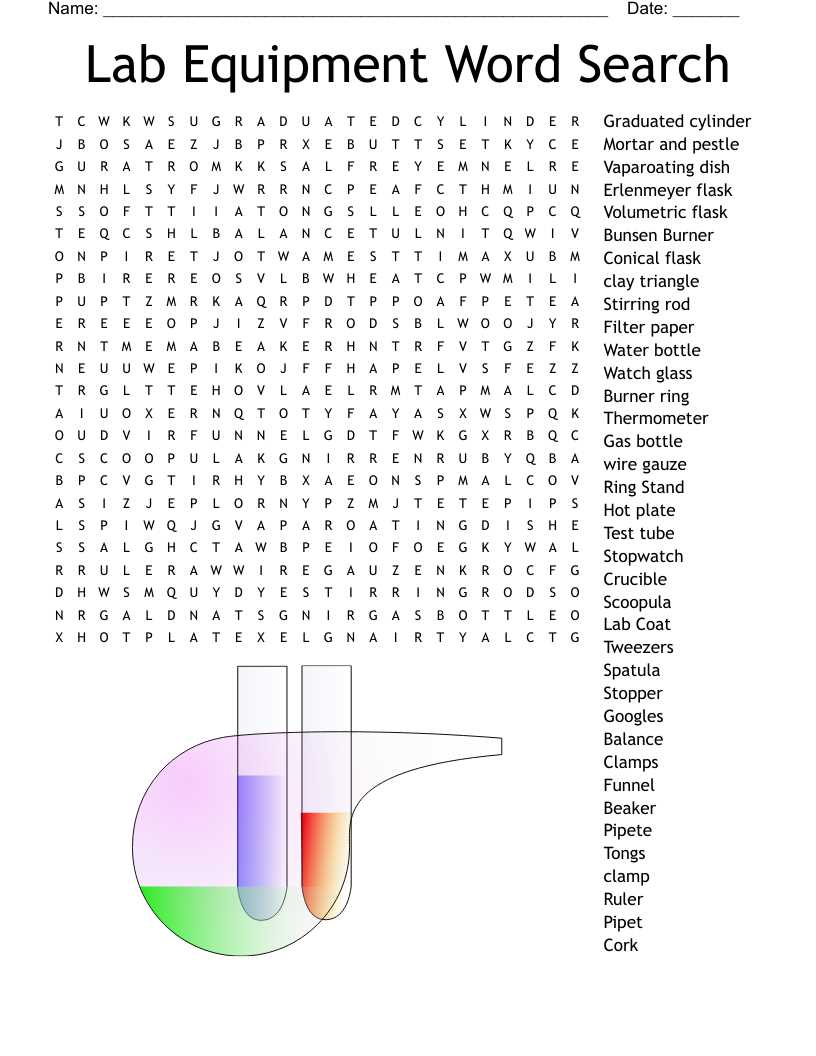
Common Lab Equipment Functions and Uses
Understanding the various tools and instruments used in scientific environments is essential for effective experimentation and research. Each device serves a specific purpose, enabling researchers to conduct tests, measure, analyze, and manipulate various substances with precision. This section highlights the roles and applications of several common tools found in such settings.
Measurement and Analysis Instruments

Devices designed for measurement and analysis are crucial in obtaining accurate data. Balances are utilized to determine the mass of samples, while pipettes enable precise liquid transfers. Spectrophotometers measure light absorption, assisting in determining the concentration of substances. These instruments ensure that experiments yield reliable and reproducible results.
Heating and Cooling Devices
Temperature control is vital in many experimental procedures. Hot plates provide a stable heat source for reactions, while refrigerators and freezers are essential for storing sensitive materials at controlled temperatures. Bunsen burners are commonly used to generate flames for various heating tasks, demonstrating the importance of maintaining appropriate thermal conditions throughout scientific work.
Safety Measures When Using Equipment

Ensuring a secure environment while handling various tools is crucial for preventing accidents and injuries. Adhering to best practices fosters a culture of safety and promotes responsible usage.
| Safety Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Personal Protective Gear | Always wear appropriate gear such as gloves, goggles, and lab coats to protect against potential hazards. |
| Proper Training | Receive comprehensive training on the correct usage and handling of tools to minimize risks. |
| Clear Workspace | Maintain an organized and clutter-free workspace to avoid accidents and ensure efficiency. |
| Emergency Protocols | Be familiar with emergency procedures, including the location of first aid kits and safety showers. |
Importance of Accurate Measurement Tools
Precision in measurement is fundamental across various scientific fields. The reliability of results often hinges on the accuracy of the tools used, directly influencing the validity of conclusions drawn from experiments. Understanding the significance of meticulous measurement fosters better practices and enhances overall quality in research and analysis.
Impact on Research Quality
Accurate measuring instruments ensure that data collected is both reliable and reproducible. Variability in measurements can lead to erroneous interpretations, ultimately affecting the outcomes of experiments and studies. By utilizing precise tools, researchers can enhance the credibility of their findings.
Safety and Compliance
In many scientific endeavors, adherence to safety standards is paramount. Utilizing accurate measurement devices helps in maintaining safe environments and compliance with regulatory requirements. This not only protects researchers but also upholds ethical standards within the scientific community.
| Measurement Aspect | Consequences of Inaccuracy |
|---|---|
| Data Integrity | Compromised results |
| Safety Standards | Increased risks |
| Regulatory Compliance | Legal issues |
| Research Reputation | Loss of credibility |
Creating a Lab Equipment Crossword Puzzle
Engaging in a puzzle that focuses on various tools used in scientific settings can enhance knowledge retention and make learning enjoyable. This activity encourages participants to explore terminology and concepts associated with scientific instruments, reinforcing their understanding through an interactive format.
Choosing the Right Terms

