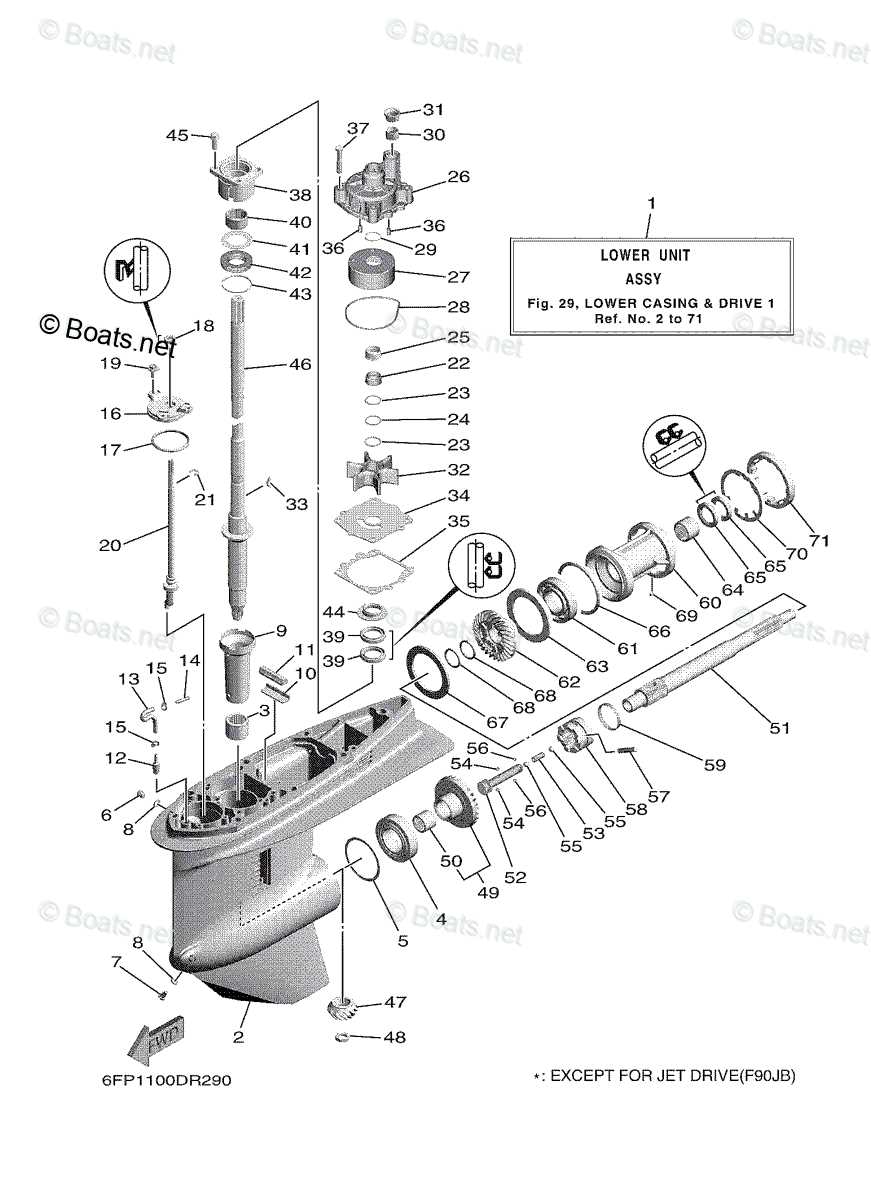
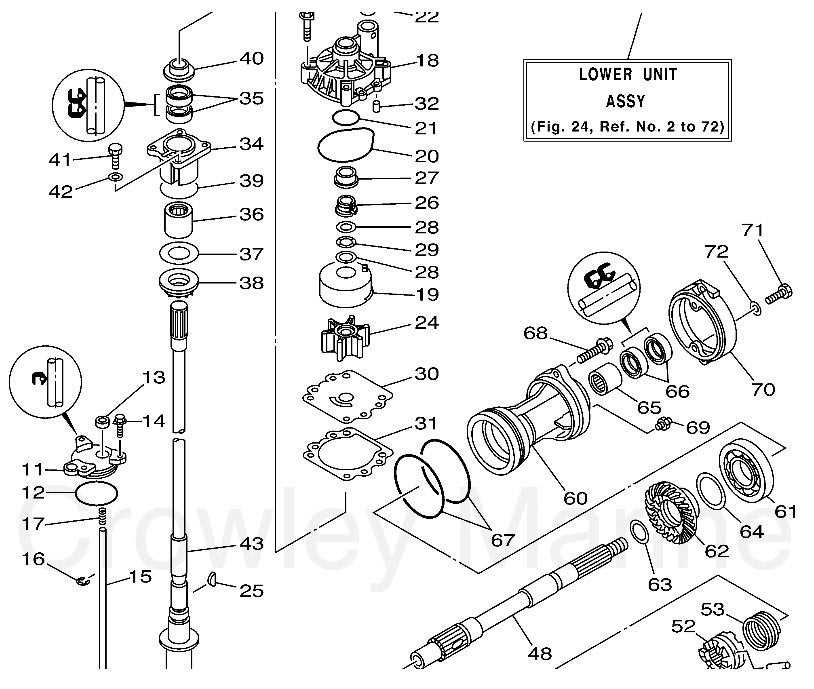
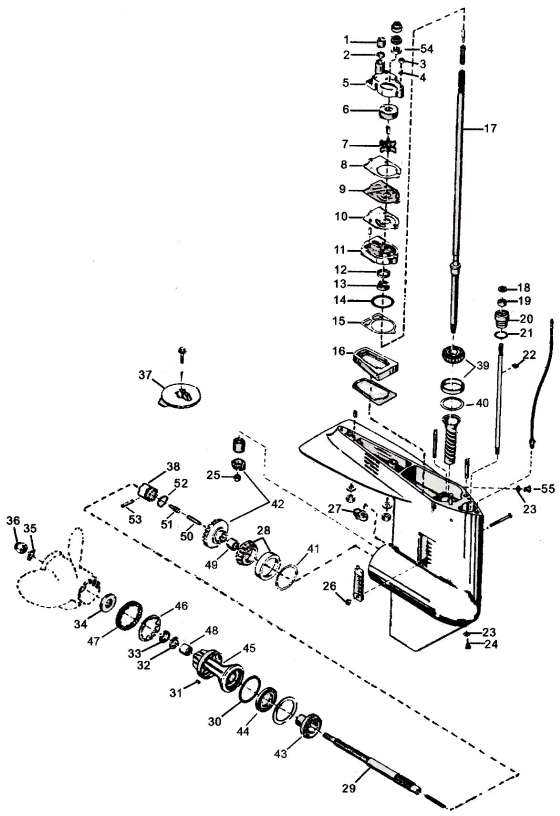
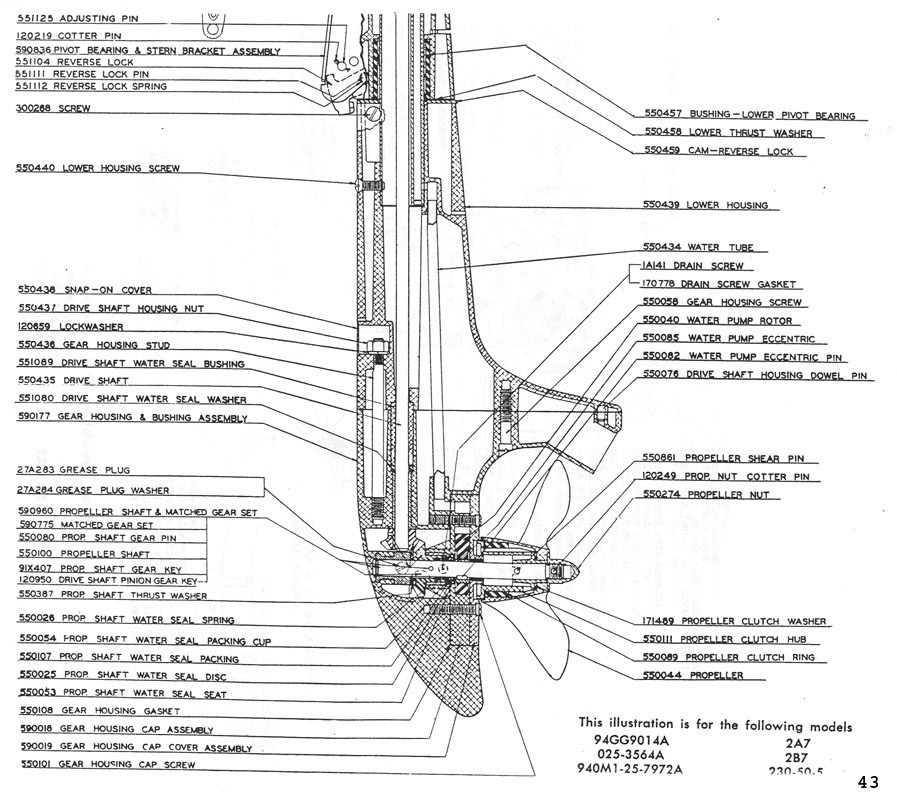
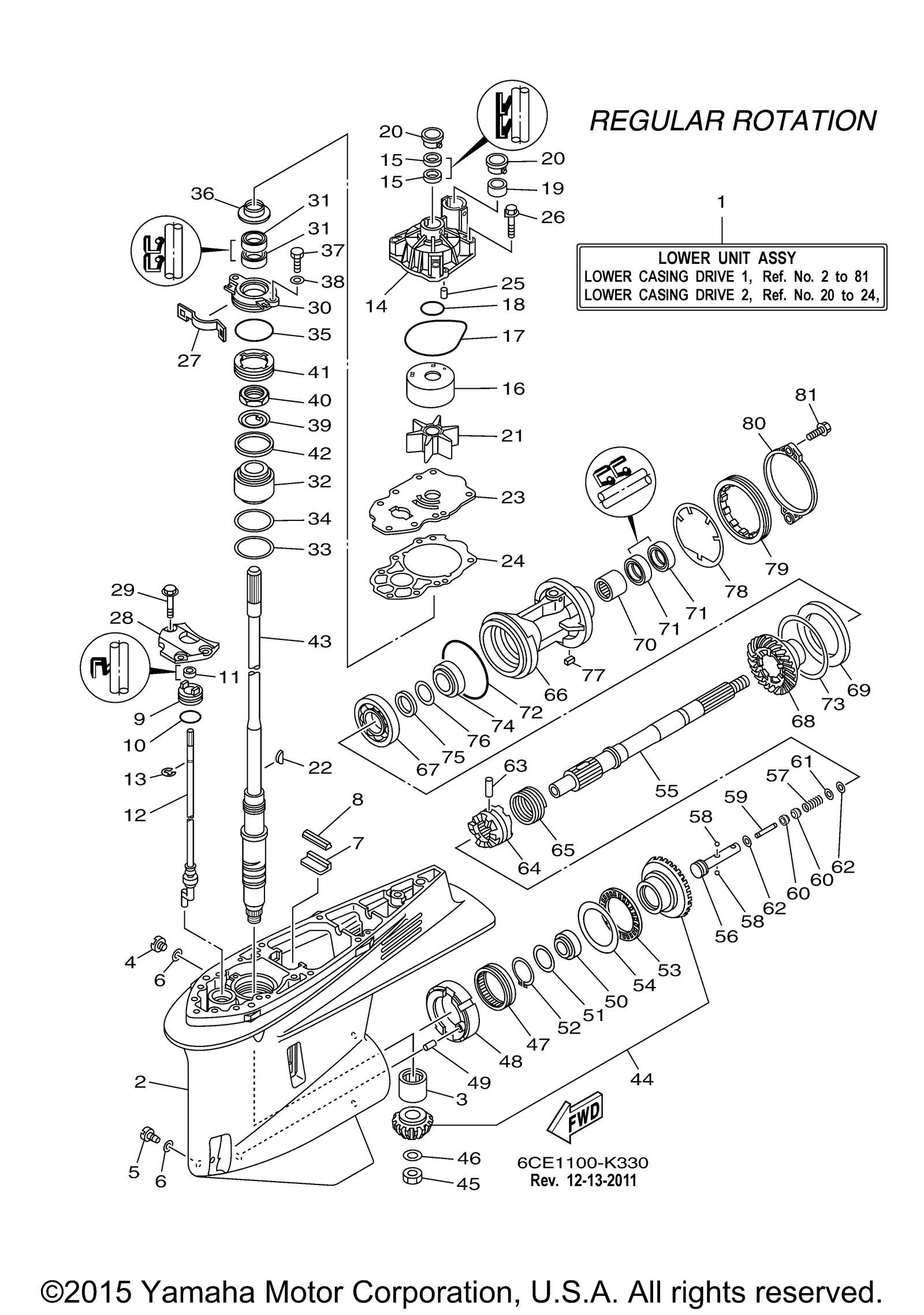
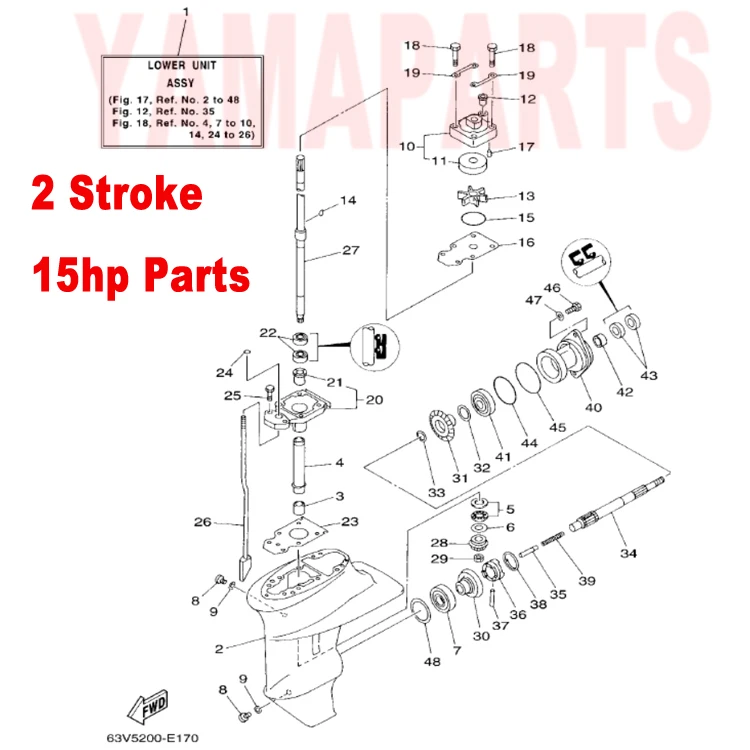
Lower Unit Parts Breakdown
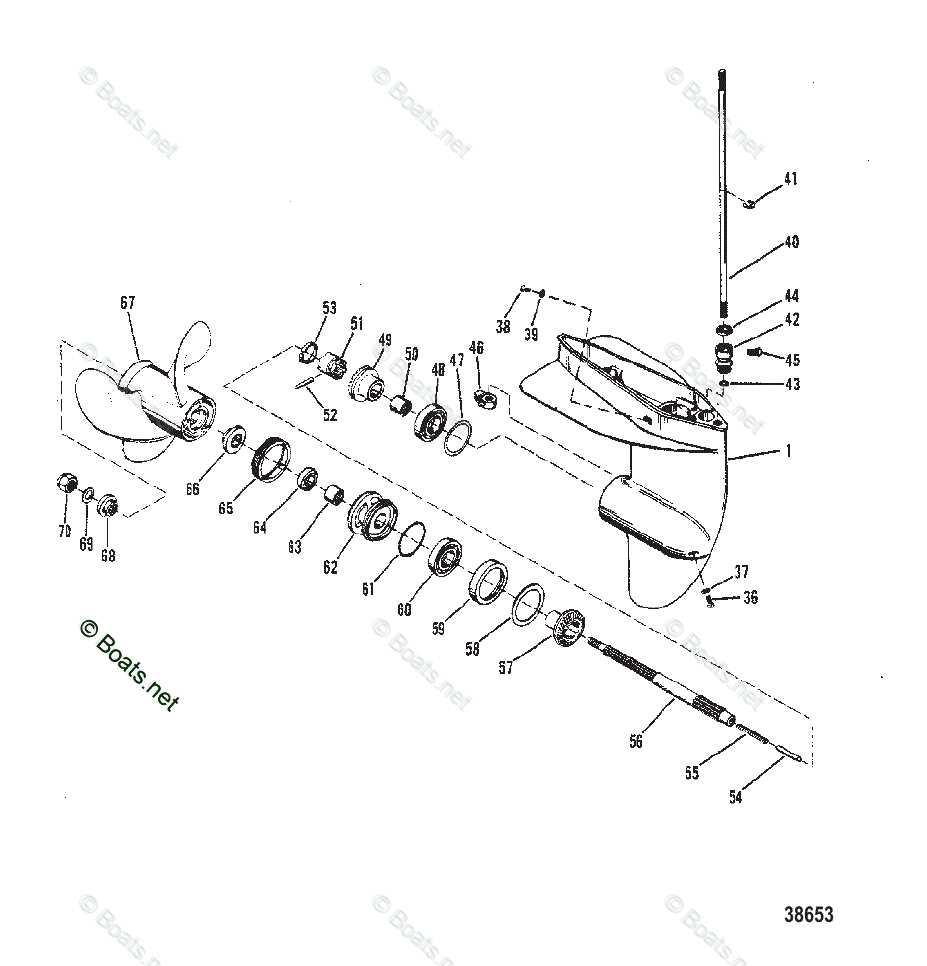
When it comes to maintaining the key elements of any marine system, understanding the intricacies of its mechanical structure is crucial. Whether you’re involved in repairs or just looking to expand your knowledge, grasping how different mechanisms work together is fundamental for seamless operation on the water.
In this section, we’ll delve into the core elements that ensure propulsion and control in marine environments. By familiarizing yourself with these essential components, you’ll gain a deeper insight into how everything functions in harmony, allowing for more efficient upkeep and troubleshooting.
Our exploration will cover the vital mechanisms, helping you recognize their roles in maintaining smooth navigation. This knowledge will not only empower you to better handle your equipment but also to spot potential issues before they become serious problems.
Understanding the Lower Unit Components
In marine engines, a set of vital mechanisms work together to transmit power from the motor to the propeller, enabling movement through the water. These mechanisms ensure that the engine’s force is converted effectively, allowing for smooth navigation and precise control over the vessel.
Drive Mechanism
The drive assembly is a crucial part of this system, responsible for directing the energy generated by the engine towards the propeller. This is achieved through a series of gears and shafts that transform the rotational power of the engine into thrust, which propels the boat forward.
Cooling System

To ensure optimal performance, the cooling assembly helps manage engine temperature by circulating water through various channels. This prevents overheating, allowing the engine to function efficiently, even during long trips.
How the Lower Section Functions
The lower section of a marine propulsion system plays a vital role in the overall performance of a boat. It ensures smooth and efficient movement through water by transforming the engine’s power into thrust. The system’s design allows it to handle high-speed rotations and direct them towards the water, creating forward or reverse motion. This process involves several key components working in unison to maintain stability and performance, while enduring various conditions encountered in marine environments.