Selecting relevant vocabulary is crucial for an enriching experience. Focus on essential items commonly found in research environments, such as beakers, microscopes, and pipettes. Incorporating a mix of basic and advanced terms ensures a comprehensive challenge.
Designing the Grid

Constructing the puzzle grid involves strategically placing words both horizontally and vertically. Ensure that the layout allows for easy navigation and that intersections create meaningful connections between terms. This structure not only aids in solving but also promotes deeper connections among the words.
Identifying Equipment Through Visual Aids

Visual representations play a crucial role in the recognition and understanding of various tools used in scientific settings. By leveraging images, diagrams, and other graphical formats, individuals can enhance their knowledge and improve their ability to identify essential instruments.
Effective visual aids offer several advantages:
- Facilitating quick recognition of items.
- Enhancing memory retention through imagery.
- Providing context for usage and function.
To maximize the effectiveness of these resources, consider the following strategies:
- Utilize labeled images to clarify names and functions.
- Incorporate comparison charts for similar tools.
- Engage with interactive resources to deepen understanding.
By actively employing visual aids, learners can significantly improve their ability to navigate the complexities of their surroundings and achieve greater proficiency in their tasks.
How to Read Lab Equipment Labels
Understanding the markings on scientific instruments is essential for safe and effective usage. Labels provide crucial information that ensures proper handling, maintenance, and compliance with safety standards.
Here are key elements to consider when interpreting these markings:
- Identification: Look for the name of the device and its model number, which help in recognizing the specific type and its intended function.
- Manufacturer Details: The name and contact information of the manufacturer may be included, offering a resource for inquiries or support.
- Safety Symbols: Recognize various icons that indicate hazards, required personal protective equipment, or special handling procedures.
- Calibration Information: Check for details regarding calibration status, including dates and frequency, to ensure accuracy in measurements.
- Operating Instructions: Many labels provide basic operational guidelines or warnings to prevent misuse.
By familiarizing yourself with these components, you can enhance your understanding and ensure the proper use of the instruments in your workspace.
Historical Development of Lab Tools

The evolution of instruments used for scientific inquiry reflects humanity’s quest for knowledge and understanding of the natural world. From rudimentary devices crafted from natural materials to sophisticated machinery powered by advanced technology, this journey highlights significant milestones that have shaped research practices across various disciplines.
Ancient Innovations
In ancient times, early scholars relied on simple tools such as the abacus and basic measuring implements to explore mathematics and astronomy. The Greeks and Romans contributed to this foundation with inventions like the astrolabe, which enabled more accurate celestial navigation and timekeeping.
Modern Advancements
The Renaissance sparked a wave of innovation, leading to the creation of more refined instruments such as the microscope and telescope. These breakthroughs opened new frontiers in biology and astronomy, allowing scientists to examine the minutiae of life and the vastness of space. The Industrial Revolution further accelerated the development of precision instruments, which became integral to experimental research.
| Era | Key Innovations |
|---|---|
| Ancient | Abacus, Astrolabe |
| Renaissance | Microscope, Telescope |
| Industrial Revolution | Precision Instruments, Analytical Devices |
Best Practices for Equipment Maintenance
Ensuring optimal performance and longevity of instruments involves a systematic approach to upkeep and care. Adhering to established protocols not only enhances reliability but also minimizes downtime and costly repairs. This section outlines key strategies for maintaining tools effectively.
| Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular Inspection | Conduct periodic checks to identify wear and tear or any irregularities in functionality. |
| Routine Cleaning | Implement a consistent cleaning schedule to prevent contamination and buildup of residues. |
| Calibration | Ensure accurate measurements by regularly calibrating devices according to manufacturer specifications. |
| Documentation | Keep detailed records of maintenance activities, repairs, and performance metrics for reference and analysis. |
| Training | Provide proper training for personnel on handling and caring for tools to promote best practices. |
Innovations in Modern Laboratory Equipment
The landscape of scientific inquiry is continually transformed by advancements that enhance precision, efficiency, and safety. These innovations empower researchers to explore new frontiers, streamline processes, and achieve results that were previously unimaginable. As technology evolves, tools are becoming more sophisticated, allowing for greater accuracy and ease of use in various fields of study.
Emerging Technologies

Recent breakthroughs have introduced cutting-edge technologies that significantly improve research capabilities. From automated systems to advanced imaging techniques, these tools are revolutionizing the way experiments are conducted and analyzed.
Benefits of Modern Solutions
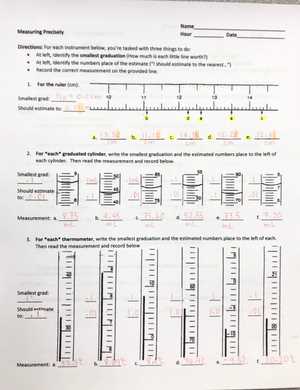
The integration of innovative solutions leads to enhanced productivity and reduced errors. These developments not only save time but also facilitate a deeper understanding of complex phenomena, fostering a culture of discovery and innovation within scientific communities.
| Innovation | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Automated Pipetting Systems | Devices that perform liquid handling tasks with high precision. | Increases throughput and reduces human error. |
| Advanced Imaging Techniques | Methods like confocal microscopy and 3D imaging. | Allows for detailed visualization of samples at a cellular level. |
| Robotic Sample Analysis | Robots that can conduct multiple analyses simultaneously. | Enhances efficiency and enables high-throughput screening. |
| Smart Sensors | Devices that monitor and collect data in real-time. | Improves accuracy and provides immediate feedback. |