Transmission of Power
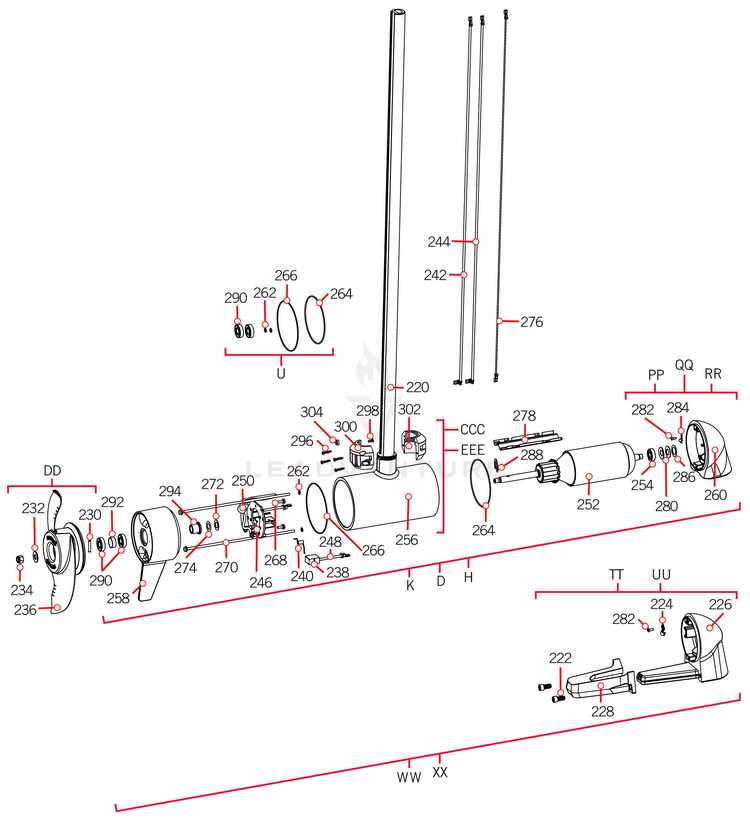
The power generated by the engine is transferred through a series of mechanical elements. Gears engage precisely, converting high-speed rotations into controlled movement of the propeller. This transfer must be seamless to avoid any loss of momentum, ensuring efficient propulsion in all directions.
Directional Control
In addition to power transmission, the section responsible for propulsion allows for precise steering. With the help of its design, water flow is manipulated, enabling the boat to turn smoothly. The control over direction is crucial, especially in tight spaces or during sharp maneuvers, providing the operator with full authority over the vessel’s path.
Key Elements in Marine Propulsion
Marine propulsion systems are complex mechanisms that convert energy into motion, driving boats and ships forward. Understanding the key components of these systems is crucial for ensuring efficient operation and maintaining peak performance. Each element plays a vital role in the propulsion process, working together to provide thrust, stability, and speed control on water.
Propeller and Shaft
The propeller, often considered the heart of marine propulsion, is responsible for generating thrust by moving water. It is connected to the engine via a shaft, which transfers the mechanical energy from the engine to the propeller. The efficiency of this connection directly impacts the speed and power of the vessel. A well-maintained shaft ensures smooth operation and reduces energy loss during motion.
Engine and Gear System
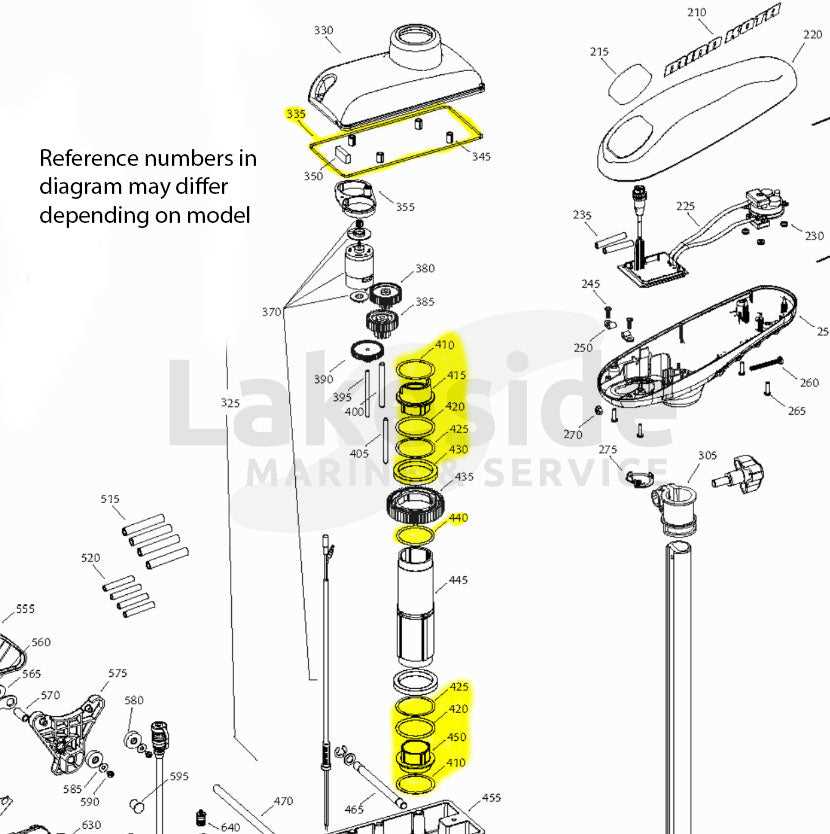
The engine provides the necessary power for propulsion, while the gear system manages speed and torque. These two elements must work in harmony to provide adequate thrust under varying conditions, such as high-speed navigation or slower, more controlled movements. Proper synchronization between the engine and the gears is key to maintaining fuel efficiency and reliable performance.
| Component | Function | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Propeller | Generates thrust by moving water | ||||||||||||||||
| Shaft | Transfers engine power to the
Inspecting the Lower Unit for Wear
Ensuring the smooth operation of a marine engine requires regular checks of its key components for potential wear. Prolonged use can lead to gradual deterioration, which may affect the performance and longevity of the entire system. By catching early signs of damage, you can prevent costly repairs and maintain efficient functionality. Signs of Damage to Look ForDuring an inspection, it’s important to search for visible issues like corrosion, cracks, or unusual wear patterns. Look closely at the housing and surrounding components, as these areas can accumulate damage over time. If any debris or water contamination is detected, it could be a sign of internal problems. Mechanical ChecksExamine the gears, bearings, and seals for any irregularities. Components such as these can experience significant stress and may show signs of pitting, grinding, or uneven movement. If you notice any of these issues, it’s essential to address them promptly before they worsen. Regular lubrication and maintenance will help keep everything in top shape, reducing friction and wear. Identifying Common Lower Unit IssuesProblems with the propulsion system of a watercraft can significantly affect its performance. Recognizing signs of wear or malfunction early on is key to maintaining smooth operation. Understanding potential trouble areas helps ensure safety and prevent costly repairs. Noise and VibrationUnusual noises or excessive vibration while operating your vessel are often indicators of underlying mechanical problems. This could be due to misaligned components, damaged gears, or worn-out bearings. It’s important to inspect the system carefully to determine the root cause and take timely action. Loss of Power or Poor PerformanceA sudden drop in power or reduced speed is another common issue. This can result from blockages, damaged propulsion parts, or fluid leaks. Regular maintenance and inspections are vital to address these problems before they escalate into more serious failures. How to Replace Damaged PartsWhen components of a mechanical assembly become worn or broken, timely replacement is crucial to maintain optimal performance. Understanding the process and having the right tools can significantly streamline this task, ensuring that the equipment functions correctly and efficiently. Identifying the Affected ComponentsThe first step in the replacement process is to thoroughly inspect the assembly for any damaged areas. Look for signs of wear, corrosion, or physical breaks. Properly identifying these issues will guide you in selecting the correct replacements and preparing for the next steps. Procedure for ReplacementOnce the damaged items are identified, proceed to remove them carefully. Utilize appropriate tools to detach the components without causing further damage to the surrounding structure. After removing the faulty parts, install the new ones, ensuring a secure fit. Finally, perform a thorough check to confirm that everything operates smoothly. Importance of Regular MaintenanceConsistent upkeep is crucial for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of any mechanical system. By engaging in routine care, one can prevent minor issues from escalating into significant problems, which can be both time-consuming and costly to resolve. Regular maintenance not only enhances performance but also guarantees safety and reliability, fostering a smoother operation. Benefits of Consistent Upkeep
Routine maintenance offers numerous advantages that extend beyond mere functionality. These benefits include:
Key Maintenance Practices
Implementing specific practices can enhance the effectiveness of maintenance efforts. Regular inspections, timely replacements, and attention to lubrication are essential actions that contribute to the overall health of the equipment. Engaging in these practices ensures a reliable operation and minimizes the risk of unexpected breakdowns. Impact of Corrosion on Lower Unit Parts
Corrosion is a significant threat to the integrity and performance of essential marine components. It occurs when metals react with environmental factors, leading to deterioration and potential failure. Understanding how this process affects various elements is crucial for ensuring longevity and reliability. Types of Corrosion
Effects of Corrosion on Performance
Lubrication and Fluid Requirements
Proper maintenance of marine machinery is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Ensuring that the right fluids are used, along with appropriate lubrication, helps prevent wear and tear, enhancing efficiency. This section outlines the essential aspects of lubrication and fluid management, emphasizing the importance of using the correct products for various components. Types of LubricantsThere are several types of lubricants used in marine applications, each serving a specific purpose:
Fluid Specifications
Choosing the right fluids is vital for the reliability of your machinery. Here are key considerations:
In conclusion, adhering to the recommended lubrication practices and fluid requirements is essential for maximizing the efficiency and lifespan of your marine equipment. Regular checks and timely replacements will contribute significantly to smooth operation. Choosing the Right Replacement PartsFinding suitable components for repairs is crucial for maintaining the performance and longevity of any equipment. Selecting high-quality alternatives ensures optimal functionality and reduces the risk of future issues. It is essential to consider several factors to make informed decisions when acquiring new items. Here are some key aspects to evaluate:
By carefully considering these factors, one can make better choices and ensure the successful restoration of equipment. Troubleshooting Common Lower Unit ProblemsWhen dealing with underwater mechanisms, various issues may arise that affect performance and efficiency. Identifying these problems promptly can save time and resources, ensuring smooth operation. This section outlines some typical challenges and offers guidance on diagnosing and resolving them effectively. Common issues encountered include:
To diagnose these issues effectively:
By following these steps, operators can efficiently identify and address challenges, ensuring reliable performance and extending the lifespan of the equipment. Understanding Gearcase Operation
The gearcase is a vital component in marine propulsion systems, serving to transmit power from the engine to the propeller. Its intricate design allows for the efficient conversion of rotational force, ensuring smooth operation and effective propulsion in various water conditions. Within the gearcase, several key functions work in tandem to optimize performance. These include gear ratios, lubrication systems, and cooling mechanisms. Each element plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and functionality of the entire assembly.
Understanding the operation of the gearcase is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. Regular inspection of its components can help identify potential issues, leading to timely repairs and prolonged service life. Tools Needed for Lower Unit RepairsWhen undertaking repairs on the essential components of marine propulsion systems, having the right tools is crucial for effective and efficient work. The proper equipment not only ensures that tasks are completed correctly but also enhances safety and minimizes the risk of damage to the machinery. Below is a list of necessary tools that should be on hand for such maintenance activities. Essential Hand Tools
Specialized Equipment
Having these tools at your disposal will greatly enhance your ability to perform maintenance tasks effectively, ensuring that your marine equipment operates smoothly and reliably. |